
Министерство образования и науки Хабаровского края
Краевое государственное бюджетное профессиональное образовательное учреждение
«Хабаровский промышленно-экономический техникум»
(для обучающихся 1 курса, имеющих нарушения слуха, зрения, опорно-двигательного аппарата)
Специальности:
23.02.04 «Техническая эксплуатация подъемно-транспортных, строительных и дорожных машин и оборудования (по отраслям)»
23.02.03 «Техническое обслуживание и ремонт автомобильного
транспорта»
09.02.04 «Информационные системы (по отраслям)»
35.02.03 «Технология деревообработки»
08.02.01 «Строительство и эксплуатация зданий и сооружений»
08.02.06 «Строительство и эксплуатация городских путей
сообщения»
Хабаровск 2017
1
Организация-разработчик: краевое государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение «Хабаровский промышленно-экономический техникум»
Автор-составитель: Полуренко Е.В., преподаватель высшей категории КГБ ПОУ ХПЭТ
Рабочая тетрадь по дисциплине «Иностранный язык» для обучающихся 1 курса, специальностей технического профиля, имеющих нарушения слуха, зрения, опорнодвигательного аппарата/ Полуренко Е. В.–Хабаровск, 2017, 101 стр.
Рабочая тетрадь по учебной дисциплине «Иностранный язык» предназначена для работы обучающихся I курса, имеющих нарушения слуха, зрения и опорно-двигательного аппарата специальностей технического профиля. Рабочая тетрадь тесно связана с программой структурно и содержательно. Основное ее назначение – помочь обучающимся закрепить и активизировать языковой и речевой материал, автоматизировать лексико-грамматические навыки, развить умения в чтении и письменной речи.
Широкий спектр разнообразных заданий позволяет реализовать личностноориентированный подход в обучении английскому языку работать с обучающимися с разным уровнем подготовки и с разными интересами. Рабочая тетрадь разработана для изучения географического положения, политического строя, природы и культуры англоязычных стран и состоит из 15 тем.
Составлена в соответствии с Федеральным государственным образовательным стандартом среднего (полного) общего образования, утвержденным приказом Министерства образования и науки РФ от 17.05.2012 г. № 413 и адаптированной рабочей программой учебной дисциплины «Иностранный язык».
СОДЕРЖАНИЕ
ПОЯСНИТЕЛЬНАЯ ЗАПИСКА 4
Инструкция для работы с тетрадью 7
Практическое занятие № 1 «Соединенное королевство Великобритании и 10
Северной Ирландии»
Практическое занятие № 2 «Политическая система страны. Политические 14 партии. Статус Королевы»
Практическое занятие № 3 «Города Великобритании» 18
Практическое занятие № 4 «Лондон- столица Великобритании» 22
Практическое занятие № 5 «Лондон. Достопримечательности» 30
Практическое занятие № 6 «Образование в Великобритании» 37
Практическое занятие № 7 «Университетское образование в 41
Великобритании»
Практическое занятие № 8 «Великие английские писатели. В.Шекспир. В. 48
Скотт»
Практическое занятие № 9 «Традиции, обычаи и праздники англичан» 56
Практическое занятие № 10 «Погода в Великобритании» 59
Практическое занятие № 11 «Соединенные Штаты Америки. 61
Географическое положение. История государства»
Практическое занятие № 12 «Политическая система США.. Символы 64 государства. Вашингтон. Достопримечательности»
Практическое занятие № 13 «Великие американские писатели.Д.Лолндон 68
М.Твен»
Практическое занятие № 14 «Праздники в США» 72
Практическое занятие № 15 «Австралия и Новая Зеландия» 76
Грамматический материал к разделу 84
Литература 105
Заключение 106
Адаптированная рабочая тетрадь по учебной дисциплине ―Иностранный язык‖ предназначена для обучающихся, имеющих нарушения зрения, слуха и опорнодвигательного аппарата.
Адаптированная рабочая тетрадь составлена в соответствии с примерной программой общеобразовательной учебной дисциплины «Иностранный язык», рекомендованной Федеральным государственным автономным учреждением «Федеральный институт развития образования» 21. 06. 2015 г., и адаптированной программой учебной дисциплины «Иностранный язык» для обучающихся 1 курса специальносте технического профиля.
Рабочая тетрадь для лиц с нарушением зрения, слуха и опорно-двигательного аппарата разработана к разделу 11 « Англоговорящие страны» и состоит из 15 тем, включает в себя информационный и контролирующий блоки. Информационный блок несет в себе информацию об учебном материале, в контролирующий блок входят задания для контроля полученных знаний и умений, задания для самостоятельной работы.
Цель данной адаптированной рабочей тетради – способствовать повышению эффективности обучения и уровня творческого развития обучаемых. Содержание тетради базируется на тематическом принципе, упражнения и задания в данной тетради подходят к конкретному тексту и представляют собой материал проверочного и обучающего характера.
Построение тетради делает работу обучающихся более осмысленной. Приступая к изучению курса, он имеет представление, какой объем работы ему предстоит выполнить, ясно представляет свои учебные задачи, имеет возможность планировать предстоящую работу, а при желании работать с опережением.
Рабочая тетрадь не содержит ответов, поэтому при самостоятельной работе обучающегося необходим систематический контроль со стороны преподавателя для проверки правильности выполнения заданий. Данное учебно-методическое пособие является инструментом текущей аттестации. Рабочая тетрадь имеет инструкцию для работы с тетрадью, правила ведения рабочей тетради, рекомендации по выполнению упражнений, критерии выставления оценок.
Для выполнения заданий по адаптированной рабочей тетради каждый обучающийся с учетом медицинских показаний обеспечивается необходимым оборудованием.
Для оформления рабочего места обучающегося, имеющего нарушения слуха используются технические средства обучения: акустическая система, развивающий центр с горизонтальным дисплеем, моноблок с сенсорным экраном, портативный тифлоплеер Smart Bee, ноутбук, машина сканирующая и читающая текст, мышь-сканер, интерактивная панель и документ-камера, стационарный увеличитель с монитором, радиокласс «Сонет-РСМ РМ5-1»(заушный индуктор и индукционная петля), слуховой аппаратный тренажер «Соло-01В» (М), магнитно-маркерная доска, проектор, активная акустическая система.
Для оформления рабочего места обучающегося, имеющего нарушения зрения, используются технические средства обучения: видеоувеличитель ручной, акустическая система, развивающий центр с горизонтальным дисплеем, моноблок с сенсорным экраном, портативный тифлоплеер Smart Bee, ноутбук, машина сканирующая и читающая текст, мышь-сканер, интерактивная панель и документ-камера, стационарный увеличитель с монитором, выносная компьютерная кнопка, принтер для печати шрифтом Брайля, магнитно-маркерная доска, проектор, активная акустическая система, дисплей брайлевский, программное обеспечение «Доступная среда для незрячих и слабовидящих».
Для оформления рабочего места обучающегося, имеющего нарушения опорнодвигательного аппарата, используются технические средства обучения: акустическая система, развивающий центр с горизонтальным дисплеем, моноблок с сенсорным экраном, ноутбук, машина сканирующая и читающая текст, мышь-сканер, интерактивная панель и документ-камера, магнитно-маркерная доска, проектор, активная акустическая система.
Обучение по данной рабочей тетради реализуется в течение одного учебного года в количестве 30 часов.
Значимость адаптированной рабочей тетради заключается в углублении лингвострановедческих знаний, овладении устной и письменной речью на базовом уровне, формировании умений применять полученные знания на практике, в обеспечении сознательного усвоения материала, развития навыков активных речевых действий, логического мышления.
Инструкция для работы с тетрадью.
Уважаемый обучающийся!
Прежде, чем Вы начнете самостоятельную работу, прочтите эти рекомендации.
Самостоятельная подготовка позволит Вам:
- гибко использовать личное время, т.е. индивидуализировать объем
самоподготовки в зависимости от опыта, навыков и уровня знаний;
- восстановить возможно имеющиеся пробелы в знаниях; во время теоретической части обучения сконцентрировать внимание на практическом компоненте программы.
Структура рабочей тетради имеет два компонента: учебно-информационные материалы и систему вопросов и заданий. Система вопросов и заданий содержит перечень заданий, позволяющих оценить уровень самоподготовки и использовать материалы самоподготовки на практических занятиях.
В процессе выполнения заданий Вы:
- овладеете национально- культурной спецификой стран изучаемого языка;
- научитесь строить речевое и неречевое поведение адекватно этой специфике, выделять общее и различное в культуре родной страны и англоговорящих стран;
- совершенствуете умения использовать грамматические структуры и языковые средства в соответствии с нормами данного языка, свободное использование приобретенного словарного запаса.
- сформируете умение использовать английский язык как средство для получения информации из англоязычных источников в образовательных и самообразовательных целях.
Выполнив все задания по данному разделу, Вы будете знать:
- социокультурную специфику англоговорящих стран;
- лексический и грамматический минимум, необходимый для чтения и перевода иностранных текстов страноведческой направленности;
- как логично и точно излагать свою точку зрения, используя адекватные языковые средства.
Рабочая тетрадь по дисциплине «Иностранный язык» предусматривает использование бумажного и электронного вариантов.
Правила ведения рабочей тетради.
В рабочей тетради представлены вопросы, различные по форме задания, тестовые задания для самостоятельной проработки.
Предусматривается письменное выполнение упражнений непосредственно в тетради, что позволит экономить время и упрощает работу.
Ваши ответы должны быть написаны разборчиво и ясно, так как они будут проверяться преподавателем.
Если при работе с каким-либо вопросом Вам будет не хватать места при ответе, то Вы можете вложить или вклеить чистый лист бумаги с указанием номера задания. Задания разнообразны. Для их правильного выполнения ниже приводится ряд рекомендаций.
Рекомендации по выполнению упражнений:
1. Работа с лексическим материалом: найдите в словаре перевод и транскрипцию незнакомых слов, выпишите в отдельную тетрадь- глоссарий. Прочитайте и запомните данные слова и выражения.
2. Работа с текстом: прочитайте и переведите текст.
3. Работа с диалогом: дополните диалог, переводя реплики с русского на английский язык.
4. Работа с грамматическими упражнениями: прочитайте грамматический материал к темам и выполните упражнения.
5. Составьте аннотацию к тексту: аннотация-это краткое изложение содержания в виде перечня основных вопросов и краткой характеристики.
Критерии выставления оценок для всех практических работ:
выполнение 65% от всей работы - оценка «удовлетворительно»;
65%-80%- оценка «хорошо»; более 80% – «отлично».
За выполнение задания помеченное звездочкой *, обучающийся получает дополнительную оценку.
Оценка за выполнение практических работ должна быть выставлена до начала следующей работы.
Форма отчета по работе в рабочей тетради
|
№ |
Тема практической работы |
Дата сдачи |
Дата контроля |
Оценка |
Роспись
|
|
|
Соединенное королевство Великобритании и Северной Ирландии |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Политическая система страны. Политические партии. Статус Королевы. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Города Великобритании. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Лондон- столица Великобритании. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Лондон. Достопримечательности Лондона. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Образование в Великобритании. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Университетское образование в Великобритании. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Великие английские писатели. В.Шекспир. В.Скотт. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Традиции, обычаи и праздники англичан. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Погода в Великобритании.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Соединенные Штаты Америки. Географическое положение. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Политическая система США. Вашингтон. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Великие Американские писатели. Д.Лондон. М. Твен. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Праздники в США. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Австралия и Новая Зеландия. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Грамматический материал |
|
|
|
|
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 1
ТЕМА: «Соединенное королевство Великобритании и Северной Ирландии»
«The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland»

