
Chemistry and production - CHEMISTRY IN the life of SOCIETY - LESSON PLANS for CHEMISTRY 11 class - lesson plans-lesson plans-author's lessons-plan-lesson summary - chemistry
Chemistry plays an important role in human life. It relates to everything — food, hygiene products, plastics, photographic materials, fertilizers, medicines, life support processes, etc. - because the subject of its study is existing substances and everything that happens to them.
The topic is studied at the end of the academic year. It does not involve mastering the complex theoretical foundations of the subject, but allows students to expand their horizons by participating in the preparation of essays-messages for lessons-seminars, press conferences, "round tables", etc. If possible, it is necessary to organize excursions to production sites in order to study the technological chain, scientific principles of production, environmental protection, and the professions required at this enterprise.
In case of absence of such excursions, it is necessary to organize watching videos of iron and steel, ammonia, plastics, and sulfuric acid production at the lessons.
Lessons 65-66. Chemistry and manufacturing
The purpose of the lesson: to give an idea of the production of ammonia and sulfuric acid, the importance of environmental protection and ways to solve problems of its protection, to teach you to explain the scientific principles of production, to solve problems with environmental content.
Basic concepts: chemical industry, chemical technology, scientific principles of production, raw materials, MAC (maximum permissible concentration), toxicity.
Equipment: tables: "Production of ammonia" and "production of sulfuric acid", videos: "Production of ammonia", "production of sulfuric acid", FeCl3, phenol, test tubes; student reports.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment
Setting goals and tasks for the lesson. Analysis of the results of control work # 4, working on errors. The teacher offers students additional tasks in order to increase the score of the test paper.
II. Learning new material
Plan of presentation
1. Chemical industry and chemical technology.
2. General scientific principles of production. The most important components of chemical production: equipment, raw materials, water, energy.
3. Environmental protection and occupational safety: assessing the quality of the environment, toxicity of substances (communications students).
4. Ways to solve problems of environmental protection (messages from students).
5. Production of ammonia. Watch the video "Production of ammonia" and discuss the following issues:
a) equipment for the production of ammonia.
b) raw materials, raw material preparation, raw material sources.
C) reaction of ammonia synthesis, selection of optimal conditions.
d) scientific principles of production.
d) protection of the environment.
6. Presence of industrial enterprises in the region of residence. Their importance.
As a homework assignment, students must answer in writing in a workbook the same questions as for the production of ammonia, for the production of sulfuric acid. § 24, records.
III. Pinning
Depending on the place of residence, excursions to chemical plants, preparation of messages related to the products of these industries are possible.
The chemical industry is a branch of the national economy that produces products based on chemical processing of raw materials. It is based on chemical technology — the science of the most economical methods and means of mass chemical processing of raw materials( natural materials) into consumer products and intermediate products used in various sectors of the national economy. The main task of chemistry and chemical technology is the production of various substances and materials with a certain set of mechanical, physical, chemical and biological properties.
The largest scale differ in the production of H2SO4, NH3, N2, Cao, O2, C2H4, NaOH, Cl2, HCl, H3RHO4, HNO3. These substances are used in large quantities, including for the production of plastics, synthetic fibers, medicines, fertilizers, detergents, perfumes, cosmetics, and food products.
Any chemical production is created on the basis of scientific principles. Get the highest product yield at the lowest cost. So, the General principles of all productions:
— creation of optimal conditions for chemical reactions: selection of temperature conditions, pressure, catalysts that significantly increase the speed of the chemical reaction. In some specific industries, particular principles are possible: the principle of counterflow, direct flow of substances; increasing the contact surface of reactants;
— complete and integrated use of raw materials: circulation, production of fluxed agglomerates (production of cast iron and steel), waste-free production, etc.;
— use of heat of chemical reactions: the principle of heat exchange, utilization of heat of reactions in the needs of production and locality;
- the principle of continuity: ensuring full automation of mechanization, computerization;
— environmental and human protection: automation of harmful industries, sealing of equipment, recycling of industrial waste, neutralization of emissions into the atmosphere.
