
The speed of chemical reactions - CHEMICAL REACTIONS - LESSON PLANS for CHEMISTRY 11 class - lesson plans - lesson plans-author's lessons-plan-lesson summary - chemistry
The purpose of the lesson: to deepen and generalize the theoretical knowledge of students about the speed of a chemical reaction; to consolidate the knowledge of formulas for expressing the speed of reactions, homogeneous and heterogeneous, its dependence on the activation energy: to teach them to perform calculations using these formulas.
Basic concepts: speed of chemical reaction, energy, chemical kinetics.
Equipment: Mg, Zn, hydrochloric acid.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment
The teacher reminds students of the corner questions of the previous lesson. The solution of calculation problems is being checked, § 12 № 1, 2, 3. to solve problems, three students are called to the blackboard.
II. Front-end survey
1) what is the cause of heat release and absorption in chemical reactions?
Answer: The reason lies in the following: there is a break in chemical bonds in the molecules of reacting substances — the expenditure of energy from outside and the formation of new bonds in the molecules of the final products of the reaction — the release of energy.
2) What reactions are called exothermic?
Answer. If eof the source products> Eof the final products, heat is released (+ Q) — an exothermic reaction.
Example: burning of magnesium: Mg + O2= 2MgO + Q.
3) What reactions are called endothermic?
Answer: If Eof the source productsEend products, heat is absorbed (- Q) - endothermic reaction.
Example: SASO3= CaO + CO2-Q.
4) What is the thermal effect of a chemical reaction?
Answer: The amount of heat that is released or absorbed as a result of the reaction is indicated by the value-there is a thermal effect.
5) What chemical equations are called thermochemical?
Answer: Equations of chemical reactions, in which the value of the thermal effect is recorded, are called thermochemical. In thermochemical reactions, the thermal effect of a reaction refers to molar quantities of initial substances and reaction products.
Example: ![]()
This thermochemical equation shows that when 1 mol of nitrogen interacts with three mol of hydrogen, two mol of ammonia is formed and 92 kJ is released. To show the thermal effect of the formation of 1 mol of the reaction product, fractional coefficients can also be used in thermochemical equations. This equation can be written as follows:
![]()
The solutions to the calculation problems of § 12 are discussed further.
Task 1. The equation of the combustion reaction of ethylene.
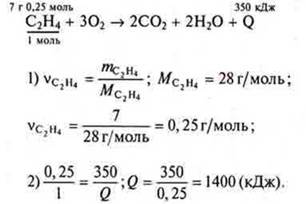
Answer: the thermal effect of the reaction is 1400 kJ.
![]()
Task 2.
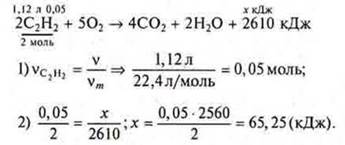
Answer: when using 1.12 liters of acetylene, 65.25 kJ will be released.
Task 3. Compilation of the reaction equation:
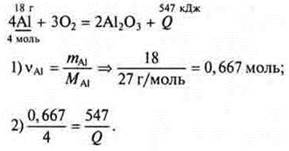
![]() — for the formation of 2 mol Al2O3.
— for the formation of 2 mol Al2O3.
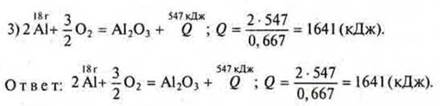
III. Learning new material
Plan of presentation
1. The concept of "chemical reaction rate". Formula for expressing the speed of a homogeneous and heterogeneous reaction.
2. The energy of activation. Possibility of chemical reactions depending on the activation energy.
3. Solving calculation problems.
The concept of reaction speed is not new to us. In the 8th grade, we studied this question, we know the formulas for expressing the reaction rate of homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions, as well as the factors that cause changes in the reaction rate.
Conduct an experiment. Let us compare the reaction rates of hydrochloric acid with the metals Mg and Zn. In terms of reducing capacity, magnesium is more active than zinc, which is what we observe in this experiment.
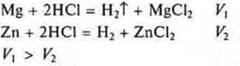
The rate of displacement of hydrogen in the reaction of magnesium with acid is greater than in the reaction of zinc with acid.
What happens as a result of the reaction?
As a result of interaction, the quantities of substances both reacting and formed in a certain volume and over a certain period of time change. The science that deals with the regularities of chemical reactions in time, predicts the speed of a chemical reaction, and elucidates its dependence on the conditions of conduct, is called chemical kinetics.