1. Read the text: «The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland».
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the official name of the British Kingdom, including England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
It is situated on the British Isles which lie off the north-west coast of the European continent.
The British Isles consist of more than 5,500 islands. The biggest island is Great Britain. There are also the Shetland Islands, the Hebrides, the Orkney Islands, the Isle of Man, Anglesey, Wight, etc.
Great Britain stretches for 1000 kilometers from the south to the extreme north, and for 500 kilometers in the widest part.
It is washed by the Atlantic Ocean in the north-west, north and south-west, and is serrated from the European continent by the North Sea, the Straight of Dover and the English Channel.
The country occupies the area of 242,500 square kilometers. The territory of Great Britain is small, yet the country has a wide variety of scenery. England, which is the richest, the most fertile and the most populated part of the country, is a vast plain. It is separated from Scotland by the Cheviot Hills running from east to west. In North-West England there are many picturesque lakes with green, wooded or grassy shores and grey mountains all around. It is famous Lake District, the real tourist attraction. Wales and Scotland are mountainous areas. In Wales the mountains are rocky and difficult to climb. The highest mountain is Showdown. The Highlands of Scotland are among the oldest mountains in the world. The highest of them is Ben Nevis. By the way, Scotland is a land of famous lakes. They are called "lochs" there. The beautiful Loch Lomond is the largest one and Loch Ness attracts millions of tourists by its legendary monster.
The rivers are not long in Britain. The largest of them are the Severn (350 km), the Clyde and the Mersey. They flow into the Irish Sea. The Thames (346 km), the Trent (274 km), the Oise keep their way to the North Sea. The Thames is the busiest and the most important river in Great Britain. The capital of Great Britain, London, stands on the Thames.
The climate of Great Britain is temperate and mild due to the influence of the warm waters of the Gulf-Stream. The summers are usually cool and rainy. There is much rain and fog in autumn and in winter. Great Britain is a damp country. The weather is a very changeable and it is the favorite topic of conversation in Britain.
The population of Great Britain is 57 million people. Population density is highest in England and lowest in Scotland. Four out of every five people live in towns and cities. The largest of them are London, Birmingham, Liverpool, Manchester, Glasgow, Edinburgh, Cardiff and Belfast.
Britain is a parliamentary democracy with a constitutional monarch. The present
Sovereign is Queen Elizabeth II. In practice, the Sovereign reigns but doesn‘t rule. The United Kingdom is governed by the Government - a body of Ministers, the Cabinet. It consists of the leading members of the political parties are the Conservatives, the Labor party and the LiberalSocial Democratic party. The Prime Minister, who heads the Government, is usually the leader of the party which has a majority in the House of Commons. The House of Commons and the House of Lords with the Monarch comprise the Parliament. Once Parliament approves legislation it receives the Royal Assent and becomes law.
Great Britain is one of the worlds major industrialized and trading nations. It enjoys long established and trading nations. It enjoys a long established democratic system of government which has provided political stability. The United Kingdom is a member of the European Community (EC), the United Nations Organization (UNO), the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and the Commonwealth.
2. Learn the words:
1. An island - остров
2. Europe - Европа
3. The North север
4. The South - юг
5. The East - восток
6. The West - запад
7. British Isles – Британские острова
8. Ireland - Ирландия
9. England - Англия
10. Scotland – Шотландия
11. Wales - Уэльс
12. Northern Ireland – Северная Ирландия
13. A coast - побережье
14. A country - страна
15. The Atlantic Ocean – Атлантический Океан
16. The Irish Sea – Ирландское море
17. The North Sea – Северное море
18. The English Channel – пролив Ла-Манш
19. The Thames - Темза
20. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland – Соединенное
Королевство Великобритании и Северной Ирландии.
21. Climate - климат
22. Mild - мягкий
23. changeable - изменчивый
24. The average temperature – средняя температура
25. Weather - погода
26. above – выше, над
27. Frost - мороз
28. To freeze - замерзать
29. foggy - туманный
30. wet – влажный, мокрый
3. Find in the text:
1. Объединенное Королевство расположено на Британских островах, которые находятся недалеко от северо-западного побережья Европы. ___________________
______________________________________________________________________
2. Англия, наиболее богатая, плодородная и наиболее заселенная часть страны, является обширной равниной._________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
3. Уэльс и Шотландия - горные районы.____________________________________
4. Четверо из каждых пяти человек живут в
городах.______________________________________________________________________
5. Погода в Британии изменчивая и является любимой темой для разговоров.
____________________________________________________________________
6. Фактически, монарх царствует, но не правит.
_____________________________________________________________________
7. Великобритания – одна из основных промышленных и торговых наций в мире.
________________________________________________________________________
4. Write down the end of the sentences.
1. Great Britain is washed by the Atlantic Ocean in the north-west, north and south-west and is separated from the European continent______________________________________
a) By the Irish Sea and the Strait of Dover.
b) By the Cheviot Hills.
c) By the North Sea, the Strait of Dover and the English Channel.
2. In Northwest England there are many picturesque_______________________
a) Lakes with green, wooded or grassy shores and grey mountains all around.
b) Mountains with green, wooded or grassy slopes.
c) Rivers with green, wooded or grassy banks and grey mountains.
3. The Highlands of Scotland are among ___________________________________
a) The highest mountains in the world.
b) The oldest mountains in the world.
c) the most rocky mountains in the world.
4. Summers are usually ________________________________________________ a) Hot and rainy.
b) Cool and rainy.
c) Warm and sunny.
5. Write the sentences in the right order according to the text.
1. The climate of Great Britain.
2. The political system of the United Kingdom.
3. The geographical position of the UK.
4. The population of Great Britain.
5. A wide variety of scenery.
6. The world is major industrialized and trading nation.
6. * Speak about:
1. The geographical position of the UK.
2. The climate of Great Britain.
3. The population of Great Britain.
4. The political system of the United Kingdom.
5. Great Britain as one of the major industrialized and trading nation
_____________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________
Вывод по теме:
________________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 2
ТЕМА: «Политическая система страны» “Political System of Great Britain”.

1. Read and translate the text:
“Political System of Great Britain”.

The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is a constitutional monarchy. Britain does not have a written constitution. Parliament is the most important authority in Britain.
The monarch serves formally as head of state. The present sovereign is Queen Elizabeth II (the second).
The House of Commons consists of Members of Parliament. General elections are held every five years. Ail citizens aged 18 have the right to vote.
There are few political parties in Britain. The main ones are: the Conservative Party, the Labour Party.
Each political party puts up one candidate for each constituency. The one who wins the most votes is MP for that area.
The party which wins the most seats in Parliament forms the Government; its leader becomes the Prime Minister.
The functions of the House of Commons are legislation and scrutiny of government activities. The House of Commons is presided over by the Speaker.
The House of Lords is presided by the Lord Chancellor. The House of Lords has no real power.
It's in the House of Commons that new bills are introduced and debated.
Parliament is responsible for British national policy. Local governments are responsible for organizing of education, police and many others.
National Emblems of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom (abbreviated from "The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland") is the political name of the country which consists of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland (sometimes known as Ulster).
Great Britain is the name of the island which is made up of England, Scotland, Wales, whereas the British Isles is the geographical name of all the islands off the north-west coast of the European continent. In everyday speech "Britain" is used to mean the United Kingdom.
The flag of the United Kingdom, known as the Union Jack, is made up of three crosses.
The upright red cross on a white background is the cross of the 1st George, the patron saint of England. The white diagonal cross on a blue background is the cross of St. Andrew, the patron saint of Scotland, The red diagonal cross on a white background is the cross of St. Patrick, the patron saint of Ireland.
The Welsh flag, called the Welsh dragon, represents a red dragon on a white and green background.
St. George's Day falls on 23 April and is regarded as England's national day. On this day some patriotic Englishmen wear a rose pinned to their jackets'. A red rose is the national emblem of England from the time of the Wars of the Roses (15th century).
St. Andrew's Day (the 30th of November) is regarded as Scotland's national day. On this day some Scotsmen wear a thistle in their buttonhole. As a national emblem of Scotland, thistle apparently first used in the 15th century as a symbol of defence. The Order of the Thistle is one of the highest orders of knighthood. It was founded in 1687, and is mainly given to Scottish noblemen (limited to 16 in number).
St. Patrick's Day (the 17th of March) is considered as a national day in Northern Ireland and an official bank holiday there. The national emblem of Ireland is shamrock. According to legend, it was the plant chosen by St. Patrick to illustrate the Christian doctrine of the Trinity to the Irish.
St. David's Day (the 1st of March) is the church festival of St. David, a 6th-century monk and bishop, the patron saint of Wales. The day is regarded as the national holiday of Wales, although it is not an official bank holiday.
On this day, however, many Welshmen wear either a yellow daffodil or a leek pinned to their jackets, as both plants are traditionally regarded as national emblems of Wales.
In the Royal Arms three lions symbolize England, a lion rampant — Scotland, and a harp — Ireland. The whole is encircled and is supported by a lion and a unicorn. The lion has been used as a symbol of national strength and of the British monarchy for many centuries. The unicorn, a mythical animal that looks like a horse with a long straight horn, has appeared on the Scottish and British royal coats of arms for many centuries, and is a symbol of purity.
2. Complete the following sentences:
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is
a___________________________________________________________________________ Parliament is the most__________________________________________________________
The monarch serves formally____________________________________________________
The House of Commons consists of_________________________________________________
There are few political parties in Britain. The main ones
are___________________________________________________________________________
Each political party puts__________________________________________________________
3. Find sentences which proved that:
1. Parliament is the most important authority in Britain.
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
2. There are few political parties in Britain______________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
3. Parliament is responsible for British national policy.____________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
4. The flag of the United Kingdom, known as the Union Jack__________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
5. The Welsh flag, called the Welsh dragon_____________________________________
6. St. George's Day falls on 23 April and is regarded as England's national day_________
_____________________________________________________________________________
7. The day is regarded as the national holiday of Wales._________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
Вывод по теме:
________________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 3
ТЕМА: «Города Великобритании». “The Towns of Great Britain”

The Towns of Great Britain
1. Read and translate the text:
The centre of everything in Great Britain is the city of London. It's situated at the centre of a vast national and international network of communication. London consists of four main districts, which differ from each other. These are the City, Westminster, the West End and the East End. London's industries are extremely varied. Among them an extensive system of docks and port industries, electrical engineering, the motor car industry and other. The other towns, situated to the north of the Thames are Oxford and Cambridge.

Oxford was first mentioned in recorded history in the tenth century and later became an important trade centre in medieval times, then it developed into leading educational centre.

Cambridge is also best known for its ancient university. Its industries are mostly concerned with electronics which has an international reputation.

Bristol dominates South-west England, both as the region's largest seaport and as its largest city. It is a major centre of metallurgy, aircraft and chemical industries. Of the towns situated in the south of England the largest ones are Southampton, Portsmouth and Brighton.
Southampton is primarily a seaport, the most important on the south coast.

Brighton is one of the most popular seaside resorts of Britain. It has mild climate, warm sea and wonderful beaches sea and wonderful beaches.

Manchester is a city of ancient origin. By the 17th century it was great commercial city, a centre of textile industry. Now engineering along with clothing manufacture are most important industries there.

Sheffield, situated in South Yorkshire, produces almost two-thirds of the country's alloy steel, it is famous for its-tools and cutlery. Other industries include paper making machinery and food processing.

In North Yorkshire the largest town is York. Its leading industries are engineering and manufacture of confectionery. York attracts many tourists because of its famous medieval city walls.
2.* Form as many names of the towns as you can using the following part of the words.
Chester, pool, fast, Brad, New, Brigh, ford, field, Liver, diff, Bel, tol, Birming, Strat, Glas, Ro, bridge, Edin, Man, ford, Castle, Lon, ton, Ox, Shef, Car, Bris, Cam, ham, gow, burgh, don, ford, chester.
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
3. Guess what town of Great Britain is it:
1) The center of everything in Great Britain is the city of …….
2) ……………. consists of three main districts, which differ from each other.
3) The towns, situated to the north of the Thames are …………………… and ……..
4) …………………… is best known for its modern university.
5) …. ………………..is primarily a seaport, the most important on the south coast.
6) ……………………. is one of the most popular seaside resorts of Britain.
7 ) ………………… has mild climate, warm sea and wonderful beaches.
8) ….. ………………..attracts many tourists because of its famous medieval city walls.
4. Speak about one of the cities.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
Вывод по теме:
________________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 4
ТЕМА: «Лондон» «London»

1. Read and translate the text:
London
London is the capital of Great Britain or the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. It is an old city, its history counts more than two thousand years. London is both the capital of the country and a huge port. London is situated upon both banks of the Thames, about forty miles from the mouth and is divided into two parts by the river: north and south. There are 17 bridges that cross the river. The population of London is more than 9 million people.
The history of London goes back to Roman times. Due to favorable geographical position, soon after the Roman conquest, a small town became an important trade centre. Actually, London can be divided into several parts: the City or Downtown of London, Westminster, the West End and the East End Westminster, the West End and the East End.

The City is the oldest part of London with narrow streets and pavements. There are many offices, companies and banks in this part of London. The City of London is the financial centre of the United Kingdom. Only a few thousand people live there, but in the day-time it is full of people: as about half a million people come to work there. The biggest Banks and offices are concentrated in the City
. 
The West End is the centre of London. It is full of richest hotels, largest supermarkets, best cinemas and concert halls. There are a lot of beautiful houses and gardens. Only well-to-do people can live there.

Another important district of London is Westminster, where most of Government buildings are situated. Westminster Palace is the seat of the British Parliament. Westminster Palace was founded in 1050. It is situated in the centre of London. Many great Englishmen were buried in the Abbey: Newton, Darwin and others.

The Towers of the Houses of Parliament stand high above the city. On the highest tower there is the largest clock in the country which is known to the whole world as Big Ben. One can hear Big Ben strike every quarter of an hour. The clock «Big Ben» came into service in 1859. Big Ben is the biggest clock bell in Britain. The official London residence of the Queen is Buckingham Palace. It was built in the 18th century.

There are many nice squares in London. Trafalgar Square is one of them and it is in the centre of the West End. One can see a statue of Lord Nelson in the middle of this square. There are many museums, libraries and galleries in London.

The Tate Gallery is one of the well-known galleries in London. Henry Tate was a sugar manufacturer. He was fond of paintings and collected many pictures.

The British Museum is a very interesting place in London. It was founded in 1753. The library of this museum has lots of books.

The East End of London is the industrial area and the place where the working people live. There are many factories, workshops and docks there. The East End, lying eastwards from the City is very large and crowded. There are many cars and buses in London.

There is the Tube (an underground) in London too. The underground, constructed in London, was the first underground in the World.
2. Translate the following sentences into English:
1. Лондон-столица Объединенного Королевства Великобритании и Северной Ирландии, один из крупнейших морских портов и самый притягательный город в мире.
![]()
2. Лондон предлагает своим гостям огромное разнообразие достопримечательностей; это город мечты для каждого, кто интересуется историей и культурой
Англии._____________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________
3. Здание Парламента – символ Лондона – величественно расположились на северном берегу Темзы._________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
4. Вестминстерское аббатство является национальной святыней, где короновались короли и королевы и похоронены знаменитые люди.________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
5. Собор святого Павла стоит на месте, где находились саксонская и нормандская церкви, разрушенные во время Великого пожара в Лондоне в 1666 году.________________
________________________________________________________________________
6. Посреди Трафальгарской площади мы видим колонну со статуей адмирала
Нельсона на вершине.___________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________
7. Восточная часть Лондона – промышленный район и место, где живут рабочие
люди.________________________________________________________________________
3. Complete the following sentences:
1. The City, the oldest part of London, is_______________________________________ a) The political heart of London.
b) The symbol of wealth and luxury.
c) The commercial and financial centre of the country.____________________________ 2. The Houses of Parliament, called officially the Palace of Westminster, were formerly ______________________________________________________________________ a) A royal prison.
b) A palace for kings and queens.
c) A national shrine where kings and queens were crowned.
3. Near the West Door of the Abbey the Unknown Warrior lies in a simple grave
_______________________________________________________________________ a) Commemorating the men who died in the First World War.
b) Commemorating Nelson is victory at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805.
c) Commemorating the men who died in different wars.
4. The pedestal of the Column is decorated with bas – reliefs representing
_______________________________________________________________________ a) The history of London.
b) Nelson is most famous victories.
c) Nelson is life.
5. The Tower of London is one of the first and most impressive castles built
______________________________________________________________________- a) After the Great Fire of London in 1666.
b) By Edward the Confessor in 1050.
c) After the Norman invasion of England in 1066.
4. Write down the correct plan of the text
1. The Tower of London.
2. London is a unique city.
3. Westminster Abbey.
4. Trafalgar Square.
5. The Houses of Parliament.
6. St. Paul is Cathedral.

