

Journal Website:
https://theamericanjou rnals.com/index.php/ta jet
Copyright: Original content from this work may be used under the terms of the creative commons attributes
4.0 licence.
Influence Of Hydrophobizing Additives On Thermal
Properties Of Ceramzito Concrete In Agressive
Environment
Senior Lecturer, Department Of Construction Of Buildings And Structures, Fergana
Polytechnic Institute, Fergana, Uzbekistan
Faculty Of Construction 1-20 Biq Group Student Fergana Polytechnic Institute, Fergana,
Uzbekistan
|
The article deals with the effect of hydrophobizing additives on the thermophysical properties of expanded clay concrete.
KEYWORDS Vapor Permeability, Sorption, Additives, Moisture, Solution, Salt. |
One of the reasons for the destruction that occurs in the enveloping structures of buildings at chemical industry enterprises is the pressure arising in the pores of building materials due to the accumulation of various salts in them, the salt formula of physical corrosion.
Salt penetrates deep into structures in the form of solutions with moisture condensing on the surface of crystals. The presence of hygroscopic salts aggravates the condition of the enclosing structures, because the sorption properties of building materials are thereby significantly increased.
Chemical analysis of samples taken, for example, from the walls at potash plants, show that the pores of the material contain solutions of salts of sufficiently high concentrations. In some cases, the salt content exceeds the solubility rate. This is the main reason for the decrease in the thermal properties of the enclosing structures and, as a consequence, their durability.
An increase in the resistance of building materials under these operating conditions can be achieved by reducing the possibility of penetration of aggressive solutions into the pores.
The works carried out by researchers (1,2,3) have shown that organosilicon compounds of various types significantly increase the durability of concretes and mortars. There is reason to believe that in this case, a positive effect can be obtained by modifying their properties with air-entraining and hydrophobic additives.
For this purpose, the possibility of using organosilicon compounds such as crystalline sodium ethylsiliconate and polyorganoalkoxysiloxane was investigated.
Organosilicon oligomers of the type of polyorganoalkoxysiloxanes are the product of joint hydrolysis and esterification of organochlorosilanes and corresponding alcohols. The molecular structure of these compounds allows them to be introduced into concrete compositions in quantities sufficient to obtain a high hydrophobic effect.
Polyorganoalkoxysiloxanes, due to the presence of active functional alkoxy groups in the molecule, chemically react with calcium oxide hydrate in the alkaline medium of concrete.
The neoformation product
(polyorganocalcium siloxane) hydrophobizes the surface of the walls of pores and capillaries, and the alcohol released as a result of a chemical reaction acts as a micro-foaming agent.
Studies have shown that oligomers such as polyphenylethoxysiloxanes FES have the best hydrophobizing properties.
Organosilicon compounds of the ESNK type (crystalline sodium ethyl sipiconate) are plasticizing, allowing to increase the mobility and workability of the concrete mixture, due to which it is possible to reduce the water-cement ratio or reduce the consumption of cement. It has an air-entraining effect, which should contribute to the formation of a structure with a uniformly distributed porosity in concrete (due to closed air bubbles of small size), giving it increased density and frost resistance. It also enters into a chemical interaction with Ca (OH) 2, and the products of new formations, mosaic, hydrophobize the walls of pores and capillaries in concrete.
We have investigated the effect of FES and ESNK hydrophobizing additives on the thermophysical properties of expanded clay concrete used in the enclosing structures of industrial buildings exposed to sodium chloride solutions.
To study the effect of additives on the thermophysical properties of expanded clay concrete, samples with ɣ = 1200 kg / m3 were made.
Additives were introduced into the concrete mixture in the following quantities: ESNK — 0.1% (based on the mass of cement). As a standard, samples were made from expanded clay concrete without additives.
Sorption properties were studied on cubes with an edge height of 30x3x30 mm.
To determine vapor permeability, samples with a diameter of 131 mm and a height of 30 mm were made.
The tests were carried out in sodium chloride solutions of various concentrations. since this salt does not enter into chemical interaction with the constituents of the cement stone, and the processes of physical
The destruction of the investigated materials is not complicated by chemical ones. The concentrations of solutions were taken as follows: saturated solution (359 g / l), 50% and І0% of saturated.
The studies were carried out on samples of samples of air hardening of sorption and vapor permeability at the age of 3 months.
