
Control work # 1 on the topic " Structure of the atom. Periodic law. Periodic system of chemical elements by D. I. Mendeleev»
The purpose of the lesson: to test the assimilation of knowledge and skills of the topic.
Equipment: a) task cards for options I—II.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment
Instruction on tasks; task cards can be taken from O. S. Gabrielyan's manual "Control and verification works" or offer independently compiled topics, taking into account the content of the studied material (see the example below).
Example
|
Option I |
Option II |
|
1. Give a characteristic of a chemical element according to its position of the Mendeleev PSE. |
|
|
№ 12 |
№ 16 |
|
2. Write down an electronic formula and an electronic graphic image of the element, and specify the family: |
|
|
№ 30 |
№ 23 |
|
3. In what order will the sublevels be filled in? |
|
|
4s, 3P, 4d, 5s, 4P, 3d |
6s, 4P, 4d, 5s, 4s, 5p |
|
4. Which element is stronger expressed for |
|
|
nemetallicheskie: and) About or . b) P or As |
metallicity: a) Li or Rb b) To orCA |
|
Give a reasonable answer. |
|
|
Additional questions |
|
|
1. What is the basis for the following elements: |
|
|
S and Cr |
SL and Mn |
|
are located in the same group of the Periodic table of chemical elements of D. I. Mendeleev, but in different subgroups? Give a reasonable answer. |
|
|
2. Define an element if the following is known: |
|
|
6s24f45d2 |
5s25p5 |
|
Give a reasonable answer. |
|
Response to question
Option I
1.
I. Mg magnesium; Ar(Mg) = 24; № 12.
III period; and group, the main subgroup.
II. a) +12; 12 protons, 12 neutrons, 12 electrons;
b)![]() s-element.
s-element.
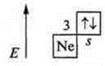 Metal
element. S. O.+2.
Metal
element. S. O.+2.
III![]() —
- magnesium oxide, the main oxide;
—
- magnesium oxide, the main oxide;
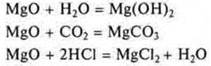
IV. Mg(OH)2— magnesium hydroxide, the base;
![]()
V. MgH2-magnesium hydride;
![]()
VI. According to the period, magnesium is metallic to aluminum, since the atomic radius of Mg is greater than the atomic radius of Al.
Magnesium is less metallicthan Na, because the atomic radius of Mg is less than the atomic radius of Na.
By group, the main subgroup Mg is more metallic than Be, since the atomic radius of Mg is greater than the atomic radius of Be. Mg is less metallicthanCA, because the atomic radius Mg is less than the atomic radiusCA.
2. № 30, Zn.
![]() d-element.
d-element.
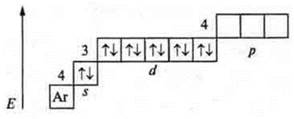
3. 3s3p4s3d4p5s4d.
4. a) O (oxygen) elements are located in the same period. The atomic radius O is less than the atomic radius C; by the end of the period, the atomic radius decreases, and nonmetallicity increases;
b) at P (phosphorus): P and As elements of one group — V, the main subgroup. The atomic radius increases towards the end of the group, the nonmetallicity weakens, and P has a smaller atomic radius than As.
Additional question
1. S and Chave a maximum CP +6, the higher oxides SO3and CGO3exhibit acidic character, their hydroxides are strong acids H2SO4; H2CGO4, so they are located in the VI group.
However, Withr - it is a metal element, d-an element, it is located in the secondary subgroup; S-it is a p-element, it is located in the main subgroup, a non-metallic element.
2. 6s25d2:
1) the sixth energy level has been opened⇒-element VI of the period;
2) sum of valence electrons s + d: 2 + 2 = 4 ⇒? group IV element;
3) this is a d-element ⇒and a side subgroup. The Hf element is hafnium.
Option II
I.
I. No. 16; S (sulfur); Ar(S)= 32; III period, VI group, main subgroup.
II.
a)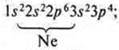 p-element.
p-element.
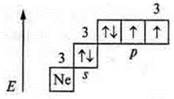
The maximum level is +6; the minimum level is -2. Non-metallic element.
III.![]() - sulfur
oxide (VI), acidic character.
- sulfur
oxide (VI), acidic character.
IV. H2SO4-hydroxide, sulfuric acid.
V. H2S-2-acidic character; hydrogen sulfide.
VI. By period: S more niemetalicznethan R, less niemetalicznethan CLbecause the atomic radius of S is less than the atomic radius R, but larger than the atomic radius of CL; the group main sub-group: S — more niemetalicznethan Se, less niemetalicznethan On, because the atomic radius of S is smaller than the atomic radius of Se, but larger than the atomic radius O
2. No. 23, V (vanadium).
![]() d-element.
d-element.
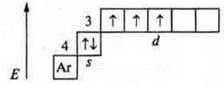
3. 4s4p5s4d5p6s.
4. a) RB (rubidium): Rb and Li are located in group I, the main subfuppet. The atomic radius Rb is greater than the atomic radius Li; Rb is more metallic, because by the end of the gas subgroup gas is less metallic, the atomic radius increases.
b) u K (potassium); K andThe CA is located in the same period. Atomic radius K is greater than the atomic radiusCA. By металличнееtheметалличностьend of the period , the metallicity decreases, because the atomic radius decreases.
Additional question
1. From CL and Mn maximum C. O. +7, higher oxides of CL2O7and mn2O7show acidic character, their hydroxides are strong acids НСlO4and Neo4, so they are in the same group VII; Cl— p-element, non-metallic, is placed in the main sub-group; MP — d-element, metallic, situated in a side subgroup.
2. 5s25p5:
1) opened the fifth energy level ⇒ V period;
2) the sum of valence electrons s + p: 2 + 5 = 7 ⇒? an element of group VII.
3) it is a p-element ⇒and a major subgroup. Element I-iodine.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.