Вывод по теме:
________________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 5
ТЕМА: «Лондон. Достопримечательности» «London's most famous places of
interest»
1 Read and translate the text:

Buckingham Palace is the official residence of Queen Elizabeth. It is located near Green
Park. When the Queen is in the residence, the Royal Standard flies over Buckingham Palace. There are 775 rooms where members of the Royal family and their servants live. There are also rooms for guests. There are offices, on-site post and even swimming pool in the palace. Throughout the year right in front of Buckingham Palace the ceremony of the Changing of the Guard takes place, attracting a lot of tourists. 2) The Tower of London

The Tower of London is one of the main London's places of interest. It is located on the north bank of the River Thames and is one of the oldest buildings. At different times the Tower was used as a royal residence, fortress, prison, mint and, even, zoo. Today the Tower of London is the place where the Crown Jewels are kept.
Every day its doors are open for tourists. A few black ravens live on its territory. The walls of the Tower are still guarded by palace guard in historical outfits.

Trafalgar Square is located in the centre of London. It was named after the victory in the Battle of Trafalgar. In the centre of the square there is Nelson's column with four lions at the bottom of it. There are beautiful fountains in the square. Some famous buildings, such as the National Gallery, St. Martin-in-the-fields and Admiralty Arch, are also located there. The square is the place where a lot of different events and celebrations are held.

Hyde Park is a big park located in central London. Today it is a popular place for meetings, celebrations and festivals.
The park is known for its artificial lake Serpentine where it is allowed to swim. There is a gallery, a museum and several sculptures on the territory of Hyde Park. During the Olympic Games 2012 Hyde Park was the place where some competitions were held.

St. Paul's Cathedral is located at the highest point of the City of London, Ludgate Hill. The Cathedral was seriously damaged during the Great Fire of London. It was redesigned by Christopher Wren, a famous architect.
There are three Galleries and 17 bells in the Cathedral. The largest bell is called Great Paul. The funerals of a lot of notable figures have occurred at the cathedral.

The British Museum is one of the largest museums in the world. It was founded in the XVIII century and in the XIX century it was already divided into different departments.
The museum houses large collections of artifacts representing different cultures of the world, both ancient and modern.
So, there is the Department of coins and medals, the Department of prints and drawings, the Department of Ancient Egypt and Sudan and many others.

The London Eye is one the largest Ferris wheels in Europe. Unforgettable views of the city open from its height of 135 meters.
The wheel consists of 32 air-conditioned capsules which symbolize 32 boroughs of London. The London Eye rotates with the speed of 0,9 km/hour. The ride takes 30 minutes. The wheel looks like a big bicycle wheel.

Oxford Street is a lively shopping street located in the centre of London. There are hundreds of shops in this street. The street is 1,9 km long. It is one of the busiest commercial streets in Europe.
During Christmas time Oxford Street is decorated with lots of lights and garlands making it one of the most popular destinations for tourists.

Westminster is a historical area of central London with several famous landmarks.
Westminster Abbey, a Gothic church, is located there. The church is a traditional place of coronation and burial site for all British kings and queens.
Not far from the church there is the Palace of Westminster which is the meeting place of the House of Commons and the House of Lords.

Big Ben is the name of the Great bell of the clock at the Palace of Westminster. Nowadays this name mostly refers to the clock and the clock tower.
In 2012 the tower was renamed to celebrate the Diamond Jubilee of the Queen and is now officially known as the Elizabeth Tower.
The height of the tower is 96,3 meters. Big Ben is one of the most prominent symbols of the United Kingdom.
2. Read and connect the parts of the sentence:
1. London is_______________________________________________________
2. The London Eye is ________________________________________________
3. Buckingham Palace is ______________________________________________
4. The Tower of London is ____________________________________________
5. The Houses of Parliament is _________________________________________
6. Big Ben is _______________________________________________________
7. Trafalgar Square is _______________________________________________________ 8. Westminster Abbey is ____________________________________________________ a) a big wheel.
b) an ancient fortress.
c) a place where Queen Elisabeth II lives when she is in London. d) a famous bell.
e) an ancient working church.
f) the capital of the UK.
g) is in the heart of London.
h) home of the British Parliament.
3. Complete the text. Use: thousands, was founded, city, of, cathedrals, interesting, famous.
London is the capital of the UK. It is a very old (1)_________. It (2)____ __________ about two thousand years ago. London is one of the most famous and (3) ___________ cities in Europe. It is (4) ___________ for its places of interest. There are lots of museums, historical buildings, ancient (5) ____________ and monuments. It is full (6) ____ history. Every year (7) __________ of tourists come to London.
4. Choose the correct ending.
1. You can see the column with a statue of Nelson in
__________________________________________________________________________ a) Piccadilly Circus
b) Hyde Park
c) Trafalgar Square
2. London Zoo is in ____________________________________________________ a) Regent‘s Park
b) St. James‘s Park
c) Hyde Park
3. Another famous sight inside the Tower of London is the _____________________ a) Pelicans
b) Ravens
c) Ducks
4. The London home of the Queen is ______________________________________ a) Buckingham Palace
b) Westminster Abbey
c) Covent Garden
5. The seat of the British Government is ___________________________________ a) Piccadilly Circus
b) Buckingham Palace
c) The Houses of Parliament
5. Answer the following questions:
1. What is the name of the famous clock in London?
__________________________________________________________________________
2. Where do the famous black ravens live?
____________________________________________________________________________
3. Where does the Queen stay when she is in London?
_____________________________________________________________________________
4. Where do the country‘s leaders speak?
_____________________________________________________________________________
5. Where are the famous English people buried?
_____________________________________________________________________________
6. What can you see in Trafalgar Square?
_____________________________________________________________________________
Вывод по теме:
________________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 6
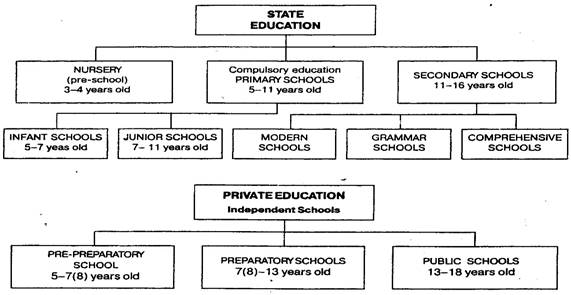
ТЕМА: « Образование в Великобритании» «The British Education System» 1 Read and translate the text:
The British Education System.

Great Britain has a very interesting system of education.
It is provided by the Local Education Authority (LEA) in each county. Until recently, each LEA was free to decide how to organize education in its own area. However, in 1988 the
«National Curriculum» was introduced. Now the government controls what is taught in schools. But education in Great Britain isn't controlled by central government as much as in many other countries.
There is state and private education in Great Britain,
State education in Britain is free. British boys and girls begin to go to school at the age of 5. But there is some free nursery school education before that age. Parents can choose to send their children to nursery schools to prepare them for the start of compulsory education. Children aged from 3 to 4 years old can go to nursery.
Pupils aged from 5 to 7 years old go to infant schools. There they draw pictures, sing songs, play games, listen to the stories and tales. Their classes aren't formal. Pupils aged from 7 to 11 years old go to junior schools. There they learn to write, to read and to do mathematics. Pupils have a regular timetable. Their subjects are English, Maths, History, Nature Study, Geography, Art, Music.
Then pupils take their examinations and enter secondary schools. English boys and girls go to secondary schools from 11 till 16 years old. There are several kinds of secondary schools.
They are modern schools, grammar schools and comprehensive schools.
90 per cent of the pupils go to comprehensive schools. These schools offer a wide choice of subjects from art and craft to the languages and computer studies. They develop the talents of each individual child.
At 16 pupils take a national exam called GCSE (General Certificate of Secondary Education). Then they сад leave school if they wish. Some 16-year-olds continue their studies in the sixth form at school or at a sixth form college. The sixth form prepares pupils for a national exam called "A" level (Advanced Level) at 18. You need "A" levels to enter a university.
7 per cent of British school children go to private schools. These schools are very expensive. They are called independent schools. There are three levels of private schools: prepreparatory schools (for children aged from 5 to 7 or 8); preparatory (prep) schools (for pupils aged from7 or 8 to 13) and public schools (for pupils aged from 13 to 18). Prep schools prepare children for the Common Entrance Exam which they take at the age of 11.
Many preparatory and most public schools are boarding schools: children live at school during the school terms.
Some "public schools" have a long history and tradition. Eton is the best known of these schools.
It is possible to enter the best English Universities after leaving public schools.
In England there are 47 universities. The oldest and most famous universities are Oxford and Cambridge.
2. Translate the words from the text:
1. is provided by _______________________
2. state and private education_____________________
3. free nursery school education_____________________________
4. compulsory education___________________________________
5. infant schools______________________________________
6. junior schools_______________________________________
7. secondary schools___________________________________
8. comprehensive schools_______________________________-
9. private schools____________________________________
10. preparatory (prep) schools______________________________
11. public schools________________________________________
12. boarding schools______________________________________
13. school terms__________________________________________

3. Answer the questions to the text.
1. Who provides the education in Britain?_____________________________________
2. When was the "National Curriculum" introduced?____________________________
3. Is education in Great Britain controlled by central government as much as in many other countries?________________________________________________________
4. What types of education are there in Great Britain? _________________________
5. Is state education in Britain free or not? __________________________________
6. When do British boys and girls begin to go to school? _______________________
7. Can British parents choose to send their children to nursery schools to prepare them for the start of compulsory education? ______________________________________
8. Where do the pupils aged from 5 to 7 years old have to go? ____________________
9. What do pupils do in infant schools?
______________________________________________________________________ 10. Are classes formal in infant schools? _____________________________________
11. Where do the pupils aged from 7 to 11 years old have to go?
______________________________________________________________________
12. What do pupils learn in junior schools?
______________________________________________________________________
13. Do they have a regular timetable in junior schools? _________________________
14. What are their subjects there? ____________________________________________
15. At what age do the English boys and girls usually begin to go to secondary schools?
______________________________________________________________________
16. There are some kinds of secondary schools in Great Britain, aren't there? What are they? _________________________________________________________________
17. How many per cent of British pupils go to comprehensive schools? Why? What do these schools develop ___________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
18. When do British pupils have to take a national exam? What is this exam called? Can they leave school after taking this exam? ____________________________________________
19. Where can 16-year-olds continue their studies? ____________________________ 20. What does the sixth form prepare pupils for? _______________________________
21. What level do you need if you want to enter a university?
______________________________________________________________________
22. How many per cent of British pupils go to private schools _____________________
23. What are these schools called? __________________________________________
24. Are they expensive or not? _____________________________________________
25. What levels are there in private school? ___________________________________
26. What exam do pupils take at the age of 11? What schools prepare children for taking this exam? ___________________________________________________________________
27. What is the difference between usual and boarding schools?
_______________________________________________________________________
28. What is the best known "public school" in Great Britain? ______________________
29. How many universities are there in England? _______________________________
30. What are the oldest and most famous universities in Britain? ___________________
4. *Speak about the education in Great Britain using the table below:
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
Вывод по теме:
________________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 7
ТЕМА: «Университетское образование в Великобритании» «University
education in Great Britain»

1. Read and translate the text:
University education in Great Britain.
For seven hundred years Oxford and Cambridge universities dominated the British education. Scotland had four universities, all founded before A. D. 1600. Wales only acquired a university in the 20th century; it consisted of four university colleges located in different cities (Cardiff, Swansea, Bangor, and Aberystwyth). The first English university after Oxford and Cambridge (sometimes referred to as Oxbridge) was Durham, in the North of England, founded in 1832. The University of London was founded a few years later in 1836.
During the nineteenth century institutions of higher education were founded in most of the biggest industrial towns, like Birmingham, Manchester, Leeds, Sheffield (sometimes called the Redbrick Universities). At first they did not have full university status but were known as university colleges; since 1945, however, all have become independent universities, and in recent years a number of other universities have been founded: Sussex, Essex, Warwick, and others. In the middle 60s there was a further new development. Some of the local technical colleges maintained by local authorities had gained special prestige. By 1967 ten of these had been given charters as universities. Many of them are in the biggest cities where there were already established universities; so now we have the University of Aston (Birmingham), Salford (close to Manchester), Strathclyde (Glasgow), Herriot-Watt University (Edinburgh), Brunei University (London).
When we add all these together we find that the number of universities in England increased within ten years from nineteen to thirty-six, and in Scotland from four to eight.

