
 |
• Plan:
1. Homologous series of carboxylic acids. Isomerism. Nomenclature.
2. Physical and chemical properties of carboxylic acids
3. Carboxylic acids, preparation and application.
A carboxylic acid molecule contains one or more carboxyl groups -СООН associated with a carbon radical.The General formula is СnH2nO2 or CnH2n+1COOH Carboxylic acids are divided into saturated, unsaturated and aromatic.
Depending on the amount of the carboxyl group, it is divided into one base, two bases, and a multi-base.
A single-base carboxylic acid molecule contains a single carboxyl group.
Example: СН3СООН, СН3 – СН2 – СООН
In order to name the saturated base, carboxylic acid according to the system nomenclature, the word "acid" is added to the name of saturated hydrocarbons.For example: N-Coon-methanoic acid; CH3-Coon-ethanoic acid.
The isomerism of saturated monobasic carboxylic acids is related to the construction of a carbon chain, the isomer begins with the number of carbon atoms above 4. C3H7COOH-two isomers; C4H9COOH-four isomers. HCOOH-formic (methane) acid; CH3-Coon-acetic (ethanoic) acid; C2H5-Coon-propionic (propane) acid; C3H7-Coon-fatty (butanoic) acid; CH3-CH(CH3) - Coon-isomay (2-methylpropanoic) acid
Chemical property.
The acidic properties of carboxylic acids depend on the carboxyl group.
СН3 - СООН « СН3- СОО- + Н+ (1)
The electron clouds of the carbon atom are displaced to the oxygen atom.
Therefore, the carbon atom was a positive charge, and
in the neighboring hydroxyl group attracts the electron clouds of the oxygen
atom. Thus, the bond between oxygen and hydrogen in the
hydroxyl group is weakened, which means hydrogen leads
to ion separation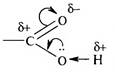 , (1) as shown. Formic acid (KD
= 10-4 ) is stronger than other carboxylic acids, for other acids KD = 10-5 .
, (1) as shown. Formic acid (KD
= 10-4 ) is stronger than other carboxylic acids, for other acids KD = 10-5 .
1. salt forms. Carboxylic acids interact with metals, alkalis, carbonates, and form salts:
2R – COOH + Mg → (RCOO)2 Mg + H2 ↑
R- COOH + NaOH → RCOONa + H2O
2R – COOH + Na2CO3 → 2RCOONa + CO2 ↑ + H2O
Мысалы: СН3СООН + Мg → (CH3COOH)2Mg + H2 ↑
the magnesium acetate
2.a complicated production of the ether. Carboxylic acids interact with alcohols, esters and water concentrate are formed. sulfuric acid is involved.
|
|
||
|
acetic acid |
methanol |
methyl acetate |
3. Amida direct:
a) when heated, ammonium salts of the carboxylic acid amide is formed, water.
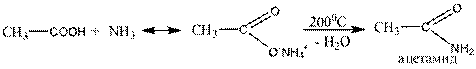
b) anhydrides of carboxylic acids in the interaction with ammonia amides are formed.
СН3-СОСl + NH3 → CH3 – CОNH2 + HCl
C) carboxylic acid penetrates the ammonia through a catalyst for pumping water, forming acidic amides
СН5-СООН + NH3 → CH3 – CОNH2 + H2О
4. Halogenation reaction. Carboxylic acid into the reaction of substitution of halogen. The substitution reaction proceeds to a halogen atom close to the carboxyl group.

5. formation of anhydrides. Two carboxylic acid molecules are added, form anhydrides, and dehydrate the acid:
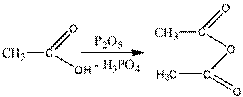
6. the reaction of recovery. Under the action of strong reduction (LiAIH4), carboxylic acids are reduced to alcohols.
![]()
Saturated monobasic carboxylic acids are found in plants in the free state or in the complex essential state.
7. the reaction of oxidation. Monocarboxylic acids are resistant to oxides, only formic acid forms and oxidizes carbon dioxide.
