
VIII Municipal Scientific and Practical students Conference
of educational organizations of the city district Egorievsk
"Step into Science"
Humanitarian direction
“Little Britain in Yegoryevsk”
Author:
Baibakov Alexey Pavlovich,
Popov Pavel Alekseevich,
Grade 10,
Municipal educational
medium institution
comprehensive school №12
with in-depth
individual subjects
Scientific adviser: Zolotova Victoria Nikolaevna,
English teacher,
Municipal educational
medium institution
comprehensive school №12
with in-depth study
individual items
Table of contents:
• Title page.
• Contents.
• Introduction.
• Main part.
• Conclusion.
• References and other sources used.
• Аppendix
Introduction
We asked ourselves: If someone or something is able to copy the behavior of a person who knows hieroglyphs with 100% accuracy, does it make him Chinese, does he even make him more human. Indeed, in fact, artificial intelligence is an algorithm that, using the rules laid down in it by a person, imitates its behavior. Because of this, many people are afraid of various manifestations of artificial intelligence in their lives, because they think that this can lead to a rebellion of machines. Their phobia is also encouraged by various films and books about postapocallipsis. We decided to go deeper into the study of this issue. And to answer the main question: Can a machine think?
Project goal: to find out: can a computer have self-awareness.
Hypothesis: a computer may have conscious thoughts, emotions, and sensory perceptions similar to human ones.
Object of study: informational, mental and emotional processes in a computer
Project Objectives:
1. Using the analysis of scientific facts to refute or prove that new complex and high-speed computers will be able to reproduce all aspects of a conscious person.
2. Draw conclusions. What is a computer? A computer, or an electronic computer, is one of the most intelligent inventions of man.
Research methods: consideration of the material, conducting a survey, analysis of the necessary literature, theoretical analysis.
The history of the development of artificial intelligence
To begin with, let's decide: how to distinguish a person from a robot. A Turing test was created for these tasks. It is named after its creator and founder of modern computer science Alan Turing. Alan Matheson Turing was born in London on June 23, 1912 in the family of an official who served in India. The young man was educated at the prestigious English school of Sherborne, showing talents in mathematics and chemistry. In 1931, he entered college at Cambridge University. After completing his dissertation in 1935 on the subject of the “central limit theorem of probability theory”, he became a member of the Royal College of Science. During this period, he began to research in the field of mathematical logic. A year later, Alan wrote an article "on computable numbers, with an application to the solvability problem", in which he introduced a new mathematical concept: "abstract equivalent of an algorithm" or "computable function". Later, she received another name - "Turing Machine". The result of his research served as an impetus for the opening of discussions on the theory of automata and became the fundamental basis for digital computers that appeared in the 40s of the twentieth century. Turing continued his studies in the United States, enrolling at Princeton University. Here, under the guidance of logic and mathematician Alonso Church, he received his Ph.D. in 1938. Returning to the UK, Turing begins working with a government school of codes and ciphers. In 1939, the British War Department instructed him to unravel the codes of Enigma, a special encryption device that was used to encrypt radio communications in the German Luftwaffe and the Navy. Six months later, the Turing team developed a bomb that read almost all of the Luftwaffe radio messages. A year later, a mathematician hacked Enigma. The scientist also worked on the development of special ciphers for the correspondence of Churchill and Roosevelt in the period 1942-1943. For his services after the end of the war, he was promoted to knight-commander of the Order of the British Empire 4th class. In 1945, a mathematician was admitted to the London National Physics Laboratory. Here he led the development of the new ACE computing device. In 1947, Alan developed the "abbreviated code instructions" that marked the beginning of the use of the programming language. A year later, he was invited to the University of Manchester as the director of a computer lab where the Madame Automatic Digital Machine, a computer with the largest memory by the time, was developed. He created several programs for her using an alphanumeric code. In addition, Turing is considered the founder of artificial intelligence. The scientist created the famous Turing Test thought experiment, which seeks answers to the question "Does the machine think?". In 1951, he was elected a member of the Royal Scientific Society. In the last years of his life, he became interested in biology and worked on the creation of a chemical theory of morphogenesis. But he did not finish it, making only a few sketches. Turing was robbed in 1952. And in the course of the criminal process, he was forced to admit his unconventional orientation. In those days, it was severely condemned and punished by prison. Alan lost his job in the field of cryptography due to the censure he received. From a brilliant and sought-after person, he turned into a miserable likeness of himself. His corpse was found at home on June 8, 1954. It is believed that the great mathematician committed suicide.
