
Control work # 3 on the topic "Chemical reactions. Disperse system. The processes occurring in solutions of" - DISPERSED SYSTEM. SOLUTIONS. PROCESSES OCCURRING in SOLUTIONS - LESSON DEVELOPMENTS in CHEMISTRY grade 11 - lesson developments-lesson developments - author's lessons - lesson plan-lesson summary - chemistry
The purpose of the lesson: to check the level of assimilation of students ' knowledge.
Equipment: task cards for options I—II.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment
Instructions for completing tasks.
II. Performance of tasks
Option I
1. To characterize the chemical reactions at well-known signs of:
![]()
2. what conditions are needed: concentration of substances, pressure, temperature of the system-to shift the balance towards the formation of carbon monoxide (II)?
![]()
3. Which of the listedств способны substances tend to be hydrolyzed ?Write the equation of the reaction:
bromoethane glucose
4. Draw up equations of possible reactions in molecular and ionic form between the proposed substances:
sodium sulfate hydrochloric acid
zinc oxide potassium sulfate
5. Calculate the mass fraction of salt in a solution obtained by adding 20 g of salt to 150 g of a solution with a mass fraction of solute of 10 %.
Option II
1. To characterize the chemical reactions in all known signs:
![]()
2.
How do you change the concentration of substances, pressure and temperature of
the system![]() to shift
the balance towards the formation of carbon monoxide (IV)?
to shift
the balance towards the formation of carbon monoxide (IV)?
3. Which of the listed substances are particularlyproneособны to hydrolysis ?Write the equation reactions of hydrolysis:
silver chloride ethyl acetate.
4. Draw up equations of possible reactions in molecular and ionic form between the proposed substances:
copper(II) chloride potassium hydroxide,
sodium sulfate is carbon monoxide (IV).
5. 300 g of water was added to the acid solution weighing 200 g with a mass fraction of 15 %. What is the mass fraction of acid in the new solution?
The answers to the questions of the control work № 3
Option I
1. ![]()
the reaction of substitution of ILB
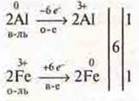
intermolecular OVR;
homogeneous reaction-by phase;
exothermic reaction - by thermal effect;
the reaction is irreversible, the reaction is not catalytic.
2. ![]()
because the reaction is endothermic, t° — increase;
since the volume increases, you can lower it.
To getCO - WithCO2-increase; withCO-reduce.

Option II
![]()
the oxidation reaction, the reaction redox reactions, intermolecular
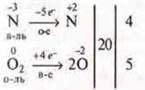
endothermic reaction - by thermal effect;
homogeneous reaction-by phase;
the reaction is irreversible, the reaction is catalytic.
![]()
in the direction of CO2, i.e. in the direction of direct reaction. This reaction is exothermic, t° — to lower; P-to increase, in the direction of a smaller volume. Concentrations WITHCOandO2-increase, withCO2-lower.
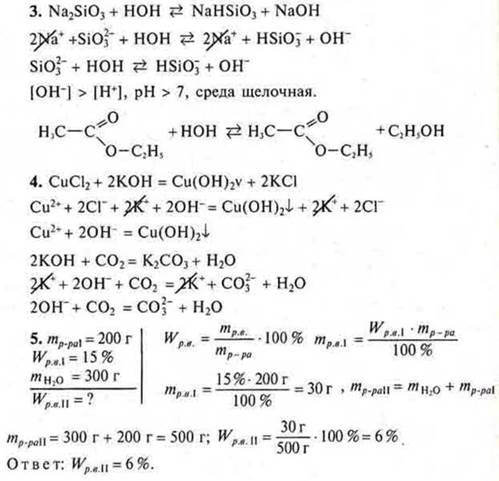
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.