
Министерство образования и науки мурманской области
Государственное автономное профессиональное образовательное учреждение
«Мурманский строительный колледж им. Н.Е. Момота»
Учебное пособие по страноведение
для технических специальностей
«How well do you know Russia and
English- speaking countries? »
Мурманск, 2021
Пояснительная записка
Учебное пособие по страноведение для технических специальностей «How well do you know Russia and
English- speaking countries?» представляет собой курс по изучению географических, политических, социально - экономических и культурных особенностей России и стран изучаемого языка.
Новые политические, социально - экономические и культурные реалии в России и во всем мире, влияние технологических достижений цивилизации на развитие мировой языковой индустрии потребовали расширения функций иностранного языка как учебного предмета.
В настоящее время в мировой практике обучения языкам ставятся задачи обучения иностранному языку как средству межкультурного общения, как способу познания достижений национальной и общечеловеческой культуры, способу осмысления себя гражданином своей страны и членами мирового сообщества.
Курс страноведения способствует развитию у студентов способностей использовать иностранный язык как инструмент общения в диалоге культур и цивилизаций современного мира. Он предполагает взаимосвязанное коммуникативное и социокультурное развитие обучающихся средствами иностранного языка для подготовки к межкультурному общению в сфере послешкольного образования, молодежного туризма, использование иностранного языка как инструмента общеевропейского и общепланетарного сотрудничества, способа билингвистического и бикультурного саморазвития. Курс страноведения предполагает взаимосвязанное коммуникативно-речевое, социокультурное и языковое развитие студентов. Он систематизирует языковые и социокультурные знания, приобретенные на более ранних этапах обучения, способствует углублению знаний о лингвокультуроведческой вариативности английской речи, развивает умения использовать иностранный язык как инструмент межкультурного общения.
Коммуникативное и социокультурное развитие школьников средствами языков международного общения направлено на:
➢ Формирование и развитие билингвистической коммуникативной компетенции, необходимой для коммуникативно приемлемого общения на иностранном языке;
➢ Культуроведческое обогащение обучающихся по принципу расширяющегося круга культур;
Изучение страноведения приобщает учащихся к культуре другого народа, делает изучение английского языка более привлекательным, расширяет кругозор, обогащает активный и пассивный словарь. Одновременно обучение страноведению способствует более точному и адекватному пониманию носителей другой культуры.
Данный курс рассчитан на обучающихся 2-3курсов среднего профессионального учебного заведения, учитывает их возрастные особенности, общеобразовательный уровень и языковую подготовку.
В учебном пособии представлены разнообразные упражнения, которые способствуют развитию навыков работы с текстом, заполнения различных таблиц, написания сочинения.
В преподавании данного курса большая роль отводится межпредметным связям иностранного языка с такими курсами, как география, история, литература, в ходе изучения которых учащиеся знакомятся с историческими особенностями, географическим положением, экономикой, литературой стран изучаемого языка.
Курс страноведения обеспечивает целостность системы знаний о странах изучаемого языка и способствует комплексной реализации целей обучения иностранному языку: воспитательной, образовательной, развивающей и практической.
Цели курса:
➢ Дальнейшее совершенствование ЗУН учащихся в зонах рецептивного и продуктивного владения всеми видами речевой деятельности на английском языке;
➢ Расширение кругозора учащихся за счет сведений о странах изучаемого языка, науке, культуре, искусстве, истории народа, быте, экономическом развитии, достопримечательностях, традициях;
➢ Обучение грамматическому и лексическому варьированию английской речи в рамках изученных разговорных тем в ситуациях повседневно -бытового, административного, учебного общения;
➢ Ознакомление с социокультурными особенностями, обучение речевому поведению на английском языке в условиях формального и неформального общения;
➢ Изучение общественной жизни и культуры Великобритании и США как члена мирового сообщества;
➢ Формирование системы мировоззренческих взглядов интернационалистической направленности, решение задач эстетического воспитания;
➢ Формирование логического мышления учащихся, развитие познавательного интереса;
➢ Развитие интеллектуальных умений школьников при сборе, обработке и интерпретации различных видов культуроведческой информации;
➢ Стимулирование школьников к осознанию себя как носителя определенных социокультурных взглядов.
Обучение иностранному языку как средству международного общения тесно взаимосвязано с его активным использованием как инструмента познания мировой культуры, национальных культур стран изучаемого языка.
Курс страноведение состоит из трех больших модулей, которые разделены на темы, согласно рабочей программе. Все модули построены по единому принципу и охватывают темы географическое положение, политическое устройство, символы государства, известные люди, традиции, образование.
Работа над пособием будет продолжена.
Организация-разработчик: ГАПОУ МО СПО «Мурманский строительный колледж им. Н.Е. Момота»
Разработчики:
Вдовина И.А., преподаватель Мурманского строительного колледжа
Ерина А.Н., преподаватель Мурманского строительного колледжа
|
Рассмотрена и одобрена предметно-цикловой комиссией «Филологические дисциплины» Председатель Петрова О.М. Протокол № _____ от «___» _______________ 2022 года. |
Рекомендована Научно-методическим советом ГАПОУ МО «МСК».
