
Публикация является частью публикации:
 ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF ACTUAL PROBLEMS OF MODERN SCIENCE,
EDUCATION AND TRAINING. 2019-IV ISSN 2181-9750
ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF ACTUAL PROBLEMS OF MODERN SCIENCE,
EDUCATION AND TRAINING. 2019-IV ISSN 2181-9750
UDC: 42/48+531.1+741
TEACHING GERMAN PREPOSITIONS WITH MNEMONICS
Xasanova Ozoda Qurvonali qizi Assistant of Faculty Productions
management of Fergana
polytechnic institute
e-mail: laie-91@mail.ru
Abstract: This article highlights the specifics of teaching and learning German prepositions using mnemonics. Unlike traditional teaching and learning, modern use of mnemotechniques is considered to have a stronger effect on language learning. At the same time, not the teacher, but the learner becomes the focus of the learning process. The lessons will be interesting, effective and it gives opportunity to memorize the new information you have learned.
Key words: teaching prepositions, mnemotechniques, movement, painting, tutorial process, memory.
Annotatsiya: Ushbu maqola nemis tilidagi ko`makchilarni mnemotexnika yordamida o`rgatish va o`rganishning o'ziga xos xususiyatlarini yoritadi. An'anaviy o`rgatish va o`rganish uslubidan farqli o'laroq, mnemotexnikadan zamonaviy foydalanishni til o`rganish samarasiga ta’siri kuchliroq hisoblanadi. Shu bilan birga dars jarayonlarining markazida o`qituvchi emas, til o`rganuvchi bo`lishiga olib keladi.
Darslarni qiziq, samarali bo`lishi va muhimi o`rganilgan yangi ma’lumotlarni yodda saqlanishiga sharoit yaratiladi.
Kalit so'zlar: ko`makchilarni o`rgatish, mnemotexnika, harakat, rasm, dasr jarayoni, xotira.
Аннотация:В этой статье освещаются особенности преподавания и изучения предлогов в немецком языке с использованием мнемоники. В отличие от традиционного преподавания и обучения, современное использование мнемотехники, считается что, сильнее влияет на изучение языка. В то же время становится центром в учебном процессе не учителя, а ученика. Уроки будут
MODERN PROBLEMS OF PHILOLOGY AND LINGUISTICS 1
интересными, эффективно и важно, чтобы иметь в виду новую информацию, которую вы узнали.
Ключевые слова: преподавание предлогов, мнемотехника, движение, рисунок, учебный процесс, память.
Teaching foreign languages is becoming more and more common trend in nearly all spheres of education. New methods and technics are coming to tutorial process. Both, German teachers and students often express the complexity of German grammar. This is true, but with the help of new techniques we can solve these problems or at least avoid them. The following are some of the problems we have in learning and teaching German prepositions and addressing them.
One of the biggest problems with the teaching and learning of prepositions is that the facilitators are quite uncertain and lack clear guidelines for their application.
In describing the difficulty of teaching and learning preposition as problematic as numerous analyses of the linguistic output of learners have revealed. Furthermore, with regard to the use of preposition in German, rules that govern the usage of preposition limits the usage of certain preposition to be usable for many function. It is stated that in German, prepositions appear in adjuncts, they mark the arguments of predicates and they combine with other parts of speech to express new meaning. The preposition and the function is not memorable to language learners. There are quite a number of them to be memorized with their function. It is said that usage errors involving prepositions are among the most common types seen in the writing of non-native German speakers. Furthermore, Horst Sperber (1989) [1] is quite famous scientist and mnemonic researcher for German as a foreign language. One way to make language learners aware is by using language learning strategy namely the use of mnemonic technique. A learning strategy is an individual’s way of organizing and using a particular set of skills to learn content or accomplish other tasks effectively and efficiently in both academic and non-academic settings. Peter Heinrich (2012) [8] is most famous internet blogger and German teacher for learning and teaching German prepositions with mnemonics. He has an internet website for learning German language.
There is also a support group in German called “Wechselpräpositionen”. They are used in both Dative and Accusative cases. Mnemonic body movements can also be used to memorize them: [6]

Pictures depict the prepositions auf, über, unter, neben, an, zwischen, vor, hinten, in. In their teaching, teacher should repeat these actions several times, making all students stand up. It is also required to pronounce the loudspeakers in accordance with the movement. Goethe-Institut teachers also use this exercise during their workouts. It is known that these prepositions are used in both Dative and Accusative cases. There are also different ways to differentiate when they are used with Dative and when used with Accusative. The most important of these are visualization:
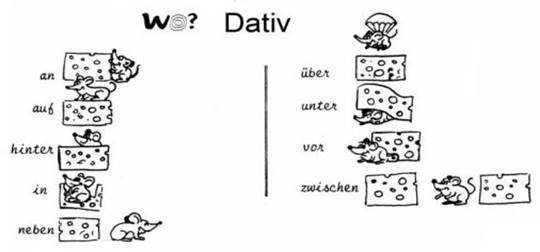
As you can see from this picture, if wo / where there is a word that answers the question, these prepositions are supported by Dative.