Oxford university is a federation of colleges, and it is impossible to understand its structure unless one first understands the nature and function of these colleges, which have no resemblance whatever with the institutions called "colleges" in America.
Oxford has twenty-three ordinary colleges for men, five for women. All these are parallel institutions, and none of them is connected with any particular field of study. No matter what subject a student proposes to study he may study at any of the men's colleges.
Each college has a physical existence in the shape of a dining-hall, chapel, and residential rooms (enough to accommodate about half the student membership, the rest living in lodgings in the town). It is governed by its Fellows (commonly called "dons"), of whom there are usually about twenty or thirty. The dons are also responsible for teaching the students of the college through the tutorial system. The Fellows elect the Head of the college (whose title varies from college to college).
The colleges vary very much in size and extent of grounds and buildings.
Colleges choose their own students, and a student only becomes a member of the University by having been accepted by a college. Students are chosen mainly on academic merit, but the policy of colleges in this respect varies from college to college. Some tend to be rather keen to admit a few men who are very good at rugby or some other sport, or sons of former students or of lords, or of eminent citizens, or of millionaires.
The colleges and university buildings are scattered about the town, mostly in the central area, though the scientific laboratories and the women's colleges are quite a long way out.
The university teachers are mostly Fellows of colleges, who may at the same time hold university appointments as lecturers or professors. Part of the teaching is by means of lectures and any student- may attend any university lecture. At the beginning of each term (there are three terms in the Oxford academic year) a list is published showing all the lectures being given during the term within each faculty, and every student can choose which lectures he will attend, though his own college tutor will advise him which lectures seem likely to be more useful. Attendance at lectures is not compulsory, and no records of attendance are kept.
Apart from lectures, teaching is by means of the "tutorial" system, which is a system of individual tuition organized by the colleges. Each Fellow in a college is tutor in his own subject to the undergraduates who are studying it. Each student goes to his tutors room once every week to read out an essay which he has written, and for an hour he and the tutor discuss the essay. A student does not necessarily go only to his own tutor but may be assigned to another don in his own college .
2. Give English equivalents to:
1. доминировать в образовании____________________________________
2. институты высшего образования_______________________________
3. был основан________________________________________________
4.колледжи сильно отличаются друг от друга______________________
5. научные лаборатории________________________________________
6. система индивидуального тьюторства___________________________ 7. посещение лекций не является обязательным________________________
3. Put ―+‖ if the sentence is right and ―-― if it is wrong.
1. For seven hundred years Oxford and Cambridge universities dominated the British education.
2. Scotland has two universities.
3. The first English university after Oxford and Cambridge (sometimes referred to as Oxbridge) was Durham.
4. Oxford university is not a federation of colleges.
5. The dons are not responsible for teaching the students of the college through the tutorial system.
6. Each college has a physical existence in the shape of a dining-hall, chapel, and residential rooms.
7. At the beginning of each term (there are three terms in the Oxford academic year) a list is published showing all the lectures being given during the term within each faculty.
4.* Test
―What do you know about education in Great Britain?‖ 1. Education in Britain is __________________________ compulsory , complicated impulsive
2. Compulsory education in Britain begins at the age of ______and ends at _______.
5, 16
7, 16
5, 18
3. Most children in Britain go to ________________schools.
Public
Grammar
Comprehensive
4. ________________consists of infant and junior schools.
Primary
Secondary
Comprehensive
5. Pupils in infant school __________________________ sit in rows and have real classes.
often listen to the teacher‘s stories sitting on the carpet. Study Geography, Chemistry, French.
6. British children go to secondary school at the age of … .
11
7
14
7. The school year is divided in … terms.
2
3
4
8. The school year begins …
On the first of September
On Monday in September
On Tuesday in September
9. The ―core‖ subjects are …
English and Mathematics
English, Mathematics and Science
English, Mathematics and French
10. Pupils in all state schools in England and Wales study ten … subjects, which are called foundation subjects. Major interesting
Main
11. Match the definitions and the types of schools: 1) comprehensive, 2) modern, 3) grammar and 4) public.
These schools are schools, which take children of all abilities. So there are no entrance examinations. Almost all secondary school pupils (90 per cent) go there. ___________
These schools give secondary education of a very high standard. Entrance is based on the test of ability, usually at 11. ___________________________________
These schools don‘t prepare pupils for universities. Education in such schools gives good prospects for practical jobs. ____________________________________________
These schools are free from state control. They are independent. Most of them are boarding schools. The education is of a high quality, the discipline is very strict. Parents pay much money for the education of their children. _______________________________________ 12. Private schools in England and Wales are __________________________
Interesting
Free
Expensive
13. Eton College, Harrow School and Winchester are the most famous ____ schools.
Grammar
Public
Modern
14. Eton College is a boarding school for _________________________
Boys and girls
Boys
Girls
15. Public schools are famous for their ____________________________
Traditions
Beautiful buildings
Teachers
16. Winston Churchill, six other British Prime Ministers, the poet Lord Byron and many other famous people were educated in ______________________________
Eton College
Winchester College
Harrow School
17. If pupils go to _____schools they have a good theoretical secondary education.
Modern
Grammar
Technical
18. Children can enter the best English universities after leaving _____ schools. Public
Grammar
Comprehensive
19. English and American school children usually get reports cards _________
Once a year
Twice a year
Two or three times a year
20. All the pupils in Britain have their own ______ to guarantee the safety of their things.
Desks
Bags
Lockers
21. At the age of ____ pupils take the General Certificate of Secondary Education.
18
16
11
22. To enter a university pupils have to take _______________
―A‖ Level Exams
GCSE
Eleven Plus Examination
23. Pupils in Britain whose behavior is not ideal can be punished. Find the Russian equivalents for the names of punishment in British schools.
Исключение из школы _______________________________
Наказание письмом ________________________________
Временное исключение из школы ___________________________
Запись в дневнике ___________________________________
Оставление после уроков ________________________________
Lines
Detention
Report Suspension exclusion
24. Schools in Britain have ________________________
Names
Numbers
Numbers and names
Вывод по теме:
________________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 8
ТЕМА: « Великие английские писатели и поэты. В.Шекспир, В.Скотт» «Great English poets and writers »

1. Read and translate the text.
William Shakespeare was an English poet, playwright and actor. He was born in 1564 in Stratford-upon-Avon. His father, John Shakespeare, was a successful artisan. William was the third child in the family. His parents had eight children in total. William Shakespeare went to Stratford grammar school.
In 1582 Shakespeare married Anne Hathaway, who was the daughter of the local landowner. At that time Shakespeare was 18 years old and Anne was 8 years older than him. In 1583 Anne gave birth to their daughter Susanna. In 1585 the couple had twins – son Hamnet and daughter Judith. Unfortunately, Hamnet, the only son of William Shakespeare, died at the age of
11.
Later Shakespeare moved to London. He lived and worked in this city for many years. During that time Shakespeare wrote most of his plays and became a successful playwright. His troupe was among the leading playing companies in London.
In 1599 a theatre was built on the south bank of the River Thames. It was named the Globe. This was the theatre where Shakespeare's company performed. Work at the theatre made Shakespeare a wealthy person. He was not only a playwright, he also took part in theatrical performances.
Several years before his death Shakespeare moved to Stratford. He died on 23 April 1616. Some research shows that at the end of his life he was in poor health.
Among his works there are such masterpieces of the world literature as "Romeo and Juliet", "A midsummer night's dream", "Othello", "King Lear", "Hamlet" and many others. Apart from that Shakespeare wrote 154 sonnets.
William Shakespeare's influence extends from theatre and literature to present-day movies, Western philosophy, and the English language itself.
2. Write down the ending of the sentences:
1) W. Shakespeare is one of the _______________________________________
2) W. was sent ____________________________________________________
3) When he had a break William liked to go_____________________________
4) He decided to become ____________________________________________
5) S. was both ____________________________________________________
6) His plays were staged___________________________________________
7) The writer‘s most famous plays are_________________________________
8) His plays are still ________________________________________________
9) S. died ________________________________________________________
3. Give your associations with the following words:
For example: 1564 (He was born in 1564.)
- Playwright - Stratford-on-Avon ___________________________________
- 37 __________________________________________________________
- 1616 __________________________________________________________ - Globe Theatre ____________________________________________________
4. Answer the questions:
- What was he? ________________________________________
- When was W.S. born? ______________________________________________
- Where was he born? ________________________________________________
- Where did he study? _________________________________________________
- What did he like to do, when he was a little boy? ___________________________
- Why did he go to London? ____________________________________________
- Why did W. decide to leave Stratford? _________________________________
- What plays by W.S. do you know? _____________________________________
- Why are his plays known by people? ___________________________________ - How many plays did he write? ________________________________________
- What language did W.S. speak? _________________________________________
- Is he an English or American poet? _____________________________________ - Why is S. one of the greatest and the most famous writers in the world? ___________________________________________________________________
5. Read some sonnets by W. Shakespeare:
1.Неужто музе не хватает темы,
Когда ты можешь столько подарить
Чудесных дум, которые не все мы
Достойны на бумаге повторить.
И если я порой чего-то стою, Благодари себя же самого.
Тот поражен душевной немотою,
Кто в честь твою не скажет ничего.
Для нас ты будешь музою десятой
И в десять раз прекрасней остальных,
Чтобы стихи, рожденные когда-то,
Мог пережить тобой внушенный стих.
Пусть будущие славят поколенья
Нас за труды, тебя – за вдохновение.
2. Crabbed age and youth cannot live together, Youth is full of pleasure; age is full of care;
Youth like summer morn; age like winter weather;
Youth like summer brave; age like winter bare;
Youth is full of sport; age‘s breath is short;
Youth is hot and bold; age is weak and cold;
Youth is wild and age is tame; Age, I do abhor thee!
Youth, I do adore thee!
Oh, my Love, my Love is young!
3. To me, fair friend, you never can be old, For as you were when first your eye I ey'd,
Such seems your beauty still. Three winters cold
Have from the forests shook three summers' pride;
Three beauteous springs to yellow autumn turn'd
In process of the seasons have I seen; Three April perfumes in three hot Junes burn'd,
Since first I saw you fresh, which yet are green.
Ah! yet doth beauty, like a dial-hand
Steal from his figure, and no pace perceiv'd;
So your sweet hue, which methinks still doth stand, Hath motion and mine eye may be deceiv'd:
For fear of which, hear this, thou age unbred, — Ere you were born was beauty's summer dead.
4. Нет, для меня стареть не можешь ты.
Каким увидел я тебя впервые,
Такой ты и теперь. Пусть три зимы
С лесов стряхнули листья золотые,
Цветы весны сгубил три раза зной,
Обвеянный ее благоуханьем,
Пронизанный зеленым ликованьем,
Как в первый день стоишь ты предо мной,
Но как на башне стрелка часовая
Незримо подвигает день к концу,
Краса твоя, по-прежнему живая,
Незримо сходит в бездну по лицу.
Так знайте же, грядущие творенья, — Краса прошла до вашего рожденья.
Walter Scott (15.08.1771 - 21.09.1832) - British writer.

Walter Scott
1. Read and translate the text:
Walter Scott was a famous British writer, poet, historian and the founder of historical novel. During his life he combined writing with being a legal administrator and a member of Tory fraction. He was born in Scotland, on August 15th, 1771. His family was rather rich and noble. His father was a successful lawyer and his mother was the daughter of a professor of medicine at the University of Edinburgh. He was the ninth child in the family. When he was little, he had polio, which left him lame. This condition had a significant effect on his further life and writing.
As a child, he spent lots of time at his grandfather‘s farm at Sandyknowe, which was close to Scottish Borders. Despite his poor health, he was an active boy with lively mind and phenomenal memory. Starting from 1779 he studied at the Royal High School. Prior to that, he received private education. At the age of 14, he entered the Edinburgh College, where he became popular among the peers for his excellent storytelling. As a student, he got interested in mountaineering. This activity helped him to become physically fit and healthier. At his free time he liked reading books, including the works of ancient authors.
He was fond of novels, poetry, ballads and legends of Scotland. For that reason, together with his peers he organized a poetic society. In 1792, he passed the most important exam in his life and became a lawyer. Since then he practiced law and became a respectable man in Edinburgh. It was then that he visited the Scottish Highlands for the first time and was highly impressed. He started his literature career in 1796. Soon, he published a three-volume set of collected ballads. His narrative poem ―The Lay of the Last Minstrel‖ (1805) became was very popular not only in Scotland, but in England. Writing his first novel ―Waverley‖ (1814), he preferred to hide his real name and did so for the subsequent 10 years.
In 1820, the writer was awarded the title of a baronet. During the 1820s and 1830s he wrote many other outstanding novels, including ―Ivanhoe‖, ―Quentin Durward‖, ―Count Robert of Paris‖. At the same time he was leading a series of historical studies. In 1829-1830, he published the two volumes of ―History of Scotland‖. The art of writing has brought Walter Scott financial independence and fame. However, at some point of his life he was trapped in debts and had to work day and night to pay them. He worked at the limit of his intellectual and physical abilities. In 1830, he suffered a stroke, which left his right hand paralyzed. It was followed by another two strokes and the writer died of a heart attack in September, 1832.
2. Answer the questions to the text:
1. Who was Walter Scott? _________________________________________
2. When and where was he born? ____________________________________
3. Who were his parents? ___________________________________________
4. What school did he study at? ______________________________________
5. Where did he enter the Edinburgh College? ___________________________
6. Did he like reading books at his free time? _____________________________
7. What can you say about his poetic society? ____________________________
8. What had happened in 1792? _______________________________________
9. When was his literature career started? _______________________________ 10. What are his novels? _____________________________________________
11. Did he work at the limit of his intellectual and physical abilities?
________________________________________________________________ 12. What had happened in September 1832? _________________________________
3.* Try to translate the extract from his novel “Ivanhoe‖:
“In that pleasant district of merry England which is watered by the river Don, there extended in ancient times a large forest, covering the greater part of the beautiful hills and valleys which lie between Sheffield and the pleasant town of Doncaster. The remains of this extensive wood are still to be seen at the noble seats of Wentworth, of Warncliffe Park, and around Rotterdam. Here haunted of yore the fabulous Dragon of Wantley; here were fought many of the most desperate battles during the Civil Wars of the Roses; and here also flourished in ancient times those bands of gallant outlaws, whose deeds have been rendered so popular in English song.
Such being our chief scene, the date of our story refers to a period towards the end of the reign of Richard I., when his return from his long captivity had become an event rather wished than hoped for by his despairing subjects, who were in the meantime subjected to every species of subordinate oppression. The nobles, whose power had become exorbitant during the reign of Stephen, and whom the prudence of Henry the Second had scarce reduced to some degree of subjection to the crown, had now resumed their ancient license in its utmost extent; despising the feeble interference of the English Council of State, fortifying their castles, increasing the number of their dependants, reducing all around them to a state of vassalage, and striving by every means in their power, to place themselves each at the head of such forces as might enable him to make a figure in the national convulsions which appeared to be impending.‖
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
Вывод по теме:
________________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 9
ТЕМА: « Праздники, традиции и обычаи англичан» «English traditions and
holidays »

1. Read and translate the text:
Every nation becomes special by means of its own traditions and customs. There is no other nation that clings to the past with the tenacity of the British. They are really proud of their traditions, they cherish them. When we think of Britain we often think of people drinking white tea, eating fish and chips, sitting by the fireplace or wearing bowler hats, but there is much more in Britain than just those things. Some British traditions are royal, such as the Changing of the Guard which takes place every day at Buckingham Palace. The Trooping of the Colors happens on the Queen‘s official birthday. It‘s a big colorful parade with hundreds of soldiers and brass bands.
British holidays (Christmas, Easter, Guy Fawkes Night, Remembrance Day) are especially rich in old traditions and customs. A traditional Christmas dinner consists of roast turkey and potatoes, cranberry sauce, sweet mince pies and Christmas pudding. On Christmas Eve children hang up their stockings around the fireplace for Father Christmas to fill with presents. At Easter chocolate eggs are given as presents symbolizing new life. Guy Fawkes Night is also known as Bonfire Night because English people burn stuffed figures on bonfires. On Remembrance Day red poppies are traditionally worn in memory of servicemen who lost their lives in wars. National Morris Dancing can be seen throughout the month of May in most of English villages. Groups of men and women wear colored costumes, carry white handkerchiefs and perform their lively folkdance.
One of Englishmen‘s traditions is their tender love for animals. Pets are members of English families and are protected by law. There are even special cemeteries for animals in Great Britain. Most English people love their gardens too. They enjoy gardening and decorating their houses with beautiful flowers and plants.
Sports play an essential part in the life of Britain and it is a popular leisure activity. Rugby, golf, cricket, polo and horse-racing are British national sports and they are played on village greens and in towns on Sundays.
Politeness and punctuality are typical features of all British people. They often say
―Sorry‖, ―Please‖ and ―Thank you‖ with a smiling face and they always try to arrive on time.
The British are also traditional about their breakfast. They usually eat bacon and eggs, a toast with orange jam, a bowl of cereals or porridge in the morning.
There are over 60 thousand pubs in the United Kingdom. Pubs are an important part of British life too. People talk, eat, drink, meet their friends and relax there.