Direction of research
The Turing test is an empirical test, the idea of which was proposed by Alan Turing in the article "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" (Eng. Computing Machinery and Intelligence), published in 1950 in the philosophical journal "Mind". Turing set out to determine if the machine can think.
The standard sound of the law is: “If a computer can work so that a person is not able to determine with whom he is communicating - with another person or with a machine - it is believed that he passed the Turing test”
Intelligent, human-like machines for many decades have been one of the main themes of science fiction works. Since the inception of modern computer technology, people's minds have been occupied with the question: is it possible to build a machine that could replace a person in something. An attempt to create solid empirical ground for solving this issue was the test developed by Alan Turing.
The first version of the test, published in 1950, was somewhat confusing. The modern version of the Turing test is the following task. A group of experts communicates with an unknown creature. They do not see their interlocutor and can communicate with him only through some kind of isolating system - for example, a keyboard. They are allowed to ask the interlocutor any questions, to have a conversation on any topic. If at the end of the experiment they cannot say whether they were communicating with a person or with a machine, and if in fact they were talking with a machine, we can assume that this machine passed the Turing test.
There are at least three main versions of the Turing test, two of which were proposed in the article “Computers and Mind”, and the third option, in the terminology of Saul Traiger, is a standard interpretation.
Along with the fact that there is a certain discussion whether the modern interpretation corresponds to what Turing described, or whether it is the result of a misinterpretation of his works, all three versions are not considered equivalent, their strengths and weaknesses differ.
Simulation game
Turing, as we already know, described a simple game for parties, which includes at least three players. Player A is a man, player B is a woman, and player C, who plays as the moderator, is of any gender. According to the rules of the game, C sees neither A nor B and can communicate with them only through written messages. When asking questions to players A and B, C tries to determine which of them is a man and which is a woman. The task of player A is to confuse player C so that he draws the wrong conclusion. At the same time, the task of player B is to help player C make the right judgment.
In the version that S. G. Sterret calls the “Original Imitation Game Test”, Turing suggests that the role of player A be played by the computer. Thus, the task of the computer is to pretend to be a woman to confuse player C. The success of such a task is estimated based on a comparison of the outcome of the game when player A is a computer and the outcomes when player A is a man. If, according to Turing, “the player leading the conversation after the game [with the participation of the computer] makes the wrong decision as often as after the game with the participation of a man and a woman,” then we can say that the computer is intelligent.
The second option was proposed by Turing in the same article. As in the "Initial Test", the role of player A is played by the computer. The difference is that the role of player B can be played by both a man and a woman.
“Let's look at a specific computer. Is it true that by modifying this computer in order to have enough space for data storage, increasing its speed and asking him a suitable program, it is possible to design such a computer so that it satisfactorily plays the role of player A in a simulation game, while the role of player B is a man doing? ”- Turing
In this version, both players A and B try to persuade the lead to the wrong decision.
The main idea of this version is that the purpose of the Turing test is to answer not the question of whether the machine can fool the host, but the question of whether the machine can imitate a person or not. Although there is debate about whether this option was implied by Turing or not, Sterrett believes that this option is implied by Turing and thus combines the second option with the third. At the same time, a group of opponents, including Trader, does not think so. But this still led to what might be called a “standard interpretation.” In this embodiment, player A is a computer, player B is a person of any gender. The leader’s task now is not to determine which of them is a man and a woman, and which of them is a computer, and which is a person.
