
CLIL WORKBOOK
1st Edition
CLIL seminars for teachers in Kazakhstan
Өзге тілдің бәрін біл, өз тіліңді құрметте!
The best way to predict the future is to create it. – Abraham Lincoln
Name:
Region:
USTAZ, Bilim-Innovation High Schools
Welcome to CLIL!
Dear teacher,
We are greatly honored by your presence! It is no secret that the importance of English language will only grow. Currently, almost 80 percent of information on the internet is available in English. The most important scientific papers are written in English. It is crucial to help our children learn the language. The purpose of CLIL is to teach English while teaching the subject. During this course we will learn the most useful CLIL methods and try to practice as many of them as possible. We hope that you find this workbook useful.
Authors:
Askhad Artykbayev Guldana Iklassova Kamila Auyelbayeva Kairat Yernazar
 Contents
Contents
...
............................................................................4
Chapter 1 - Matter......................................................................................... 5
Chapter 2 - Motion........................................................................................ 9
Chapter 3 - Force......................................................................................... 12
Chapter 4 - Pressure.................................................................................... 16
Chapter 5 - Work, Energy, Power............................................................. 19
Chapter 6 - Heat and Temperature............................................................ 23
Chapter 7 - Thermodynamics.................................................................... 26
Chapter 8 - Electricity................................................................................. 28
Chapter 9 - Magnetism............................................................................... 33
Chapter 10 - Optics..................................................................................... 36
Chapter 11 - Nuclear physics..................................................................... 39
Chapter 12 - Astronomy............................................................................. 43
..
 SELF STUDY
SELF STUDY
.............................................................................45
Chapter 1 - Matter....................................................................................... 46
Chapter 2 - Motion...................................................................................... 47
Chapter 3 - Force......................................................................................... 48
Chapter 4 - Pressure.................................................................................... 49
Chapter 5 – Work, Energy and Power....................................................... 51
Chapter 6 - Heat and temperature.............................................................. 53
Chapter 7 - Thermodynamics.................................................................... 54
Chapter 8 - Electricity................................................................................. 55
Chapter 9 - Magnetism............................................................................... 57
Chapter 10 - Optics..................................................................................... 59
Chapter 11 - Nuclear Physics..................................................................... 63
Chapter 12 - Astronomy............................................................................. 65
 VOCABULARY
VOCABULARY
.........................................................................66
..
Chapter 1 – Matter...................................................................................... 67
Chapter 2 – Motion..................................................................................... 68
Chapter 3 - Force......................................................................................... 69
Chapter 4 - Pressure.................................................................................... 70
Chapter 5 - Work, Energy, Power............................................................. 71
Chapter 6 - Heat and Temperature............................................................ 72
Chapter 7 – Thermodynamics.................................................................... 74
Chapter 8 - Electricity................................................................................. 75
Chapter 9 – Magnetism.............................................................................. 77
Chapter 10 – Optics.................................................................................... 78
Chapter 11 - Nuclear physics..................................................................... 80
Chapter 12 – Astronomy............................................................................ 82
For Notes...................................................................................................... 83

Tell me, I’ll forget Show me, I’ll remember
Involve me, I’ll understand!
Chapter 1 - Matter
Task #1
1.A These pictures illustrate different states of matter. Fill in the blanks with right words.
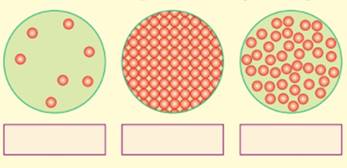 |
1.B. Sort all examples of matter according to their state.
|
Solid |
Liquid |
Gas |
|
|
|
|
|
Socks, Vapor, Ice, Air, Phone, Apple, Hair, Juice, Oxygen, Book, Scissors, Oil, Bread, Gasoline, Helium, Water |
||
Task #2
Fill in the blanks. Write definitions and draw pictures for each term in your own words.
|
Words |
My definition |
My picture |
|
mass |
|
|
|
volume |
|
|
|
matter |
|
|
|
liquid |
|
|
|
solid |
|
|
|
gas |
|
|
|
shape |
|
|
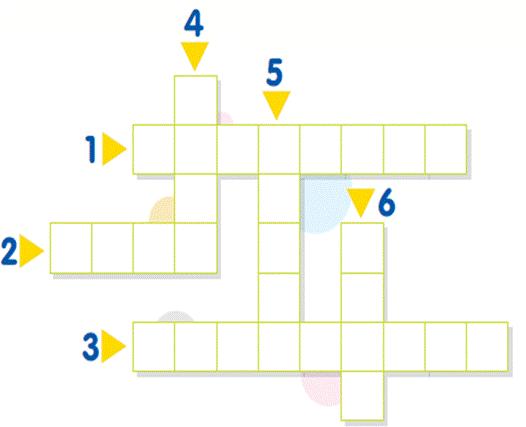
Review - Matter
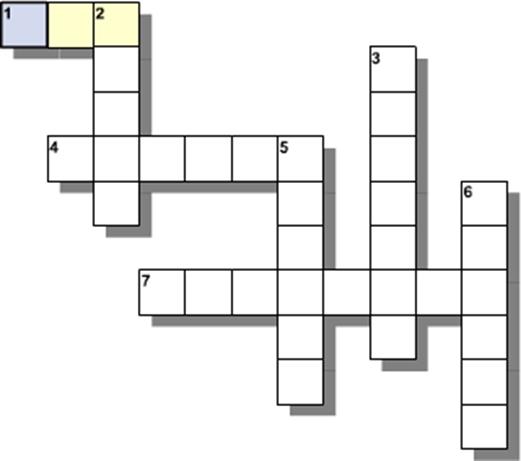 |
Crossword Hints
1. _ _ state – заттың агрегаттық күйі, нақты пішін мен көлемі жоқ.
2. _ _ state – заттың агрегаттық күйі, нақты пішін мен көлемі бар.
3. _ _ - әлемді және оның қозғалысын зерттейтін ғылым.
4. _ _ state – заттың агрегаттық күйі,нақты көлемі бар, бірақ пішіні жоқ.
5. _ _ - дене массасының, дене көлеміне қатынасы.
6. _ _ – материяның кеңістікте алатын орны.
7. _ _ body – физикалық денелер.
Check your knowledge.
|
|
көрдім/ естідім |
айта аламын |
мағынасын айта аламын |
әріптеп айта аламын |
сөйлемде қолдана аламын |
мүлдем білмеймін |
|
body |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mass |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
measurement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
direction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
volume |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
solid state |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
liquid state |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
gas state |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
shape |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
видел(-а) / слышал(-а) |
могу проговор ить |
могу дать определение |
могу сказать по буквам |
могу использовать в предложении |
не знаю |
|
body |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mass |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
measurement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
direction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
volume |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
solid state |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
liquid state |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
gas state |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
shape |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chapter 2 - Motion
Task #1
1.A. Match the terms with illustrations.