2. Find in the text:
1. традиции и обычаи _______________________________________________
2. гордиться традициями_____________________________________________
3.королевские традиции_____________________________________________
4.официальный День рождения королевы_____________________________
5.популярный вид отдыха__________________________________________
6.типичные черты британцев________________________________________
3. Fill the table and guess the holiday:
|
A traditional … dinner consists of roast turkey and potatoes, cranberry sauce, sweet mince pies and pudding. |
|
|
English people burn stuffed figures on bonfires. |
|
|
Red poppies are traditionally worn in memory of servicemen who lost their lives in wars. |
|
|
Groups of men and women wear colored costumes, carry white handkerchiefs and perform their lively folkdance. |
|
|
Chocolate eggs are given as presents symbolizing new life. |
|
4. Say about politeness and punctuality of all British people.
____________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
5. Prove that Englishmen tender love animals.
__________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________
6. Does sport play an essential part in the life of Britain?
______________________________________________________________________
7. What is British traditional breakfast?
_____________________________________________________________________
Вывод по теме:
________________________________________________ _______________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________ Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 10
ТЕМА: « Погода в Англии» « The weather in Great Britain»

1. Read and translate the text:
The weather in Great Britain.
The common ideas people have about the weather in Britain are: "It rains all the time, it's very damp"; "There's a terrible fog in London, just like in Sherlock Holmes'...", "The sun never shines in July or August".
Britain has a variable climate. The weather changes so frequently that it is difficult to forecast. It is not unusual for people to complain that the weathermen were wrong. Fortunately, as Britain does not experience extreme weather conditions, it is never very cold or very hot. The temperature rarely rises above 32°C (DOT) in summer, or falls below 10°C (14°F) in winter.
Summers are generally cool, but due to global warming they are starting drier and hotter. Newspapers during a hot spell talk of "heat waves" and an "Indian summer" (dry, hot weather in September and October). Hot weather causes terrible congestion on the roads as Britons rush to the coastal resorts. Winters are generally mild, with the most frequent and prolonged snowfalls in the Scottish Highlands, where it is possible to go skiing. If it does snow heavily in other parts of Britain, the country often comes to a standstill. Trains, buses and planes are late. People enjoy discussing the snow, complaining about the cold and comparing the weather conditions with previous winters.

Contrary to popular opinion, it does not rain all the time. There is certainly steady rainfall throughout most of the year, but the months from September to January are the wettest. Thanks to the rain, Britain's countryside is famous for its deep green colour.
Since the 1950's, most British cities have introduced clean air zones. Factories and houses cannot burn coal and must use smokeless fuel. The dirt caused by smoke used to cause terrible fogs, particularly in London. Such fogs are now a thing of the past, but you can still see them in old films where they add mystery and atmosphere to murder stories and thrillers.
2. Prove that Britain is a wet and foggy country.
____________________________________________________________________
3. Why do the British people say: “Other countries have a climate, in England we have the weather”
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
4. When do the British say “It’s raining cats and dogs”
______________________________________________________________________
5. True or false:
1. The weather in England is as cold as in Russia and Canada.
2. It is very cold in winter and very hot in summer.
3. The weather in England changes very quickly.
4. The British talk about the weather all the time.
5. A conversation about the weather is a good way to start talking with a stranger.
6. What do you know about London fogs?
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 11
ТЕМА: « Соединенные штаты Америки» «The USA»

1. Read and translate the text:
The USA
1. General
The United States of America was formed by emigrants in 1382. The USA makes up of 62 states. Washington, the capital of the United States is situated on the Rotomac River in the District of Columbia. The district is a piece of land which doesn't belong to any state but to all the states. All these states are sovereignty.
2. Geographical position and physical features:
The USA occupy a large territory and are situated in the central and southern part of North America. The USA is washed by the Atlantic ocean in the east and by the Pacific ocean in the west. In the north, the USA has borders on Canada and in the south on Mexico. The USA is divided into three areas: Eastern area is a highland, central area is a plain and Western area is mountains including the Rocky Mountains and the Sierra Nevada. There are five great lakes in the northern part of the USA. There are: Huron, Michigan, Supireo, Ontario and Erie. They are connected by fast rivers. There is the most famous to the whole world fall called Niagara Fall.
Mississippi together with its tributary Missouri is the longest river in the world.
3. Climate:
Mountain ranges cross the country from north to south and don't protect it against cold air from the north and warm one from the south. The USA has a continental climate.
4. National Economy.
The USA is a highly developed industrial country. Large reserves of oil, coal, iron and other minerals are solid base of development of Americans industry. Heavy industry prevails in USA, including such branches as the mining, metallurgical, engineering, chemical and high-tech industries. USA has also well-developed light industry which includes textile, tanning and footwear industries. The food industry is well developed too. Both animal husbandry and farming takes big place in the economy of the USA.
5. Political system
Under the Constitution, the federal government is divided into three branches. The Congress is vested with the legislative power and made up of two houses: the Senate and the House of Representatives. There are 435 members in the House of Representatives and 100 senators. Each state elects two members of the Senate.
The executive branch is headed by the President, who proposes bills to Congress, serves as commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces. The President is chosen in nation-wide elections every 4 years. The second person in executive branch is vice President. The vice President, elected from the same political party as the President
The judicial branch consists of Federal District Courts, 11 Federal Courts and the Supreme Court. Federal judges are appointed by the President. Federal courts decide cases involving federal law, conflicts between citizens of different states.
American Symbols
The American flag is often called "The Stars and Stripes", it is also called "Old Glory". It represents the growth of the nation. It has 13 horizontal stripes,7 red and 6 white which stand for the original 13 states. In the top left hand corner there are 50 white stars on a blue background:
one star for each state. The national anthem of the United States is "The Star Spangled Banner".
The words written during the Anglo-American war of 18X2-1814and set to the music of an old song. Every state has its own flag, its own emblem and its own anthem too.
The eagle became the national emblem of the country in 1782. It has an olive branch (a symbol of peace) and arrows (a symbol of strength). You can see the eagle on the back of a dollar bill.
The Statue of Liberty is the symbol of American democracy. It stands on Liberty Island in New York. It is one of the first things people see when they arrive in New York by sea. This National Monument was a present from France to the USA. France gave the statue to America in 1884 as a symbol of friendship. Liberty carries the torch of freedom - in her right hand. In her left hand she is holding a tablet with the inscription "July 4, 1776" - American Independence Day.
2. Answer the questions:
Where is the USA situated? ___________________________________
What is the population of the country? ____________________________________
What is the official language? ____________________________________________
Name main cities of the country. __________________________________________ Who is the head of the country? ___________________________________
3. Choose the correct answer:
1. Where does the President of the USA live & work?
a) in Congress
b) in the White House
c) in the Pentagon
2. What is the biggest state in the USA?
a) Texas
b) California
c) Alaska
3. How many states are there in the USA?
a) 48
b) 52
c) 50
4. When did the American Civil War end?
a) 1789
b) 1865
c) 1776
5. Who was the 1st President of the USA?
a) George Washington
b) Abraham Lincoln
c) Ulysses Grant
6. Why do Americans celebrate the 4th of July?
a) the 1st moon landing
b) Declaration of Independence
c) the end of the American Civil War
7. In which city is Hollywood?
a) New York
b) San Francisco
c) Los Angeles
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 12
ТЕМА: «Вашингтон. Достопримечательности»

1. Read and translate the text:
Washington
Washington, the capital of the United States of America, is situated on the Potomac River in the District of Columbia. The district is a piece of land ten miles square and it does not belong to any separate state but to all the states. The district is named in honour of Columbus, the discoverer of America. The capital owes much to the first President of the USA -George Washington. It was G. Washington, who chose the place for the District and laid in 1790 the corner-stone of the Capitol, where Congress sits.
Washington is not the largest city in the USA. It has a population of 900 000 people. Washington is a one-industry town. That industry is government. It does not produce anything except very much scrap paper. Every day 25 railway cars leave Washington loaded with scrap paper.
Washington has many historical places. The largest and tallest among the buildings is the
Capitol with its great House of Representatives and the Senate chamber.

There are no skyscrapers in Washington because no other building must be taller than the Capitol

The White House is the President's residence. All American presidents except George Washington (the White House was not yet built in his time), have lived in the White House. It was built in 1799. It is a two-storied, white building.

Not far from the Capitol is the Washington Monument, which looks like a very big pencil. It rises 160 metres and is hollow inside. A special lift brings visitors to the top in 70 seconds from where they can enjoy a wonderful view of the whole city.

The Jefferson Memorial was built in memory of the third President of the USA, Thomas Jefferson, who was also the author of the Declaration of Independence. The memorial is surrounded by cherry-trees. The Lincoln Memorial devoted to the memory of the 16th President of the US, the author of the Emancipation Proclamation, which gave freedom to Negro slaves in America.
On the other bank of the Potomac lies the Arlington National Cemetery where President Kennedy was buried. American soldiers and officers, who died in World Wars I and II are buried there too.
2. Answer the questions:
1. Where is Washington located in? __________________________________________
2. What river blows through Washington D.C.?
____________________________________________________________________________
3. Is Washington green town?
_____________________________________________________________________________
4. Are there any big industrial objects in Washington?
_____________________________________________________________________________
5. Are there any sky-scrapers in Washington?_______________________________
6. What sights of Washington do you know?
____________________________________________________________________________
7. Is Washington a big city?
_____________________________________________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 13
ТЕМА: « Великие американские писатели: Д. Лондон, М. Твен » «The great American writers. M. Twain. J. London »

1. Read and translate the text:
Mark Twain, whose real name was Samuel Clemens, was born in 1835. This great American writer was the son of a lawyer. He spent his boyhood in the small town of Hannibal on the great Mississippi river. There he went to school and had many friends. He was a bright lovely boy. He could easily swim across the Mississippi and was the leader in all the boys‘ games.
In 1847, when Samuel was eleven, his father died and the boy had to leave school and look for work. For ten years he worked as a printer. All his life Samuel was fond of reading. While he was a printer he spent his free time in libraries. He began ti write for newspapers and other publications, sent travel letters to them as he travelled about the country from job to job. In 1857 he found a job on a boat and travelled up and down the Mississippi. This is where he got his pen-name ―Mark Twain‖ (mark two). It was taken from the call of the Mississippi pilots when they measured the depth of the river. Clemens worked as a pilot for more than four years.
Later the young man went to Nevada where silver had been discovered. He worked as a miner for some time in Nevada. He suffered great hardships but found no silver and left the mining camps as poor as he had come to them. That time he began ti write short stories and send them to newspapers. The publisher of one newspaper liked them and he was invited to work as a journalist. The writer‘s pen-name appeared in print for the first time in 1863. Samuel started his literary career as a humorist. His humorous stories about the life of common people of America became very popular.
In 1876 Mark Twain‘s ―The Adventures of Tom Sawyer‖ was published. As Mark Twain said later, many of the events described in the biio really took place and the characters came from real life. Tom Sawyer was very often the portrait of the writer himself, Huckleberry Finn was his friend, Aunt Polly was his mother, Tom‘s brother Sid was like his own brother.
2. Did you read Mark Twain‘s ―The Adventures of Tom Sawyer‖? Try to guess its main characters:
He is a boy with ideas. He goes to school, but he hates it. He likes to play. He knows many interesting games. He has many friends. His best friends are Huck and Joe. He has no mother and father but he has got an aunt. He likes fishing, playing games, Becky and sugar. He doesn‘t like school. What is his name? ____________________________________
She is neither very small nor very tall. Her hair is grey. She wears a dark dress. She takes care about her house and her family. Her hobby is cooking. She doesn‘t go to school. I think she loves Tom very much and Tom loves her. What is her name? ___________________________
She has got a father and a mother. She lives in a big house. She goes to school every day.
She can read and write. She is little. She is a beautiful girl. Who is she? ____________________
3.* Read Famous twain‘s Quotes on advice to kids.
Always obey your parents when they are present.
Always respect your superiors if you have any.
On being good.
Honor is a harder master than law.
Do you duty today and respect tomorrow.
On Books.
If books are not good company, where will I find it?
Books are the liberated spirits of men.
On Truth,
When in doubt, tell the truth.
If you tell truth you don‘t have to remember anything.
Do you agree with the statements? Why? Why not? ______________________________ ___________________________________________________________________
4. Read and translate the text:
Jack London

Jack London was born in 1876 in San Francisco. His real name was John Griffit. His father was a farmer. The family was extremely poor and the boy had to earn his living after school. He sold newspapers, worked at a factory. Later he became a sailor; during some time he wandered with the unemployed.
For a year he attended the Oakland High school and spent a semester at the University of California, but as he had no money he had to stop his studies and went to work again.
This time it was a laundry. In 1897 he went to the Klondike as a gold miner. He didn‘t bring any gold back with him but those years left their mark in his best short stories; among them The Call of the Wild, White Fang, The Son of the Wolf, and The white silence. They are gripping narratives of a man‘s struggle with nature. His novel The Sea Wolf was based on his experiences at sea.
The problems of the individual and society as well as some of the difficulties London himself met during the first years of his literary work are described in The Iron Heel and Martin Eden.
During the sixteen years of his literary career Jack London published about fifty books:
short stories, novels and essays. In his best stories London described the severe life and struggle of people against nature.
He died at the age of forty in 1916.
Questions:
1. When was Jack London born? ___________________________________________
2. What was his real name? ______________________________________________
3. How long did he attend the Oakland High school? ___________________________
4. Why did he have to stop his studies? ______________________________________
5. What did he do in the Klondike? _________________________________________
6. What did he describe in his books? ________________________
5. Look! There are titles of Jack London’s books. Try to translate it.