Заключение Научно-методического совета №_____ от «____»____________ 20__ г.
Содержание:
|
|
Themes |
Pages |
|
|
The Russian Federation |
|
|
1 |
The tsars of Russia |
2 |
|
2 |
The national symbols of the Russian Federation. |
3-5 |
|
3 |
Geographical position of the Russian Federation |
6-10 |
|
4 |
The Political system of the Russian Federation.. |
11-15 |
|
5 |
Famous Russian cities |
16-20 |
|
6 |
Geographical position of our region. Murmansk. |
21-23 |
|
7 |
Famous people |
23-26 |
|
8 |
The system of education |
27-28 |
|
9 |
Holidays and traditions |
29-31 |
|
|
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland |
|
|
10 |
Geographical position of the United Kingdom and Northern Ireland |
33-34 |
|
11 |
The Political system of the UK. The Royal family. The national symbols. |
34-43 |
|
12 |
London. The biggest cities. |
43-46 |
|
13 |
The system of education |
47-52 |
|
14 |
Holidays and traditions |
52-53 |
|
15 |
Famous people |
54-56 |
|
|
The United States of America |
|
|
16 |
Geographical position of the United States of America |
56-57 |
|
17 |
The Political system of the USA. The White House. |
57-61 |
|
18 |
The system of education |
61-62 |
|
19 |
Holidays and traditions |
62-66 |
|
20 |
Famous people |
66-68 |
I. THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
The tsars of Russia
The first tsar of Russia was Ivan IV
(Ivan the Terrible) who was crowned in 1547. He was fond of impaling people,
he also boiled thousands of people in oil, and killed estimated 60 000
during his reign. He was accused of killing his own son and he is still
considered to be the cruelest Russian tsar. However, many defend his deeds on
the ground of living in cruel times. But we should mention that Ivan IV was
not only famous with his cruelty and violence, there were some positive facts
connected nowadays with his name. First printed books and the first pharmacy
appeared in his times. During his reign the first fire brigade was created but
before the previous rulers considered fire the act of God and didn’t allow put
it out. Ivan IV also created the first official Russian Secret Police.

The most famous Tsarina was Catherine the Great. The longest ruling Tsarina wasn’t even Russian, she was Prussian princess who married into Romanov family. This powerful woman forced her husband to abdicate and she is considered to be involved in his murder. But besides all these negative facts Catherine the Great will be always remembered for her reforms and love of learning.
The last tsar of Russia was Nikolas
II who became the Tsar at the age of 26. When he was asked about Russian
policies he was known to say- “Ask my mother”. He is best known for completing
the Trans-Siberian railroad started by his father. Nikolas II instigated the
war with Japan.
He is characterized with incompetent handling of Russian army in World War I and mishandling Bloody Sunday riot that led to the death of thousands of people. During the Bolshevik Revolution of 1917 he was forced to give up his crown to save his life, but was later executed anyway with his entire family.
Task 1. Find all the forms of the Passive Voice in the text
Task 2. Try to make up sentences using these words: powerful, mishandling (неумелое ведение), reforms, impale(сажать на кол), abdicate(отрекаться), boil, deeds(поступки), violence, instigate(разжигать (войну)), to be involved.
Task 3. Ask 5 special questions to the first passage, 5 general questions to the second one and 2 who-questions and 3 tail questions to the last passage.
Task 4. What other Russian tsars do you know? Speak about them
THE NATIONAL SYMBOLS OF
THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
Key words:
Orb- шар, сфера, земля
Scepter- скипетр
Sickle – серп
Wreath – венок
Claw – коготь
Decline – падение, закат
Decree- декрет, указ
Ensign – знамя, флаг
Stripes –полосы
Coat of Arms – герб
Slavic - славянский
State Emblem is a symbol of a country. It may be different in shape and colour. It may be state, royal, town, region and family.
The original State Emblem of Russia shows St. George, the patron saint of Moscow and the Russian State since the 13th century, with the double headed eagle as a supporter. The Russian national coat of arms changed with the flow of time. Every era introduced its own elements to the coat of arms. The orb and scepter were also added in the claws of the eagle as symbols of sovereignty of the czars.
After the revolution in 1917, the State Emblem of the Russian Socialistic Federal Soviet Republic was adopted on the 10th of July 1918. The description is as follows: "Against the red background above a rising sun, a golden sickle and hammer, placed crosswise, handles downwards, circled by the ear wreath bearing the sign: a)The Russian Socialistic Federal Soviet Republic; b) " Proletarians of all countries unite!"
After the decline of the Soviet Union new State Emblem was considered necessary. By the presidential decree of November 30, 1993 new National Coat of Arms was adopted.
Task: Try to make up question to the given answers::
1. A symbol of a country
2. The patron saint of Moscow
3. Its own elements to the coat of arms.
4. In the claws of the eagle
5. After the revolution in 1917
6. new National Coat of Arms
Task: make a list of key words which help you to retell the text and retell it.
National Flag.