|
1. acceleration |
|
|
|
2. relative motion |
|
|
|
3. uniform motion |
|
|
|
4. deceleration |
|
|
|
5. circular motion |
|
|
|
6. simple harmonic motion |
|
|
|
7. projectile motion |
|
|
|
8. free fall |
|
Task #2
Find the words
|
T |
E |
C |
S |
J |
J |
F |
E |
N |
C |
U |
C |
P |
N |
U |
|
Q |
N |
R |
S |
L |
B |
C |
K |
O |
T |
U |
A |
Y |
O |
G |
|
G |
Y |
E |
N |
R |
N |
O |
N |
L |
X |
G |
B |
J |
I |
B |
|
F |
G |
A |
M |
A |
P |
S |
A |
P |
U |
E |
F |
S |
T |
R |
|
A |
D |
O |
T |
E |
T |
P |
F |
D |
C |
K |
O |
A |
A |
E |
|
P |
F |
S |
H |
A |
C |
D |
E |
E |
P |
S |
N |
J |
R |
Y |
|
K |
I |
K |
N |
P |
Q |
A |
I |
Q |
H |
L |
R |
H |
E |
F |
|
D |
X |
T |
D |
T |
A |
W |
L |
N |
E |
D |
Y |
C |
L |
N |
|
L |
G |
P |
E |
W |
H |
R |
K |
P |
C |
E |
G |
S |
E |
E |
|
L |
J |
V |
C |
V |
B |
D |
G |
G |
S |
R |
V |
Q |
C |
M |
|
W |
U |
C |
R |
C |
S |
Q |
Q |
P |
C |
I |
E |
C |
C |
I |
|
Q |
P |
K |
E |
O |
K |
F |
C |
F |
N |
U |
D |
A |
A |
T |
|
W |
M |
E |
A |
V |
E |
L |
O |
C |
I |
T |
Y |
U |
S |
H |
|
G |
W |
T |
S |
M |
U |
H |
S |
D |
M |
L |
T |
V |
G |
E |
|
A |
V |
M |
E |
U |
A |
W |
E |
N |
V |
C |
D |
G |
B |
M |
ACCELERATION CONSTANT
DECREASE DISPLACEMENT
DISTANCE GRAPH
INCREASE SPEED
TIME VELOCITY
Review - Motion
1. What does SI stand for?
Answer: 2.What is unit of length?
A. kg
B. second
C. metre
D. newton
E. degree
3.Give examples for Vector and Scalar physical quantities
Answer:
B. Time
C. Velocity
D. Distance
E. Acceleration
7. can be analysed in the x and y directions separately. What word is missing?
8. All motion is considered relative to a chosen frame of reference (or state of motion of an object). Translate the underlined word into Russian and Kazakh
![]()
![]()
4. 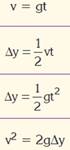 The
change in the position of an object is called
the which is also a vector quantity.
The
change in the position of an object is called
the which is also a vector quantity.
5. Add a missing quantity to the formula
![]() Average Velocity = _
Average Velocity = _
Time Taken
6. The area under the velocity-time graph, which gives the displacement
A. Displacement
9. Fill in the table following the example
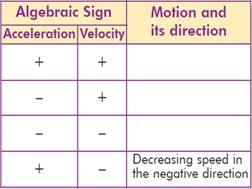 |
10. What type of motion do these formulas describe?
Answer:
Chapter 3 - Force
Task #1
Fill in the blanks. Determine type of force and name the action on the picture.
|
Name the action |
Contact Force |
Field Force |
Pictures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Evaluation: Excellent. You're right. Very close to the answer. You are a little confused. I agree with you. Very good. Great. Super
Task #2
Fill in the table according to the picture
 |
|
Description of force |
amount in N |
|
Force applied by a tugboat |
|
|
Engine force of a car |
|
|
Force applied by the engine of a train |
|
|
Force between the nucleus and the electron of a hydrogen atom |
|
|
Force applied by the engine of an aeroplane |
|
|
Gravitational force between the Earth and the Moon |
|
|
Gravitational force acting on 1 kg-mass |
|
|
Gravitational force acting on a child |
|
Task #3
Work with text. Find translations of terminologies and answer the questions on next page.
What Causes Friction?
In reality, there are no perfectly smooth surfaces as seen in Figure. All surfaces have irregularities. However, the friction does not arise from contact of irregularities on the surfaces. Experiments show that the real causes of friction are "the electrostatic forces" which occur between the molecules of the surfaces.
The actual area of contact is proportional to the normal force. When the normal force is constant, actual area of contact is also constant. The actual contact area remains the same even when the apparent contact area is reduced because increased normal force per unit actual area brings more molecules closer to interact. That is to say, the number of molecules forming bonds between the surfaces in both cases of having small and large apparent contact area is the same. Consequently friction force is the same. As a block slides over a surface, the bonds between the surfaces form and break. Up to a certain extent, smoothing a surface removes the irregularities and decreases friction. However, it brings more molecules, capable of bonding, closer and in this way it actually increases friction.
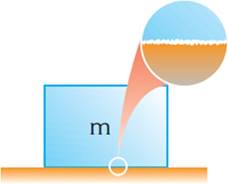 |
Friction force does not arise only from the mechanical interactions of irregular surfaces. It actually occurs due to the bonds formed between the molecules at high points on the surfaces
|
Қазақша |
Русский |
English |
|
|
площадь |
|
|
материя |
|
|
|
|
|
surface |
|
|
гладкий, ровный |
|
|
дөрекі (кедір-бұдыр) |
|
|
|
|
|
electrostatic |
|
|
явный, видимый |
|
|
сыну, бұзу, үзу |
|
|
|
|
|
molecule |
|
|
связывать, склеивать |
|
1. Are there any objects with an absolutely smooth surface?
2. What force is the cause of friction?
3. What happens when the block slides over a surface?
4. By smoothing a surface of an object, do we reduce or increase the friction?
Evaluation:
0-11 correct translations - alright 12-15 correct translations - good 16-20 correct translations - great
Chapter 4 - Pressure
Task #1
1. Match the words and definitions.
1. pascal
2. buoyancy
3. pressure
A. Force per unit area.
B. The SI unit of pressure
C. the ability to float
2. True/False questions
1. the distance from the top to the bottom → depth T/F
2. the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object → atmospheric pressure T/F
3. the pressure caused by the weight of the atmosphere → gas pressure T/F
Task #2
1. Pressure 2.Liquid pressure 3.Piston 4.Gas pressure 5.Buoyancy 6.Water displaced 7.Pascal 8.Depth 9.Hydraulic lift 10.Atmospheric pressure 11.Аrchimedes principle 12.Object
a) ......................... equals to 101325 Pa
b) The unit of pressure is ……..…………..
c)
The .................
of the river is 3 meters. d) This is a
......................... ![]()
e) The ......................... under the piston is equal to 5000 Pa.
f) The equation for ......................... is
density times gravitational acceleration times height
g) .......... – describes the ability to float.
h) According to …...……………… .................. buoyant force equals
density times gravitational acceleration times height.
i) ……………... is any matter.
j) .......... .….......... -
k) ………… …............. is used to lift heavy weights using liquid pressure.
Task #3
Fill in the table using these words:
pressure, liquid pressure, piston, gas pressure, atmospheric pressure, archimedes principle, fluid, buoyancy, Pascal, depth, hydraulic lift
|
Words |
Meaning |
|
|
Force per unit area. |
|
|
density * gravity * depth. |
|
|
used to compress a gas in a cylinder |
|
|
the pressure exerted by a gas |
|
|
the ability to float |
|
|
The SI unit of pressure |
|
|
the distance from the top to the bottom |
|
|
a large and a small chamber connected by a tube, filled with fluid, and used to produce large forces |
|
|
the pressure caused by the weight of the atmosphere |
|
|
the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object |
|
|
A substance that flows |
|
|
the number of square units needed to cover a surface |
Chapter 5 - Work, Energy, Power
Task #1
Solve the puzzle
1. Where there is work, there is ...............
2. A type of energy related to an object's position.
3. The ability to do work.
4. A type of energy related to an object's motion.
5. It is a measure of how fast work is done or the rate of converting energy.
6. The product of the force applied to an object and the distance moved in the direction of the force.
7. The ratio of work output to energy input.
8.
 |
Task #2
Each group solves one problem. One member of the group explains the solution to the next group. (Jigsaw method)
Group#1
A man carrying a load of 6 kg runs upstairs. If the work that the man does on the load is 300 J, find the height of the stairs
Group#2
The kinetic energy of a 100 g pencil falling vertically is 1.8 J at point x. What is the speed of this pencil at that point?
Group#3
The object of mass m is released from a height of 5m as shown in the figure. What is the speed of the object just before is strikes the ground? (Hint: First
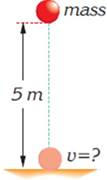 |
Group#4
Missy Diwater, the former platform diver for the Ringling Brother's Circus, had a kinetic energy of 12 000 J just prior to hitting the bucket of water. If Missy's mass is 40 kg, then what is her speed?