___________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 14
ТЕМА: « Праздники в США » « Holidays in the USA »
1. Read and translate the text:
Holidays in the USA .
There are a lot of holidays in the USA. Many of them are associated with the history of the nation. The main holidays of the USA are New Year's Day, Easter, Memorial Day, Independence Day, Thanksgiving Day and Christmas.
The New Year's Eve is a time for merriment. Most Americans spend this night with friends, at home or in restaurants. Thousands of people gather in New York in Times Square to see the New Year in.
The Tournament of Roses takes place in Pasadena, California, on January 1 each year. Prizes are given to the cities with the most unusual floral compositions.
At Easter there is a tradition for people to buy new clothes. After church services many people take walks along the streets of their towns, wearing their new Easter hats and suits.
This is usually called the "Easter Parade".

Memorial Day comes on May 30. It is dedicated to the memory of those who died for America in different wars

. The national flags are put on the graves of soldiers on this day.

The 4th of July, an Independence Day, is the biggest national holiday of the USA. On this day in 1776 a document, known as the Declaration of Independence, was adopted. During this holiday American cities have parades, people shoot off fire-works in parks and fields.

Thanksgiving Day comes on the fourth Thursday of November. When the first settlers landed in America, their first year was very hard and 50 of 100 people died. But the Indians taught people how to plant corn and wild vegetables and in autumn they got a large harvest. Thanksgiving Day was their holiday, the day of giving thanks to God. It is a family holiday and Americans try to gather all family at home on this day.
There are also some holidays which are not celebrated nation-wide, but only by each state separately.

2. Answer the questions:
1) When do Americans celebrate Christmas? ___________________________________ 2) What holiday do people celebrate on the 14th of February?
_____________________________________________________________________________
3) What holiday is Irish in America?
_____________________________________________________________________________
4) What holiday is celebrated on the second Sunday in
May?_________________________________________________________________________
5) When do people color eggs?
_____________________________________________________________________________
6) Why is Independence Day celebrated on July 4?
_____________________________________________________________________________
7) What holiday is one of the best holidays for children?
Why?_________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________
3. Read the dialog and guess what is wrong.
1. A group of pupils dressed in green (except one) meets at school.
- Hi!
- Hallo!
- How do you do!
- are you ready to have fun?
- look! What a nice sweater I have!
- And I‘ve bought a new green tie for the party! - And why are you in red?
- Don‘t you remember that today is Halloween? And everybody wears green on this day. - Because everybody is Irish on Halloween!
- Sorry. I‘ve clean forgotten about it! - take my cap.
- Thank you.
- Look! I have a present for all of us!
- A green shamrock? Are you kidding?
- No! A green fur-tree! Now we shall decorate it with pumpkins… - And have a nice party.
(Children decorate the fur-tree, stand round it and sing ―Happy Birthday!‖) - It‘s a fine funny party!
- Now… let‘s go outdoors and congratulate people with Halloween!
(Children go out shouting ―Dance or sing!‖)
___________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________
2. A group of children celebrates Christmas.
- Happy Christmas! - says a boy dressed like a ghost.
- Happy Christmas! – says a girl, dressed like a witch.
- Hallo! How are you? Where is the main symbol of Christmas?
- What do you mean?
- A pumpkin, of course!
- Are you crazy? Pumpkin is a symbol of Thanksgiving day. And the symbol of Christmas is a green shamrock-tree.
- Of course you are right!
- Let‘s decorate it!
(Suddenly a Christmas Bunny comes!)
- Hallo, boys and girls! I have some presents for you!
- Hurray! We are glad to see you!
- Now we shall play ―trick or treat‖ if you choose trick? I‘ll make you laugh, if you choose treat, I‘ll give you a sweet present. - Treat! Treat!
- O‘K, O‘K. Take your presents. Have fun! And I must go. There are a lot of other children waiting for me. Good-bye… - See you!
____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
ПРАКТИЧЕСКОЕ ЗАНЯТИЕ № 15
ТЕМА: « Австралия и Новая Зеландия. Географическое положение. Флора и фауна. » «Australia and New Zealand»

1. Read and translate the text:
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the Southwest Pacific Ocean. It lies about 1600 km southeast of Australia and about 10 500 km southwest of California. New Zealand belongs to a large island group called Polynesia. The country is situated on two main islands — the North
Island and the South Island — and several dozen smaller islands. Most of the smaller islands are hundreds of kilometers from the main ones.

Wellington is the capital of New Zealand and Auckland is the largest city. English is the official language of New Zealand and is spoken throughout the country. Many native people speak their own language» Maori, in addition to English.
The country once belonged to the British Empire. Today it is an independent member of the Commonwealth of Nations, an association of Britain and a number of its former colonies.
New Zealand is a constitutional monarchy. The British Monarch, Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom, is the monarch of New Zealand. She appoints a governor general to represent her, but the governor general has little power. The legislation, prime minister, and Cabinet run the national government.
Britain gave New Zealand a constitution in 1852, when it was a British colony. But through the years the New Zealand legislature has changed almost all its provisions. Today, the nation has no written constitution.
The first people who settled in New Zealand were a brown-skinned people called Maoris. They came from Polynesian islands located northeast of New Zealand. The country was discovered by Europeans in 1642, but they did not start to settle in the islands until the late 1700's. Today, most New Zealanders are descendants of the early European settlers. Maoris make up about 12 % of the country's population.

New Zealand has one of the highest standards of living in the world. For many years, the economy of the country depended largely on agriculture. Today agriculture, manufacturing, and service industries are all important to the economy. New Zealand's economy depends on trade with many countries — Australia, Britain, Japan and the United States.
2. Answer the questions
1. Where is New Zealand situated?
____________________________________________
2. What country is its nearest western neighbor? _________________________________
3. Is the area of New Zealand 270,000 square km? _______________________________
4. What islands does the country consist of? ____________________________________
5. Who are the Native people of New Zealand? _________________________________
6. Was James Cook the first European to visit New Zealand? _______________________
7. What are the official languages in the country? _________________________________
8. Wellington is the capital of New Zealand, isn‘t it? ______________________________
9. Is Christchurch the largest city in the country? _________________________________
10. Who is the head of New Zealand? ___________________________________________
3. True or false
1. New Zealand is situated in the Atlantic Ocean. _______________________________
2. The area of the country is about 270,000 sq km. _______________________________
3. The two main islands are separated by Tasman Strait. ___________________________
4. Most of New Zealanders live in the South Island. ______________________________
5. Europeans first visited New Zealand in 1642. _________________________________
6. James Cook claimed the land for the British crown. ____________________________
7. Maori are 80% of the population of the country. _______________________________
8. Wellington is the largest city of New Zealand. ________________________________
9. Auckland is the capital of the country. _______________________________________
10. New Zealand is an independent state. _______________________________________ 11. The head of state is the governor-general. ____________________________________
3.Annotation:
As the title implies the text describes
________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
The text gives a valuable information on
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
It describes in short
________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
It shown that
________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
4. Read and translate the text:

Australia is the only country in the world that is also a continent. It is the sixth large country and the smallest continent. The capital of the country is Canberra. The official language is English.
Australia is the driest continent on the Earth. The unique climate and the isolation of Australia from other continents explain the existence of unusual plants and animals.
The commonest tree of Australia is the eucalyptus. In the drier areas there is the Australian acacia or mimosa. In those areas one can also find strange bottle trees. They preserve water in their trunks.
Australian animals are also very unusual. Among them there are kangaroos, duck-bills, koala bears, and others.
Australian population is about 23 million people. The natives of the country are called
Aborigines. Now they comprise a very small part of the country‘s population due to the former extrusion of the indigenous people in the past.
There are 5 big cities in Australia: Sydney, Melbourne, Adelaide, Perth and Brisbane.
Canberra was specially planned as a capital. All the government buildings are situated there.
Sydney is the oldest and largest city in Australia. It is a big industrial centre. About 5 million people live in the city.

Australia has a lot to offer to tourists.
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands.The most famous building in the country is the Sydney Opera House. Its roof looks like sails. It is a masterpiece of architecture. More than 5,000 people can visit concerts, operas, theatre performances and other events.
Cacadu National Park is in Australia‘s Northern Territory and covers about 20,000 square kilometers. It is a wetland with over 200 kinds of birds and 1,700 plant species.

The Commonwealth of Australia is a self-government federal state. It has six states: new south Wales, Victoria, Queens land, south Australia, western Australia and two internal territories. It is situated in the southwestern of the Pacific Ocean. The area of this country has 7000000 square kilometers. Australia is the largest island in the world and the smallest continent. The Dutch were the first Europeans to visit Australia. In the 1770 the English captain James Cook discovered the East Coast of Australia. Nearly 20 millions people live in Australia.