On the 20th of January 1705 Peter I adopted merchant flag. But this flag was naval ensign since 1693 (without official adoption). Originally the civil ensign, the tricolour was officially recognized for use on land on 7 May 1883. In 1917 the state flag is red one with golden letters “USSR”.
In 1924 instead of “USSR” appeared a golden sickle and hammer with a red star. In 1991 the USSR flag was replaced by the RF flag-white, blue and red.
On the 25th of December 2000 the Federal Law On National Flag of Russia was adopted. This document governs that «National Flag is a rectangular banner, which consists of three equal horizontal stripes: the top one is white, the middle one is blue, and the bottom one is red. The width of the flag is related to length as 2 to 3» What do the colours mean? Meaning of the current flag: white: nobility, frankness; sky-blue: loyalty, honesty, irreproachability, chastity; red: courage, self-sacrifice, generosity, love.
In Russia the white color symbolizes generosity and frankness; blue — loyalty, honesty, faultlessness, wisdom; red — courage, magnanimity, love. The Russian tradition may have the following interpretation as well: red colour is associated with Russian people, blue — with the Ukrainians, and white — with the Belo Russians. So, the use of these three colours has a long history in Slavic states, mean the sacred union of the Slavs with a unique cultural heritage of each nation.
Task 1: Decide if the sentence is true or false, don’t forget to correct the false ones.
1. In 1705 Peter I adopted the 1st national flag.
2. In 1917 the state flag is red one.
3. In 1992 the national flag is white, blue and red.
4. White colour means nobility and frankness.
5. Blue colour means loyalty, honesty, irreproachability, chastity
6. Red colour means courage, self-sacrifice, generosity, love.
Task 2: Answer the questions
1. Does the national flag have a long and interesting history?
2. What colour was the flag in 1917?
3. Does the use of these three colours have a long history in Slavic states?
4. May the Russian tradition have the other interpretation of these three colours?
“The National Anthem of Russia”
Key words:
anthem – гимн
highlight – событие
moving – трогательный
complex – сложный
member states – государства-члены
adopt – принимать
collapse – распад
piece of music – музыкальное произведение
failed to inspire – не вдохновила
reinstate - восстановить
Text “National song”
One major cultural highlight of the closing ceremony of the 2014 Sochi Winter Olympics was a large group of children singing Russia’s moving National anthem. Formally known as “The State Anthem of the Russian Federation”, this powerful patriotic song was adapted from the National Anthem of the Soviet Union, composed by Alexander Alexandrov with original lyrics by Sergey Mikhalkov and Gabriel El-Registan.
The history of national anthems in Russia is a bit complex. Before 1944, Russia and all other member states of the Soviet Union considered the song “The Internationale” as the national anthem of the USSR. At that point, the USSR saw a need for a national song that spoke more about the Soviet experience and the National Anthem of the Soviet Union was adopted.
After the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia adopted a new instrumental piece of music as their national anthem. It was composed by Mikhail Glinka and titled “Patrioticheskaya Pesnya”. When that melody failed to inspire and no perfect set of lyrics could be found, Vladimir Putin reinstated the old Soviet anthem and sponsored a contest for updated lyrics. This new anthem, in its current form, became official in 2000.
Task 1: Answer the questions
1. What was the highlight of the closing ceremony of the 2014 Sochi Winter Olympics?
2. What is the formal name of the national anthem?
3. Who was the composer of the Anthem?
4. What song was the national anthem of the USSR?
5. What happened to the national anthem after the USSR collapse?
6. Who was a composer?
7. Why did Vladimir Putin reinstate the old Soviet anthem?
8. When did the new anthem become official?
Task 2: Make 10 sentences with new words
Task 3: Open the brackets using the Passive Voice or Active Voice:
1) Merchant flag (to adopt) on the 20th of January 1705 by Peter I.
2) National Flag is a rectangular banner (to consist of) three equal horizontal stripes
3) The powerful patriotic song (to adapt) from the National Anthem of the Soviet Union.
4) “Patrioticheskaya Pesnya” (to compose) by Mikhail Glinka.
5) The song “The Internationale” (to be) the national anthem of the USSR.
6) The white color (to symbolize) generosity and frankness.
7) In 1991 the USSR flag ( to replace) by the RF flag-white, blue and red.
Task 4: Draw the national Russian flag and subscribe the meanings of the colours:
The Geographical Position of a Country,
its Nature and Climate.
Key words:
1. to occupy – занимать
2. to border on – граничить c
3. to be situated on/ in/ to – находиться на/к …
4. to be situated in the south of… — находиться на юге от …
5. to be situated to the west of… — находиться к западу от…
6. to be located in/on – располагаться в/ на …
7. to cover with — лежать, покрывать; расстилаться
8. to cover the territory of — занимает территорию …
9. to lie in (to) – лежать на (к)
10. to lie in the north of… — лежать на севере …
11. to lie to the east of… — лежать к востоку …
12. to wash — омывать
13. to be washed by — омываться (морем, океаном)
14. main — главный
15. to flow — течь (о реке)
16. to flow into (run into) — впадать
17. to differ from – отличаться от…
18. temperate, moderate – умеренный (о климате)
19. to stretch over — простираться
20. to strech from … to… — простирается от… до…
21. to separate — отделять
22. to be separated by — отделяться …
23. densely (thinly) populated — густо населена
(мало населена)
24. consist of — состоять из
25. in the east – на востоке
26. in the west – на западе
27. in the south – на юге
28. island (on the island) – остров (на острове)
29. in the north – на севере
30. land – суша
31. continent (on the continent) – континент (на континенте)
Task. Read the text.