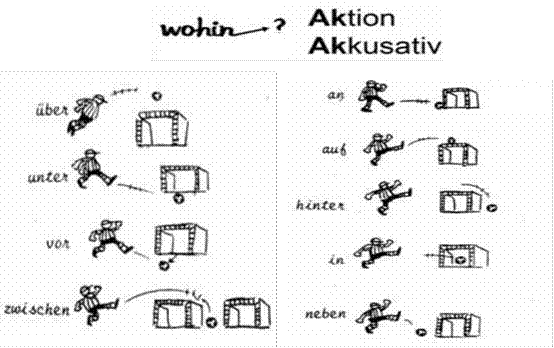
For Accusative, the wohin / where to needs to be used, that is, the direction of the movement.
The following pictures can also be used to learn these prepositions: [7], [1]
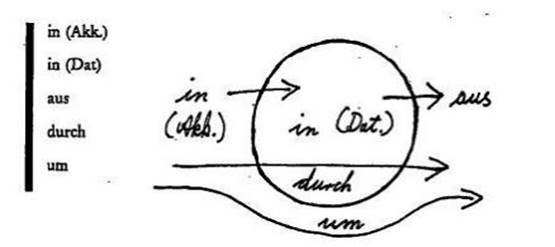
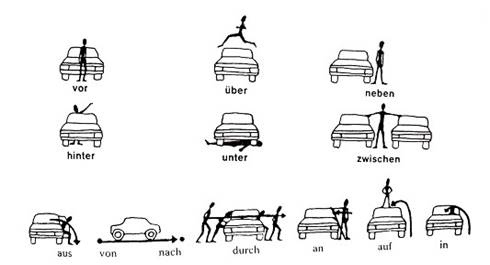
Temporal prepositions also mislead learners. Rhythmic poems can be used to remember them. In addition, the use of a picture or form can also make it easier to remember:[6]

As you can see, the words wann / when answering the question, if the month is the name with the "im" ( in + dem = im), if the day of the week with the "am" ( an + dem = dem), the hour is used with the preposition"um". In order to rhyme with these words, each of them added a "p" sound, resulting in a "pim-pam-pum" rhythm. It is pleasant and easy to remember.
For many foreign German teachers, the use of the following poetic rhythms for Dative supporters is as follows:
Herr AusBeiNach und
Frau von SeitZuMit
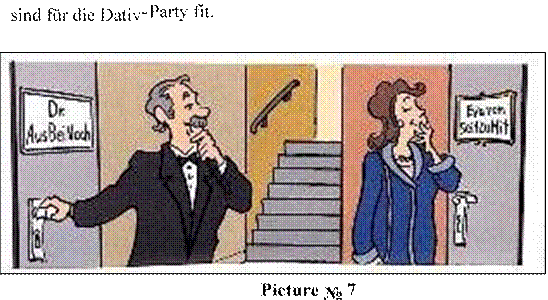
You can also see the appropriate image.
Using of the following imageis also useful:

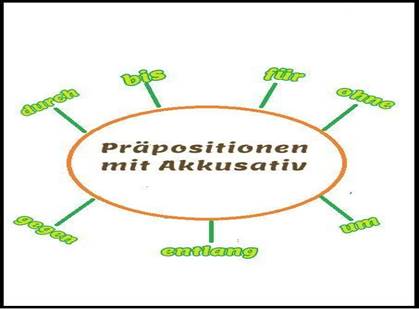
It is necessary for language learners to remember that the most effective way to create pictures themselves. One of the easiest ways to accomplish this task is to use anassociograms. For example, the language learners can provide the following associograms for Accusative prepositions: [2]
:
The Mind Map, which is a bit more complex than the associograms, can be used to describe all prepositions: [9]
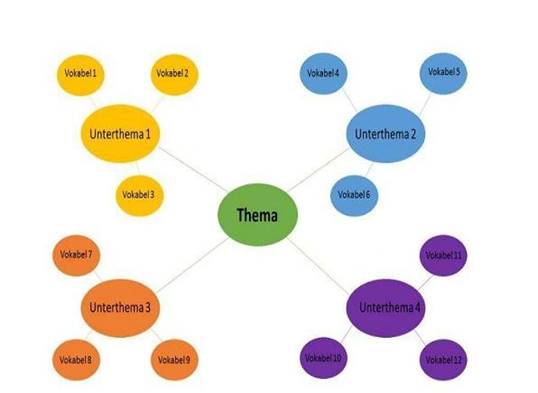
In this case, the main theme is Prepositions and the other four sub-themes need to write each kind of prepositions, and its branches will have to write the sub prepositions. Such a scheme can also be used to duplicate or strengthen all prepositions once they have been studied.