Task #3
Fill in the blanks.
|
Physical quantities |
Abbreviation |
Unit |
Tool |
|
|
|
|
speedometer |
|
Time |
|
|
|
|
|
|
kilogram |
|
|
|
V |
|
|
|
weight |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
barometer |
|
|
|
meter |
|
|
|
|
|
ruler |
|
temperature |
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
Review
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words
1. The work done when a force of 1 N acts over a distance of 1 m is
or
2. Energy can be defined as the _ to do work
3. There are two main kinds of energy: _ _ and
4. energy is the energy of an object due to its position
5. The energy of an object due to its motion is called energy
6. When a pencil falls from a height its energy changes into
energy
Chapter 6 - Heat and Temperature
Task #1
This is a group activity. Follow the teacher’s instructions.
|
№ |
Words: |
Definitions: |
|
1 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
Task #2
Write the words that fit the definitions
1. The temperature at which a liquid changes to a gas
_
2. vapor that still can condense
3. a temperature of 0 kelvins
4. the transfer of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves
5. the temperature at which the water vapor in the air becomes saturated and condensation begins
Task #3
True/False questions
1. The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid → melting point
2. (chemistry) a change directly from the solid to the gaseous state without becoming liquid → evaporation
3. the energy needed to change a unit mass from the liquid to the vapour phase at constant temperature → specific latent heat of
fusion
4. the change of state from a gas directly to a solid → evaporation
Review Heat and Temperature
What types of heat transfers are illustrated?
 |
Chapter 7 - Thermodynamics
Try to solve and explain to your partner in English
 |
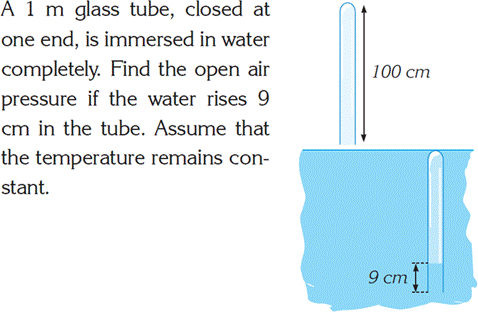 |
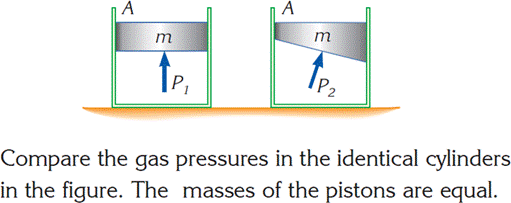 |
Task #4
 |
Chapter 8 - Electricity
Task #1
Watch the video, and fill in the blanks according to video.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KSirdRnje_E
atom, attract, charge, cloth, conductor, current, electrons, friction, insulation, negative, ohmmeter, plastic rod, positive, protons, repel, rubber, rubbing, spark, static
Lightning is a dramatic natural force. But what causes it? On a smaller scale, a ………. can be produced in the lab. Sparks and lightning are both the flow of …….. . In each case the charge is built up by ……... . Some objects can become charged simply by …….. them. The charge on this ………. is too small to form a spark, but big enough to ……... pieces of paper, and big enough to influence the path of this stream of water. To find out why the rod becomes charged you have to think about what’s happening to the atoms it’s made up of. Atoms contain ……….. charges called ……... and ………….. charges called electrons. Normally the number of protons and electrons is the same so the
………. has no overall charge. It’s neutral. Friction between the ………... and rod changes this balance. In this case the cloth rubs ………….. off the atoms in the rod so the rod becomes positively charged. A Van de Graaff generator produces enough charge to generate a spark. Take a look inside and you can see a motorized …………. belt. It passes around a perspex roller at the bottom and at the top. As the belt rubs against the roller it acts like the cloth on the plastic rod. It rubs off electrons leaving the rod positive, while the belt becomes negative. The electrons are collected by a spring and transferred to the metal dome. Because it has nowhere else to go the charge builds up. It can’t move from the dome so it’s called static charge. Place a ………... near it, like this small metal sphere and the charge can move. It leaps across producing a spark. Charge builds up on anything in contact with the dome. Each fibre of Lindsey’s hair becomes negatively charged. Like charges ………... so they move as far away as possible from each other. But for this to work the charge needs to be ………... It mustn’t leak away. Standing on polystyrene blocks acts as good ……….... What would happen if Lindsey stepped down onto the floor? Connecting a wire to the dome provides a path for the charge to flow along. It travels through an ……….. which is connected to the base of the generator to complete a circuit. The ohmmeter registers a flow of current. Electricity is simply a flow of negative charge. Static electricity becomes a flow of electricity as soon as it’s able to move. A fluorescent tube held next to the charged dome flickers as ……..flows.
Task #2
Write down the names of these devices
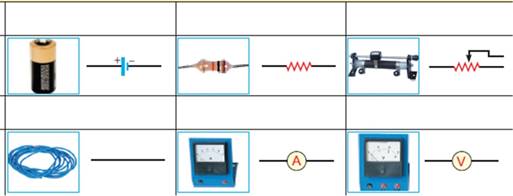 |
 |
Task #3
Write down whether the bulbs Will light/Will not light
 |
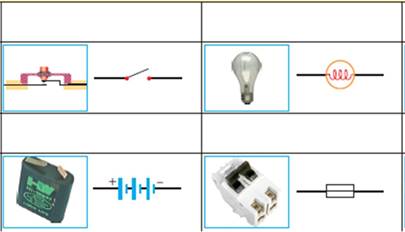
Review - Electricity
Matching.
Substitute the right words for the parts of the lamp
Words: argon gas (inside), filament, glass bulb, coil of tungsten wire,contacts
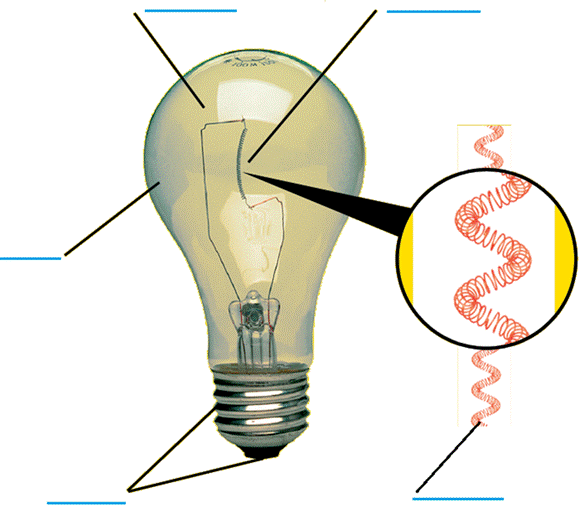 |
Puzzle.
1. The coiled wire inside a lamp
2. A wire carrying high voltage mains electricity
3. An effect of electricity
4. A circuit element used to protect circuits from excessive current
5. One of the colours of the mains electricity wires
6. The unit of power
 |
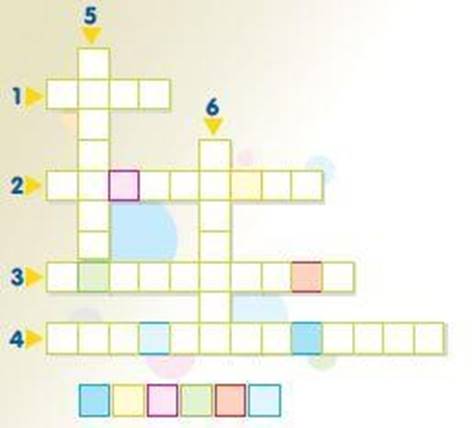
Chapter 9 - Magnetism
Task #1
Fill in the boxes correctly. Then using the letters in the grid fill in the corresponding coloured boxes below the puzzle. You will find the name of an animal which uses Earth’s magnetism to navigate.
1. The region of a magnet where the force of attraction is greatest
2. The attraction property of magnets.
3. A method of suspending objects in air.
4. A region of the Earth’s magnetic field.
5. An instrument indicating direction.
6. Unlike poles ... each other.
 |
Task #2
What is the magnetic field strength at a distance of 0.05 m from a long, straight wire carrying a current of 5 A?