All types of testing were preceded by saturation of the samples at atmospheric pressure and complete immersion in sodium chloride solutions for 3 days. Control samples were not saturated in salt solutions.
The determination of the sorption moisture content of saline and control samples was carried out by a standard method. (4)
In contrast to the standard method, the determination of the vapor permeability coefficient was carried out not over water, but over a saturated solution of sodium chloride, which made it possible to avoid moisture condensation in the bulk of the sample under study.
The data obtained during the experiment are presented in table. 1 and Fig. 1. It can be seen from them that as the concentration of solutions in which the samples were saturated, the content of sodium chloride in the latter increases. The introduction of additives of organosilicon substances into expanded clay concrete leads to a decrease in the amount of salt in the dried samples. The difference is especially pronounced in the case of using FES additives.
This can be explained mainly by the fact that concretes, in which the oligomer is introduced, have high hydrophobic properties.
In this case, the surface at the interface is significantly reduced in comparison with concrete without additives, which prevents the penetration of the solution into the depth of the sample.
The air entrainment of the ESNC additives turned out to be less effective,
Table 1
|
Sample batch number |
Materi alsamp les |
Concentration of the solution for saturation of samples with sodium chloride |
The content of sodium chloride in the sample in% by weight after |
Vapor permeabilit y coefficient 10 6 in kgm / min.sec. |
Sorption |
|||
|
Desiccator relative humidity% |
||||||||
|
40 % |
60 % |
75 % |
95 % |
|||||
|
|
|
(in grams per 100 g of water) |
drying the sample |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Expan ded clay concre te |
0 |
0 |
16,8 |
2,50 |
2,92 |
3,0 5 |
5,35 |
|
2 |
3,59 |
1,41 |
13,1 |
4,33 |
4,3 8 |
4,91 |
8.57 |
|
|
3 |
17,95 |
3,0 |
12,38 |
4,73 |
4,7 9 |
8,3 4 |
14.13 |
|
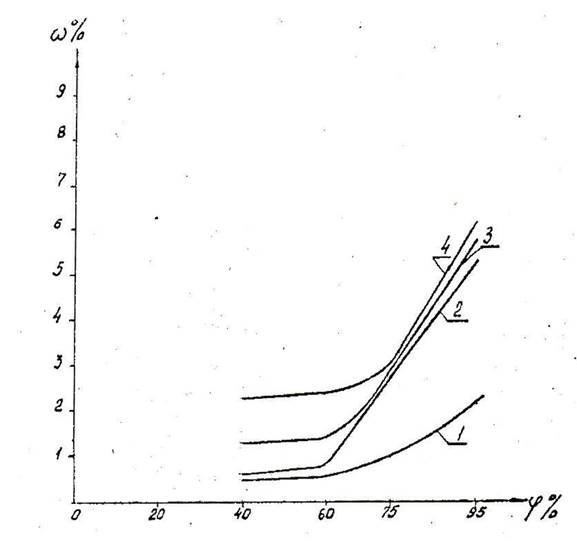
Rice. 1. Dependence of the sorption moisture content of building materials on the degree of salinity with sodium chloride.
Rice. 1. Dependence of the sorption moisture content of building materials on the degree of salinity with sodium chloride.
a) Expanded clay concrete;
b) Expanded clay concrete with ESNK additives;
c) Expanded clay concrete with FES additives. 1. sodium chloride is absent
2. when soaking in a solution of 3.59% concentration per 100 g of water
3. when soaking in a solution of 17.95% concentration per 100 g of water
4. when soaking in a solution of 35.9% concentration per 100 g of water
Notes:
1. The salt content in the test samples is shown in Table 1.
2. Dotted lines show the level of sorption moisture content of non-saline samples.
But she still somewhat reduced the content of salts in the samples in comparison with the standard. This is apparently due to the ordering of the structure of the solution part and mosaic hydrophobization of the walls of pores and capillaries.
The introduction of organosilicon additives into expanded clay concrete also affects its vapor permeability; as concrete acquires hydrophobic properties, it increases. Moreover, this pattern takes place both in the study of unsaturated concrete, and in the study of concretes that have been saturated with salt solutions.
This phenomenon under conditions of filling the pores of the material with salt solutions should be considered positive for the outer insulating layer of lightweight concrete in the presence of dense vapor-impermeable salt on the inside of the fence, because helps to dry the structure from the outside.
