
Lesson of exercises in the composition of OVR equations - CHEMICAL REACTIONS - LESSON PLANS for CHEMISTRY 11 class - lesson plans - lesson plans-author's lessons-plan-lesson summary - chemistry
The purpose of the lesson: to improve skills in the compilation of IIA by electronic balance method, to give an idea of the compilation of IIA by subscript and electron-ion method.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment. Checking students ' knowledge
Completing homework at the blackboard.

Oral questioning of students on the following issues (totransport).
Theoretical part
1. What reactions are called redox?
2. Called the restore process? How does the CP of an element change during recovery?
3. What is the process of oxidation? How does the S. O. of an element change during oxidation?
4. Definition of the concept of "reducing agent".
5. Definition of the concept of "oxidizer".
6. What types of IBS do you know?
7. how can I predict the function of a substance according to the S. O. of an element?
8. What are the most important oxidizing and reducing agents known?
Practical part
9. Which of the following processes are: oxidation (o-e), which are reduction (b — e). Determine the number of electrons given or received.
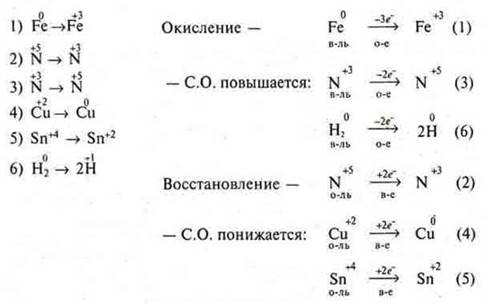
10. What happens to the restorer's CP? Oxidizing agent?
11. Predict the functions of the following substances in the OVR.
a) H2SO4; b) SO2; C) S; d) H2S.
a
—![]() - an
oxidizer, since the element sulfur exhibits the maximum C. O.
- an
oxidizer, since the element sulfur exhibits the maximum C. O.
b
—![]() - an
oxidizer and reducing agent, since the element sulfur exhibits an intermediate
s O.
- an
oxidizer and reducing agent, since the element sulfur exhibits an intermediate
s O.
C
—![]() -
reducing agent, since the element sulfur exhibits a minimum C. O.
-
reducing agent, since the element sulfur exhibits a minimum C. O.
12. Draw up the OVR equations using the electronic balance method.

II. Independent work
|
Option I |
Option II |
|
|
|
Answers to self-study questions
|
Intermolecular OVR |
Intermolecular OVR |
|
Intermolecular OVR |
Intermolecular OVR |
|
IDW intermolecular |
Reaction of disproportionation of |
II. Additional information
In the remaining time of the lesson, students should be introduced to the subscript method of composing an IAB. This method allows you to save time in compiling an IAB when completing test tasks.
Task: Determine the sum of coefficients in the OVR equation.
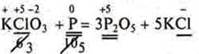
1) Define the CP of all elements
2) taking into account the indices, determine the number of received and given electrons by the elements.
3) under the formula in the equation put the number of separate or received electrons:
a
—![]() - S. O.
has fallen, 6 electrons are taken;
- S. O.
has fallen, 6 electrons are taken;
b)![]() - S. O.
has increased, given 2 * 5 = 10 electrons.
- S. O.
has increased, given 2 * 5 = 10 electrons.
If it is possible to reduce the values by the same number, you should reduce them. In our case, we'll cut it by two.
4) we set the values Found so that the number of electrons given away appears before the formula of the substance, where they are accepted and Vice versa:
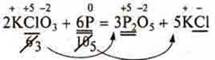
5) Then compare the number of all the atoms of the left side of the equation and the right side in the same sequence, as hydrogen is compared next to last, oxygen — last.
The electron-ion method makes it possible to eventually reach almost immediately all the coefficients of the equation. Why electron-ion? Since most OVR occur in solutions, the medium can be alkaline or neutral, then all substances in solutions are in the form of cations and anions, because their dissociation has passed. The balance diagram does not record individual elements, but the cations and anions that they are part of. Substances that do not dissociateare written with a molecular formula. The number of oxygen atoms in these particles and, most importantly, the medium must be taken into account. If the time of the lesson allows, then students can be shown this method on a specific IAB:
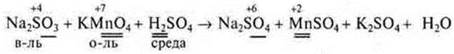
General ionic appearance:

We transfer the obtained coefficients to the equation:
![]()
If subscribed, then so:
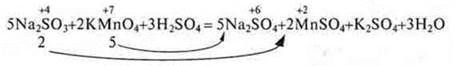
III. Homework assignment
Create an IAB using three methods:
![]()
Answer:
a) Subscript:
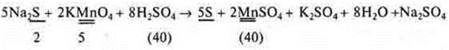
b) Electronic balance:
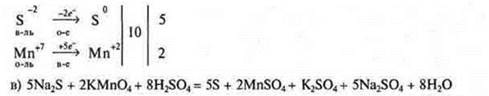
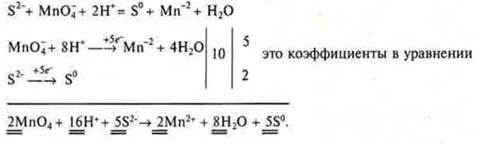
Electron-ion battery:
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.