Task #3
. The magnetic field at the center of a circular loop of 50 turns of wire carrying a current of 2 A is 6 x10–4 T. What is the radius of the loop?
Task #4
3. A solenoid of length 20 cm consists of 1000 turns of wire, as shown in the figure. If the solenoid carries a current of 0.1A, find the magnetic field inside the solenoid.
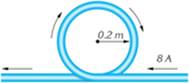
Task #5
4. A conductor carrying a current of 8 A consists of a circular loop of radius
0.2 m and two straight, long sections. Determine the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field at the center of the loop.
 |
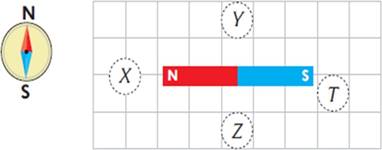
Review
If we put compass at points X,Y,Z,T, what will the orientation of compass be?
 |
Using these magnets, which of the figures can not be obtained?
 |
Classic Compass:
 |
1. O . . . . .
Chapter 10 - Optics
Task #1
Fill in the gaps with the proper term related to optics.
 |
 |
||

 2. S . . . . . 3. P . .
. .
2. S . . . . . 3. P . .
. .

 4. S . . . . e . . . . . . 5.
C . . . . . . m . . . . .
4. S . . . . e . . . . . . 5.
C . . . . . . m . . . . .
6. D . . . . . . r . . . . . . . . . 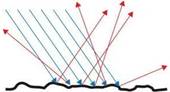
7. V . . . . . . 
8. C . . . . . m . . . . .  9. L . . . .
9. L . . . . 
10. L . . . 
Task #2
Fill in the gaps with the proper term related to optics.
|
R |
B |
O |
L |
F |
S |
F |
K |
A |
R |
B |
M |
U |
N |
E |
P |
|
R |
B |
J |
O |
I |
P |
L |
U |
M |
I |
N |
O |
U |
S |
T |
Y |
|
T |
U |
M |
S |
I |
R |
P |
H |
O |
U |
D |
L |
D |
F |
D |
G |
|
W |
G |
O |
U |
F |
E |
D |
Z |
G |
R |
E |
A |
L |
G |
F |
T |
|
O |
O |
F |
T |
I |
N |
D |
Y |
J |
S |
J |
E |
O |
D |
N |
A |
|
D |
E |
D |
L |
R |
E |
L |
E |
Z |
B |
U |
L |
J |
E |
S |
O |
|
A |
Y |
C |
O |
N |
C |
A |
V |
E |
V |
B |
F |
O |
C |
U |
S |
|
H |
L |
G |
U |
H |
K |
U |
P |
N |
J |
D |
I |
V |
U |
H |
H |
|
S |
C |
N |
T |
V |
S |
T |
I |
T |
H |
C |
G |
M |
X |
K |
F |
|
K |
N |
S |
O |
L |
A |
R |
E |
C |
L |
I |
P |
S |
E |
L |
D |
|
G |
H |
J |
I |
K |
Q |
I |
C |
I |
O |
P |
K |
J |
N |
G |
A |
|
N |
J |
E |
V |
S |
N |
V |
E |
D |
S |
V |
O |
Y |
B |
T |
E |
|
O |
E |
N |
G |
L |
I |
S |
R |
G |
R |
E |
P |
T |
G |
O |
P |
|
R |
E |
F |
R |
A |
C |
T |
I |
O |
N |
U |
T |
A |
E |
Y |
U |
|
U |
L |
D |
A |
N |
A |
M |
L |
T |
A |
P |
I |
I |
V |
R |
G |
|
E |
T |
O |
M |
I |
M |
T |
O |
K |
Z |
I |
C |
R |
O |
A |
N |
|
F |
A |
T |
I |
O |
N |
D |
I |
O |
P |
T |
R |
E |
L |
D |
E |
1) Optics
2) Solar eclipse
3) Concave
4) Virtual
5) Prism
6) Shadow
7) Real
8) Refraction
9) Penumbra
10) Dioptre
11) Focus
12) Luminous
Review
Puzzle
Fill in the boxes correctly. The coloured region will give you the name of the apparatus used in submarines to observe objects on the surface of the sea.
1. An electrical device producing light.
2. The name of a projector which has a plane mirror at the top.
3. A piece of glass which shows images.
4. The light falling upon a surface: ………. light.
5. The light and heat source of the Earth.
6. An artificial light source made of wax.
7. The giant sunlight reflector in the sky seen at night.
8. Flat mirror: ………. mirror.
9. A surface upon which the images fall.
 |
Chapter 11 - Nuclear physics
Task #1
Match definitions with right words.
|
1. nucleus |
|
time required for a quantity to reduce to half its initial value. |
|
2. proton |
energy required to separate an atomic nucleus completely into its constituent protons and neutrons |
|
|
3. half-life |
a central part about which other parts are grouped or gathered. |
|
|
4. isotope |
a discrete quantity of energy proportional in magnitude to the frequency of the radiation it represents. |
|
|
5. nuclear binding energy |
a positively charged elementary particle. |
|
|
6. quantum |
an atomic reaction in which multiple atoms combine to create a single, more massive atom |
|
|
7. nuclear fission |
one of two or more atoms with the same atomic number that contain different numbers of neutrons. |
|
|
8. nuclear fusion |
an atomic reaction in which nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei |
Task #2
Fill in the gaps with following words
electrons protons nucleons reactions isotopes number element neutrons chemical
Atomic Number (Z) is the of in the nucleus. It “defines” the element. The number of protons is always the same for a given .
Atomic Number also designates the number of in an element. If an element either gains or loses electrons, the resulting particle is called an _. For example, if a sodium atom (Na) loses an electron it becomes a sodium ion (Na+ .)
Mass Number (A) – is the total number of .
Isotopes form when the number of _ vary in the nucleus of a given element.
Only 112 elements are known, but the total number of is about 2000.
Some elements have several isotopes (like carbon – 12C, 13C, 14C). Isotopes of a single element have the ‘same’ properties (due to same number of electrons), but they have different masses (due to varying number of
.)
Due to their various masses isotopes behave slightly different during
.
Task #3
Translate the following text
Fusion vs. Fission
On a kilogram for kilogram comparison, more energy comes from fusion than from fission. The fission of 1 kg of 235U provides energy equal to the burning of 2 million kg of coal. The fusion of 1 kg of deuterium releases energy equal to the burning of 40 million kg of coal.
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _ __
___ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _
Review
Solve these problems, explain solutions in english.
1.
90
When a
radioactive daughter nucleus?
230 Th isotope undergoes α-decay, what is the resulting
2.
11
24Na undergoes beta decay. What is the resulting daughter nucleus?
Chapter 12 - Astronomy
Task #1
Fill in the names of the planets in our solar system.
Task #2
Fill in the gaps.
1. – the scientific study of the universe beyond Earth’s atmosphere
2. – everything, all energy, matter, and space
3. – one of 50 billion galaxies scattered throughout the universe 4. – contains our sun and 9 planets
5. – supplies the energy for nearly all life on the planet earth
Task #3
Use the table to answer the questions.
![]()
Self-learning is the best learning.
Chapter 1 - Matter
PART A
Translate these words into your native language.
1) Matter: 9) Particle:
2) Mass: 10) Area:
3) Volume: 11) Space:
4) Length: 12) Amount:
5) Liquid: 13) Width:
6) Gas: 14) Height:
7) Solid: 15) Stopwatch:
8) Atom: 16) Molecule:
PART B
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
1) Matter can be defined as anything.
Which has & in space.
2) Matter exists in three states:
, and
4) In a , the forces between particles are very weak.
5) Show the shape of atoms in solid, liquid and gas.
Solid Liquid Gas
6) One milliliter is equal to one
cubic meters.
7) One liter is equal to one .