It can be explained by a decrease in sorption by hydrophobized samples and, consequently, an increase in the free section of through pores and capillaries, which increases the vapor permeability coefficient of the material.
With an increase in the amount of salt in the pores of the material, the vapor permeability of the latter decreases, which is caused by a decrease in the free section of the pores and capillaries. Attention is drawn to an increase in vapor permeability with an insignificant salt content (lines 6 and 10), which should be explained by an increase in sorption moisture during salinity. With an increase in the salt content in the material, the process of reducing vapor permeability due to a decrease in the free cross-section of pores and capillaries is predominant.
The data obtained during the determination of the sorption moisture content of concretes is completely consistent with the previous results: as the salt content in the samples increases, their moisture content increases. However, it decreases when additives are added to the composition of concrete. A particularly significant decrease is observed in the case of using a hydrophobizing additive FES.The maximum sorption moisture content of samples with the addition of FES at a salt content of 1.54% by weight, which corresponds to preliminary moistening of the sample in a saturated solution, is 2 times less than the sorption moisture of a non-saline sample without an additive (Fig. 1c).
The sorption moisture content of the samples without additives with a salt content of 1.41% by weight, which corresponds to saturation in a 10% solution, is 1.5 times higher than the sorption moisture content of a non-saline sample without additives.
The introduction of various types of organosilicon additives into the composition of the concrete mixture and mortars during their manufacture is one of the ways to protect the enclosing structures operated under conditions of the salt form of physical corrosion or high humidity.
It is more effective to impart hydrophobic properties to the cement stone of concretes and mortars throughout the structure, which becomes possible in the case of using the addition of polyphenylethoxysiloxane.
The FES additive increases the thermal properties of the enclosing structures due to a significant decrease in sorption moisture, including in the presence of salts.
Significantly increases the vapor permeability of expanded clay concrete with the addition in the presence of salts also plays a positive role, since it contributes to a more intensive drying of the structure.
1. Huseynov E.I. Influence of watersoluble organosilicon compounds on concrete resistance. Abstract of the dissertation for the degree of candidate of technical sciences. M., 1974.
2. Silina E.S. Investigation of the resistance of concretes and mortars modified with some types of organosilicon oligomers. Abstract of dissertation for the degree of candidate of technical sciences. M., 1974.
3. Nabiev M. Humidity regime and durability of panel walls in the presence
of water-soluble salts. Dissertation M., 1979.
4. Methods for determining the moisture characteristics of building materials. NIISMI Gosstroy of the Ukrainian SSR. Kiev, 1970.
5. Djurayevna, T. N. (2020). Influence Of Surface Additives On Strength Indicators Of Cement Systems. The American Journal of Applied sciences, 2(12), 81-85.
6. Djurayevna, T. N. (2020). Building Materials Determined In The
Architectural Monuments Of Central Asia. The American Journal of Applied sciences, 2(12), 77-80.
7. Ashurov, M., Sadirov, B. T., Xaydarov, A. M., Ganiyev, A. A., Sodikhonov, S. S., & Khaydarova Kh, Q. (2021). Prospects for the use of polymer composite fittings in building structures in the republic of Uzbekistan. The American Journal.
8. Ogli, X. A. M. (2021). Construction Of Flexible Concrete Elements In Buildings. The American Journal of Engineering and Technology, 3(06),
101-105.
9. Gayradjonovich, G. S., Mirzajonovich,
Q. G., Tursunalievich, S. B., & Ogli, X. A.
M. (2021). Corrosion State Of Reinforced Concrete Structures. The American Journal of Engineering and Technology, 3(06), 88-91.
10. Ogli, X. A. M. Development of effective cement additives for the production of heat-resistant concrete based on technogenic waste. International Journal of Researchculture Society.
India (2019. 12. 12).
11. Usmonov, Q. T., & Xaydarov, A. M. (2021). Yirik shaharlarda turar-joy maskanlari uchun xududlarni muhandislik tayyorgarlik va obodonlashtirish ishlarini amalga oshirish yo ‘llari. Scientific progress, 2(6), 1297-1304.
12. Mirzajonovich, Q. G., Ogli, A. U. A., & Ogli, Х. AM (2020). Influence Of Hydro
Phobizing Additives On
Thermophysical Properties And LongTerm Life Of KeramzitObetona In An Aggressive Medium. The American Journal of Engineering and
Technology, 2(11), 101-107.