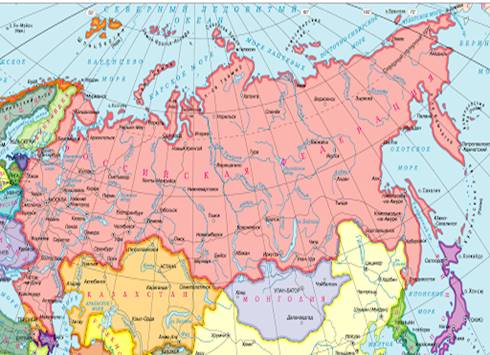
Russia is situated (located) in the eastern part of Europe and the northern part of Asia. It covers almost twice the territory of either the United States or China. It occupies about the one seventh of the earth’s surface. Russia covers the eastern part of Europe and the northern part of Asia.
The population of Russia is 145.5 million people. 83 percent are Russians. The capital of the country is Moscow. It is the largest city and has a population of about 12 million people (2016).
Russia borders on 12 countries on land. In the south Russia borders on China, Mongolia, Korea, Kazakhstan, Georgia and Azerbaijan. In the west it borders on Norway, Finland, the Baltic States, Belorussia, and the Ukraine. It also has a sea border with the USA.
The main areas of Russia are European part, Siberia and Far East. There is hardly a country in the world with such a variety of scenery and vegetation. Russia has steppes in the south, plains and forests in the central region, tundra and taiga in the north, highlands and deserts in the east. Russia is located on two plains. They are the Great Russian Plain and the West Siberian Lowland.
There are several mountains chains on the territory of the country: the Urals, the Caucasus, the Altai and others. The largest mountain chain, the Urals, separates Europe from Asia
The Ural Mountains separate Europe from Asia. Russia is washed by 12 seas and 3 oceans. Russia is connected with the Atlantic Ocean through the Baltic Sea in the west and the Black Sea in the south. The Arctic Ocean and its seas including the White, Barents, Kara, Laptev, and East-Siberian Seas wash Russia in the north. The Pacific Ocean and its seas the Bering, Okhotsk and Japanese Seas wash Russia in the east.
Russia’s greatest rivers are the Don and the Volga in its European part, and the Ob and the Yenisey in West Siberia. The largest river in Asian part of Russia is the Lena. The Volga flows into the Caspian Sea. The main Siberian rivers, the Ob, the Yenisei and the Lena, flow from south to north. The Ob is the longest river in Russia, but the Volga is the most important one. Many Russian towns are located on the Volga river: Vladimir, Tver, Yaroslavl, Kazan, and Nizhny Novgorod. Altogether there are over two million rivers in our country. Lake Baikal is the largest fresh water lake in the world, one of the Seven Natural Wonders of the World, the pearl of Siberia. It’s 636 kilometers long and 80 kilometers wide and is surrounded by forests and mountains peaks, the waters of the lake are transparent to a depth of 40 metres in summer. The lake has more than 2000 rare plants and animals – bears, elk (лось), lynx (рысь), sables (соболь), freshwater seal (тюлень), trout (форель), salmon (лосось) and sturgeon (осетр). It is fed by 336 rivers, with only one river feeding out (the Angara).
The climate of Russia differs from one part to another, from arctic in the north to subtropical in the south. But the prevailing one is a type of climate with four seasons. It is called temperate (умеренный). Winters are cold and windy with a lot of snow. Summers are hot and dry.
Russia is rich in mineral resources such as coal, oil, natural gas, as well as of iron ore, copper, zinc, lead and others. Natural resources determine the development of the Russian economy.
Task 1. Read the text and complete the following table:
|
1 |
Location |
|
|
2 |
Boarders |
|
|
3 |
Surface |
|
|
4 |
Water resources |
|
|
5 |
Mineral resources |
|
|
6 |
Climate |
|
Task 2. Answer the questions:
1. Where is Russia situated?
2. How large is Russia compared to other countries?
3. What countries does it border on?
4. What are Russia’s main regions?
5. What seas and oceans is Russia washed by?
6. What are the most important rivers in Russia?
7. What is the deepest lake in Russia?
8. What types of climate are there on the territory of Russia? Which is the prevailing one?
9. Is Russia rich in natural resources?
Task 3. Complete the sentences:
 |
1. Russia ___________ about one seventh of the earth’s surface.
2. Russia _______________China, Mongolia, Korea, Kazakhstan, Georgia and Azerbaijan in the South.
3. Russia______________ the Eurasia continent.
4. Russia_________________ two continents: Europe and Asia.
5. Russia _________ almost twice the territory of either the United States or China.
6. Tundra is a kind of frozen desert, which ____________ in the Arctic region.
7. Twelve seas __________ the shores of Russia.
8. Russia ____________ 12 seas and 2 oceans.
9. The __________ Siberian rivers – the Ob, the Yenisei and the Lena __________ from south to north.
10. The Volga ____________ the Caspian Sea.
11. The climate of Russia ______________ one part to another.
12. The middle part of Russia has a ___________ climate.
13. Russia _____________ a vast expanse of Eastern Europe and Northern Asia.
14. The Ural Mountains ____________ Europe from Asia.
15. The European part of Russia is ___________, but Siberia is ___________.
16. Russia ___________ the two parts which ___________ the Ural mountains.
Task 4. Finish the sentences:
1. The country is washed by …
2. Its total area is about …
3. The largest mountain chain, the Urals, separates … …
4. Russia is very rich in …
5. Russia is a … …
6. There is hardly a country in the world …..
Task 5. Make the interrogative and negative forms of these sentences:
1. The Russian Federation is the largest country in the world. 2. The country is washed by 12 seas of 3 oceans.
3. It has a sea-border with the USA.
4. There are two Great Plains in Russia.
5. The climate of Russia differs from one part to another, from arctic in the north to subtropical in the south.
6. The largest river in Asian part of Russia is the Lena.
Task 6. Make the sentences using the words and words combinations:
1. Surface; occupies; one-seventh; about; it; of the; earth’s. 2. Covers; the eastern part; Europe; of; it; and; of Asia; the northern; part.
3. The USA; it; has; with; also; a sea-border.
4. Of the country; there are; chains; several; mountain; on the territory.
5. The Duma; by; the legislative; are; powers; exercised.
Task 7. Fill in the gaps with the words from the box:
|
endowed, bountifully, Midlands, density, planes, unequally, vegetation, indispensable, mountain chains |
1) There are two great ____ in Russia.
2) There are several ____ on the territory of the country.
3) The climate in the _____ is moderate.
4) No nation has been as ____ supplied with rivers as Russia.
5) There is a great variety of ____ in Russia: tundra, taiga and so on.
6) Russia is one of the most richly ___ nations in the world with mineral wealth.
7) There are immense deposits of iron, ore and other elements ____ to modern industry.
8) The population is quite ____ distributed with the highest ____ in the European part.
Task 8. Mark on the map:
1) The capital of our country
2) the main rivers, the main seas, oceans
3) the main mountain chains/ the highest peaks.
4) the Laker Baikal
5) the Murmansk region (Murmansk)
6) the countries which we have land and sea boards
7) the main lowlands
THE POLITICAL SYSTEM OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
Key words:
|
1. executive [ɪg’zekjutɪv], [eg-] adj |
– исполнительный, принадлежащий к структурам исполнительной власти |
|
2. legislature [‘leʤɪsləʧə], [-leɪʧə] n |
– законодательная власть; законодательные учреждения |
|
3. judicial [ʤuː’dɪʃ(ə)l] adj |
– судебный; законный, принадлежащий закону |
|
4. Federal Assembly |
– Федеральное собрание |
|
5. State Duma [‘duːmə] |
– Государственная дума (нижняя палата парламента Российской Федерации) |
|
6. Federation Council [‘kaun(t)s(ə)l] |
– Совет Федерации (Россия) |
|
7. vest v |
– наделять правом, давать право |
|
8. court [kɔːt] n |
– суд |
|
9. the Ministry of Justice |
– министерство юстиции |
|
10. elect [ɪ’lekt] v |
– избирать (голосованием) |
|
11. consecutive [kən’sekjutɪv] adj |
– последовательный; консекутивный; (непрерывно) следующий друг за другом |
|
12. commander-in-chief [kə͵mɑ:nd(ə)rınʹtʃi:f] n |
– (главно)командующий |
|
13. resolve v |
– решать, разрешать |
|
14. bill n |
– законопроект, билль |
|
15. decoration n |
– награда, орден, знак отличия |
|
16. pardon [‘pɑːd(ə)n] n |
– помилование; амнистия |
|
17. implementation [ˌɪmplɪmen’teɪʃ(ə)n] n |
– выполнение, исполнение |
|
18. budget [‘bʌʤɪt] n |
– бюджет; финансовая смета |
|
19. monetary policy |
– кредитно-денежная политика, валютная политика |
|
20. bicameral [baɪ’kæm(ə)rəl] adj |
– двухпалатный (о парламенте) |
|
21. treaty [‘triːtɪ] n |
– договор, соглашение, конвенция |
|
22. power of the purse |
– власть кошелька |
|
23. entity [‘entɪtɪ] n |
– организация |
|
24. representative [ˌreprɪ’zentətɪv] n |
– представитель |
|
25. amendment [ə’men(d)mənt] n |
– поправка |
|
26. youngster [‘jʌŋ(k)stə] n |
– ребенок |
|
27. reject [rɪ’ʤekt] v |
– отвергать, отклонять |
|
28. Supreme [s(j)uː’priːm] Court |
– Верховный суд |
|
29. trial court [͵traıəlʹkɔ:t] |
– суд первой инстанции |
|
30. superior court |
– главный суд первой инстанции |
Read the text:
According to the Constitution adopted in 1993, the Russian Federation is a presidential republic. Just like political systems in other countries, our political system also has three branches of power˸ legislative, executive and judicial.