8) The volume of liquids is generally measured in .
9) The unit of volume is .
10) The volume of a regular object is found by multiplying the of the object with its height.
.
3) In , the particles are held strongly but not as tightly as in a
.
Chapter 2 - Motion
PART A
Fill in the blanks with True (T) or False (F).
1. Displacement and distance are the same concepts.
2. Position is a scalar quantity.
3. Speed and velocity are the same concepts.
4. The unit of speed in SI is km/h.
5.Speed is a scalar quantity.
6. Velocity is a vector quantity. 7.The area under the velocity-time graph gives the displacement of the moving object.
PART B
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
1. An object is in if its place changes with respect to a fixed point.
2. Position is a
4. Distance is a quantity.
5. Speed is a quantity.
6. is calculated by dividing the total distance by the total time.
7. In a position-time graph, the slope of the line gives the _.
8.In a velocity-time graph, the area under the graph gives the .
9. Acceleration is a quantity.
PART C
Solve the following problems.
1. A car moves with a velocity of 25 m/s for 10 seconds. What is the distance covered by the car?
2. A car moves 180 m within 3 seconds and then moves 70 m within 2 seconds. What is the average speed of the car?
quantity.
3. The change in position of an object is called .
Chapter 3 - Force
PART A
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words
1) is either a push or a pull that acts on an object.
2) A force can change or
of the object.
3) Weight is directly proportional to
and .
4) Force is a quantity.
5) Mass is the scalar quantity, because it has no .
7) Scalar quantity has only
.
PART B
Fìll ìn the parenthesìs wìth T (True) or F (False)
1) ( ) Force is measured with spring balance or dynamometer.
2) ( ) Weight = Mass· Distance.
3) ( ) The weight of an object on the Earth is more than on the moon.
4) ( ) The gravitational force on 100 g mass is equal to 1 N on the earth.
5) ( ) The mass of object is the same on all planets.
6) ( ) The friction force is directly proportional to weight of the moving object.
7) ( ) The scalar quantities have direction.
PART C
Solve the problem
1) The mass of object is 1500 g. Find the weight of object on the earth? (g = 10N/kg)
2) The object’s weight is 100 N on the earth. What is the weight of object on the moon? (gearth = 10N/kg, gmoon= 1,7N/kg)
3) If the force is 40N, what is the mass of homogeneous rod?
Chapter 4 - Pressure
PART A
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
1) The amount of force acting on a unit area is called .
2) The more area means
pressure.
3) The unit of pressure is .
4) Pressure= /Area.
5) Pascal is also N/ .
6) Solids transmit pressure in
direction.
7) When the gas volume is increased at constant temperature, the gas pressure is .
8) Barometer is used for measuring of
.
9) The denser liquid causes
pressure.
PART B
Fill in the parenthesis with True or False
1) The force acting on unit area is called pressure. ( )
2) Gases exert pressure in all directions ( )
3) If the force increases, the pressure also increases. ( )
PART C
Solve the problems
1) A man weighs 800N. The surface area of one shoe is 80cm2. What is the pressure exerted by the man on the ground if he stands on both feet?
2) If the pressure of the object in figure 1 is P. What is the pressure of same object in figure 2 in terms of P?
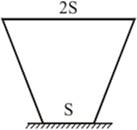
3) The object exerts pressure of P on the bottom. If the object is turned
upside down, what is the new pressure in terms of P?
4) If the pressure exerted at point L is 10P.
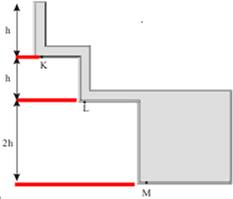
a) What is the pressure at point K in terms of P.
b) What is the pressure at point M in terms of P.
2) The pressure at bottom of a cylinder full of water is 27200 N/m2. What is the height of water column?
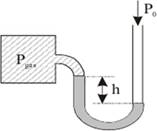
5) If the gas in the container has 55 cm- Hg find the outside pressure in terms of cm-Hg (h=20 cm)
2) The altitude of a mountain is 2400 m.
The air pressure at sea level is 720 mm- Hg. Find the air pressure at the top of the mountain. (1 cm-Hg change for each 105 m)
Chapter 5 – Work, Energy and Power
PART A
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words
1) Work = _ × Distance.
2) If there is no there is no work.
3) can be defined as the ability to do work.
4) Work & energy are measured in
.
5) is the energy of an object due to its position.
6) is the energy of an object due to its motion.
PART B
Fill in the parenthesis with True or False 1) Pushing a car and lifting a weight are both work¸ because there is motion. ( ) 2) Work and energy can be measured in newtons. ( )
3) When a pencil falls, its kinetic energy changes into potential energy. ( )
4) The total energy in constant. ( )
5) In dams, potential energy changes into kinetic energy. ( )
6) Efficiency = Work Output / Energy input ( )
PART C
Solve the problems
1) A car is pushed for 10 m with a force of 300 N. Find the work done on the car.
2) A man lifts 200 N weight to 4 m. Find the work done by the man.
3) A boy of 50 kg climbs a wall 2 m high.
Calculate the change in potential energy of the boy.
4) A 50 kg boy is running with a speed of 2 m/s. Find his kinetic energy.
5) Boy weighs 50 kg. He climbs 4 m
ladder in 5 s. What is his power?
6) What is the power of a motor which raises 200 kg of load to 8 m in 20 s?
PART D
Choose the correct answer
1) A boy pushed a box for 8 m. if the work done on the box is 400 J. Calculate the force applied by the boy?
A) 40N B) 50N C) 60N D) 80N
2) A man whose mass is 60 kg climbs a rope of 5 m in 6 s. Find man’s power.
A) 400 W B) 200 W C) 500 W D) 100 W
3) A motor can fill a tank, which is at a height of 10 m above the ground in 4 minutes. Capacity of the tank is 2400 kg water. Find the power of motor.
(g=10 N/kg)
A) 100W B) 1000 W C) 500 W D) 250 W
4) Three different objects are raised to different heights. What will be the relationship between works done on the objects?
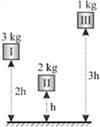
A) WI >WII>WIII
B) WI =WII=WIII
C) WI >WIII>WII
D) WIII>WI >WII
5) The same object is raised to the same point by using different paths. Compare work done to raise object to point A.
A) W1 > W2 > W3 > W4 B) W1 = W4 > W2 = W3 C) W1 = W2 = W3 = W4 D) W4 > W3 > W2 > W1
Chapter 6 - Heat and temperature
PART A
Fill with appropriate words.
1) of a substance is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of all particles in that substance.
2) On Kelvin scale¸ the boiling point of the water is .
3) The instrument which is used to measure the temperature is called
_.
4) Freezing is when
turns to .
PART B
Fill in the parenthesis with True or False
1) Heat energy is also known as thermal energy. ( )
2) Heat and temperature are the same. ( )
3) Heat is measured with thermometer and temperature is measured with calorimeter. ( )
4) Heat is a kind of energy but temperature is a measurement. ( )
5) Solids can turn to gas without becoming liquid. ( )
6) Temperature of a substance is a measure of the average kinetic energy of an object. ( )
PART C
Solve problems
1) 127 °C is equal to K
2) 10 °C is equal to K
3) 283 K is equal to °C
4) One ice cube served in restaurant weighs 50g, and is kept at -10°C. The customer added 2 ice cubes to his glass of 200g water at 20°C. What is the final temperature? Neglect heat exchange with surroundings.
(cwater = 2cice = 4.2 J/g Lfucion = 330 J/g )
Chapter 7 - Thermodynamics
PART A
Answer these questions in your own words
1. On which macroscopic parameters does the internal energy of an ideal gas depend?
2. Does the energy of a system increase or decrease, when it does work on the surroundings?
4. What is the difference between work done by a system and work done on a system?
5. Does a gas sample do positive or negative work as its volume increases against external forces?
PART B
1. A gas sample does 320 J of work, as it absorbs 700 J heat from the surroundings. What is the internal energy change of the gas?
