
What is a CPU? Core Function and Purpose
 The CPU acts as the
"brain" of any computing system, from smartphones to supercomputers.
Its primary purpose is to execute instructions that make up computer
programs.
The CPU acts as the
"brain" of any computing system, from smartphones to supercomputers.
Its primary purpose is to execute instructions that make up computer
programs.
It performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output operations, enabling software to run and users to interact with their devices seamlessly. Without a CPU, your digital world would simply not exist.
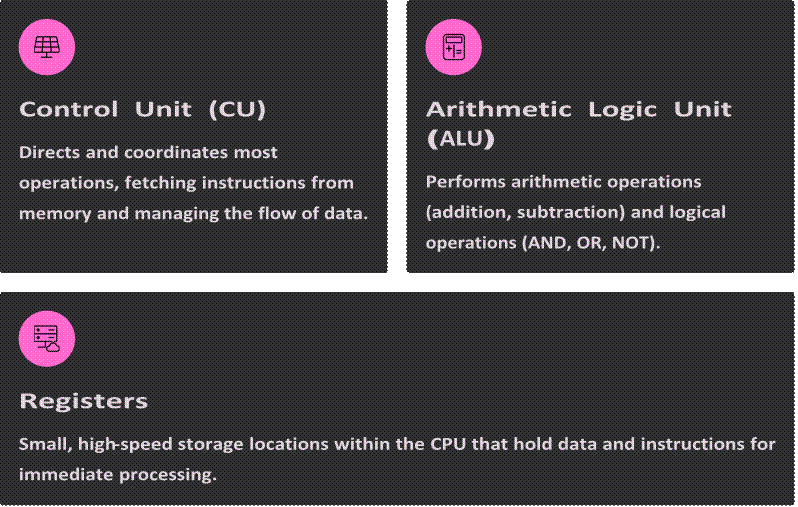
 Main Components:
Control Unit, ALU, Registers
Main Components:
Control Unit, ALU, Registers
The CPU orchestrates all computer operations through several key internal components working in harmony.
How it Works: The Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle
The CPU continuously repeats a fundamental sequence known as the Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle to process instructions.
![]()
01 02
 |
03
The CPU performs the operation specified by the instruction, such as an arithmetic calculation or data movement.
Clock Speed: GHz and Instruction Processing
 Clock speed, measured
in Gigahertz (GHz), indicates how many cycles per second the CPU can perform. A
higher clock speed generally means the CPU can process more instructions per
second.
Clock speed, measured
in Gigahertz (GHz), indicates how many cycles per second the CPU can perform. A
higher clock speed generally means the CPU can process more instructions per
second.
While crucial, clock speed isn't the sole determinant of performance; architecture, cache, and core count also play significant roles in overall processing power.
Cores and Threads: Parallel Processing Power
Modern CPUs utilize multiple cores and threads to significantly enhance performance through parallel processing.

More cores and threads allow a CPU to handle multiple applications or complex tasks simultaneously, greatly improving multitasking and demanding workload performance.
CPU Cache: L1, L2, L3 - Speed vs. Size
CPU cache is a small, ultra-fast memory that stores frequently accessed data and instructions, reducing the time the CPU spends waiting for data from main memory (RAM).

This hierarchical structure ensures that the CPU has rapid access to critical data, boosting overall system responsiveness.
Major Manufacturers: Intel vs. AMD
The CPU market is largely dominated by two technological giants, Intel and AMD, each pushing the boundaries of innovation.

|
Intel Known for strong single-core performance and long-standing industry presence. Intel CPUs are widely used in enterprise and consumer markets. |
AMD Gained significant market share with competitive multi-core performance and value. AMD's Ryzen series has been particularly impactful. |
Their intense competition drives advancements in processor technology, benefiting consumers with better performance and more choices.
CPU in the Ecosystem: Connection to RAM and Motherboard
The CPU doesn't operate in isolation; it's intricately connected to other vital components that form the computer's ecosystem.
 CPU
CPU Processes data and
executes instructions.
Processes data and
executes instructions.
Motherboard
The central hub, connecting the CPU to all other components via buses and sockets.
Random Access Memory, provides fast, temporary storage for data and programs the CPU needs to access quickly.
This interconnected system ensures efficient data transfer and overall system functionality, making all parts work together seamlessly.
Evolution and Future of CPU Technology
From humble beginnings to powerful multi-core processors, CPU technology has undergone a remarkable transformation, and its evolution continues at an astonishing pace.
 Early Days
Early Days
Single-core, low clock speeds, basic instruction sets (e.g., Intel 4004).

Multi-core,
hyper-threading, integrated graphics, advanced cache systems.
AI acceleration, specialized chips (e.g., neural processing units), heterogeneous computing.
Quantum computing, neuromorphic chips, even greater integration and efficiency for a connected world.
The relentless pursuit of speed, efficiency, and new computing paradigms promises an exciting future for CPU development.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.