
 Worksheet
Worksheet
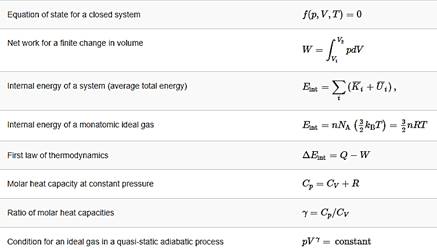
1 A monatomic ideal gas undergoes a quasi-static adiabatic expansion in which its volume is doubled. How is the pressure of the gas changed?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1]
2 An ideal gas has a pressure of 0.50 atm and a volume of 10 L. It is compressed adiabatically and quasi-statically until its pressure is 3.0 atm and its volume is 2.8 L. Is the gas monatomic, diatomic, or polyatomic?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 Pressure and volume measurements of a dilute gas undergoing a quasi-static adiabatic expansion are shown below. Plot ln p vs. V and determine γ for this gas from your graph.
|
P/atm |
V/L |
|
20.0 |
1.0 |
|
17.0 |
1.1 |
|
14.0 |
1.3 |
|
11.0 |
1.5 |
|
8.0 |
2.0 |
|
5.0 |
2.6 |
|
2.0 |
5.2 |
|
1.0 |
8.4 |
[2]
4 (a) An ideal diatomic gas at 80 K is slowly expanded adiabatically and reversibly to twice its volume. What is its final temperature?
final temperature = …………………………. K [2]
(b) Compare the charge in internal energy of an ideal gas for a quasi-static adiabatic expansion with that for a quasi-static isothermal expansion. What happens to the temperature of an ideal gas in an adiabatic expansion?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
[2]
5 On an adiabatic process of an ideal gas pressure, volume and temperature change such that pVγ is constant with γ=5/3 for monatomic gas such as helium and γ=7/5 for diatomic gas such as hydrogen at room temperature. Use numerical values to plot two isotherms of 1 mol of helium gas using ideal gas law and two adiabatic processes mediating between them. Use T1=500K, V1 = 1L,and T2=300K for your plot.
[3]
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.