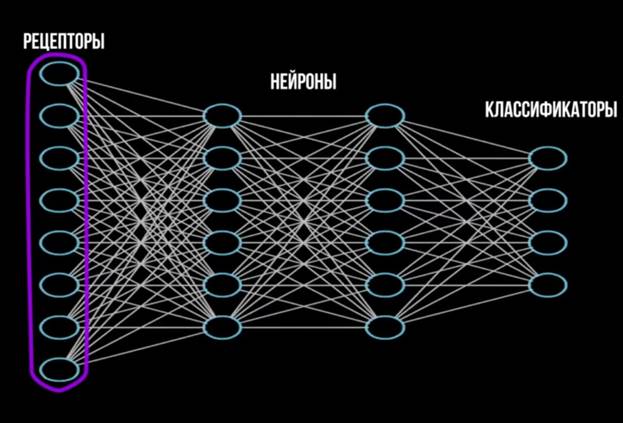
The first neirokompyuter appeared in 1958, he received the name mark 1. His brain consists of a layer of receptors, neurons and classifiers. (see Appendix 1)
Receptors receive a signal, as the retina of our eye does, and transmits it to neurons. Each receptor is associated with each neuron. Because of this, so many wires. (see Appendix 2)
Neurons summarize all signals and transmit the signal to the classifiers. They recognize images. Each image has its own classifier. The strength of the connection between receptors and neurons, in the learning process, is changing. The connections leading to the correct recognition are strengthened, to the wrong one weakened. As a child, over time, he realizes that the iron is hot and the ice cream is cold. So mark 1 eventually learns to recognize numbers and letters. But now this is not difficult, since in 2000 there were quite powerful computers that allow non-networks to solve more complex problems. Now neural networks consist of many layers.
The first layer only recognizes color and blurry silhouettes. The second layer recognizes elements and textures. The third mechanisms, parts of the body of people and animals. The fourth already classifies the objects, and understands what they show him. In fact, non-network is just a program, but it can learn itself. If the decision is correct, the program is encouraged, if not correctly, the strength of the neural connections is reduced.
Self-learning mechanisms work as follows: one neural network is the generator of the task, and the second checks the correctness of the execution of the same task. For correct or incorrect answers, a person encourages the network or reduces the strength of neural connections. Subsequently, neural networks go on to independently change their code, i.e. to self-study.
Artificial intelligence has several levels of “development”: at the first, artificial intelligence learns to recognize objects, to distinguish, for example, yellow from red or tomato from a person. At the second level of artificial intelligence, it begins to observe the actions of others, memorize them and repeat them later. At the last - third level, artificial intelligence is already moving into a “self-learning mode”, that is, it is developing on its own, gaining more and more “knowledge”.
In our world, artificial intelligence is increasingly being used in various areas of society.
You never paid attention to the fact that your favorite application picks music to your liking, that maps build the fastest route, that advertising becomes personalized, all this is the work of artificial intelligence. It simplifies our lives, makes the media space around us personalized.
In medicine, with the help of artificial intelligence, healthy patients have found propensities for very dangerous diseases such as cancer and oncology. But if doctors could detect these diseases, though at later stages, then they certainly could not detect a tendency to mental illness in people, and artificial intelligence could, he assigned part of the patients to a group prone to the development of schizophrenia and a split personality. Scientists have no idea how the machine did this, but its forecast turned out to be correct. In humans, this ability is called intuition.
Also, intuition helps people in games with incomplete information, such as poker, blackjack and DotA 2. Previously, artificial intelligence triumphed over people in games with full information, we have long been no champions in games such as chess, checkers and backgammon. But thanks to self-learning mechanisms, the machine can simulate 180 years of play in 1 day, and to beat the strongest player in DotA 2, the machine took only 2 weeks of training.
Now there are artificial intelligences capable of creating images that do not exist. The machine was able to deceive experts from people who could not distinguish a photo of a real person from a photograph taken by artificial intelligence. He is also able to recreate the video.