The executive power is vested in the Chief of the Government and the Cabinet. The legislature is represented by the Federal Assembly of Russia. It has two chambers: the State Duma – the lower house, and the Federation Council – the upper house. The judicial power is vested in courts and administered by the Ministry of Justice.
The Federal Assembly represents the legislative branch of power. It is also made up of two houses˸ the Federation Council and the State Duma, which make laws. Both houses are headed by chairmen called speakers. Russia is divided into 89 federal subjects. Each subject elects two representatives to the Federation Council, so there are 178 members in the Federation Council. The State Duma consists of 450 deputies. 225 members are elected directly by the people. The other half of deputies is appointed by their parties after party-list voting according to which every party gains a number of seats. The main function of the Federal Assembly is to make laws. Every law must be approved by the State Duma and the Federation Council, and signed by the President.
The Federal Government represents the executive branch of power. It consists of the Prime Minister and the Cabinet of Ministers.
Russian political system also has "the system of checks and balances" like that in the USA. For example, the President appoints the heads of the Federal Government and the Chairman of the Government, but the State Duma must approve his appointment. The President can veto laws passed by the Federal Assembly, but the Federal Assembly can pass laws over the President's veto by a two-thirds majority. The Constitutional Court has the right to declare actions of the President, the Federal Assembly and the Federal Government unconstitutional.
There are many political parties in our country. The most well-known are the Communist Party, the Liberal Democratic Party, the "Unity" Party, the Union of the Right Forces and the "Apple" Party.
Two types of court make up the Russian judiciary:
I. The courts of general jurisdiction (including military courts), subordinated to the Supreme Court;
II. The Constitutional Court (as well as constitutional courts in a number of federal entities). The Constitutional Court is empowered to rule on whether or not laws or presidential decrees are constitutional. If it finds that a law is unconstitutional, the law becomes unenforceable and governmental agencies are barred from implementing it. The judges of the Constitutional Court, the Supreme Court are appointed by the parliament’s upper house, the Federation Council.
Task 1. Complete the scheme:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Task 2. Answer the following questions:
1. What political system does the Russian Federation represent?
2. How many branches are there in the political system of Russia?
3. Which institutions exercise the legislative, executive and judicial power?
4. What is each branch of power responsible for?
5. Can you explain how the branches of power interact?
6. Who is the head of state in Russia? Does he have much power?
7. Are there many political parties in Russia?
8. What are the most well-known parties?
Task 3. Are these statements true or false? Correct the false
ones.
1. The Russian Federation is a parliamentary monarchy.
2. The President is the head of state and is elected by the State Duma.
3. The President is involved in the work of the legislative and judicial
branches of power.
4. The government consists of the Federal Assembly and the Federation Council.
5. The executive power is vested in the Federal Assembly.
6. The Federation Council is elected by popular vote.
7. The Federation Council is formed of the heads of the regions. 8. Each
Chamber of the Federation Council is checked and balanced by the President.
9. The legislative power is represented by the Constitutional Court, the
Supreme Court and regional courts.
10. The Russian Federation was set up by the Constitution of 1991.
Task 3. Complete the sentences using the Passive voice:
1) The executive power ________(to vest) in the Chief of the Government and the Cabinet.
2) The legislature __________ (to represent) by the Federal Assembly of Russia.
3) The Federal Assembly _____________ (to make up) of two houses˸ the Federation Council and the State Duma.
4) Both houses ___________(to head) by chairmen called speakers.
5) Russia ___________ (to divide) into 89 federal subjects.
6) Members of Duma __________ (to elect) directly by the people.
Task 4. Make a test:
1. The official name of Russia is …..
1. Russia
2. the Russian Federation
3. the Republic of the Russian Federation
2. The national Government of Russia consists of ….
1. the President and the Prime Minister
2. the President and the Council of Ministers
3. the President, the council of Ministers and the Federal Assembly
3. There are ……Houses in the Federal Assembly.
1. two
2. three
3. four
4. The lower House of the Federal Assembly is….
1. the State Duma
2. the Council of Ministers
3. the Federal Council
5. The Head of the Republic of Russian Federation is….
1. the President
2. the Prime Minister
3. the Speaker of the State Duma
6. The Duma consists of …. deputies.
1. 540
2. 450
3. 400
7. The Chairman in Russia is…..
1. elected
2. invited
3. appointed
8. In Russia ……can declare laws unconstitutional.
1. the President
2. the Supreme Court
3. Constitutional Court
9. ……..elect the members of Federal Assembly.
1. the government
2. the people
3. the president
SUPPLEMENTARY TEXTS
Text 1. Russian State Flag
The existing three-color Russian national flag was adopted by the Order of President Boris Yeltsin of December 11, 1993, replacing it’s Soviet-time red predecessor. According to the Constitution, “The national flag of the Russian Federation consists of three equal horizontal stripes – white, blue and red.”
