
Classification of organic substances-SUBSTANCES AND their PROPERTIES - LESSON PLANS for CHEMISTRY 11 class - lesson plans-lesson plans-author's lessons-plan-lesson summary - chemistry
The purpose of the lesson: to generalize and systematize knowledge about the classification of organic substances by different characteristics, to consolidate knowledge about the causes of the diversity of organic substances and the dependence of their properties on the structure.
Basic concepts: hydrocarbons: saturated, marginal, unsaturated, unsaturated; heterocyclic; monofunctional, heterofunctional; cycloalkanes.
Equipment: collections "Oil and refined products"; coal, acetic acid, glycerin, fat. parafin, water, oleic acid, glucose, sucrose.
Lesson progress
I. Checking students ' knowledge
Formulas of compounds are given:
Fe(HE)2, SiO2, HNO3, SO2, N2O, KOH, C, Mg, NaOH, Li2O, ZnO, Cr(OH)3, Ca(HCO3)2, (FeOH)Cl2, H2S, P, Fe, BaO, NaHSO4, Pb(OH)2, CO, HCl, (CuOH)2CO3, H2SO3.
|
Option I |
Option II |
|
Write out and give names according to the classification: |
|
|
Non-metals, Acidic oxides |
Metals Basic oxides |
|
* * * |
|
|
Bevarious oxides A soluble base is an Amphoteric base Basic salts of oxygen containing Acids |
, Amphoteric oxides The Foundation of the insoluble Acidic salts of the Acid anoxic Indifferent oxides |
|
Write the answers on the back of the Board. |
|
|
* * * |
|
|
C-carbon P-phosphorus SiO2-silicon oxide SO2— sulfur oxide (IV) N2O — nitrous oxide I CO-carbon monoxide II CO-potassium hydroxide NaOH-sodium hydroxide Cr(OH)3-hydroxide of chromium (III) (Alo))Withl2-aluminum hydroxochloride (CuOH)2CO3 — gidroksicarbamida copper (II) N2O-nitric oxide (I) H2SO3-sulfuric acid |
Mg-magnesium Fe — iron Li2O — lithium oxide Bao-barium oxide ZnO-zinc oxide Fe(OH)2-iron hydroxide (II) Pb(HE)2-lead hydroxide (II) Ca(NSO3)2-calcium bicarbonateNaHSO 4-sodium hydrosulfate H2S-hydrogen sulfide HCl-hydrochloric acid acid CO-carbon monoxide (II) HNO3-nitric acid |
At the end of the task, perform a self-check (the answers are written on the back of the Board).
II. Learning new material
Study plan
Classification of organic compounds by their characteristics:
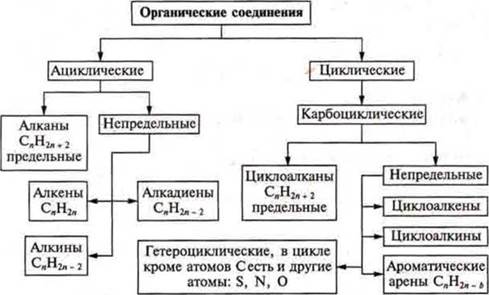
a) type of carbon chain: acyclic — open chain; cyclic-closed chains; consisting of carbon atoms-carbocyclic; and different atoms-heterocyclic;
b) the presence of multiple links.
Classification of organic compounds
acyclic: alkanes — extreme saturated, single bonds; alkenes — double bond (unsaturated unsaturated); alkadiens — two double bonds (unsaturated unsaturated); alkynes — triple bond (unsaturatedunsaturated);
cyclic: arenes — aromatic rings in carbocyclic and heterocyclic; cycloalkanes — all bonds are single; cycloalkenes-there is a double bond; cycloalkines — there is a triple bond.
Consider the classification of organic compounds, if we assume that one or more hydrogen atoms in a compound are replaced by a group of atoms that determine the physical and chemical properties of a substance. Such groupings are called functional groupings.
Organic compounds can be monofunctional — one functional group; polyfunctional-several identical functional groups; heterofunctional — different functional groups in a compound.
Depending on which atom is in the functional group, compounds are nitrogen-containing, oxygen-containing, halogen-derived, and so on.
If the hydrocarbon radical is marginal, the compound belongs to the limits; if the unsaturated-compound will be unsaturated, of the series, what is the multiplicity of the bond.
III. The tutorial
Working with table 15 on page 183 of the textbook. Students remember all the functional groups, the name of classes based on the functional group, the General formula. In order to consolidate the knowledge of the classification of organic compounds, together with the teacher, students perform a task: give a classification to an organic compound, name the compounds:
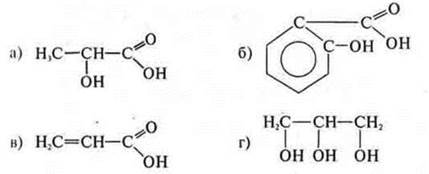
Answer:
Substance " a»:
acyclic, limiting — - ON-monoatomic alcohol.
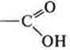 -
carboxylic
-
carboxylic
heterofunctional compound: alcohol acid;
2-hydroxypropanoic acid.
Substance " b»:
cyclic, Ahren; carbocyclic:
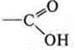 —
carboxylic acid-aromatic;
—
carboxylic acid-aromatic;
—OH-group is bound to an aromatic ring; phenol, i.e. a heterofunctional compound.
2-hydroxy-benzoic acid.
Substance " b»:
acyclic, unsupervised (double bond)
 — carboxylic
acid.
— carboxylic
acid.
Monofunctional compound: propenoic acid.
The substance "g»:
Acyclic, limit value;
IT was also the group of alcohols, (three) multifunctional, a triatomic alcohol. Propane-triol-1,2,3.
