
The hydrogen indicator is DISPERSED SYSTEMS. SOLUTIONS. PROCESSES OCCURRING in SOLUTIONS - LESSON DEVELOPMENTS in CHEMISTRY grade 11 - lesson developments-lesson developments - author's lessons - lesson plan-lesson summary - chemistry
The purpose of the lesson: to give the concept of "hydrogen indicator"; to give an idea of the ionic product of water, the water dissociation constant, to teach how to apply the concept of "hydrogen indicator" to characterize the medium of electrolyte solutions and for experimental determination of the medium.
Basic concepts: hydrogen indicator-pH, ionic product of water, acidic, neutral, alkaline media, indicators.
Equipment: indicators (methylorange, phenolphthalein, blue litmus, universal indicator), solutions of acids, alkalis, water; soap solution (household, toilet), gastric juice, shampoo, electrolytes № 1, 2, 3, test tubes.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment
The lesson combined. At the time of the survey — test tasks. At the moment of learning a new material — the teacher's story.
II. Discussion of test tasks
Students submit homework according to the options.
Based on the material of the past lesson, test tasks are performed, and then discussed.
1. Select a row that lists the following ions: a) that can simultaneously exist in an aqueous solution:
![]()
b) unable to simultaneously exist in an aqueous solution:
![]()
2. magnesium Chloride reacts with each of the two substances:
a) H2S and NaOH;
b) CON and AgNO3;
C) CO and NaCl;
d) Vasl2and H2CO3.
3. Reduced ionic equation![]() corresponds
to the molecular equation:
corresponds
to the molecular equation:
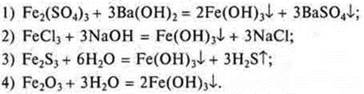
4. Establish a correspondence between the abbreviated ionic equations and the typeof ion exchangereactor.
Abbreviated ion equation:
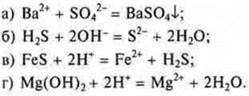
The reaction of ion exchange:
A) Strong acid + weak base = salt + water.
B) Salt + strong acid = salt + weak acid.
B) Weak acid + strong base = salt +H2O.O.
D) Salt + strong base = salt + weak base.
E) Salt + salt = salt + salt.
E) Strong acid + strong base = salt + water.
5. The sum of the coefficients in the equation of electrolytic dissociation Rb2Sr2(SO4)3 =
6. The sum of coefficients in the short ionic equation for the reaction between chromium hydroxideand(W) and hydrochloric acid.
7. the Sum of the coefficients in the complete ionic equation of the reaction between iron(II) hydroxide and sulfuric acid.
8. Specify a pair of substances that can simultaneously be in the same solution without reacting with each other:
![]()
II. Learning new material
Plan of presentation
1. Water is a weak electrolyte. Water dissociation. Constant of water. Ionic product of water.
2. a) the pH of the;
b) the environment is acidic, alkaline, neutral.
3. Qualitative determination of the type of environment. Indicators and their response to different types of media.
4. Characteristics of the environment in a living organism using a hydrogen indicator.
Water is a very weak electrolyte.
The water dissociation equation is as follows:
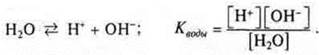
Since a диссоциируетnegligible number of water molecules dissociate, the value of the equilibrium concentration of water [H2O] is very small, it can be ignored.
![]()
The product of the concentration of hydrogen cations and hydroxide ions is called the ionic product of water; at t = 25 °C Tob= 10-14. This value is constant. The ionic product of water makes it possible to calculate the concentrations of hydroxide ions, if the concentrations of hydrogen cations are known and Vice versa.
Example.
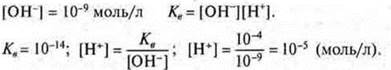
Accordingto the concentrationof hydrogen ions of hydroxide anions, there are different types of media:
neutral medium - [H+] = [OH-] = 10-7;
acidic environment - [N+] > [OH-] > 10-7;
alkaline medium - [N+] < [HE-] < 10-7.
However, for the characterization of media, the concept of "hydrogen index", pH (pH), introduced by a Danish chemist, is more applicableBy Sorensen. p - from the initial word powerful — a mathematical degree, the letter H — the chemical sign of hydrogen. the pH-hydrogen indicator is called the negative decimal logarithm of the concentration of hydrogen cations.
pH = -lg [H+], if [H+] = 10-8, pH = - lg10-8= 8,
if [H+] = 10-3, then pH = 3.
For the convenience of determining the medium by pH, a scheme of dependence between the concentration of hydrogen cations, the pH value and the reaction of the medium is used.
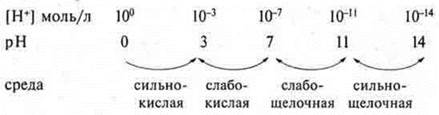
pH = 7-neutral medium;
pH < 7 — acidic environment;
pH > 7 is an alkaline medium.
For qualitative determination of the type of medium, pH of an aqueous electrolyte solution, indicators are used.
Indicators — substances that change their color depending on the solution medium.
Experiment:
Determine the reaction of the electrolyte medium in solutions # 1, 2, 3, using indicators: a) universal; b) methylorange; C) phenolphthalein; d) blue litmus.
Drawing up a table by students based on laboratory experience.
|
Indicator |
# 1 |
# 2 |
# 3 |
|
Universal |
green pH = 7 neutral |
pink pH < 7 acidic |
blue pH > 7 alkaline > |
|
Phenolphthalein |
- |
- |
raspberry |
|
Methylorange |
orange |
pink-red |
yellow |
|
Litmus blue |
purple |
red |
blue |
The teacher conducts an experiment to determine the medium: soap solution, shampoo, gel, liquid soap, stomach juice.
Thus, knowing the pH of the electrolyte, you can determine the type of medium and explain many processes of ongoing chemical reactions with a certain speed and direction depending on the medium. Both the speed and direction of its flow change.
In a living organism, pH is not the same both at the cellular level and in the intercellular space: blood, lymph, saliva, gastric juice.
рНblood pH= 7.4 — slightly alkaline medium;
the pHof saliva= 7 is close to neutral;
pHof gastric juice= 1,7-strongly alkaline.
Og pH depends on the work of the enzyme-catalyst. The blood enzyme catalase works at pH = 7, the gastric juice enzyme pepsin works at pH = 1.5-2. All this is important to know when making a medical diagnosis.
Knowledge of the concept of hydrogen index in the course of chemistry is necessary when determining the medium, especially the medium of solutions of salts. This is something to learn in the next lesson.
III. Homework assignment
§ 15, p. 151 — 153 (records), p. 156, no. 7.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.