This is the third time this three-color
flag becomes the national symbol. The first to use it was Peter the Great, who
on January 20, 1705 ordered to hoist this flag as a trade one on all Russian
ships on Moscow, Volga and Dvina rivers. In those times the lower red stripe
symbolized the Earth, the blue stripe – the sky, and the upper white stripe
meant the world of God. At the same time, according to the Russian tradition,
white color meant nobility, blue – honesty, red – courage and love.
1) How does the national flag look like?
2) When did our flag use firstly?
3) What does each stripe mean?
Text 2. Russian State Seal (Coat of arms)
As a state symbol two-headed eagle first appeared in Russia, those times Moscovia, in the XV-th century. It came from Visantium with Sophia Paleolog, member of the last Visantium Emperor dynasty, who became the wife of Ivan III, the Great Duke of Moscow.
Two-headed eagle remained the symbol of Russian Monarchy and
Russian State for more than four hundred years, till the October Revolution of
1917, and regained it’s status in 1993 according to the order of President
Boris Yeltsin of November 30, 1993.
There are different interpretations of this symbol. The most common version says that two heads of the eagle symbolize that Russia consists of two part – European and Asian, and they are of equal importance for the country.
The State insignia survived some changes during the pre-revolutionary history of Russia, though these changes were not too much significant. When the old Rurick dynasty ended in the XVII-th century and Romanovs came to power, the two-headed eagle remained as the symbol of Russia, though three crowns were added above the eagle. They were to embody the unity of three nations – Russian, Ukrainian and Belorussian.
1) What is a state symbol of our country?
2) Where did it come from?
3) What are there the interpretations of this symbol?
FAMOUS CITIES AND TOWNS: HISTORY AND SIGHTSEEING.
Text 1. Moscow, its places of interests.
Words for the text:
1. principal — главный
2. remain — оставаться
3. target — цель
4. seat — место нахождения
Moscow stands on the Moskva River. It was founded in the year of 1147 by Uriy Dolgoruky. It began to rise in the 14th century. Under Ivan the Great it became the principal city of Russia. Though Peter the Great moved the capital to St. Petersburg in 1712, Moscow remained the heart of Russia. That’s why it became the main target of Napoleon’s attack. Three quarters of the city was destroyed by fire during Napoleon’s occupation but it was completely restored later.
Nowadays Moscow is the largest city of Russia. It is its political, administrative, economic, industrial, educational and cultural centre. Moscow is the seat of the Russian Parliament (the Duma).
Moscow has become one of the largest city in the world. Its total area is about 2561 square kilometers (2016). By the way, the ancient Moscow occupied the territory of the present-day Kremlin.
List of Moscow Sights and Places of Interest:
1. Red Square
1. the Kremlin — Кремль
2. the Mausoleum — Мавзолей
3. the Kremlin Palace — Кремлевский дворец
4. the St. Basil Cathedral — Собор Василия Блаженного
2. The Moscow Underground
3. Moscow churches and monasteries
1. the Novodyevitchi Convent — Новодевичий монастырь
2. the Danilov Monastery — Даниловский монастырь
3. the Temple of Christ the Savour — Храм Христа Спасителя
4. Museums
1. the State Tretyakov Gallery — Государственная Третьяковская галерея (famous for its collections of paintings, sculpture, drawings, icons)
2. the Museum of Fine Arts named after Pushkin — Музей изобразительных искусств имени Пушкина (the second after the Hermitage in Russia)
3. the Shilov Gallery — Галерея Шилова
4. The Kremlin Armoury /Oruzheynaya Palata — Оружейная Палата (famous for its collections of royal plates and dishes, arms and armour, state symbols such as thrones, the crowns, etc.)
5. the Diamond Fund — Алмазный Фонд (has the exhibition of unique precious stones)
5. Moscow Theatres
1. The Bolshoi Theatre — Большой театр
2. The Maly Theatre — Малый театр
3. the Moscow Art Theatre (the MkhAT) — МХАТ
4. The Operetta Theatre — Театр оперетты
6. The Moscow University — Московский государственный университет
7. The State Library — Государственная библиотека им. Ленина
8. Parks and Gardens
1. Gorky Park — Парк Горького
2. Sokolniky Park — Парк Сокольники
3. Ismailovsky Park — Измайловский парк
8. Estate Museums — Музеи — усадьбы
1. Tsaritsino — Царицино
2. Kolomenskoye — Коломенское
3. Kuskovo — Кусково
Task 2. «Outings and Sightseeing in Moscow»
Before reading the text, make sure that you know the words on the topic «Culture and Arts»:
outings, amusement parks, estate museums, get acquainted with, performance, exhibition, be sure to know, be worth visiting, artifacts, sculpture, historic pieces.
Try to remember the adjectives: world-famous, the most visited, various, brilliant, valuable, commercial
Remember the phrases:
1. There is no need to rack your brains — Не стоит ломать голову …
2. Any foreigher is sure to know … — Любой иностранец знает
There is no need to rack one’s brains about outings in Moscow as it has a lot of world-famous theatres and galleries, amusement parks and estate museums.