The most important components of any production process are:
apparatus — technological equipment for the processing of raw materials and waste disposal, as well as the implementation of all stages of obtaining the production product itself. The equipment is installed permanently and operates for a certain period of admission:
raw material is either a natural material that has not undergone chemical treatment, but is used to produce various products; or a product obtained in chemical production; it can be industrial waste, as well as products that have served their time. Raw materials by composition are mineral and organic; by aggregate state, liquid (oil), solid (ores, solid fuel), gaseous (natural gas, associated petroleum gas, air); auxiliary raw materials are water, fuel, oxidizers, catalysts, splitters. In the textbook on page 273, scheme 14 gives a fairly detailed classification of raw materials. The teacher and students consider this scheme;
water plays a very important role in chemical production. Somewhere it is a raw material, somewhere a reagent involved in chemical reactions. Water is an excellent solvent; it catalyzes many chemical reactions. Water is a heat carrier, since it has a high heat capacity. It is available and safe to use. Cold water cools the reacting masses heated as a result of exothermic reactions, and hot water vapor, hot water preheats the interacting substances to accelerate reactions, especially endothermic.
Water consumption in modern enterprises is huge. To get 1 ton of ammonia requires 1500m3 of water. All businesses are built near water sources. One of the main tasks of modern production is to create a recycled water supply, which will reduce water consumption; to replace water cooling with air; to treat waste water and reuse it.
Most chemical processes require energy. It is spent on transporting raw materials and finished products, compressing gases, crushing solids, operating control and measuring devices, and running endothermic reactions. The production of 1 ton of NH3requires 3,200 kW/h; 1 ton of aluminum — 1,900 kW/h.
In the chemical industry, electric, thermal, and nuclear power are used. хchromatic and light energy.
What industries use ha млн- other energy is covered in detail in the textbook on pages 274-275. Some application areas should be read out.
IV. Messages to students
Earliest report
All branches of the chemical industry produce useful products that are necessary for direct use or for other chemical industries. However, any production is threatened by the release of production products into the environment, and poor-quality utilization of production waste can cause them to get into the soil, sewers, rivers, and the atmosphere. All this adversely affects wildlife and human health. Therefore, chemical enterprises are not built directly in cities. The companies themselves have strict OT requirements, which makes working for them safer. The chemical enterprise is obliged to dispose of waste, build treatment facilities in accordance with modern requirements for environmental quality. There are environmental quality standards. This is the maximum permissible concentration of pollutants, i.e. the maximum amount of a substance-pollutant in a unit volume of air or water, which during daily exposure to the human body for a long time does not cause pathological changes or diseases, does not disrupt normal vital activity.
Example:
MPC (in mg / m33)
|
Location |
NH3 |
Pb |
Hg |
Phenol |
Benzene |
|
In the working area |
20 |
0.01 |
0.01 |
5 |
5 |
|
In the airthe air. |
: 0.04 |
0.007 |
0.001 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
|
points, daily average |
|||||
|
Maximum one-time share in the air of a locality |
0,2 |
0,007 |
— |
1,0 |
1,5 |
|
In various reservoirs |
2 mg/l |
0.005 |
0.0005 |
0.001 |
0.5 |
Toxicity — the property of substances to cause poisoning of the body. According to toxicity, substances are divided into groups:
very high toxicity — Hg, Pb, Be, Cd, Tl;
high toxicity — Ba, Se, As, Sb;
the average toxicity — Cr, Ag, Al;
low toxicity — Withu, Fe, Mi, Zn, Ni, Ye, Sr, Rb, Cs.
T. Paracelsus — "the Medicine in large doses is a poison!» Some elements are toxic even in very small vines (Hg, Cd), and for someпр, their absence in small doses is important in the body. Se-0,1-0,2 millionth of a fraction is necessary so that animals do not develop muscular dystrophy, tissue necrosis.
The toxicity also depends on the form of the element's compound: in the case of mercury, for example, (CH3)2Hg is more highly toxic than Hg2Cl2; since (CH3)2Hg is easily soluble in blood, lymph and poisons the body faster.
Antiseptic properties of silver cation in the composition of colloidal sols or in solution are higher than that of silver atom.
Often in natural conditions, a harmless substance can become toxic under the influence of bacteria. The water areas of many ports of the world are currently poisoned with organo-tin substances, which are formed when microorganisms act on tin, which is used in alloys and solders.
Many toxic elements have similarities with biogenic elements and are included in the cycle of substances, attacking vital centers.
Example:
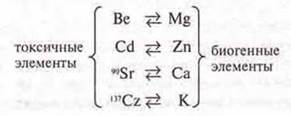
Some toxic elements accumulate in the food chain: fish have a concentration of Hg 1000 times higher than in the water from which this fish is caught. The person who eats such fish is the last in the chain.
Second message
What are the ways to solve environmental problems?
1. ultra-Fine dedusting of gases and air: the use of high-performance fiber filter materials: glass fiber. metalfiber, polymers.
