
Test # 2 on the topic "the Structure of matter" - the STRUCTURE of MATTER - LESSON PLANS in CHEMISTRY 11 class-lesson plans-lesson plans-author's lessons-plan-lesson summary-chemistry
The purpose of the lesson: to identify the level of assimilation of knowledge of the topic.
Equipment: cards of test work options. The first level and the advanced level.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment
Instructing students on the implementation of the control work.
II. Performing control work on options I, II (first level)
Option 1
Task 1
Draw a diagram of the formation of a bond in the hydrogen chloride molecule.
Task 2
How does the polarity of a chemical bond change in a series of compounds CH4-H2S—NSL? Give a reasonable answer.
Task 3
Determine the degree of oxidation of elements in substances whose formulas are Na2S, SO2, KNO3, Al2(SO4)3, OF2.
Task 4
Write the structural formulas of substances corresponding to the molecular formula C4H8. Name them according to their systematic nomenclature, and determine the type of isomerism.
Option 2
Task 1
Draw a diagram of the formation of a bond in a hydrogen sulfide molecule.
Task 2
How does the polarity of a chemical bond change in a series of compounds HF-H2O-NH3? Give a reasonable answer.
Task 3
Determine the degree of oxidation of elements in substances with formulas CCL4, Ba(NO3)2, Al2S3, HClO,. Na2Cr2O7.
Task 4
Write the structural formulas of substances corresponding to the molecular formula C4H8O2. Name them according to their systematic nomenclature, and determine the type of isomerism.
III. The results of the lesson. Homework
Repeat the types of chemical reactions.
Advanced level
|
Option I |
Option II |
|
1. Determine the type of chemical bond in these compounds, and give a reasonable answer. |
|
|
magnesium fluoride, bromine. sulfur (IV) chloride, water |
nitric oxide (II), oxygen, sodium sulfide, hydrogen peroxidehydrogen peroxide |
|
2. Determine the type of hybridization and the geometry of the molecule. |
|
|
SO3 |
NCl3 |
|
3. Suggest a structural formula for this compound and name it. Specify which types of isomerism are typical for it. Make up one isomer of each species and name them. |
|
|
S2N12 |
S5N8 |
|
4. To make the synthesis reaction. |
|
|
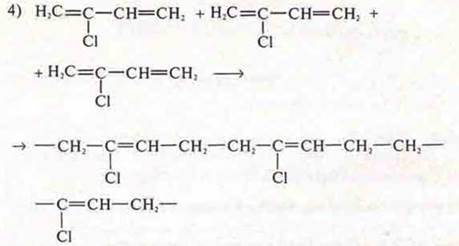
chloroprene rubber. monomer 2-chlorobutadiene-1,3 |
волокна -enant; monomer amino-enant acid
|
|
Write down the formula of the structural link, name the synthesis reaction. |
|
Answers to questions from the first-level options
Option I
1) HCl-hydrogen chloride, covalent polar bond.
|
one unpaired s-electron |
at the p-sublevel one unpaired p-electron |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2)
the Polarity of the chemical bond in the row![]() will
increase, because the EO in the row of constituent elements C, S, Cl increases,
and the EO of hydrogen remains unchanged.
will
increase, because the EO in the row of constituent elements C, S, Cl increases,
and the EO of hydrogen remains unchanged.
The greatest difference in the EO will be in the connection NCl.
![]()
4) C4H8:
CnH2n-alkene, an interclass isomer of cycloalkane
CnH2n-iycloalkane, an interclass isomer of an alkene
![]() -
butene-1
-
butene-1
![]() — butene-2
(isomerism of the position of the multiple bond)
— butene-2
(isomerism of the position of the multiple bond)
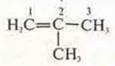 —
2-methylpropene (carbon skeleton isomerism)
—
2-methylpropene (carbon skeleton isomerism)
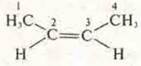 -
CIS-butene-2 (spatial geometric isomerism)
-
CIS-butene-2 (spatial geometric isomerism)
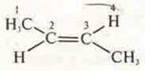 -
TRANS-butene-2
-
TRANS-butene-2
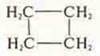 -
CYCLOBUTANE (interclass isomerism)
-
CYCLOBUTANE (interclass isomerism)
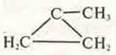 —
methyl-cyclopropane (isomerism of the carbon cycle)
—
methyl-cyclopropane (isomerism of the carbon cycle)
Option II
1) H2S-covalent polar bond hydrogen sulfide;
|
one unpaired s-electron |
two unpaired p-electrons |
|
common electron pairs |
|
2)
the Polarity of the chemical bond in the row![]() decreases,
because The EO of elements forming compounds decreases: EOF> E0O>
EON, and hydrogen remains unchanged. The greatest difference in the
EO of elements in the HF connection.
decreases,
because The EO of elements forming compounds decreases: EOF> E0O>
EON, and hydrogen remains unchanged. The greatest difference in the
EO of elements in the HF connection.
3) ![]()
4) C4H8O2— an oxygen-containing compound, either an acid or an ester.