The research based on descriptive and comparative methods of analysis.
Firstly, information has been obtained through the research that has been done before. Then, appropriate information has been completed in the literature review.
For the benefit of analysis of alternative ways of teaching prepositions, the researcher collected data on the basis of questionnaires from teachers and observations of teachers' ways of assessing students' knowledge. For the research methodology, the researcher gained data collection from the teachers and students of Fergana polytechnic Institute during 2018-2019 study years.
Diagram 1: Using mnemonics in teaching foreign languages.
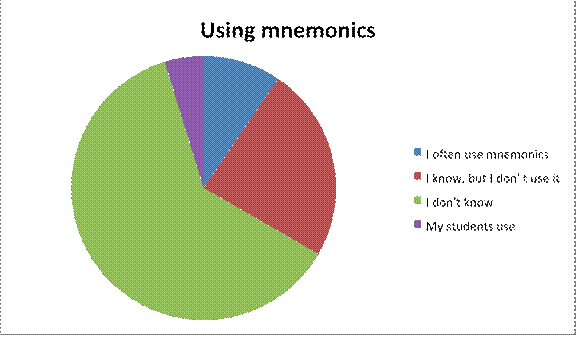
From the diagram we can see only some participants know about mnemonics and use it in their lessons. Some teachers know mnemonics but they don’t use it. The most common answer was “I don’t know”, it means they don’t use mnemonics. Little part of teachers say “My students use mnemonics”. It means, they have heard about mnemonics from their students.
|
|
Students quantity |
percent % |
|
interested |
42/48 |
87,5 % |
|
not interested |
4/48 |
8,3 % |
|
neutral |
2/48 |
4,1 % |
From the table we can see, that 87,5 % participants are interested in using the mnemonic in learning German prepositions.
Table 2: Effect of using mnemonics in teaching and learning prepositions:
Results of students test before using mnemonics:
|
Students quantity |
percent of right answers % |
percent of false answers % |
|
48 |
70 % |
30 % |
Table 3: Effect of using mnemonics in teaching and learning prepositions:
Results of students test after using mnemonics:
|
Students quantity |
percent of right answers % |
percent of false answers % |
|
48 |
90 % |
10 % |
From the tables 3 and 4 we can see result of using mnemonics.
This is an important innovation that will help language learners learn German prepositions more effectively and in an interesting way. Mnemonic learning strategy such as communicative method is a potentially effective learning method because it provides a novel and different way of learning components of German language. The use of this learning method should be encouraged in the classroom as this learning strategy is useful for learners and for teachers too. It makes it easy for students to remember all prepositions.
[1] H.Sperber. Mnemotechnik im Fremdsprachenerwerb. 1989.
[2] K. Sojkova. MNEMOTECHNISCHE HILFSMITTEL IM UNTERRICHT
DER DEUTSCHEN SPRACHE AN DER МITTELSCHULE DIPLOMOVÁ
PRÁCE. Plzeň 2013.
[3] METZIG, Werner, SCHUSTER, Martin, Lernen zu lernen: Lernstrategien wirkungsvoll einsetzen, Veröffentlicht von Springer, 2005. ISBN 3540260307
S. 56-59
[4] Nordkämper-Schleicher, U. (1998). Besser Behalten: Mnemotechniken beim Sprachenlernen am Beispiel "Deutsch als Fremdsprache" für
Erwachsene. Dissertation. Pädagogische Hochschule Freiburg. S.85
[5] Possin, W. (2003). Alles im Kopf: Mit Merktechniken zum
Supergedächtnis. München: mvg Verlag.
[6] https://www.google.com/search?q=mnemotechniken_deutschlehrerta gbcn1&rlz=1C1GGRV_enUZ783UZ783&oq=mnemotechniken_deutschlehrert agbcn1&aqs=chrome..69i57.1789j0j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8
[7] Heyd. Verbildlichung der Bedeutung von den Präpositionen in, aus, durch, um. Quelle: 1990. B. 98
[ 8] https://www.beste-tipps-zum-deutsch-lernen.com/author/web70/ bekommen am. 7.08.2019. 12:15
[9] A.Ščerbinska. EINSATZ VON MNEMOTECHNIKEN FÜR EFFEKTIVEN WORTSCHATZERWERB IM DAF-UNTERRICHT FÜR
ANFÄNGER DIPLOMARBEIT. Riga 2016
[10] M. Brezović. Umfrage zur Verwendung der Mnemotechniken im DaF-
Unterricht. Diplomski rad. Zagreb. 2015
MODERN PROBLEMS OF PHILOLOGY AND LINGUISTICS
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.