2. Flameless catalytic combustion of fuel with the use of catalysts (CuO, MgO, SG2O3, deposited on the granule Al2O3). The fuel burns completely to CO2and H2O, reducing the amount of nitrogen oxides by 40%, carbon monoxide by 20%, and sulfur oxides by 500 times.
3. high-Temperature incineration of toxic waste. All flue gases are first cleaned from ash in a cyclone in an electrofilter, and then sprayed with water and alkali. As a result, acids and salts are formed.
4. Neutralization of gases from organic impurities occurs by the use of catalysts Pi, Pd or alumomedium, alumomanganese oxides for the oxidation of organic substances.
5. Purification of gases from sulfur compounds:
a) from SO2-non-reactive gas is returned to production; circulation is carried out (in the production of H2S04);
b) from H2S-gas is formed during oil processing, coking of coal, fuel combustion. H2S-finish burning.
![]()
Burn so that unburned H2S and SO2fall on the catalyst Al2O2.
![]()
The resulting sulfur is sent to production H2SO4;
C) catalytic purification of gases from nitrogen oxides. Catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with ammonia is carried out. The degree of purification is up to 99.5 %. Catalysts: V2O5/Al2O3;V2O5/WO3/TiO2.
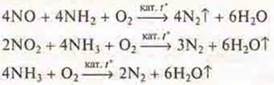
d) use of industrial and household waste as a potential raw material source for the chemical industry. During the year, waste from one person — 1.5 tons. The Earth has accumulated from 6 to 8 billion people. tons of waste.
Waste recycling is well organized in France, Denmark, Germany, and the United States.
A chemical scientist from Tula, Platonov, developed and patented a method for converting tires to gasoline and solaroil. From 1 ton of tires you can get 250 kg of high octane aviation gasoline and 200 kg of salt oil or fuel oil;
e) chemical neutralization of oil-containing wastes and oil spills. This method is half the cost of incineration, eliminates secondary damage to the environment and allows you to get a useful product. Oil-containing products are treated with lime and stearic acid. The result is a dry hydrophobic powder that can be used in road construction.
To
extract petroleum products from the surface of reservoirs and from wastewater,
liquids with magnetic properties are used — colloidal systems consisting of
water, mineral oils, and magnetic materials![]() — these
liquids are well-soluble in petroleum products. They are sprayed on the surface
of reservoirs, and then the resulting mixture is collected using a magnetic
device that moves through the water;
— these
liquids are well-soluble in petroleum products. They are sprayed on the surface
of reservoirs, and then the resulting mixture is collected using a magnetic
device that moves through the water;
f) integrated processing of raw materials and waste-free production: during the production of H2SO4, Fe2O3 is formed, which is used in the production of pig iron during pyrite firing.
When receiving N3RO4from CA3(RO4)2nepheline wastes are formed; KNa3[AlSiO4] is used to produce Al, Na2CO3— soda and cement.
V. the Solution of problems with environmental content
1. How to detect the presence of phenol in the wastewater? Give the reaction equation.
Experiment:
![]()
2. Hard water contains calcium hydrogen carbonate. This water is treated with aluminum sulfate. The resulting aluminum hydroxide surrounds the surface of the colloidal particles and cause their precipitation. How was Al formed(IT)3?
Answer: Witha(NSO3)2-calcium bicarbonate, acidic salt, weak alkaline reaction, because the salt is formed by a strong base and a weak acid.
![]()
3. Suggest a method for removing iron ions from water in which the MPC is exceeded. Excess iron ions in drinking water increases the incidence of gastrointestinal diseases and increases coronary heart disease. In water, iron (II) cation is found as Fe(HCO3)2.
Answer:
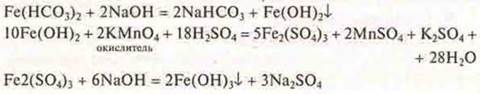
4. Explain why the fight against metal corrosion is both a fight to preserve the environment.
Answer: As a result of the corrosion of iron and its alloys in the soil, water are iron cations, as a result of corrosion does not necessarily corrode iron, can also corrode Zn, Cu, Pb, and their cations are very toxic.
VI. Watch the movie and discuss it
Then students watch the video "Production of ammonia", and then answer the questions put by the teacher in writing. Scheme of the ammonia production plant in the textbook on page 278, Fig. 49.
VII. Homework assignment
Make a characteristic of methanol production, work with a textbook, § 24.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.