13. Ogli, Х. AM, Ogli, AUA, &
Mirzajonovich, QG (2020). Ways Of Implementation Of Environmental Emergency Situations In Engineering Preparation Works In Cities. The American Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2(11), 108-112.
14. Ogli, Х. AM, Ogli, AUA, &
Mirzajonovich, QG (2020). Hazrati Imam Architecture The Complex Is A Holiday Of Our People. The American
Journal of Engineering and
Technology, 2(11), 46-49.
15. Ogli, X. A. M. Development of effective cement additives for the production of heat-resistant concrete based on technogenic waste" International Journal of Researchculture Society.
India (2019. 12. 12).
16. Usmоnov, Q., & Хaydarov, A. (2021). The Methods for Implementing Engineering and Preparatory Works and Improvement in Cities. CENTRAL ASIAN JOURNAL OF THEORETICAL &
APPLIED SCIENCES, 2(11), 218-225.
17. Tolkin, A. (2020). Reconstruction of 5storey large panel buildings, use of atmospheric precipitation water for technical purposes in the building. The American Journal of Applied sciences, 2(12), 86-89.
18. Tolqin, A. (2021). Ancient greek and ancient rome architecture and urban planning. The American Journal of Engineering and Technology, 3(06), 82-
87.
19. T. Axmedov GOTIKA USLUBINING
ARXITEKTURADAGI AHAMIYATI // Ilmiy taraqqiyot. 2021 yil. 6-son. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/gotika -uslubining-arxitekturadagi-ahamiyati (kirish sanasi: 10.12.2021).
20. Ibrohim Numanovich Abdullayev, Azizxon Abbosxonovich Marupov, Tulqin Ahmedov. (2020). Analysis of land in protected areas of gas pipelines of different pressure on the example of the ferghana region. EPRA International Journal of
Multidisciplinary Research+ (IJMR+) - Peer Reviewed Journal, 6(5), 311-314.
21. Usmonjon Turgunaliyevich Yusupov, 2 Akhmedov Tulkin Obidovich. (2019). Development of polyfunctional additives based on secondary resources and technologies of portland cement production. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH CULTURE
SOCIETY, 3(12), 200-208.
22. Nabiev, M., GM, G., & Sadirov, B. T. (2021). Reception of improving the microclimate in the houses of the fergana valley. The American Journal.
23. Abdukhalimjohnovna, M. U. (2021). Technology Of Elimination Damage And Deformation In Construction Structures. The American Journal of Applied sciences, 3(5), 224-228.
24. Mirzaahmedov, A. T. (2020). Algorithm For Calculation Of Multi Span Uncut Beams Taking Into Account The Nonlinear Work Of Reinforced Concrete. The American Journal of Applied sciences, 2(12), 26-35.
25. Мирзаахмедов, А. Т.,
Мирзаахмедова, У. А., & Максумова, С. Р. (2019). Алгоритм расчета предварительно напряженной железобетонной фермы с учетом нелинейной работы железобетона.
Актуальная наука, (9), 15-19.
26. Mirzaakhmedova, U. A. (2021).
Inspection of concrete in reinforced concrete elements. Asian Journal of Multidimensional Research, 10(9), 621628.
27. Abdukhalimjohnovna, M. U. (2020). Failure Mechanism Of Bending Reinforced Concrete Elements Under The Action Of Transverse Forces. The American Journal of Applied sciences, 2(12), 36-43.
28. Mirzaahmedov, A. T. (2020).
Accounting For Non-Linear Work Of Reinforced Concrete In The Algorithms Of Calculation And Design Of Structures. The American Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2(11), 54-
66.
29. Мирзаахмедов Абдухалим
Тахирович, & Мирзаахмедова Угилой Абдухалимжановна (2019). Алгоритм расчета железобетонных балок прямоугольного сечения с односторонней сжатой полкой. Проблемы современной науки и образования, (12-2 (145)), 50-56.
30. Mirzaeva, Z. A. (2021). Improvement of technology technology manufacturing wood, wood with sulfur solution. Asian Journal of Multidimensional Research, 10(9), 549-555.
31. Мирзаева Зарнигор Алишер Кизи, & Рахмонов Улмасбек Жуманазарович (2018). Пути развития инженерного образования в Узбекистане.
Достижения науки и образования, 2
(8 (30)), 18-19.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.