
Laboratory work №9
Subject: Aldehydes. Ketones.
Objective: a) practical development of qualitative reactions to the aldehyde group and their interpretation; b) study of the properties of acetone.
Reagents and equipment: formaldehyde, ethyl alcohol, fuchsin sulfuric acid, silver nitrate solution (AgN03), ammonia (NH3), sodium bisulfite solution, 10% NaOH solution, acetone, iodine solution, potassium iodide solution, chromium mixture solution, test tubes, tripod, glass stick, pumice sawdust, film, alcohol lamp, test tube, thin glass, microscope.
Experience the № 1. Preparation of acetic aldehyde by oxidation of alcohols.
Reagents and equipment: ethyl alcohol, К2Сr204 / powder/.
Progress: 0.5 g of potassium bichromate is placed in a test tube with a gas outlet tube, then the mixture is whipped in 2 ml of liquefied and Н2 S04 2 ml of alcohol. The color of the mixture changes, and heat is released. The test tube is installed connecting the gas pipe,the second end of the gas outlet tube is placed to the bottom of the receiver with 2 ml of cold water. Each test tube is placed in a glass of cold water. The reaction mixture heats evenly. After 2-3 minutes, the heating stops if there is a volume of liquid in the receiver. From the product in the receiver, there is a sharp smell of vinegar aldehyde. The resulting liquid is used for the following operations.
Experience №2. Preparation of aldehydes from alcohols by decomposition of hydrogen.
Reagents and equipment: methyl alcohol, metallic copper.
Progress: wooden stoppers are made for the test tube. Then take a thin copper mesh and wrap it in such a way as to freely penetrate this test tube and a tight cylinder.
In a dry test tube, pour 3 ml of alcohol and 2 ml of water. Packed copper mesh heats up. At this time, the copper washes away. The hot mesh is quickly placed in the alcohol tube and closes the tube mouth to release the tube mouth. Alcohol gets very hot. At the end of boiling alcohol, the cork is Packed and the test tube is cooled in a glass of cold water. Then remove the stopper and pour the liquid into another tube. In a test tube with a grid, pour water into the volume of this liquid, drain it into a test tube with a liquid. An aqueous alcohol solution of formaldehyde (methyl alcohol) and acetaldehyde (methyl alcohol) is obtained. The resulting formaldehyde and acetaldehyde are used for the following works.
Experience №3. Oxidation of copper II valence compounds under the influence of aldehyde.
Reagents and equipment: formaldehyde, acetaldehyde.
Progress: in 1 ml of aldehyde, 0.5 ml of a dilute alkali solution and a solution of CuS04 are drop-filled until a precipitate is formed. The resulting mixture is heated to a boil. Meanwhile, the color of the tincture changes.
Experience №4. Oxidation of silver compounds under the influence of aldehyde.
Reagents and equipment: formaldehyde, acetaldehyde
Process: add a solution of liquefied ammonia to 4-5 ml of AgN03 solution before removing the first precipitate and prepare a solution of silver oxide in ammonia.
The aldehyde solution (1 drop) is poured into 2 test tubes and 1 drop of the newly prepared silver oxide solution is added to each test tube in ammonia. In one of the same two test tubes, add 2-3 drops of a dilute alkali solution. The test tube is shaken and placed on a tripod. In which test tube is the change rapidly observed? If a silvery luster is not formed, the test tube is heated in a water bath (50-90oC) simultaneously with the liquid. Note: to remove the mirror of the silver layer in the test tube wall, wash the test tube with hot alkaline solution and distilled water before the experiment. After working with a solution of silver oxide in ammonia, wash the dishes immediately.
Experience №5. Reaction of aldehydes with fuchsin sulphate.
Reagents and equipment: formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, sulfuric acid fuchsin solution
Progress: 1 ml of a colorless solution of fuchsin sulphate is poured into two test tubes and a few drops of formaldehyde are added to one of the two test tubes, and a solution of acetaldehyde in the same amount is added to the second test tube. Controls the color change of impurities in the test tube. Then 0.5 ml of concentrated НСІ (or liquefied H2S04 ) is poured into two test tubes and color change is monitored (immediately and after 5-10 minutes).
Experiment №6. The reaction of hexamine.
Reagents and equipment: urotropin.
A. 1 ml of liquefied Н2S04is added to 0.2-0.5 urotropin. Heat this mixture to a boil. There is a sharp smell of formaldehyde. Then carefully drain 1 ml of concentrated alkali solution with liquid cooling. Preheat the mixture to a boil and smell the exhaust steam.
B. in 2-3 ml of water, dissolve 0.2-0.5 g of urotropin and divide it into two parts. First of all, drops are instilled with AgN03, in 2-pour a solution of urotropin. Then denotes the observed phenomenon.
C. several urotropin crystals are heated in a dry test tube and placed for some time. As a result, it monitors the appearance of a gaseous product with an odor.
Control question:
1) What reagents it is possible to determine the aldehyde group?
2) Write the reaction of oxidation of the aldehyde group by the Сu2- ion.
3) How to implement?
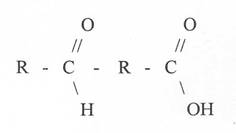
4) What reagents it is possible to determine the aldehyde group?
5) Write the reaction of aldehydes oxidation with a Сu2- ion.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.