
 МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ САРАТОВСКОЙ ОБЛАСТИ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ АВТОНОМНОЕ ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ САРАТОВСКОЙ ОБЛАСТИ
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ САРАТОВСКОЙ ОБЛАСТИ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ АВТОНОМНОЕ ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ САРАТОВСКОЙ ОБЛАСТИ
«ЭНГЕЛЬССКИЙ ПОЛИТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ КОЛЛЕДЖ»
|
Рассмотрены на заседании ПЦК аэронавигации и эксплуатации авиационной и ракетно-космической техники Протокол №___ от «___»____________2025 г. Председатель ПЦК ______________/Шингалиева В.А./
Одобрены методическим советом техникума Протокол №____от «___»____________2025 г. Председатель методсовета Зам. директора по УМР ___________/Слинчук А.И./ |
|


Методические пособие разработано в соответствии с требованиями Федерального государственного образовательного стандарта среднего профессионального образования по специальности 25.02.08 «Эксплуатация беспилотных авиационных систем» на базе основного общего образования для реализации основной профессиональной образовательной программы СПО на базе основного общего образования с получением среднего общего образования.
Организация – разработчик: ГАПОУ СО «Энгельсский политехнический колледж»
Сотникова Елена Владимировна преподаватель иностранного языка ГАПОУ СО «Энгельсский политехнический колледж».
|
РАССМОТРЕНО и РЕКОМЕНДОВАНО К ИСПОЛЬЗОВАНИЮ На заседании предметно-цикловой комиссии аэронавигации и эксплуатации авиационной и ракетно-космической техники Протокол № ___ «____» __________ 202 ___ г. Председатель ____________ ______________ |
19 Main Parts of Drone: Complete Guide with Names, Functions & Diagram
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Представьте себе мир, в котором небо заполнено изящными футуристическими чудесами, бесшумно скользящими в воздухе. Эти летательные аппараты называются дронами.
Дрон — это беспилотный летательный аппарат (БПЛА) без пилота, экипажа или пассажиров на борту. Он может управляться дистанционно человеком-оператором или дистанционно пилотируемым летательным аппаратом (ДПЛА), а также обладать различной степенью автономности — от автопилота до полной автономности без вмешательства человека. Передатчик и приёмник — это основные части дрона, которые обеспечивают связь и выполнение команд. В настоящее время многие страны активно используют дроны в военных целях, для доставки товаров, в сельском хозяйстве и т. д. В результате ожидается значительный рост спроса на беспилотные летательные аппараты и их комплектующие.
В этом пособии рассмотрены различные компоненты дрона и их функции, чтобы лучше понять эту технологию.
INTRODUCTION
Imagine a world where the skies are filled with sleek, futuristic marvels silently gliding through the air. These airborne wonders are called drones. A drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. It can be controlled remotely by a human operator or a remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) or possess varying levels of autonomy, ranging from autopilot assistance to full autonomy without human intervention. The transmitter and receiver are essential drone parts that enable communication and execution of instructions. Nowadays, many countries extensively employ drones in the military, consumer, delivery, and farming sectors. As a result, the demand for UAVs and parts of a drone is expected to increase significantly.
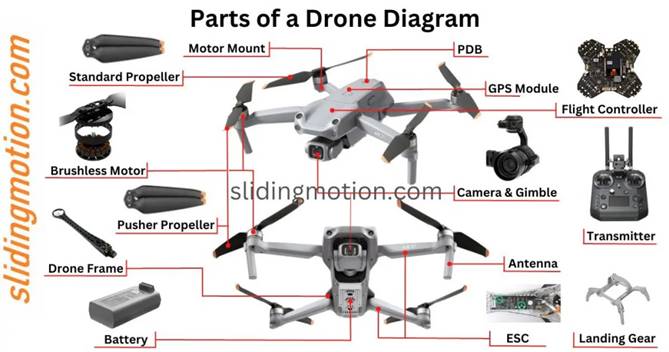
Standard propellers are the regular propellers meant for a drone to fly. The whole drone moves just because of the propeller. Two of four propellers are standard propellers that rotate to push air downward to create a lift.
Plastic is a common material for most drones. However, in recent years, many companies have been utilizing carbon fibre to make strong propellers. Carbon fibre eventually increases the cost.
Various developments are going on to make propellers more efficient and lightweight for small and big drones. So, it is necessary to check the condition and design of the propeller before the drone takes flight. Propeller guards protect these propellers to avoid damage.
The pusher propeller is the propeller that pushes the drone to fly. These propellers determine the drone’s movement, whether it is moving forward or backwards.
Propellers help cancel out motor torques during stationary flights. They are usually at the back of the drone. These propellers are also made of plastic and carbon fibre, relying on the drone’s quality and size. The pusher propeller also comes with a guard to avoid damage.
Brushless motors have a permanent magnet at the centre, which rotates around the coil. In contrast, regular motors have coils in the centre that rotate around the permanent magnet.
This motor is the best choice for the drone due to its better performance, efficiency, high speed, and performance.
These motors rotate clockwise and anti-clockwise, and the drone is dragged up. The brushless motors provide extra speed to the drone with minimum possible noise. The speed of this motor is faster, and energy loss is less due to not having the brushes rubbing against each other.
It helps to save costs and frequent maintenance. Also, it requires less energy; hence, the battery discharges much less and increases the flight timing.
Generally, the motor mount is part of the drone frame. It is a fixing arrangement of the motors. It has fewer parts present and is easy to replace.
It is a structure for landing the drone on the ground. We can see the helicopter-style landing gear in some drones. Some drones require more ground clearance, which has modified landing gear for increasing safety.