2. The internal energy of a gas sample increases by 280 J when it does 185 J of work. What amount of heat
is absorbed by the gas?
3. 800 J of work is done on a gas sample as it releases 150 J of heat. What is the internal energy change of the gas?
4. The internal energy of a system increases by 100 J, when it absorbs 400J of heat. What is the work done by the system on the surroundings?
Chapter 8 - Electricity
PART A
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
1) The closed path through which the electrons flows is called
.
2) Device that produces steady current flowing around a circuit is called
.
3) The acidic solution used to conduct electricity is called
.
4) Materials which allow electrons to pass through them are called
_.
5)Current is measured by an instrument called .
6) Potential difference is measured by an instrument called .
PART B
![]() Fill in
the parenthesis with T (True) or F (False)
Fill in
the parenthesis with T (True) or F (False)
1) represents battery ( )
2) Rheostat is symbolized by ( )
3)
![]() Direction of the current
is opposite to the direction of the electrons. ( )
Direction of the current
is opposite to the direction of the electrons. ( )
4) Current = charge / time ( )
5) Voltmeter is connected in series to a circuit element. ( )
6) Ammeter is connected in series to a circuit ( )
PART C
Choose the correct answer
1) How many coulombs of charge passes through a 2 A lamp in 5 minutes?
A) 300 B) 600 C) 200 D) 400
2) What is the equivalent voltage?
A) 2 V B) 5 V C) 1,5 V D) 1 V
3) 15×1021 electrons passes through the cross-sectional area of a conducting wire within 5 minutes. What is the
current flowing through the wire? (e=1,6×10-19C)
A) 4 A B) 3 A C) 8 A D) 7,5 A
4) The charge passing through a cross-sectional area of a wire
varies with time. What is the current passing through the wire?
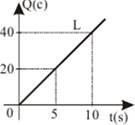
A) 4 A B) 0,25 A C) 8 A D) 2 A
5) Which of the following symbolizes the switch in a circuit?

6) Which of the following measures the voltage?
A) Voltmeter B) Ammeter
C) Resistor D) Dynamometer
7) Which of the following is incorrect?
A) The unit of charge is coulomb
B) Current moves in the direction of motion of electrons
C) The voltage is measured in volts.
D) The current is measured by ammeter
8)Which of the following is a conductor?
A) air B) wood
C) plastic D) copper
13) Which of the following circuits is correctly constructed?
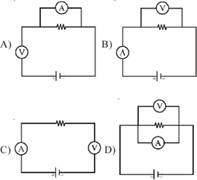
Chapter 9 - Magnetism
PART A
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words
1) Materials which are attracted by a magnet are called
.
2) Materials which are not attracted by a magnet are called
.
3) Like poles each other and attract each other.
4) The direction of magnetic field lines are from _ pole to pole.
5) When a piece of iron or steel is stroked with a the iron or steel become magnetized.
PART B
Fill in the parenthesis with T (True) or F (False)
1) If a magnet is cut into pieces, each piece behaves as a magnet. ( )
2) The magnetic field strength is the greatest at the poles. ( )
3) Iron, steel, nickel and cobalt are ferromagnetic materials. ( )
4) When an iron nail touches the magnet, a nail is magnetized. ( )
5) Electric motors and generators have magnets inside ( )
PART C
Answer the questions
1) How many poles are there in a magnetized material?
2) Is it possible to make a magnet with single pole?
3) Draw the picture of the magnetic field around the bar magnet given below
4) What is transformer?
5)Give examples of devices which use electromagnetism to work.
PART D
1) According to the diagram given below. What is the possible poles K, L and M?
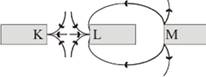
K L M
A) SNS B) NSN C)NSS D)SSN
5) Which of the following doesn’t have electromagnetic mechanism?
A) Tape player B) Telephone
C) Lamp D) The hard disk
6) A transformer has an input voltage of 240V and output voltage of 24V. If the number of turns of primary coil is 800, what is the number of turns of secondary coil?
A) 40 B) 80 C) 100 D) 120
7) Which of the following statements is not correct for transformer?
A) Includes two coils, the primary and secondary
B) It only works with alternating current (AC)
C) Changes the voltage from one value to another
D) It is device which produces electricity
8) Which of the statement below is not correct?
A) A generator is a device which produces electricity
B) Electric motors include magnet to work
C) There are two kinds of generator, AC and DC
D) Electric motors produce electricity
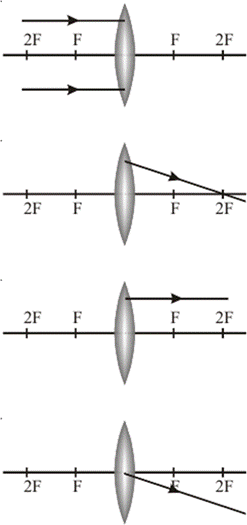
Chapter 10 - Optics
PART A
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words
1) An object which produces its own light is called a source.
2) Light travels km in one second.
3) There are two types of curved mirror
10) Diverging lens causes parallel light rays to .
PART B
Fill in the parenthesis with T (True) or F (False)
1) Sun and stars are examples of self- luminous sources. ( )
2) The image in plane mirror is real. ( )
3) Humans can sense electromagnetic
which are
.
and
waves. ( )
4) The image formed by a concave
4) The distance between the focus and mirror is called .
5) A light ray travelling parallel to the principal axis at a concave mirror is reflected back through .
6) The centre of lens is called _.
7) The distance from centre of the lens to F is called .
8) If the object is at the focus then the image is formed at .
9) A light ray parallel to the principal axis passes through the after being refracted by the converging lens.
mirror is always real. ( )
5) If the object is at the infinity, its image forms at the focus of a convex mirror. ( )
6) At a convex mirror the image always forms between focus and mirror. ( )
7) A converging lens is thinner at center and thicker at outside. ( )
8) A converging lens collects parallel light rays at a focus. ( )
9) Optical center is denoted by F. ( )
10) A light ray passing through the optical center travels without changing its direction. ( )
![]() PART C
PART C
Solve the problems
1) A ray of light strikes a plane mirror as shown in figure. Draw the reflected ray.

2) A man looks to a mirror from distance of 3 m. He moves toward the mirror 50 cm. What is the new distance between him and his image?
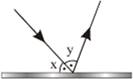
3) If the angle x is equal to angle y, find the angle x.
4) Two plane mirrors are located as in figure. Find the number of image in the mirrors.
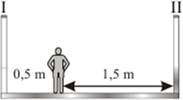
5) A child stands between two plane mirror. What is the distance between his first images in mirror I and II?
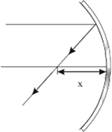
6) The radius of concave mirror is 2m.
The light ray parallel to the principal axis is reflected as in figure. Find x.
7) Draw the image of the object and write the properties of the image.
![]()
![]() Complete the figures.
Complete the figures.
8) Write three examples to using concave and convex mirror in daily life.
9) Draw the shadow on the screen
Chapter 11 - Nuclear Physics
Answer the questions and solve the problems
1).What is the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion reactions?
2) What are the main components of nuclear reactor?
3) Find the missing particle in the following nuclear reactions
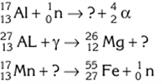
4) Where do we use radiation in medicine?
5) What are the harmful effects of radiation on living tissue?
6) What must the minimum energy of photons falling on a copper plate be in order to observe the photoelectric effect? (W=4.7 eV)
7) What is the maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted from caesium (W=1.8eV), when light of frequency 1015 Hz falls upon the metal?
8) The photoelectric effect is observed on barium oxide at a minimum frequency of 0.24 PHz (P=1015). Find the work function of barium oxide in eV.
9) The cut-off wavelength for the photoelectric effect of platinum is 220nm. Find the work function of platinum in eV.