In these cases, one artificial intelligence plays the role of a counterfeiter, and the other is an expert on data verification.
But artificial intelligence is also easy to fool. So the voice assistant Alice, the development of Yandex Corporation, can perceive the commands sent at the ultrasonic frequency. That is, the offender can pretend to be a team in the US frequency and send it to your phone, thereby hacking it and getting full access to it
Artificial intelligence also recognizes the noise that is invisible to the simple eye in the picture. So, the experts managed to mislead one of the best non-networks by adding noise to the photo of the panda, due to which it was recognized as a hot dog (see Appendix 3)
Artificial intelligence is also used in mechanical engineering. Companies such as BMW Mercedes and Porsche have long been using blind spot monitoring and adaptive cruise control in their cars. Their action is based on the analysis of surrounding objects using a variety of sensors. After that, the information received information is processed using artificial intelligence. If he notices the danger, he will take the actions laid down in him by the program. For example, a warning signal sounds or the machine starts to brake itself. And a company like Tesla introduces a full-fledged autopilot into its cars, its operation is based on the same principles that were mentioned above.
But in history, there were some sad cases with artificial intelligence. For example, on March 19, 2018, an unmanned vehicle shot down a cyclist to death. So the first lethal accident occurred with the participation of artificial intelligence. But there are no perpetrators of this accident, as the cyclist ran onto the road in the wrong place, and the autopilot could not do anything.
To avoid such cases, we must teach artificial intelligence to act correctly in every situation. In fact, we must develop a system of fines for autopilot, for example: bring down a dog 5 points, a person 100 points, a woman with a child 300 points.
This means that it will act exactly as we teach it, that is, on the shoulders of the developers of the rules for and lies a huge responsibility, responsibility for people's lives.
People who are engaged in the development of artificial intelligence answer a question about the uprising of machines with genuine laughter. They understand that artificial intelligence is free in its actions, only in a certain area that people assigned to it. It is also limited by a number of rules that it cannot change. Unfortunately, or fortunately, machine revolts, at least in the near future, cannot happen. And to answer the question: can a machine think much more difficult. It is true that the machine itself can make decisions based on algorithms. So, she can only imitate human behavior, but unfortunately she cannot think, he simply analyzes a huge amount of information, and follows thousands of rules.
Poll
We conducted a survey among students in grades 6, 7, and 10 and obtained the following results:
1) Do you know what artificial intelligence is?
76% know what AI is
24% do not know
2) Do you know any examples of artificial intelligence?
67% don't know AI examples
33% may post AI examples
3) Do you think that artificial intelligence can become smarter than humans?
70% think AI can be smarter than humans
30% think that AI cannot be smarter than humans
4) Do you think that artificial intelligence can have human feelings?
82% think AI cannot have people's feelings
18% think AI can have people's feelings
5) Do you think robots will take over the world?
24% think AI will take over the world
37% are not sure about this
39% think that all lies
Conclusion
After conducting a study, we found that computers can have neither thoughts, nor feelings, nor emotions. Thoughts, feelings and emotions are synapses between neurons in the brain. Neural computers have not yet been invented, and simple computers can only portray emotions. Computers do not have consciousness due to insufficient technology. Most modern robots do not recognize themselves, although they can say: "I - this is me." But this is set in them by the program. If in the future there will be computers with developed artificial intelligence, then in order for it to have real, similar to human thoughts, feelings and emotions, then the computer must have the structure of a real biological brain, made of real neurons. In addition, in order to prove that a computer has a mind and self-awareness, it needs to pass the Turing test completely. Not a single computer in the world has passed it at the moment. Summing up, we want to say that the world for at least twenty or more years will not see truly intelligent computers.
List of references
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2YM-qQrXwcg
https://promdevelop.ru/iskusstvennyj-intellekt/
https://yandex.ru/images/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5Xiv-rHc5qo
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EFd1uWNT0AU
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r0aK7josHMM
Аppendix 1
Аppendix 2

Аppendix 3
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.