![]()
Depending on the structure of formic acid, they exhibit reducing properties and give a "silver mirror" reaction similar to aldehydes
.
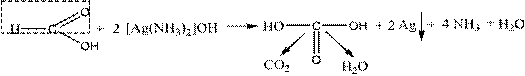
Another distinctive property of formic acid is its rupture when heated with concentrated sulfuric acid:
![]()
Monobasic acids, not saturated. Download.
Physical and chemical properties
General formula of the ethylene series of acids on a single base unsaturated
CnH2n-1COOH.
СН2 = СН-СООН – propene (acrylic) acid
СН2 = СН-СН2 - СООН – vinylacetic (3-butenic) acid
СН3 - СН=СН-СООН – Croton (2-butenoic) acid
СН2=СН(СН3)–СООН - метаакрил(a-метилакрил, метилпропен) қышқылы
СН3 – (СН2)7- СН=СН – (СН2)7СООН - oleic acid
Production method
There are 2 General methods for producing unsaturated acids:
1. introduces the carboxyl group into the primary substance with a multiple bond
![]()
2. conversion of saturated acids to unsaturated acids
СН2Сl-СН2 СООН + 2КОН ® KCl + СН2 = СН-СООК + H2O
In contrast to saturated monobasic
acids in contrast to saturated monobasic acids: at high density and
dissociation constant. Unsaturated acids also form salts, anhydrides, halides,
amides, esters. Also, the multiple bond is used in the reaction of compounds,
oxidation, and polymerization.
Dibasic acids are unsaturated and saturated. Download.
Physical and chemical properties
General formula of saturated dibasic acids CnH2n (COOH)2 .
НООС-СООН - acid Kumasawa
НООС-СН2-СООН – malonic acid
НООС-(СН2)2 -СООН - amber acid
Methods for obtaining dibasic acids, such as methods for obtaining monobasic acids:
|
|
||
|
PROPANEDIOL -1.3 |
|
malonic acid |
1. glycol oxidation:2. hydrolysis of Dinitriles (wash)):

3. the oxidation of oxides
СН2ОНСН2СООН + [О] ® НООС-СН2-СООН
Dibasic acids are colorless, crystalline substances, well soluble in water. The melting point in dibasic acids with paired carbon atoms, like monobasic acids, is higher than the melting point of acids with odd carbon atoms.
Dibasic acids are enhanced from monobasic acids, as the interaction of carboxylates facilitates dissociation. Like monobasic acids (under the same conditions), both basic acids give complete and incomplete acid formation: neutral and acidic salts, such as potassium oxalate К2С2О4 , acidic potassium oxalate КНС2О4, esters that are completely or incompletely complex, such as malonic acid diethyl ether С2Н5ООС-СН2 –СООС2Н5, malonic acid monoethyl ether НООС-СН2 –СООС2Н5 ,complete and incomplete amides.
|
cumic acid diethyl ether |
|
sodium salt of cumic acid |
|
|
|
|
|
monotropy cumic acid |
|
|
|
|
||
|
sodium oxalate |
However, group 2 of carboxyl in a single molecule is a specific and chemical property. At temperatures above the melting point, one group of carboxyl releases and loses carbon dioxide:
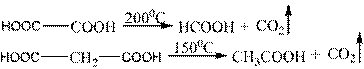
Succinic and glutaric acids can form cyclic anhydrides:
|
|
|
|
amber acid |
succinic anhydride |
|
|
|
|
glutaric acid |
glutaric anhydride |
Adipine and pimelic acids are separated from the pyrolysis of calcium or barium CO2 salts and ketones are formed.
|
|
|
|
adipic acid |
cyclopentanone |
The most famous of the 2 unsaturated basic acids are fumaric acid and maleic acid, one of CIS-one TRANS-acid, the formulas are the same: НООС-СН=СН-СООН.
Can be heated with acid acid apples in two:
НООС-СН2СНОН-СООН ® Н2О + НООС-СН=СН-СООН
These acids also form a salt by carboxyl groups, esters, and amides.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.