10) Find the cut-off wavelength for the photoelectric effect in tungsten. (W=4.5 eV)
11) Green light with a wavelength of 5461 Å, emitted from a mercury lamp, ejects photoelectrons with a maximum kinetic energy of 0.13 eV from a metal surface. (Å=10-10)
a) Calculate the work function of the metal.
b) Calculate the cut-off frequency of the metal.
c) Calculate the cut-off wavelength of the metal in angstroms.
12) If light of wavelength 5166 Å falls on the cathode of a photocell lamp, the maximum kinetic energy of the scattered electrons is 0.8 eV.
a) What is the work function of the metal in eV?
b) What is the cut-off wavelength in angstroms?
c) What is the cut-off frequency in Hz?
13) Photons of energy 5 eV, cause the emission of electrons from the surface of a metal. The work function of
the metal is 4.7 eV. What is the maximum momentum of the photoelectrons on the surface of the metal?
Chapter 12 - Astronomy
PART A
Fill in the blanks
1) The largest planet in solar system is
2) The distance travelled by light in a year is called _
3) A heavenly body that revolves around a planet
4) A group of stars
5) A meteor that falls to Earth after entering Earth's atmosphere
6) Which planet in the solar system is the smallest?
7) Which of the heavenly bodies shown has an atmosphere? _
8) Which pair of planets is nearest and farthest from the Sun?
9) Which is the largest planet?
10) Which planets are Earth’s neighbors?
11) Which planets have rings around them?
12) Which planet is usually called Earth’s ‘twin’?
13) 1 _ = 149.6 million km
14) Earth's rotation axis is tilted by
degrees with respect to its orbital plane.
15) What is the main property of the equinoxes?
16. What are Kepler's laws of planetary motion?
PART B
Solve the problems
1) If we want to make one year last for 730 days, what should be the new average radius of the Earth’s orbit in terms of R0?
2) How much energy do we need to send the Moon to open space?
![]()
"Good words are worth much, and cost little."
George Herbert
Chapter 1 – Matter
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
1 |
nature |
|
|
|
2 |
matter |
|
|
|
3 |
body |
|
|
|
4 |
substance |
|
|
|
5 |
particle |
|
|
|
6 |
atom |
|
|
|
7 |
molecule |
|
|
|
8 |
measurement |
|
|
|
9 |
unit |
|
|
|
11 |
scalar quantity |
|
|
|
12 |
vector quantity |
|
|
|
13 |
magnitude |
|
|
|
14 |
direction |
|
|
|
15 |
amount |
|
|
|
16 |
length |
|
|
|
17 |
area |
|
|
|
18 |
volume |
|
|
|
19 |
mass |
|
|
|
20 |
density |
|
|
|
21 |
time |
|
|
|
22 |
space |
|
|
|
23 |
shape |
|
|
|
24 |
state |
|
|
|
25 |
solid |
|
|
|
26 |
liquid |
|
|
|
27 |
gas |
|
|
Chapter 2 – Motion
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
1 |
motion |
|
|
|
2 |
trajectory, path |
|
|
|
3 |
position |
|
|
|
4 |
reference point |
|
|
|
5 |
displacement |
|
|
|
6 |
distance |
|
|
|
7 |
speed |
|
|
|
8 |
velocity |
|
|
|
9 |
average speed |
|
|
|
10 |
uniform motion |
|
|
|
11 |
acceleration |
|
|
|
12 |
deceleration |
|
|
|
13 |
linear motion |
|
|
|
14 |
circular motion |
|
|
|
15 |
elliptic motion |
|
|
|
16 |
projectile motion |
|
|
|
18 |
initial |
|
|
|
19 |
final |
|
|
|
20 |
increase |
|
|
|
21 |
decrease |
|
|
|
22 |
constant |
|
|
Chapter 3 - Force
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
1 |
force |
|
|
|
2 |
dynamics |
|
|
|
3 |
types of force |
|
|
|
4 |
lift |
|
|
|
5 |
push |
|
|
|
6 |
pull |
|
|
|
7 |
dynamometer |
|
|
|
8 |
gravitational force |
|
|
|
9 |
weight |
|
|
|
10 |
Hooke's law |
|
|
|
11 |
deformation |
|
|
|
12 |
magnetic |
|
|
|
13 |
electrostatic force |
|
|
|
14 |
tension |
|
|
|
15 |
normal force |
|
|
|
16 |
frictional force |
|
|
|
17 |
inertia |
|
|
|
18 |
resultant force |
|
|
|
19 |
statics |
|
|
|
20 |
equilibrium |
|
|
|
21 |
center of gravity |
|
|
|
22 |
action |
|
|
|
23 |
reaction |
|
|
Chapter 4 - Pressure
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
1 |
pressure |
|
|
|
2 |
atmospheric pressure |
|
|
|
3 |
actual weight |
|
|
|
4 |
apparent weight |
|
|
|
5 |
depth |
|
|
|
6 |
Pascal's principle |
|
|
|
7 |
hydraulic lift |
|
|
|
8 |
piston |
|
|
|
9 |
barometer |
|
|
|
10 |
mercury |
|
|
|
11 |
pump |
|
|
|
12 |
Bernoulli's principle |
|
|
|
13 |
tube |
|
|
|
14 |
buoyancy |
|
|
|
15 |
Archimedes' principle |
|
|
|
16 |
up thrust force |
|
|
|
17 |
water displaced |
|
|
|
18 |
volume immersed |
|
|
|
19 |
transmit |
|
|
|
20 |
sink |
|
|
|
21 |
float |
|
|
Chapter 5 - Work, Energy, Power
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
1 |
work |
|
|
|
2 |
energy |
|
|
|
3 |
potential energy |
|
|
|
4 |
elastic potential energy |
|
|
|
5 |
kinetic energy |
|
|
|
6 |
mechanical energy |
|
|
|
7 |
height |
|
|
|
8 |
compress |
|
|
|
9 |
conservation of energy |
|
|
|
10 |
power |
|
|
|
11 |
efficiency |
|
|
|
12 |
torque |
|
|
|
13 |
lever |
|
|
|
14 |
equilibrium |
|
|
|
15 |
statics |
|
|
|
16 |
simple machines |
|
|
|
17 |
load |
|
|
|
18 |
mechanical advantage |
|
|
|
19 |
fulcrum, pivot |
|
|
|
20 |
pulley |
|
|
|
21 |
fixed pulley |
|
|
|
22 |
movable pulley |
|
|
|
23 |
wheel and axle |
|
|
|
24 |
inclined plane |
|
|
|
25 |
equal-arm balance |
|
|
Chapter 6 - Heat and Temperature
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
1 |
heat |
|
|
|
2 |
brownian motion |
|
|
|
3 |
diffusion |
|
|
|
4 |
molecular-kinetic theory |
|
|
|
5 |
thermal expansion |
|
|
|
6 |
expand |
|
|
|
7 |
contract |
|
|
|
8 |
thermometer |
|
|
|
9 |
absolute zero |
|
|
|
10 |
degree |
|
|
|
11 |
Celsius scale |
|
|
|
12 |
conduction |
|
|
|
13 |
convection |
|
|
|
14 |
radiation |
|
|
|
15 |
specific heat capacity |
|
|
|
16 |
heat exchange |
|
|
|
17 |
melting |
|
|
|
18 |
freezing |
|
|
|
19 |
condensation |
|
|
|
20 |
evaporation |
|
|
|
21 |
sublimation |
|
|
|
22 |
deposition |
|
|
|
23 |
boiling |
|
|
|
24 |
specific latent heat of fusion |
