
Power engineering of chemical reactions - CHEMICAL REACTIONS - LESSON PLANS for CHEMISTRY class 11 - lesson plans - lesson plans-author's lessons-plan-lesson summary - chemistry
Lesson objectives: to give an idea about what causes the chemical reactions release or absorption of energy; to deepen students ' knowledge about the law of energy conservation and transformation in chemical reactions; to consolidate knowledge on the thermal effect, the thermal reaction equations; to learn to perform the calculation on thermochemical equations.
Basic concepts: thermal effect, exothermic-endothermic reactions; thermochemical equation; enthalpy, heat of formation.
Equipment: H2SO4 Mg, Lucina, malachite, CuSO 4 solution electrolysis device4, NH4SCN ammonium rodanide (HSCN, wooden plank, rodanistovod. acid) metal tripod, test tubes, thermometer.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment
One of the signs of classification of chemical reactions is the thermal effect. According to this feature, reactions are divided into exothermicо- or endothermic. The task of the lesson is to find out the causes that cause a certain thermal effect of the reaction. This requires familiarity with the law of conservation of energy, the conversion of energy as a result of chemical reactions, and the ability to solve calculation problems using thermochemical equations. The study of new material will be convincingly proved by experiments.
First, we will test the students ' knowledge by performing a chemical dictation, which will reveal knowledge about the characteristics of chemical reaction classification, as well as knowledge of definitions of types of chemical reactions.
Task: to define the type of chemical reaction. Give an example согласно признакаof a classification feature type.
|
1) allotropization |
1) OVR 2) isomerization 3) reversible 4) compounds 5) heterogeneous 6) endothermic |
|
2) homogeneous |
|
|
3) exchanges |
|
|
4) substitutions |
|
|
5) decompositions |
|
|
6) exothermic |
II. Learning new material
Plan of presentation:
1. Causes of release or absorption of energy in chemical reactions. Thermal effect of the reaction.
2. Lomonosov's Law of conservation of energy. Converting the energy of a chemical reaction into thermal, light, or mechanical energy.
3. Thermochemical equation. Heat of formation. Enthalpy.
4. Calculations based on thermochemical equations.
Question. What common feature unites the following chemical reactions: burning of magnesium, burning of alcohol, explosion of TNT, reaction of acid with alkali, interaction of Na with water, quenching of lime, burning of fuel?
Answer. All these chemical reactions are accompanied by the release of energy. These are exothermic reactions. A common feature of photosynthesis, cracking of hydrocarbons, hydrolysis of starch, conversion of oxygen to ozone, interaction of nitrogen with oxygen — energy absorption. These are endothermic chemical reactions.
What is the reason for the release and absorption of energy?
Let's remember again, what happens to the substances that react? In all cases, chemical bonds in the molecules of reacting substances are destroyed and new bonds are formed in the final products of the reaction.
The process of breaking chemical bonds occurs with the absorption of energy, and the formation of new bonds (we already know this) — with the release of energy. These energies cannot be equal, because the internal energy of the reagents differs from the energy of the final products of the reaction.
For chemical reactions, the energy that is associated with the movement of electrons in the atom, their attraction to the nucleus — i.e., the energy of chemical bonding-is taken into account. Therefore, any chemical reaction is accompanied by either the release of energy or the absorption of energy. According to the law of conservation of energy, energy does not arise from nothing and does not disappear without a trace, but only passes from one form to another. This law was formulated by M. V. Lomonosov (working with the textbook, Fig. 23).
Methane combustion and diagram of changes in the internal energy of a substance.
This is an exothermic reaction, since it is not a chemical reaction.Evnut. > Eprod.
![]()
Decomposition of calcium carbonate and diagram of changes in internal energy:
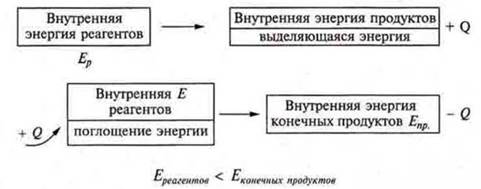
This is an isothermal reaction. The value Q is called the thermal effect of the reaction. It is the same absolute value for the forward and reverse reaction.
The forms of energy release and absorption in chemical reactions are diverse. Often there are several of them, almost always thermal.
Experiment 1. Dissolution of H2SO4(conc.) in water. Observing the rules of TB, pour a glass rod of sulfuric acid into the water and gently stir. The thermometer shows an increase in t °. The solution is heating up.
Experience 2. Carefully in a spoon for burning substances, we show the burning of magnesium, if there is no metal, then we show the burning of a splinter. Energy is released in the form of heat and light exothermic reaction.
