
Lesson of generalizing repetition on the topic "Hybridization of atomic orbitals. Geometry of molecules, particles" - structure of MATTER - LESSON PLANS for CHEMISTRY 11 class - lesson plans-lesson plans-author's lessons-plan-lesson summary - chemistry
The purpose of the lesson: to consolidate the knowledge of definitions of the type of chemical bond, the type of hybridization of the geometry of molecules, particles by algorithm, the ability to determine hybridization in compounds of inorganic chemistry of a more complex structure.
Equipment: text of § 7 of the textbook, hybridization tables, theory notes in workbooks.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment
Familiarize students with the work plan in the lesson, its goals and objectives.
The lesson consists of the following stages.
1) Working at the blackboard.
Give a monologue answer by completing homework # 3 and 4 (two students) about the types of hybridization and geometry of molecules, particles.
2) at the time of preparing students for the monologue answer, the students of the class work on the task:
a) the Work of the students of the class. Determine the type of chemical bond in the following compounds and give a reasonable answer.
CO2; K2; NaCl; Mg; H2S; CCl4; CO;
b) in connections with2 andTo determine the type of hybridization and the geometry of the molecules.
3) If the students are ready with the answer at the blackboard, then it is necessary to listen to them, and then check the work done by the students of the class. As a control, the teacher asks for totransport correctly completed tasks.
Students independently check, determine their mistakes, correct answers to questions.
As a rule, the teacher controls their work, focuses on the main points of completing tasks, since the next stage of work will be a small independent work.
Determine the type of hybridization and geometry of molecules using the algorithm
OF2 NH3
The teacher summarizes the summary lesson and offers a more complicated homework assignment. To determine the type of hybridization and geometry
ClF3; SCl4; (CO3)2-
II. Approximate monologue responses of students at the blackboard
Task # 3 § 7
|
One unpaired p-electron, and you need three. In the atom there is a steaming process:
Three unpaired electrons, 1s-electron and 2p-electron. sp2-hybridization three hybrid orbitals; the angle of 120°.
|
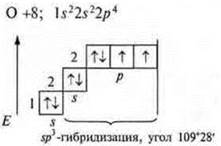
There are three unpaired electrons in an atom; a pair of paired 2s electrons and three unpaired p-electrons enter hybridization; SP3-hybridization. Four hybrid orbitals. Direction in space 109°28':
On this model we mark three Sigma links:
|
|
The geometry of the molecule is a flat triangle:
F +9: 1s22s22p5
1 p-electron |
F +9; 1s22s22p5
1 unpaired p-electron
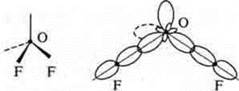
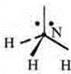
Trigonal pyramid; angle 107°, reduced due to the action of increased density of the nitrogen atom, which has an unsheltered pair of electrons |
The task № 4 § 7
|
The tetrahedral structure.
It requires 4 unpaired e-, and there are only two of them, excitation and steaming 3s2
Hybridization sp3; one s -orbital and three p -orbitalsare involved , four hybrid orbitals angle 109°28', since 4 σ-bonds, the shape of the molecules is tetrahedral
|
A flat triangle.
One unpaired electron, and you need three, 2s-electrons are steamed
Three unpaired electrons, with one s -orbital and 2P-orbitals involved in hybridization. sp2-hybridization, angle 120°
flat triangle |
III. The work of students in the class
1) Metal bond-Mg; simple substance-metal.
The ionic bond is NaCl; the compound is formed by metal Na, nonmetal CL, which differ sharply in EO.
Covalent polar coupling — CCL4; H2S; CO2; CO.
Compounds are formed by nonmetal atoms, which do not differ sharply in EO.
|
With +6; 1s22s22p2
Two unpaired electrons, and it is necessary — four, there is a steaming of two s-electrons
The hybridization involves two orbitals s-and p -, since 2σ-bonds; sp-hybridization, 180°
linear shape of the molecule |
With +6; 1s22s22p2
One unpaired electron, and you need three, 2s-electrons are steamed
The 2s-orbital and 2P-orbital enter hybridization; sp-hybridization
is a linear form of the molecule |
If the lesson time allows, the teacher helps students draw overlapping orbitals.
|
|
1 σ-bond; 1 π-bond one bond according to the donor-acceptor mechanism |
IV. Independent work
Option I
![]() 2
unpaired electrons in an atom;
2
unpaired electrons in an atom;
![]() 2σ-bonds
in the molecule.
2σ-bonds
in the molecule.
 орбиталиThe
s - and p-orbitals are involved in hybridization.
орбиталиThe
s - and p-orbitals are involved in hybridization.
 We select two bonds: the angular shape of the molecule
We select two bonds: the angular shape of the molecule
Option II
![]() three
unpaired electrons in an atom;
three
unpaired electrons in an atom;
![]() 3
σ-bonds in the molecule.
3
σ-bonds in the molecule.
![]()
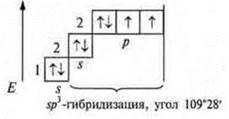 The hybridization involves s - and p-orbitals; sp3-hybridization,
angle 109°28’ four hybrid orbitals.
The hybridization involves s - and p-orbitals; sp3-hybridization,
angle 109°28’ four hybrid orbitals.
 We select three associations.
We select three associations.
A trigonal pyramid in a nitrogen atom at the top of the pyramid, the hybridization angle changes due to a pair of nitrogen electrons and becomes 107°.
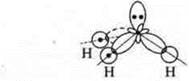
The overlapping orbitals
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.