|
|
|
25 |
specific latent heat of vaporization |
|
|
|
26 |
melting point |
|
|
|
27 |
boiling point |
|
|
|
28 |
humidity |
|
|
|
29 |
absolute humidity |
|
|
|
30 |
relative humidity |
|
|
|
31 |
dew point |
|
|
|
32 |
saturated vapor |
|
|
|
33 |
unsaturated vapor |
|
|
Chapter 7 – Thermodynamics
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
1 |
thermodynamics |
|
|
|
2 |
internal energy |
|
|
|
3 |
absorb |
|
|
|
4 |
release |
|
|
|
5 |
surrounding |
|
|
|
6 |
piston |
|
|
|
7 |
isolated system |
|
|
|
8 |
adiabatic process |
|
|
|
9 |
isovolumetric process |
|
|
|
10 |
isothermal process |
|
|
|
11 |
isobaric process |
|
|
|
12 |
hot reservoir |
|
|
|
13 |
cold reservoir |
|
|
|
14 |
heat engine |
|
|
|
15 |
internal combustion engine |
|
|
|
16 |
reversible |
|
|
|
17 |
irreversible |
|
|
|
18 |
disorder |
|
|
|
19 |
cycle |
|
|
|
20 |
fuel |
|
|
|
21 |
steam |
|
|
|
22 |
gasoline |
|
|
Chapter 8 - Electricity
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
1 |
electrostatics |
|
|
|
2 |
electricity |
|
|
|
3 |
charge |
|
|
|
4 |
positive |
|
|
|
5 |
negative |
|
|
|
6 |
neutral |
|
|
|
7 |
conductor |
|
|
|
8 |
insulator |
|
|
|
9 |
dielectric |
|
|
|
10 |
electroscope |
|
|
|
11 |
Сoulomb`s law |
|
|
|
12 |
electric field |
|
|
|
13 |
potential |
|
|
|
14 |
potential difference |
|
|
|
15 |
voltage |
|
|
|
16 |
capacitance |
|
|
|
17 |
capacitor |
|
|
|
18 |
parallel plate capacitor |
|
|
|
19 |
medium |
|
|
|
20 |
permittivity |
|
|
|
21 |
current source |
|
|
|
22 |
cell |
|
|
|
23 |
battery |
|
|
|
24 |
electromotive force |
|
|
|
25 |
current |
|
|
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
26 |
electrostatics |
|
|
|
27 |
electricity |
|
|
|
26 |
circuit |
|
|
|
27 |
wire |
|
|
|
28 |
switch |
|
|
|
29 |
bulb |
|
|
|
30 |
voltmeter |
|
|
|
31 |
ampermeter, ammeter |
|
|
|
32 |
resistance |
|
|
|
33 |
resistivity |
|
|
|
34 |
rheostat |
|
|
|
35 |
resistor |
|
|
|
36 |
series connection |
|
|
|
37 |
parallel connection |
|
|
|
38 |
Ohm's law |
|
|
|
39 |
Kirchhoff's rules |
|
|
|
40 |
short circuit |
|
|
|
41 |
fuse |
|
|
|
42 |
grounding |
|
|
|
43 |
superconductivity |
|
|
|
44 |
semiconductor |
|
|
|
45 |
electrolysis |
|
|
|
46 |
electrolyte |
|
|
|
47 |
electrode |
|
|
|
48 |
cathode |
|
|
Chapter 9 – Magnetism
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
1 |
magnetism |
|
|
|
2 |
magnet |
|
|
|
3 |
North pole |
|
|
|
4 |
South pole |
|
|
|
5 |
compass |
|
|
|
6 |
natural |
|
|
|
7 |
artificial |
|
|
|
8 |
permanent |
|
|
|
9 |
temporary |
|
|
|
10 |
electromagnetism |
|
|
|
11 |
electromagnetic induction |
|
|
|
12 |
coil |
|
|
|
13 |
solenoid |
|
|
|
14 |
electric motor |
|
|
|
15 |
generator |
|
|
|
16 |
direct current |
|
|
|
17 |
alternating current |
|
|
|
18 |
transformer |
|
|
|
19 |
primary coil |
|
|
|
20 |
secondary coil |
|
|
|
21 |
step-down transformer |
|
|
|
22 |
step-up transformer |
|
|
Chapter 10 – Optics
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
1 |
optics |
|
|
|
2 |
light |
|
|
|
3 |
luminous source |
|
|
|
4 |
shadow |
|
|
|
5 |
umbra |
|
|
|
6 |
penumbra |
|
|
|
7 |
solar eclipse |
|
|
|
8 |
lunar eclipse |
|
|
|
9 |
plane mirror |
|
|
|
10 |
reflection |
|
|
|
11 |
regular reflection |
|
|
|
12 |
diffuse reflection |
|
|
|
13 |
incident ray |
|
|
|
14 |
reflected ray |
|
|
|
15 |
angle |
|
|
|
16 |
curved mirror |
|
|
|
17 |
concave mirror |
|
|
|
18 |
convex mirror |
|
|
|
19 |
focus |
|
|
|
20 |
focal length |
|
|
|
21 |
image |
|
|
|
22 |
real |
|
|
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
23 |
virtual |
|
|
|
24 |
upright, erect |
|
|
|
25 |
inverted |
|
|
|
26 |
refraction of light |
|
|
|
27 |
index of refraction |
|
|
|
28 |
critical angle |
|
|
|
29 |
total internal reflection |
|
|
|
30 |
prism |
|
|
|
31 |
spectrum |
|
|
|
32 |
rainbow |
|
|
|
33 |
converging lens |
|
|
|
34 |
diverging lens |
|
|
|
35 |
mafnification |
|
|
|
36 |
optical centre |
|
|
|
37 |
power of lens |
|
|
|
38 |
dioptre |
|
|
|
39 |
long-sightedness (hyperopia) |
|
|
|
40 |
near-sightedness (myopia) |
|
|
Chapter 11 - Nuclear physics
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
1 |
dualism of light |
|
|
|
2 |
photon |
|
|
|
3 |
quantum |
|
|
|
4 |
photoelectric effect |
|
|
|
5 |
work function |
|
|
|
6 |
cut-off (threshold) frequency/wavelength |
|
|
|
7 |
stopping potential |
|
|
|
8 |
nucleus |
|
|
|
9 |
nucleon |
|
|
|
10 |
proton |
|
|
|
11 |
neutron |
|
|
|
12 |
electron |
|
|
|
13 |
atomic number |
|
|
|
14 |
atomic mass |
|
|
|
15 |
isotope |
|
|
|
16 |
nuclear binding energy |
|
|
|
17 |
mass difference (mass loss) |
|
|
|
18 |
alpha decay |
|
|
|
19 |
beta decay |
|
|
|
20 |
gamma decay |
|
|
|
21 |
half-life |
|
|
|
22 |
nuclear fission |
|
|
|
23 |
nuclear fusion |
|
|
|
24 |
nuclear chain reaction |
|
|
|
25 |
critical mass |
|
|
|
26 |
nuclear reactor |
|
|
|
27 |
moderator |
|
|
|
28 |
control rods |
|
|
Chapter 12 – Astronomy
|
|
English |
Қазақ тілі |
Русский язык |
|
1 |
astronomy |
|
|
|
2 |
heavenly bodies |
|
|
|
3 |
planet |
|
|
|
4 |
star |
|
|
|
5 |
constellation |
|
|
|
6 |
asteroid |
|
|
|
7 |
comet |
|
|
|
8 |
meteor |
|
|
|
9 |
meteoroid |
|
|
|
10 |
meteorite |
|
|
|
11 |
satellite |
|
|
|
12 |
universe |
|
|
|
13 |
horizon |
|
|
|
14 |
celestial sphere |
|
|
|
15 |
summer solstice |
|
|
|
16 |
winter solstice |
|
|
|
17 |
heliocentre system |
|
|
|
18 |
geocentre system |
|
|
|
19 |
vernal equinox |
|
|
|
20 |
autumn equinox |
|
|
|
21 |
solar system |
|
|
|
22 |
Sun |
|
|
|
23 |
Mercury |
|
|
|
24 |
Venus |
|
|
|
25 |
Earth |
|
|
|
26 |
Mars |
|
|
|
27 |
Jupiter |
|
|
|
28 |
Saturn |
|
|
|
29 |
Uranus |
|
|
|
30 |
Neptune |
|
|
|
31 |
Black hole |
|
|
|
32 |
Milky Way |
|
|
|
33 |
orbit |
|
|
For Notes
![]()
![]()
![]()
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.