
Worksheet 1 Fluid flow
Name…………………………………………..class……………………..Date………………….
1. The principle of fluid pressure that is used in hydraulic brakes or lifts is that:
A) pressure is the same at all levels in a fluid
B) increases of pressure are transmitted equally to all parts of a fluid
C) the pressure at a point in a fluid is due to the weight of the fluid above it
D) increases of pressure can only be transmitted through fluids
E) the pressure at a given depth is proportional to the depth in the fluid
2. A fluid is undergoing “incompressible” flow. This means that:
A) the pressure at a given point cannot change with time
B)the velocity at a given point cannot change with time
C)the velocity must be the same everywhere
D)the pressure must be the same everywhere
E)the density cannot change with time or location
3. All fluids are:
A) Gases B ) liquids C) gases or liquids D) non-metallic E) transparent
4. Barometers and open-tube manometers are two instruments that are used to measure pressure.
A) Both measure gauge pressure
B) Both measure absolute pressure
C) Barometers measure gauge pressure and manometers measure absolute pressure
D) Barometers measure absolute pressure and manometers measure gauge pressure
5. The diagram shows a U-tube with cross-sectional area A and partially filled with oil of density ρ. A solid cylinder, which fits the tube tightly but can slide without friction, is placed in the right arm. The system is in equilibrium. The weight of the cylinder is:
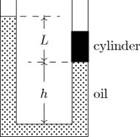
A) ALρg B) L3ρg C) Aρ(L + h)g D) Aρ(L–h)g E) none of these
6. An object hangs from a spring balance. The balance indicates 30 N in air and 20 N when the object is submerged in water. What does the balance indicate when the object is submersed in a liquid with a density that is half that of water?
A) 20 N B) 25 N C) 30 N D) 35 N E) 40 N
7. Mercury is a convenient liquid to use in a barometer because:
A) it is a metal B) it has a high boiling point
C) it expands little with temperature D) it has a high density E)it looks silvery
8. Which one of the following statements best describes fluids?
a) Fluids are liquids. b) Fluids are gases.
c) Fluids are transparent d) Fluids are gases or liquids.
e) Fluids are opaque.
9. Which one of the following substances is not a fluid?
a) mercury b) air c) water d) liquid nitrogen
e) all of the above are fluids
10. The density of mercury is 1.36 × 104 kg/m3. What is the mass of a 4.00 × 10–4-m3 sample of mercury?
a) 6.29 kg b) 5.44 kg c) 2.94 kg d) 0.0343 kg
e) 0.002 94 kg
11. Which of the following choices is equivalent to the SI unit of pressure, the pascal?
a) N/m b) N/m s2 c) kg/m s2 d) N/s e) kg m/s2
12. Complete the following statement: Pressure is a measure of
a) the force exerted by a fluid. b) the force per unit area that a fluid exerts.
c) the force per unit time that a fluid exerts. d) the impulse of a fluid.
e) the energy in a fluid.
13. Which one of the following statements best describes the pressure in a static, homogeneous liquid?
a) The pressure is the same at all points in the fluid.
b) The pressure is not dependent on the atmospheric pressure exerted at the surface of the liquid.
c) At a given depth in the liquid, the pressure is the same at all points at that depth.
d) The pressure depends on the type of liquid. The denser the liquid is, the smaller the pressure will be.
e) The pressure decreases as the depth increases.
14. Consider the drawing of the liquid within the U-shaped tube that has both sides open at the top. Is this fluid in equilibrium?
a)
Yes, the fluid must be in equilibrium. 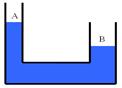
b) No, side A should be lower than side B.
c) No, side B should be lower than side A
d) No, both sides should be at the same height.
e) The answer may be yes or no, depending on the density of the fluid.
15. Which one of the following statements concerning the buoyant force on an object submerged in a liquid is true?
a) The buoyant force will increase with depth if the liquid is incompressible.
b) The buoyant force depends on the volume of the liquid displaced.
c) The buoyant force depends on the weight of the object.
d) The buoyant force depends on the mass of the object.
e) The buoyant force is independent of the density of the liquid.
16. Consider the drawing of the liquid within the U-shaped tube that has one side sealed. Is this fluid in equilibrium?
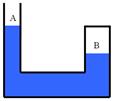
a) Yes, the fluid can be in equilibrium. b) No, side A should be lower than side B.
c) No, side B should be lower than side A d) No, both sides should be at the same height.
e) The answer may be yes or no, depending on the density of the fluid.
17. Which one of the following statements concerning the buoyant force on an object submerged in a liquid is true?
a) The buoyant force will increase with depth if the liquid is incompressible.
b) The buoyant force depends on the volume of the liquid displaced.
c) The buoyant force depends on the weight of the object.
d) The buoyant force depends on the mass of the object.
e) The buoyant force is independent of the density of the liquid.
Answers
1. B
2. E
3. C
4. D
5. A
6. B
7. D
8. D
9. E
10. B
11. C
12. B
13. C
14. D
15. A
16. B
17. B
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.