Depending on what phase substances are in in a given chemical reaction, they are called homogeneous and heterogeneous. If the homogeneous phase — the reaction is homogeneous, and heterogeneous-if the phase is inhomogeneous. Formulas for expressing the rate of such reactions differ.
The speed of a homogeneous reaction is determined by the change in the amount of substance per unit time in the unit volume.
Vhas homog.— the rate of homogeneous reaction;
Δv-change in the number of moles of one of the reactants (mol);
Δt-time interval (sec, min);
K — volume of gas or solution (l).
Since![]() the
ratio of the change in the amount of a substance to the unit volume represents the
molar concentration. Thus the rate of homogeneous reaction is determined by the
change in the concentration of one of the substances per unit time:
the
ratio of the change in the amount of a substance to the unit volume represents the
molar concentration. Thus the rate of homogeneous reaction is determined by the
change in the concentration of one of the substances per unit time:
![]()
If the reaction is between substances in different aggregate States (solid — liquid, solid — gas) or between substances that are not able to form a homogeneous medium (two immiscible liquids), then it takes place only on the contact surface of the substances. Such reactions are called heterogeneous.
The rate of heterogeneous reaction is defined as the change in the amount of substance per unit time per unit area (surface):
![]()
S is the area of contact of substances (m22, cm2).
The reaction rate is not a constant value. It is determined only in a certain time interval, as the average, and also depends on the change in the concentration of what substance it is calculated.
Example. N2+ CL2= 2hcl.
If you determine the reaction rate by changing the concentration of hydrogen, then the equation follows that from 1 mol of hydrogen 2 mol of hydrogen peroxide is formed, in the case of determining the reaction rate by changing the concentration of hydrogen peroxide, then in the second case it will be twice as large.
All the processes of chemical reactions are carried out at the micro level; in order for the particles of molecules, the atomsof reacting substances toreact, they must "collide" effectively, so that "old bonds" are broken and "new ones"can be formed. This requires energy.
The maximum excess energy that a particle (or pair of particles) must have in order for an effective collision to occur is called the activation energy Ea.
Thus, the particles entering the reaction must overcome the energy barrier, which is equal to Eand. If Eais small, then the reaction speed is high, otherwise a "push" is needed, it is necessary to acquire additional energy due to heating, a flash of light, a mechanical impact.
E activation of endothermic reactions is greater than that of exothermic reactions. Therefore, more energy is required for endothermic reactions. Many reactions are practically impossible, because they require highаEfficiency . All of this matters a great deal in our lives. If all reactions could go without having an energy barrier-Ea, then the oxygen in the air would react with all substances that can burn or simply oxidize. As a result, all organic substances would suffer, they would be oxidized to the final products of CO2and H2O. Therefore, we exist because of the presence of Ea, which does not allow reactions to go at a significant speed. If Eais very small, in the case of ionic reactions, the reactions are instantaneous under normal conditions.
For students who are studying chemistry in more depth and are preparing to go to University, it is recommended to read and analyze in section 13 how chemical reactions take Placein theenvironment .
IV. Solving calculation problems
In the lesson, it is necessary to explain to students the solution of computational problems using homogeneous and heterogeneous reaction formulas.
Task 1. Calculate the rate of a chemical reaction occurring according to the equation A(r) + B(r) = 2AB (r).
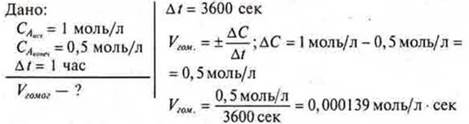
Answer: change in concentration per second = 0.000139.
3adache 2. What is the average reaction rate of A + B = C, if the initial reaction Rate ofb = 0.84 mol/l, and after 20 seconds it became 0.62 mol/l?
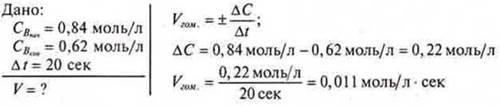
Answer: var .cpeдdom.= 0.011 mol/l sec.
Generalizations and conclusions.
III. Homework assignment
N/ a § 13 (up to factors) (abstract).
Problem 3. at the initial moment of time, the concentration of the initial substance (x) was equal to 2 mol/L. Determine the concentration of the substance (x) after one minute, if the reaction rate is 0.01 mol/l · sec.
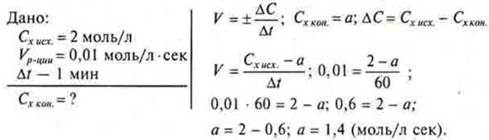
Answer: Withx con.= 1.4 mol/l sec.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.