3. Malachite Experience (CAON)2CO3can decompose when heated, i.e. when heat is absorbed from the outside. Signs of decomposition: water, gas, discoloration. Endothermic reaction.
Experience 4. To carry out the electrolysis of a solution of CuSO4 on graphite electrodes. This is an example of the conversion of electrical energy into chemical reaction energy.
![]()
Experience 5. Obtaining CO2, a large volume that performs mechanical work and pushes out the plug that closes the flask.
Experiment 6. Dissolution of ammonium rhodanide NH4SCN is a highly endothermic process. Add 50 g of ammonium rhodanide to the glass, put the glass on a thick sheet of paper or wooden Board, moistened with water, add 50 ml of water and stir. After 1-2 minutes, the glass will freeze to the paper (Board). You can use the salt ammonium nitrate NH4NO3.
So, the thermal effect of a chemical reaction is the most important energy indicator and it is often introduced into the equation of a chemical reaction.
C + O2= CO2+ Q-reaction with thermal effect, + Q-exothermic
C + O2= CO2+ 394 kJ — the equation specifies the thermal effect, 394 kJ of heat is released when 1 mol of carbon is burned, i.e. 12 g
An equation that specifies the thermal effect is called a thermochemical equation.
Depending on the aggregate state of the reactants and the final products of the reaction, the thermal effect of the same reaction will differ.
![]()
Q1
Q1<
Q2, since ![]()
1) you can Calculate the thermal effect of a chemical reaction by knowing the energy of the chemical bonds of the compound.
Example. Textbook page 119.
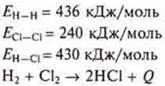
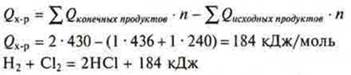
The thermal effect of a chemical reaction is always equal to the sum теплотof the formation heats of all the final products of the reaction minus the sum теплотof the formation heats of all the initial products, taking into account the coefficients in the equation.
If a substance is non-molecular in structure, how can we determine which bonds are involved in the chemical reaction and are destroyed? In this case, it should be known that the value теплотof the formation heats of all substances involved in the reaction is used to calculate the thermal effect of the reaction. Heat of formation QOBR. — this is the thermal effect of the reaction of formation of one mole of a substance from simple substances in standard conditions (t° = 25 °C, P = 1 ATM)
![]()
Since each substance has a certain store of internal energy, which includes the energy of particle formation, the energy of particle movement, and the energy of their interaction, capable of performing mechanical work, the concept of enthalpy h should be introduced.
Enthalpy is the sum of all types of energy of a substance, its total energycontent is measured in j and kJ. It is impossible to measure exactly the enthalpy, since it is impossible to take into account the energy of all the particles, you can only judge the change in the system by the thermal effect of a chemical reaction. It should be remembered that the change in energy of the system DN° (at t° = 25 °C, P = 1 ATM) is always numerically the same as the thermal effect, but opposite in sign: DN° = - Q.
Example:
![]()
since DN° = - Q, therefore, the thermochemical equation of the chemical reaction
N2+ 3H2= 2NH3+ 92 kJ.
Thermochemical equations can be used for calculations.
Problem 1. how Much heat is released when burning coal weighing 2.4 g, if the thermal effect of the reaction is equal to +394 kJ?
We create a thermochemical equation of the reaction and solve it using the algorithm of any calculation of the equation
![]()
![]()
Making up the proportion:
![]()
Answer: combustion of 2.4 g C releases 78.8 kJ.
Task 2. Make a thermochemical equation for the formation of water (1 mole of gas) from simple substances, knowing that the formation of 9 g of water released 123 kJ of heat.
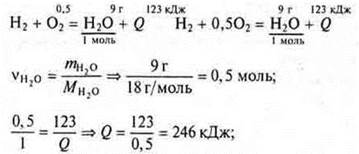
thermochemical equation for 2 mol of water:
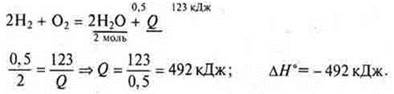
III. Generalizations and conclusions based on the studied material
The reason for the release and absorption of energy in chemical reactions is the energy content of substances that react and are formed as a result of the reaction. The energy content of substances is characterized by the concept of "enthalpy".
Thermochemical equation of a reaction-a record of an equation where either the typical effect or the DN° is specified; and since ΔH° = - Q, it is possible to find out which reaction is exothermicor endothermic in terms of thermal effect. Knowing the heat of the formation of substances, you can calculate the Q of the chemical reaction.
Using thermochemical equations, you can perform calculations and solve problems.
IV. Homework assignment
§ 12. № 1, 2, 3 (calculation issues).
V. Pinning
Proceed to the solution of problems of homework.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.