The teacher explains to the students the correctness of making General formulas for certain organic alcohols (limit values).
Oxygenated:
alcohols: ![]()
phenols: ![]()
aldehydes: ![]()
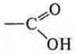
carboxylic
acid: 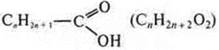
ether: ![]()
ester: 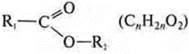
Nitrogen-containing products:
amines: ![]()
nitro
connections: ![]()
amino
acid: 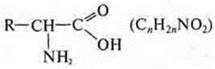
IV. Generalizations and conclusions
1) the Combination of different elements of structure and composition among themselves creates a variety of the world of organic substances. The complete characteristic of the compound includes classification according to the structure of the carbon chain, taking into account multiple bonds in it, and the presence of functional groups. It is necessary to remember about the isomerism of organic compounds, its types.
2) General physical properties of organic substances.
Aggregate state: gases (CH4), liquids (CH3COOH-acetic acid, C2H5IT is alcohol), solid — paraffin, stearic acid, phenol.
The bond type in organic compounds is predominantly covalent, since organic compounds are formed by the atoms of non-metals C, N, O, K, and not by ions.
Crystal lattices — molecular or atomic. Intermolecular interactions are weak. Therefore, typical organic compounds are most often liquids or solids with a low melting and boiling point, non-electrolytes, and many are insoluble or poorly soluble in water.
Lower alcohols, aldehydes, acids, phenols, esters have an odor; volatile substances.
Experience:
a) melting of paraffin;
b) the distillation of naphthalene or benzoic acid.
C) organic compounds are charred when heated. Charring of wood, sucrose, and starch.
V. Homework assignment
§ 17. № 2, 3, 4, prepare for independent work. Give a classification characteristic; determine the properties of which classes are displayed:
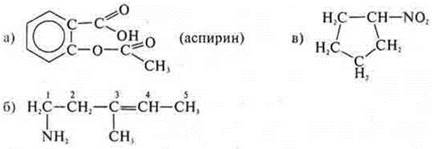
Answers to homework questions
§ 17 № 2
C4H10O, oxygen-containing
![]() —
acyclic, limit; monoatomic alcohol (one group-ON); butanol-1.
—
acyclic, limit; monoatomic alcohol (one group-ON); butanol-1.
Isomers of the position of functional groups:
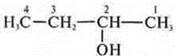 —
butanol-2;
—
butanol-2;
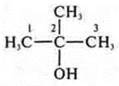 —
2-methylpropanol-2.
—
2-methylpropanol-2.
Isomer in the carbon chain and position of functional groups:
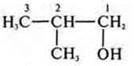 —
2-methylpropanol-1.
—
2-methylpropanol-1.
SN, HE
Interclass isomer:
ether:
N3S—O—S3n7methylpropyl ether,
C2H5—O—C2H5diethyl ether.
§ 17 № 3
With dual properties — substances that exhibit the properties of two classes of organic compounds.
Methanol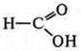 —
aldehidelor.
—
aldehidelor.
like
acid 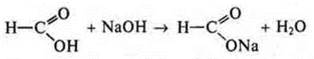
as
an aldehyde 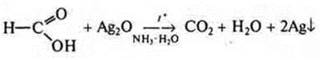 hhe
hhe
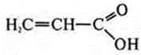 -
propylene acid
-
propylene acid
According to the radical — unsaturated acid
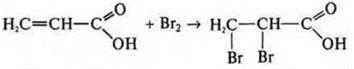
like acid:
 —
2-hydroxypropanoic acid.
—
2-hydroxypropanoic acid.
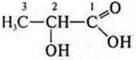
Lactic acid; alcohol acid:
like
alcohol: 
like
acid: 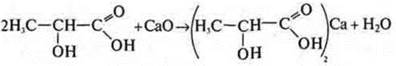
§ 17 № 4
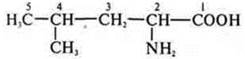 -
acyclic, limiting, nitrogen-oxygen-containing.
-
acyclic, limiting, nitrogen-oxygen-containing.
-NH2-amine; - C- acid.
Amino acid, 2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid.
Homologues:
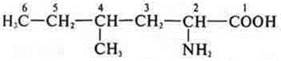
2-amino-4-methylhexanoic acid
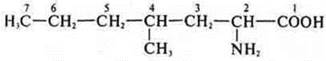
2-amino-4-methylpentanoate acid
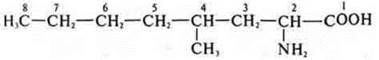
2-amino-4-methyloctanoic acid.
Isomers:
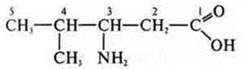
3-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid
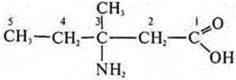
3-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid
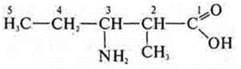
3-amino-2-methylpentanoic acid
Characterization of compounds
a) aspirin
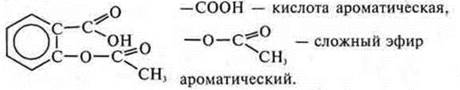
Properties of acids, esters, and arenes.
Cyclic, carbocyclic, aromatic, oxygen-containing.
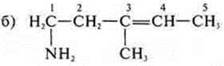
Acyclic, unsaturated — - NH2-amine.
1-amino-3-methylpentene-3. Properties of amines and unsaturated hydrocarbons with a double bond.
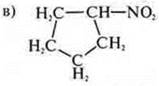
Cyclic, carbocyclic, limit, nitrogen-oxygen-containing.
-NO 2-nitrocompound .
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.