The capital of the country is Canberra, this city become a capital in 1927. Federal government works in Canberra in the government buildings. There are no industrial plants in the town. The population of Canberra is about 300 000 people. There are many sits in the city. They are the buildings of Australian academy of sings, the Australian national university and others. There are two big industrial cities in Australia: Sydney and Melbourne. Australian climate is dry and warm. Australia is situated in the Southern Hemisphere and that is why it has summer when we have winter. January is the hottest month in Australia.
5. Say if these statements are true or false with the help of the words:
- I strongly disagree, because…
- I strongly agree… - You're absolutely right.
- I totally disagree, because…
1. Australia is the largest continent of the world.
_____________________________________________________________________________
2. Its official name is Commonwealth of Australia.
_______________________________________________________________________
3. Australia‘s name is derived from the Latin word ―Australis‖ meaning ‗northern‘. ______________________________________________________________________
4. Australia is the largest continent in the world.
______________________________________________________________________
5. In 1603 the Dutch ship sailed along the coast on Northern Australia with a great
interest
________________________________________________________________________
6. In 1642 another Dutch ship captained by James Cook sailed South Australia and discovered the island.
________________________________________________________________________
7. The British Government sent a ship led by James Cook to know more about Australia.
______________________________________________________________________
8. Captain Cook reached the coast of Australia in 1776.
______________________________________________________________________
9. Australia celebrates its National Day on July 26th.
______________________________________________________________________
10. Australia lies in the Southern Hemisphere and in the Eastern Hemisphere.
_______________________________________________________________________
11. Australia is bordered by the Indian Ocean in the west and the Pacific Ocean in the East. __________________________________________________________________________________
Рефлексия:
У меня получилось _____________________________
Было трудно___________________________________
Интересно_____________________________________
Итоговое обобщение:
Вы познакомились с географическим положением, политической системой, праздниками и традициями, знаменитыми писателями англо-говорящих стран. Используя полученные знания, составьте статью для журнала об одной из англоговорящих стран.
_____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
Грамматический материал
1.«Типы вопросительных предложений»
1. Прочтите грамматический комментарий:
В английском языке существуют следующие типы вопросительных предложений:
Общие вопросы (General questions).
Специальные вопросы (Special questions).
Вопросы к подлежащему (Questions to the subject).
Альтернативные вопросы (Alternative questions).
Разделительные вопросы (Disjunctive questions).
Общие вопросы (General questions) требуют ответа "да" – "yes" или "нет" – "no". При постановке общего вопроса глагол to be ставится перед подлежащим. В английском языке общие вопросы произносятся с повышающейся интонацией, также как и в русском языке.
Сравните: Is Anna ill? Анна больна?
На общий вопрос можно дать краткий утвердительный или отрицательный ответ, состоящий только из слов "Yes" или "No".
– Are you tired? – Ты устал?– Yes. – Да.
– Are you hungry? – Ты голоден?– No. – Нет.
На общий вопрос можно дать более развернутый ответ. В этом случае после слов "yes" или "no" следует местоимение, соотнесенное с подлежащим вопросительного предложения, а затем глагол to be в соответствующей форме.
– Are Anna and Nick students? – Анна и Ник студенты?
– Yes, they are. – Да.– Are Pete and Alex workers? – Пит и Алекс рабочие?
– No, they are not./ No, they aren't. – Нет.
На общий вопрос можно дать полный ответ.
– Is it cold in the room? – В комнате холодно?– Yes, it is cold in the room. – Да, в комнате холодно.
– Is the room dark? – Комната темная?– No, it is not dark. / No, it isn't dark. – Нет, она не темная.
–Are the flowers beautiful? – Цветы красивые?
– Yes, they are beautiful. – Да, они красивые.
– Are the shoes old? – Туфли старые?– No, they are not old. / No, they aren't old. – Нет, они не старые.
Форма глагола в ответах (кратких или полных) согласуется с формой глагола в вопросе. В примерах, приведенных выше, глагол to be употреблен в настоящем неопределенном времени и в вопросах и в ответах. Если в вопросе глагол to be употреблен в прошедшем неопределенном времени или в будущем неопределенном времени, то и в ответе должен употребляться глагол to be либо в прошедшем неопределенном времени или в будущем неопределенном времени.
Примеры кратких ответов:
– Are you busy? – Yes, I am. / No, I am not. / No, I'm not.
– Were they angry? – Yes, they were. / No, they were not. / No, they weren't.
– Was Nick ill last week? – Yes, he was. / No, he was not. / No, he wasn't.
– Will Ann be happy? – Yes, she will. / No, she will not. / No, she won't.
– Will you be at home tomorrow? – Yes, we will. / No, we will not. / No, we won't.
– Yes, we shall. / No, we shall not. / No we shan't.
Специальные вопросы (Special questions) начинаются с вопросительных слов. Затем порядок слов в специальных вопросах такой же, как и в общих вопросах, т.е. после вопросительного слова сначала ставится глагол to be в соответствующей форме, а затем подлежащее.
Выучите вопросительные слова, которые употребляются в специальных вопросах:
What? – Что? Какой?
Which? – Который?
When? – Когда?
Where? – Где? Куда?
Whom? – Кому? Кого?
Whose? – Чей? Чья? Чье? Чьи?
Why? – Почему? Зачем?
Специальные вопросы могут начинаться со слова how: How? – Как?
How long? – Как долго? Сколько времени?
How old? – Сколько лет? (вопрос о возрасте)
How many? – Сколько? (употребляется с исчисляемыми существительными).
How much? – Сколько? (употребляется с неисчисляемыми существительными).
Можно спросить о цене: How much is it? (Сколько это стоит?)
How far? – Как далеко? (об удаленности)
Специальные вопросы предполагают полный логически сформулированный ответ, однако в разговорной речи ответ может состоять только из нескольких слов, которые являются сокращенным ответом на вопрос, например:
– Where were you yesterday? – Где ты был вчера?
– I was at the cinema. (At the cinema.) – Я был в кино. (В кино.)
Если при вопросительном слове есть предлог, то он обычно ставится в конце предложения, например:
– Where are you from? – Откуда ты?– I am from Russia. – Я из России.
– What is the book about? – О чем эта книга?– The book is about animals. – Эта книга о животных.
Вопросы к подлежащему (Questions to the subject), строго говоря, относятся к специальным вопросам. Они начинаются с вопросительного слова Who? (Кто?), если подлежащее одушевленное, или What? (Что?), если подлежащее неодушевленное.
При постановке вопроса к подлежащему необходимо обращать внимание на согласование глагола to be с последующим существительным в числе.
Например:
Anna is a secretary. Who is a secretary?
Emma and Mary are economists. Who are economists?
Но сравните следующие предложения: The table is white. What is white?
The shoes are new. What is new?
We were late for classes yesterday. Who was late for classes yesterday?
Nick and Mike are ill today. Who is ill today?
We will be in Paris tomorrow. Who will be in Paris tomorrow?
The vase is on the table. What is on the table?
The cups are on the table. What is on the table?
В приведенных выше примерах (1-7) глагол to be употреблен в форме 3-го лица единственного числа соответствующего времени. В повседневной речи при постановке вопроса к подлежащему после вопросительного слова глагол обычно употребляется в третьем лице единственного числа.
Альтернативные вопросы (Alternative questions) всегда включают слово or (или). Собеседнику предлагается альтернатива, он должен сделать выбор. Альтернативные вопросы строятся как общие вопросы, но содержат слово "или". Они начинаются с глагола to be в соответствующей форме, затем следует подлежащее, затем предлагается выбор. Следует обратить внимание на то, что первая часть вопроса до союза or произносится с повышением голоса, а после союза – с понижением голоса. На альтернативные вопросы нельзя отвечать словами "Yes" или "No", нужно обязательно сделать выбор. На альтернативные вопросы обычно даются полные ответы. Сравните предложения:
– Is your father at home or at work? – Ваш отец дома или на работе?
– He is at home now. – Он сейчас дома.
– Were the children at the Zoo or at the cinema yesterday? – Дети были в зоопарке или в кино вчера?– They were at the Zoo. – Они были в зоопарке.
– Will it be rainy or sunny tomorrow? – Завтра будет дождливо или солнечно?
– It will be sunny. – Будет солнечно.
Разделительные вопросы или "вопросы с хвостиком" (Disjunctive questions или tailquestions) состоят из двух частей. Первая часть вопроса представляет собой утвердительное или отрицательное предложение, а вторая часть ("хвостик") образуется как краткий общий вопрос, состоящий из глагола в соответствующей форме и соответствующего местоимения. Следует запомнить, что, если первая часть предложения строится как утвердительное предложение, то в "хвостике" глагол употребляется в отрицательной форме, и наоборот, если в первой части вопроса что-то отрицается, то "хвостик" строится как утверждение. Обратите внимание на то, что первая часть разделительного вопроса произносится с понижающейся интонацией, а вторая часть разделительного вопроса обычно произносится с повышающейся интонацией, как в общем вопросе. Вторая часть разделительного вопроса переводится на русский язык словами не так ли? не правда ли? Разделительные вопросы задаются для того, чтобы получить подтверждение высказывания, содержащегося в первой части вопроса. Таким образом, если в первой части вопроса употреблен глагол to be, то и "хвостик" состоит из глагола to be в соответствующей форме и соответствующего местоимения. Рассмотрим следующие примеры:
Max is twenty, isn't he? Максу двадцать лет, не так ли?
Max isn't twenty, is he? Максу нет двадцати лет, не так ли?
Anna was at work on Saturday, wasn't she? Анна была на работе в субботу, не так ли?
Anna wasn't at work on Saturday, was she? Анна не была на работе в субботу, не так ли?
The weather will be rainy tomorrow, won't it? Завтра будет дождливая погода, не правда ли? The weather won't be rainy tomorrow, will it? Завтра не будет дождливой погоды, не правда ли?
На разделительные вопросы даются краткие утвердительные или отрицательные ответы, однако следует обратить внимание на то, какой была первая часть вопроса – утвердительное или отрицательное предложение. Если первая часть разделительного вопроса содержит отрицательное предложение, то выражение согласия и несогласия (т.е.
"да" и "нет") в английском и русском языке не совпадает.
Разделительный вопрос Ответ, выражающий согласие Ответ, выражающий несогласие
It is Monday today, isn't it?
Сегодня понедельник, не правда ли? Yes, it is. Да. No, it isn't. Нет. It isn't Monday today, is it?
Сегодня не понедельник, не правда ли? No, it isn't. It isn't Monday, it's Tuesday.
Да. Сегодня не понедельник, а вторник. Yes, it is. It's Monday today.
Нет. Сегодня понедельник.
Таким образом, при ответе на разделительный вопрос нужно ориентироваться на реальную ситуацию, а не пытаться переводить свой ответ с русского языка на английский.
Если сегодня не понедельник, то вы говорите: No, it isn't Monday.
Если сегодня понедельник, то вы говорите: Yes, it is Monday.
В английском языке нельзя сказать "Yes", а затем давать отрицательный ответ. Нельзя сказать "No", а затем давать утвердительный ответ. Если вы говорите "No", то далее обязаны давать отрицательный ответ. Если говорите "Yes", то дальше обязаны давать утвердительный ответ.
Ниже приведены примеры постановки разных типов вопросов (общего, вопроса к подлежащему, альтернативного, разделительного).
Max is ill.
Is Max ill?
Who is ill?
Is Max or Alex ill? Max is ill, isn't he?
Max isn't ill, is he?
Anna and Emma are lazy.
Are Anna and Emma lazy?
Who is lazy?
Are Anna and Emma or Nick and Pete lazy?
Anna and Emma are lazy, aren't they?
Anna and Emma are not lazy, are they?
Вопросы для самоконтроля
1. Какие типы вопросов существуют в английском языке?
2. Какие два ответа всегда можно дать на общий вопрос?
3. Какое слово обязательно должно присутствовать в альтернативном вопросе?
4. Как строится "хвостик" в разделительном вопросе?
5. Почему можно сказать, что вопрос к подлежащему является разновидностью специального вопроса?
6. Чем отличается порядок слов в общем вопросе от порядка слов в специальном вопросе?
Упражнения:
Упр. 1. Постройте общие вопросы и дайте краткие утвердительные ответы.
Образец: Tom is a driver.
Is Tom a driver? – Yes, he is.
The teacher was busy yesterday.
The child is ill today.
It will be hot tomorrow.
Our friends are in France.
The cake will be nice.
Упр. 2. Постройте общие вопросы и дайте краткие отрицательные ответы.
Образец: Ann is a teacher.
Is Ann a teacher? – No, she is not. / No, she isn't.
The boy is five. ________________________________________________________
The girls are lazy._______________________________________________________
My friends were right.___________________________________________________
The song was sad. ______________________________________________________
The party will be nice. ___________________________________________________
The films will be bad. ___________________________________________________
Упр. 3. Заполните пропуски соответствующей формой глагола to be.
– Where … you from? – I … from Tomsk.
– Why … you so happy today? – Because I … at the concert of my favourite pop group tomorrow.
– Where … my favourite music CDs? Can you see them? – One disc … on the table and three discs …on the bookshelf.
– This … your new mobile phone, … it? – Yes, it … . – … your phone number new or old? – It … old.
– What colour … your new coat? – It … green and brown.
– What … your favourite colours? – My favourite colour … grey.
Yesterday it … cold. Today it … warm. Tomorrow it … cold again, … it?
Упр. 4. Переведите вопросы на английский язык и ответьте на них.
1.Как вас зовут? ___________________________________________
2. Сколько вам лет? _________________________________________
3. Откуда вы? ______________________________________________
4. Какой ваш адрес? ___________________________________________
5. Какой номер вашего мобильного телефона? ______________________
6. Вы студент, не правда ли? _____________________________________
7. Вы студент первого или второго курса? __________________________
8. Какие ваши любимые предметы? _______________________________
9. В каких предметах вы хорошо разбираетесь (to be good at)? _________ _______________________________________________________________
10. Вам нравится английский язык, не правда ли (to be fond of)?
______________________________________________________________
11. Какие у вас хобби? _________________________________________
12. Вы любите спорт? _________________________________________
13. Вам нравятся виды спорта, которыми занимаются на открытом воздухе (outdoor sports) или в помещении (indoor sports)? __________________________________
14. Какие ваши любимые виды спорта? _______________________________ 15. Какие ваши любимые книги? _____________________________________
16. Вам нравится классическая или популярная музыка?
_________________________________________________________________
17. Кто ваши любимые актеры? ______________________________________
18. Вам нравится лето или зима? _____________________________________
19. Какое ваше любимое время года? ________________________________
20. Почему лето ваше любимое время года? __________________________ 21. Вы не боитесь мышей, не так ли? _________________________________ Упр. 5. Ask the questions begin with the words in brackets.
1. We are going to go to school. (Where….?)
____________________________________________________
2. I often go to my friend on Sunday. (Who….?)
____________________________________________________
3. Children are going to have a party. (What….?)
______________________________________________________
4. My sister will buy a car next month. (When…?)
_______________________________________________________
5. We played on computer yesterday. (When…?)
_______________________________________________________ Упр. 6. Ask tag-questions.
We are going to study History,……………………?
We will visit our friends in Britain,………………..?
His friend can speak English well,…………………….?
I don‘t swim in winter,…………………………………..?
You are a teacher,……………………………………….?
2. Конверсия как способ словообразования. Словосложение.
В современном английском языке имеется несколько способов словообразования:
1) конверсия (образование новых слов без изменения их написания и произношения)
2) словосложение (образование нового слова путем сложения двух слов в одно) 3) изменение ударения в слове (и получение нового слова другой части речи).
4) аффиксация (прибавление к корню суффикса или префикса)
Иногда слово может менять свое значение и выполнять новую синтаксическую функцию в предложении, не изменяя при этом написания и произношения (конверсия). Наиболее распространенным является образование глаголов от существительных: master
(хозяин) - to master (управлять), house (дом) - to house (размещать), water (вода) - to water (поливать). Но глаголы могут быть образованы и от прилагательных: empty (пустой) - to empty (опустошать) white (белый) - to white (белить).
Словосложение - это объединение полнозначных слов или их основ в сложное слово. Вновь образованное сложное слово пишется слитно или через дефис: airfield - аэродром (air - воздух, field - поле), air-base - авиабаза (air - воздух, base - база), airman - авиатор (air - воздух, man - мужчина), schoolday - школьный день (school - школа, day - день), birthplace - место рождения (birth - рождение, place - место).
Сложные слова могут состоять из двух существительных, первое из которых приобретает значение прилагательного. В этом случае слова пишутся отдельно. Например: service dress - форменная одежда, одежда для службы (service - служба, dress - платье), shop window - витрина (shop - магазин, window - окно), skim milk - снятое молоко (to skim - снимать (накипь и т.д.), milk - молоко).