Some countries like USA and Dubai supply parcels with delivery drones throughout the country. In this case, more space or clearance is necessary for holding the parcels in landing gears.
The requirement of the landing gear varies depending on the type of drone and its applications. Not all drones need landing gear. Without it, they can land safely on the ground.
There are two types of landing gear available. The first is fixed, and the other is retractable. When it is necessary to land on the ground, retractable landing gear comes out and retracts while the drone is in the air.
The ESC has four main functions.
In modern drones, ESC is the main component. So many drone companies are doing innovations to make the ESC more efficient for high efficiency, high power,
The flight controller is the motherboard responsible for processing all the commands received from the pilot. It helps to interpret inputs such as monitoring batteries, GPS, sensors, and IMU.
It controls various features like
Flight control is the drone’s whole function.
There are two types of antennas present in the drone and its system. The transmitting antenna converts electrical signals into electromagnetic waves and radiates them. The receiving antenna converts electromagnetic waves into electrical signals.
The standard radio receiver receives the radio signal sent to the drone through the controller. The minimum number of channels to control a quad is 4, but 5 is usually recommended. We can find various manufacturers of receiver units on the market.
The function of the transmitter is to transmit the radio signal from the controller to the drone to implement various commands.
The transmitter and the receiver use a single radio signal to communicate with the drone. Each signal has a code to differentiate the signals from the other radio signals in the air.
GPS stands for the Global Positioning System, which helps to locate the precise location of the drone. It is a navigation of the drone responsible for the latitude, longitude, elevation, and compass.
With this GPS, we can track the location of the drone and its timing. It gives the drone the ability to track the earth’s surface or any other surface to maintain clearance while flying in a zig-zag way. It is done through satellites.
In some drones, we can safely return to home function when we lose the connection to the controller.
It is a power source for every part of a drone. It makes every action possible to execute. Lithium and lithium polymer batteries are a good choice due to their correct efficiency and battery backup.
The size of the battery varies depending on the drone’s size. Big drone mandates for applications like farming and delivery require big batteries with high efficiency and power backups.
The monitoring system of the drone tells about how much battery remains and how much distance the drone will fly. It also gives you an indication of when the battery comes to its critical level—all the details we can see on the controller.
The primary function of the camera is to take photographs and videos. Cameras capture and store the images and videos or send them to the controller. We can find the various types and qualities of the camera depending on the requirement.
In some drones, we can find the built-in camera, whereas, in some, it is detachable. Depending on the budget and the type of application, we have to select the camera. As we go for the high-resolution camera, the cost of the drone increases.
A gimbal is a pivoted support that permits the rotation of an object about an axis x, y, and z to stabilize the camera for better quality images and videos.
We can only take professional photos and videos if the gimble is high-grade. So, it is necessary to have a good quality gimble for the drone.
These are brushless DC motors. Its function is to smooth the horizontal and vertical directional rotations using the directional and balancing sensors.
Its primary function is to control the gimble motor for the drone position. It helps stabilize the camera in the x, y, and z directions by analyzing the data from the sensor and GPS for better image and video quality.
The function of the sensor is to collect the data and transfer it to the controller to take necessary action. We can see the various types of sensors on the drone, like motion sensors, thermal sensors, lidar, GPR sensors, tilt sensors, magnetic sensors, Lightweight Portable radiometers (LPR), etc.
These sensors sense the various parameters and send them to the controllers to take necessary action for better drone performance.
These sensors avoid the drone’s collision with any other object while flying. Ultrasonic, lidar, infrared, monocular vision, ToF (Time of Flight), and vision sensors are common examples.
Используемая литература
1. Алайчиев, У. К. Беспилотные летательные аппараты в современных вооруженных конфликтах (история, основы применения) / У. К. Алайчиев. – DOI 10.26104/NNTIK.2023.52.18.003 // Наука, новые технологии и инновации Кыргызстана. – 2023. – № 5. – С. 11-17. – URL: https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=59741976 (дата обращения: 12.12.2024). – Режим доступа: для авторизованных пользователей.
2. Дроны и беспилотные летательные аппараты / АПР: агентство промышленного развития Москвы. – Москва, 2020. – 53 с. – URL: https://leader-id.storage.yandexcloud.net/event_doc/436213/648af99336c1a573583773.pdf (дата обращения: 12.12.2024).
3. Каршов, Р. С. Классификация беспилотных летательных аппаратов / Р. С. Каршов // Проблемы Науки. – 2016. – №11 (53). – С. 38-40. – URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/klassifikatsiya-bespilotnyh-letatelnyh-apparatov (дата обращения: 12.12.2024).
4. Ковалёв, М. А. Беспилотные летательные аппараты вертикального взлета: сборка, настройка и программирование : учебное пособие / М. А. Ковалёв, Д. Н. Овакимян. – Самара: Издательство Самарского университета, 2023. – 96 с. – URL: https://repo.ssau.ru/bitstream/Uchebnye-izdaniya/Bespilotnye-letatelnye-apparaty-vertikalnogo-vzleta-sborka-nastroika-i-programmirovanie-107946/1/978-5-7883-2025-0_2023.pdf (дата обращения: 12.12.2024).
5. Моисеев В.С. Беспилотные летательные аппараты: Отечественная история создания и современная классификация. Препринт. – Казань: Редакционно-издательский центр «Школа», 2022. – 40 с. – URL: https://xn----8sbccoat3acurs.xn--p1ai/images/files/Preprint1.PDF (дата обращения: 12.12.2024).
Скачано с www.znanio.ru
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.