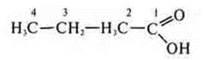 — butane acid
— butane acid
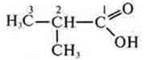 — 2-methylpropanoic acid (carbon skeleton isomerism)
— 2-methylpropanoic acid (carbon skeleton isomerism)
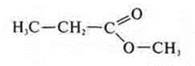 — propanoic acid methyl ester (interclass isomerism)
— propanoic acid methyl ester (interclass isomerism)
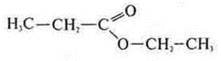 — ethyl ether of ethanoic acid (interclass isomer)
— ethyl ether of ethanoic acid (interclass isomer)
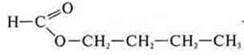 — propyl ether of methane acid (interclass isomer)
— propyl ether of methane acid (interclass isomer)
Responses to advanced-level tasks
Option I
1) MgF2-ion bond. The compound is formed by a typical nonmetal and a typical metal, the elements have a sharp difference in EO.
![]() —
covalent polar coupling, the connection is formed by non-metals that differ
slightly in the EO.
—
covalent polar coupling, the connection is formed by non-metals that differ
slightly in the EO.
![]() covalent
polar coupling, a compound formed by non-metals that differ slightly in the EO.
covalent
polar coupling, a compound formed by non-metals that differ slightly in the EO.
VG2 is a covalent polar bond formed by nonmetal atoms with the same EO.
2)![]() six
unpaired electrons in an atom;
six
unpaired electrons in an atom;
![]() 3
σ-bonds in the molecule.
3
σ-bonds in the molecule.
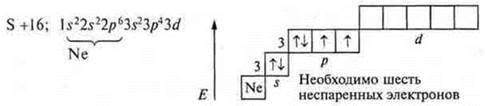
There is a steaming of 3p2-electrons and 3s2-electrons.
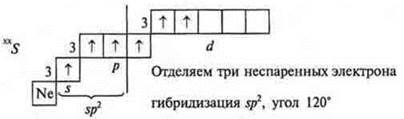
A flat triangle.
The remaining unpaired p-electrons go to form p-bonds with oxygen atoms
Structural
formula SO3: 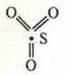
3) FROM6НTO 12. SincenN2n — alkene or yyclearin.
Consider the alkene isomerism.
![]() -
HEXEN-1
-
HEXEN-1
The isomers of position of multiple bonds:
![]() -
HEXEN-2
-
HEXEN-2
![]() -
HEXEN-3
-
HEXEN-3
Isomerism of the carbon skeleton:
 —
2-methylpentene-1
—
2-methylpentene-1
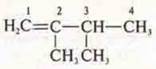 —
2,3-dimethylbutene-1
—
2,3-dimethylbutene-1
Spatial isomerism, geometric:
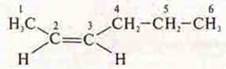 -
CIS-HEXEN-2
-
CIS-HEXEN-2
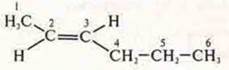 -
TRANS-HEXEN-2
-
TRANS-HEXEN-2
Interclass isomerism:
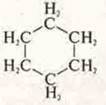 -
cyclohexane
-
cyclohexane
Structural
link: 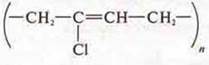
Polymerization reaction.
Option II.
1)![]() ionic
bond; the compound is formed by a typical metal and a typical nonmetal, a sharp
difference in the elements in the EO.
ionic
bond; the compound is formed by a typical metal and a typical nonmetal, a sharp
difference in the elements in the EO.
![]() —
covalent polar coupling, the connection is formed by elements non-metals,
slightly differ in the EO.
—
covalent polar coupling, the connection is formed by elements non-metals,
slightly differ in the EO.
![]() —
covalent polar coupling, the connection is formed by nonmetal elements,
slightly differ in the EO.
—
covalent polar coupling, the connection is formed by nonmetal elements,
slightly differ in the EO.
O2-covalent nonpolar bond, the compound is formed by nonmetal atoms with the same EO.
2)![]() three
unpaired electrons in an atom;
three
unpaired electrons in an atom;
![]() three
σ-bonds in the molecule.
three
σ-bonds in the molecule.
![]()
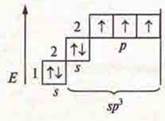 three unpaired p-electrons
three unpaired p-electrons
SP3-hybridization, four hybrid orbitals
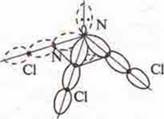 The shape of the molecule is a trigonal pyramid.
The shape of the molecule is a trigonal pyramid.
FROM5НTO 8. CnH2n-2, alkyne or alkadiene
![]() -
Pentin-1
-
Pentin-1
The isomers of position of multiple bonds:
![]() - Pentin-2
- Pentin-2
Isomerism of the carbon skeleton:
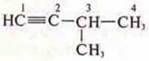 -
2-methylbutan-1
-
2-methylbutan-1
Interclass isomerism:
![]() -
pentadiene-1,3
-
pentadiene-1,3
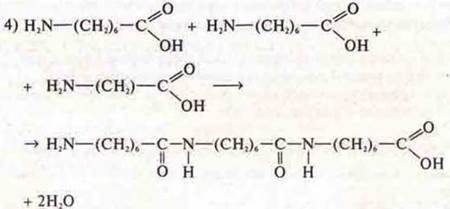
Structural link: 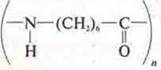
The reaction of polycondensation.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.