Многие существительные совпадают по форме с глаголами, но отличаются ударением. Как правило, в существительных ударение падает на первый слог, а в соответствующих глаголах - на второй: export (экспорт) - to export (экспортировать) present (подарок) - to present (дарить).
Словообразование с помощью аффиксации.
Образование новых слов может происходить при помощи присоединения к основе слова суффиксов или префиксов (приставок). Префиксы присоединяются к корню слова в начале, а суффиксы - в конце. Слова, образованные с помощью префиксов или суффиксов, в отличие от простых слов, называются производными.
Самым продуктивным является этот вид словообразования. В ходе обучения английскому языку уделяется большое внимание этому способу словосложения.
Префиксы, как и суффиксы, могут присоединяться к различным частям речи, изменяя при этом значение основы слова, например: happy (счастливый) - unhappy (несчастный) - happiness (счастье) - happily (счастливо); help (помощь) - helper (помощник) - helpful (полезный) - helpless (беспомощный).
Наиболее употребительные приставки (префиксы) и их значения:
1. Префикс со значением ―снова‖, ―заново‖, ―вновь‖, ―пере‖: re-
to construct (строить) - to reconstruct (перестроить), to read (читать) - to reread (перечитать), to write (писать) - to rewrite (переписать)
2. Префиксы, которые придают слову противоположное значение или обозначают противоположное действие:
un- dis- de- anti- counter- contra- to dress (одеваться) - to undress (раздеваться), to tie (связывать) - to untie
(развязывать) to appear (появляться) - to disappear (исчезать) formation (формирование) - deformation (деформация) fascist (фашист) - anti-fascist (антифашист) attack (атака) - counterattack (контратака) to contradict (противоречить, возражать)
3. Префиксы, имеющие отрицательное значение: a- ab- un- im- in- ir- il- dis- mis- non-
amoral (аморальный, безнравственный) absent (отсутствующий), abnormal (ненормальный) kind (добрый) - unkind (недобрый)
possible (возможный) - impossible (невозможный) ability (способность) - inability (неспособность) regular (регулярный) - irregular (нерегулярный) legal (легальный) - illegal (нелегальный) honest (честный) - dishonest (нечестный), to understand (понимать) - to misunderstand (неправильно понять) interference (вмешательство) - non-interference (невмешательство)
Приставка, которая начинается на ―i‖ изменяется в зависимости от того, какая за ней стоит буква: il + l, ir + r, im + b, m, p.
4. Префиксы, имеющие значение ―сверх‖, ―пере‖, ―чрезмерно‖:
over- super- ultra- extra-
to pay (платить) - to overpay (переплатить)
human (человеческий) - superhuman (сверхчеловеческий) short (короткий) - ultra-short (ультракороткий) extraordinary (необычный)
5. Префиксы со значением ―между‖, ―взаимно‖: со- inter-
existence (существование) - co-existence (сосуществование) national (национальный) - international (интернациональный)
6. Префиксы, которые переводятся как
а) ―перед‖:
рге- fore-
war (война) - pre-war (довоенный), historic (исторический) - prehistoric
(доисторический) to foresee (предвидеть)
б) ―после‖:
post-
war (война,) - post-war (послевоенный), revolutionary (революционный) - post-
revolutionary (послереволюционный)
в) ―недостаточно‖, ―недо-―:
under- to pay (платить) - to underpay (оплачивать низко, т.е. недостаточно оплачивать,
недоплачивать), production (производство) - underproduction (недопроизводство) г) ―под‖:
sub-
division (разделение) - subdivision (подразделение), committee (комиссия, комитет) -
subcommittee (подкомиссия)
д) ―экс‖, ―бывший‖:
ex-
champion (чемпион) - ex-champion (бывший чемпион) е) само-, авто- auto-
autobiography (автобиография), automatic (автоматический) ж) полу-
semi-
semifinal (полуфинал), semicircle (полукруг) з) через-, транс- trans-
transatlantic (трансатлантический)
и) вверх, кверху, наверху up- upstairs (вверх по лестнице), upside (верхняя часть), to uproot (вырывать с корнем) к) двойной, два, дважды
bi-
bilingual (двуязычный), bi-monthly (выходящий два раза в месяц)
л) имеющий дело с книгами
bibli(o)-
bibliography (библиография)
м) относящийся к жизни
bio- biography (биография)
н) второстепенное значение
by-
by-street (переулок, улочка) о) много-, мульти-, поли- multi- poly-
multicolored (многоцветный), multimillionaire (мультимиллионер) polyglot (полиглот), polytechnic (политехнический)
п) второстепенное значение
by-
by-street (переулок, улочка)
7. Префикс глагола, имеющий значение ―делать‖: en-
large (большой) - to enlarge (увеличивать, делать больше), danger (опасность) - to
endanger (подвергать опасности), force (сила) - to enforce (принуждать, настаивать)
Основные суффиксы существительных:
1. Суффиксы, обозначающие принадлежность к
а) политическому направлению профессии или нации:
-ist
-an, -ian
Communist (коммунист), Marxist (марксист}, materialist (материалист); artist (художник), typist (машинистка), pianist (пианист), historian (историк), librarian
(библиотекарь), musician (музыкант); Russian (русский), Bulgarian (болгарин)
2. Суффикс, обозначающий учение, теорию, качество: -ism marxism (марксизм), heroism (героизм)
3. Суффиксы, обозначающие действующее лицо, его занятие или должность:
-ег, -or
-ee, -eer
to teach (учить) - teacher (учитель), to direct (руководить) - director (руководитель) employee (служащий), refugee (беженец, эмигрант), auctioneer (аукционер),
4. Суффикс, обозначающий результат действия:
-ment -ade achievement (достижение), agreement (согласие), government (правительство) lemonade (лимонад), blockade (блокада)
5. Суффиксы, обозначающие
а) состояние:
-hood
-ship -cy, -acy brotherhood (братство), childhood (детство), manhood (мужественность) dictatorship (диктатура), friendship (дружба), leadership (руководство) accuracy (точность), infancy (младенчество), supremacy (превосходство) б) действие, состояние:
-age
-ing
-ence
-ance
-ion, -tion
-ition, -ation
-sion
al
shortage (нехватка), marriage (брак, супружество), voyage (путешествие) hunting (охота), crossing (пересечение, перекресток), living (житье) silence (молчание), difference (различие) importance (важность), resistance (сопротивление) collection (собрание, коллекция), dictation (диктант, диктовка) competition (соревнование), hesitation (сомнение, колебание) decision (решение)
removal ( удаление), arrival (прибытие), refusal (отказ), approval (одобрение) в) качество или состояние:
-dom
-ness
-ty
freedom (свобода), kingdom (королевство), wisdom (мудрость)
coldness (холод), darkness (темнота), kindness (доброта), weakness (слабость) activity (активность), safety (безопасность)
г) место действия, занятие или состояние -ery bakery (булочная), surgery (кабинет хирурга), cookery (кулинария), slavery (рабство) д) род занятий, отрасль науки
-ics
physics (физика), politics (политика)
Основные суффиксы прилагательных:
1. Суффикс, образующий прилагательные от существительных и обозначающий национальную принадлежность или слабую степень качества:
-ese
-ish
Chinese (китаец, китайский), Japanese (японец, японский)
Pole (поляк) - Polish (польский), Scott (шотландец) - Scottish (шотландский) red (красный) - reddish (красноватый), child (ребенок) - childish (ребячливый,
детский)
2. Суффиксы, образующие прилагательные от глаголов и обозначающие наличие качества:
-ive
-ent
ant
to act (действовать) - active (активный), to talk (разговаривать) – talkative (разговорчивый) to differ (различать) - different (различный), to insist (настаивать) - insistent (настойчивый) to observe (наблюдать, замечать) - observant (наблюдательный, внимательный)
3. Суффиксы, образующие прилагательные от существительных и обозначающие наличие качества, свойства:
-ic
-al
-ful
-ous
-у
base (основа) - basic (основной), economy (экономика) - economic (экономический) centre (центр) - central (центральный) culture (культура) - cultural (культурный), beauty (красота) - beautiful (красивый) peace (мир) - peaceful (мирный), fame (слава) - famous (знаменитый) cloud (облако) - cloudy (облачный), sun (солнце) - sunny (солнечный)
4. Суффиксы, образующие прилагательные от различных частей
речи и обозначающие
а) качество, свойство:
-аrу -огу element (элемент) - elementary (элементарный) illusion (иллюзия) - illusory (обманчивый, иллюзорный) б) способность что-либо сделать, состояние, качество:
-able - ible
to change (изменить) - changeable (изменчивый)
to eat (есть) - eatable (съедобный), reason (разум) - reasonable (разумный) в) отсутствие качества:
-less
useless (бесполезный), windless (безветренный)
Основные суффиксы глаголов:
-ate
en
-fy, -ify -ize, -ise
active (активный) - to activate (активизировать) short (короткий) - to shorten (укоротить) pure (чистый) - to purify (очищать), simple (простой) - to simplify (упрощать) character (характер) - to characterize (характеризовать)
Основные суффиксы наречий Суффиксы, образующие наречия от
а) прилагательных, иногда - существительных, порядковых числительных и
причастий:
-ly
bad (плохой) - badly (плохо), part (часть) - partly (частично), first (первый) - firstly
(во-первых)
б) существительных и наречий и обозначающие направление (или направленность): -wards
-ward
![]() North
(север) - northward(s) (к северу, на север), after (после) - afterwards
(впоследствии, позже, потом), back (обратно, назад) - backward(s) (назад, в
обратном направлении) home (дом, домой) - homeward (к дому, по направлению к
дому)
North
(север) - northward(s) (к северу, на север), after (после) - afterwards
(впоследствии, позже, потом), back (обратно, назад) - backward(s) (назад, в
обратном направлении) home (дом, домой) - homeward (к дому, по направлению к
дому)
Упражнения:
Упр. 1. Переведите следующие слова, выделите в них суффиксы и префиксы:
Untrue, prehistoric, ultramodern, postwar, ex-champion, anti-body, decompose, decode, deform, depart, discover, disappearance, reread, reconstruct, coauthor, unequal, misunderstand, undress, disarm, anti-fascist, cooperation, co-existence, interaction, superhuman, ultra-violet.
_____________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________
Упр.2. Определите, к какой части речи относятся следующие слова. Переведите их:
Achievement – achieve ______________________________________ resistance – resistant ______________________________________________ assistance - assist – assistant_________________________________________ celebration – celebrate ______________________________________________ difference – different ______________________________________________ city – citizen _____________________________________________________
nation - national – nationality
__________________________________________
measure – measurement
_______________________________________________
develop – development
_________________________________________________
act - active – activity
_____________________________________________________
discovery – discoverer
____________________________________________________
literature – literary
_______________________________________________________ graduate - graduation - undergraduate - post-graduate
__________________________
________________________________________________________________________
____
educate – education
____________________________________________________
progress – progressive
___________________________________________________
act - action - activity – active
_________________________________________________
govern - governor –
government______________________________________________
Упр. З. Образуйте от данных глаголов существительные с помощью суффикса
-ег или -or. Переведите на русский язык:
To lead, to write, to read, to visit, to speak, to sleep, to act, to direct, to conduct, to drive, to fight, to mine, to report, to sing, to skate, to swim, to teach, to travel, to sail, to invent, to found, to compose. ________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________
Упр. 4. Образуйте от данных слов существительные с помощью суффикса -ist, -ism,
-ian. Переведите на русский язык:
Special, social, art, capital, economy, international, piano, technic, mathematics, statistics, politics, music, electric, Russia, Hungary, Canada, India.
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________
Упр. 5. Образуйте от данных глаголов существительные с помощью суффикса ment. Переведите на русский язык:
Develop, achieve, move, arrange, treat, state, improve, agree, equip, govern, require, measure, announce, pave.
________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________
Упр. 6. Образуйте прилагательные с помощью суффиксов -ful и -less, переведите их на русский язык:
Beauty, thank, hope, doubt, care, aim, use, shape, fruit, power, thought, harm, colour.
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________
Упр. 7. Образуйте прилагательные с помощью суффиксов -able, -ible, переведите их на русский язык:
Change, convert, prevent, break, compare, desire, profit, read, comfort, respect, expect. _______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________
Упр. 8. Найдите и выделите суффиксы в данных словах и определите, к какой части речи эти слова относятся:
British, foolish, understandable, heartless, pitiless, successful, experiment, function, musician, socialist, artist, capitalism, professional, fundamental, industrial, doubtful, useful, different, treatment, creative, attractive, peaceful, dangerous, elementary, childish, active, economic, director, worker, passage, marriage, silence, freedom, kingdom.
Упр. 9. Образуйте глаголы с помощью суффикса -en:
Red, tight, soft, deep, short, dark, bright, weak, black, white, sweet, sharp, strength.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________
Упр. 10. Образуйте наречия с помощью суффикса -1у и переведите их:
Bad, first, part, quick, strong, short, silent, rapid, wide, extreme, cruel, kind, happy.
___________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________
Упр. 11. Образуйте глаголы от данных существительных. Переведите их:
Turn, smile, smoke, snow, start, stay, step, stop, study, talk, visit, rest, air, paper, cover, handle, cause, watch, act, address, answer, brush, clean, cross, crowd, wave, wish, work, dance, doubt, dress, end, fight, help, hope, joke, laugh, lift, light, love, mind, paper, pencil, place, plan, play, post, reply, report, return, sail, show.
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________
Упр. 12. Выделите словообразующие элементы. Определите, к какой части речи относятся данные слова:
React, reaction, reactor, reactivity; science, scientific, scientist; industry, industrial, industrious; cold, coldly, coldness; dark, darkness, darken; happy, happily, happiness, unhappy; equal, equally, unequal, equality; free, freedom, freely; attention, attentive, attentively; sun, sunny, sunless; care, careful, careless, carefully, carelessness; to differ, different, difference, indifferent; England, English, Englishman; fame, famous.
Упр. 13. Переведите следующие сложные слова:
Airport, armchair, bathroom, bedroom, bookcase, bookshelf, classroom, custom-house, dining-room, drawing-room, fireplace, folksong, gentleman, hairbrush, icebox, newspaper, notebook, postcard, post-office, raincoat, sportsman, sunshine, writing-table.
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________
Упр. 14. Определите, к каким частям речи относятся выделенные слова:
1. Не works as a teacher. 2. I saw one of his works at the exhibition. 3. I was waiting for your report. 4. They report the results of their experiment every Monday. 5. His report contains some of his thoughts about the experiment. 6. You‘ll make progress if you work hard. 7. He thought about his new work. 8. I have a present for you. 9. I am busy at present. 10. He presented me with a book.
Упр. 15. Распределите прилагательные по трем группам: 1) люди, 2) места, 3) вещи:
Obstinate, unspoilt, hand-made, waterproof, easy-going, breathtaking, aggressive, deserted, overgrown, overcrowded, cunning, picturesque, arrogant, long-lasting, spoilt, automatic, accurate, artificial.
Упр. 16. Напишите слово противоположное по значению, используя префикс
Kind, honest, credible, appear, fair, equal, pleased, continue, fasten, normal, employed, friendly, trust, professional, known, cover, safe, use, probable, important, emotional. ________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________ Литература
1. И.П. Агабекян ―Английский язык для средних специальных заведений‖ Изд-во ―Феникс‖, г. Ростов-на-Дону, 2015г.
2. И.П. Агабекян ―Английский язык для для ССУЗОВ‖
Изд-во ―Проспект‖, г. Москва, 2014г
3. Е.Л. Занина ―95 устных тем по английскому языку‖.
Изд-во ―Айрис‖, г. Москва, 2015г.
4. А.С. Сушкевич ―Английский язык. Устные темы‖.
Изд-во ―Аверсэв‖, г. Минск 2013г.
5. М.А. Моисеев ―Английский язык. Тексты для чтения и понимая‖.
Изд-во ―Аквариум‖, г. Москва, 2013.г.
6. В.Н. Трофимов ―Английский язык. Пособие по английскому языку для поступающих в вузы‖.
Изд-во ―Рученькина‖, г. Москва, 2013г.
7. Р. Картер ―Грамматика английского языка. Современный курс‖.
Изд-во ―University Press‖, г. Кэмбридж, 2014г.
8. Ю.Б. Голицынский , Изд-во ―Каро‖ г. С-Петербург, 2015г.
Интернет - ресурсы:
1. Коллекция тестов, контрольных вопрос – Self Study Quizzes for ECL Students
2. Коллекция материалов по английскому языку: грамматика, упражнения, тексты, фонетика – https://english-zone.com\index.htm
3. Английский для всех: уроки, материалы – www.abc-english-
grammar.com\index.htm
4. Онлайн библиотека на английском языке – www.bibliomania.com
Заключение
Выполнив все задания в данной тетради, вы познакомились с географическим положением, политической системой, праздниками и традициями, знаменитыми писателями англо-говорящих стран.
Вы узнали:
Ø Значения новых лексических единиц, связанных с тематикой данного этапа обучения, отражающих особенности культур стран изучаемого языка; А также научились:
Ø читать аутентичные тексты, используя основные виды чтения
(ознакомительное, изучающее, поисковое) ;
Ø представлять социокультурный портрет стран изучаемого языка;
Ø использовать приобретенные знания и умения в практической деятельности и повседневной жизни для общения с представителями других стран.
Материалы страноведческого характера способствуют передаче иноязычной культуры, содействуют вовлечению в диалог культур, развивают творческие и познавательные умения, способствуют развитию лингвострановедческой компетенции: приобретению обширных культуроведческих знаний.
Крепкое владение этим материалом является важной составляющей при изучении английского языка и полностью обосновывает составление данной рабочей тетради.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.