
Start. Energy transformation in electric circuits
Teacher asks learners to draw a simple circuit consisting of electric source lamp, switch and wiring. Question:
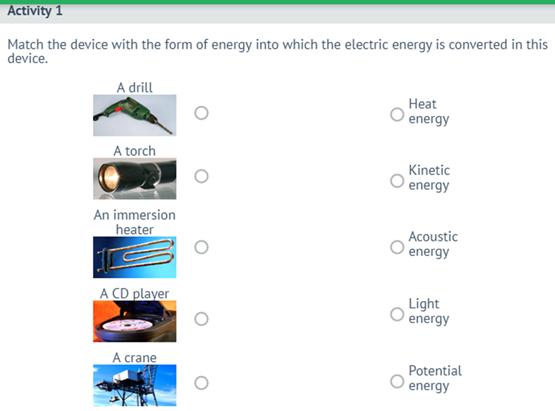
(W) Whole class discussion. Energy transformations
Electric energy is useful to us because it can be easily transformed into other forms of energy. Motors transform electric energy into mechanical energy. In other devices such as electric heaters, stoves, toasters, and hair dryers, electric energy is transformed into thermal energy in a wire resistance known as a “heating element.” And in an ordinary lightbulb, the tiny wire filament becomes so hot it glows; only a few percent of the energy is transformed into visible light, and the rest, over 90%, into thermal energy. Lightbulb filaments and heating elements in household appliances have
resistances typically of a few ohms to a few hundred ohms.
Electric energy is transformed into thermal energy or light in such devices, and there are many collisions between the moving electrons and the atoms of the wire. In each collision, part of the electron’s kinetic energy is transferred to the atom with which it collides. As a result, the kinetic energy of the wire’s atoms increases and hence the temperature of the wire element increases.
The increased thermal energy can be transferred as heat by conduction and convection to the air in a heater or to food in a pan, by radiation to bread in a toaster, or radiated as light.

(T) Teacher explanation. Joule-Lenz's law
Joule-Lenz's law shows the relationship that exists among:
Joule’s law formula: Q = I2 × R × t
where:
Q is the amount of heat, in Joules (J)
I is the electric current that flows through the wire, in amperes (A)
R is the value of the electrical resistance of the wire, in ohms (R)
t is the amount of time that current passes through the wire, in seconds (s).
Heating effect
Joule’s law can be established as the amount of heat (Q) generated in a wire with resistance (R), when a current (I) passes through it for a period of time (t).
This heat is directly proportional to:
(I) Individual work (differentiation)
Able students can answer for this question and teacher asks them to other learners.
Worked example
Calculate the amount of energy supplied by
a 4.5 V battery when:
(a) a charge of 20 C passes through it
(b) a current of 25 mA flows through is for
3 minutes
Solution:
Energy = potential difference x
Q = 4.5 x 20 = 90 J
(b) Energy = potential difference x Q =
p.d x current x time
Therefore:
Energy = 4.5 x 25x10-3 x 180 = 20.25 J
(f) Formative assessment.
Set of calculations for electrical energy
1. Calculate the electrical energy produced in 5 minutes when a current of 2 A is sent through a conductor by a potential difference of 500 volts.
[1]
2. A current of 5 ampere is passed through a conductor of 12 ohms for 2 minutes. Calculate the amount of heat produced. [1]
3. What is heating effect of current? List two electrical appliances which work on this effect.
[2]
Answers
1. W=3 ∙ 105 J [1]
2. 3.6 104 J [1]
3. When electric current passes through a high resistance wire, the wire becomes and produces heat. This is called heating effect of current. electric Iron, Electric Heater are two appliances which work on this effect
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.