Let us start getting acquainted with the Moscow city with its theatres. The most famous of them, the Bolshoi and Maly Theatre, are just in the centre, in Teatralnaya Square. One more popular theatre, Moscow Art Theatre (the MkhAT), is just round the corner. Altogether in Moscow there are about ninety theatres, where you can find performances to every taste from classical to modern ones.
Also in Moscow there are more than seventy museums and a lot of exhibitions of all kinds.
As for the galleries, any foreigner is sure to know the most popular gallery in Moscow. It is the Tretyakov Gallery, which is the center of Russian cultural life. It houses various exhibitions and it is the most visited gallery in the city. Also the Pushkin Museum of Fine Arts and the Shilov Gallery are definitely worth visiting because there you will enjoy not only paintings by brilliant artists but also a collections of different artifacts, sculpture and other valuable historic pieces.
Tastes differ, you know. But in summer Moscow’s shady amusement parks are waiting for everybody. The most popular of them are Gorky Park, Sokolniky Park and Ismailovsky Park, to say nothing of the great estate museums such as Tsaritsino, Kolomenskoye or Kuskovo. They may not be at the top of the list of Moscow entertainment, but promise great enjoyment for a person of any age and background.
All in all, the Moscow’s places of public entertainment are so different that you will never be bored. Everybody will find where to go out, the only problem is what to choose: more real or more commercial. To my mind, it just depends on the money you are going to spend.

![]()
Text 3. Suzdal: the old Russian city.
There are a lot of interesting towns and cities in Russia which are worth visiting. If you want to get acquainted with Russian culture you should visit old Russian towns. They are especially attractive by their cathedrals, churches and monasteries. It is Suzdal, Vladimir, Yaroslavl, Kostroma and others, known as towns of “Golden ring”. You can see a photo of Suzdal.

Complete the gaps with the words:
|
tourist destination; at the height of the tourist season; churches, monasteries, convents; lack funds; prosper and flourish; renovated; scare tourists off; spires and onion domes; local residents; restricts; sustainable tourism |
Nearly all old Russian cities and towns have a lot of historical monuments, such as …. (1). They are valuable symbols of old Russian culture and catch the eye with such particular details as … (2). Some of them have become ruined by time and nearly have to be … (3). But local authorities usually … (4) and it …. (5) the possibilities for developing the town. The situation could be saved by making a city or a town … (6) as tourism could provide good profits for … (7), especially … (8) when a lot of people are on holiday. Although … (9) requires such facilities as good hotels, souvenir shops, coaches, well-trained guides, and other things, it is worth doing because it will make a city … (10) as the present state of many of Russian old cities and towns may only … (11).
Text 4. Read the text “Veliky Novgorod” and choose the correct adjectives:

Veliky Novgorod is one of the (oldest, youngest) cities in Russia. The town is located on the (picturesque, wonderful) banks of the river Volkhov. Novgorod was first mentioned in chronicles in 859. In those days, it was called New town. These two words put together gave the name of Novgorod.
Novgorod played a (great, significant) role in the history of (old, ancient) Russia. Novgorod, at the beginning of the last millennium, had got a form of (direct, straight) democracy, or вече (a popular assembly of men on the (major, main) square of the city to decide the (express, urgent) problems of the city’s administration and its protection) was normal. Regardless of the social status and wealth, everyone had the same right to vote. Because a hundred years ago Veliky Novgorod had a great authority in Ancient Russia, the town was called Господин Великий Новгород (Lord Novgorod the Great).

In the end of the 13th century and until the (early, soon) 16th century, Novgorod was one of the (biggest, greatest) centres of Ancient Russia. Now Novgorod is a (small, big) modern city. The heart of the city is the Kremlin of Novgorod. On its territory stands (old, young, ancient) monuments: St. Sophia Cathedral, a monument from the 11th century, and churches from the 12th to 16th centuries. In the centre of the Kremlin we can see a monument of the second half of the 19th century “the Millennium of Russia”.
The city was severely damaged during WWII. Now it is (difficult, hard, easy) to believe that this (beautiful, pretty) city has reborn from ruins. Priceless monuments of the culture of ancient Russian has been restored.
Task: Answer the questions:
1) What role did Novgorod play in the history of ancient Russia?
2) Novgorod is located on the picturesque banks of the river Volkhov, is not it?
3) What a democracy from did Novgorod have?
4) What monuments can you see in the kremlin of Novgorod?
5) Was the city severely damaged during WWII?
Questions on the topic «Moscow, St. Petersburg and the Towns of Golden Ring»
1. What is the centre of the city?
2. What is the ceremonial centre of Moscow?
3. What is the residence of the Russian President?
4. What monuments would you recommend your foreign guests to see?
5. What Moscow theatres and art galleries are world –known?
6. What places of interest are most popular in St. Petersburg?
1. And what about visiting….? — А как насчет того, чтобы посетить…
Murmansk.
Task 1. How much do you know about Murmansk?
1) When was Murmansk founded?
2) What is Murmansk famous for?
3) What places of interest are there in Murmansk?
Murmansk is the capital of the Murmansk region and a unique town. It was founded on the 4th of October in 1916 and was originally called Romanov-on-Murman.
The foundation of the town is connected with World War 1. Russia was isolated from allies in this war, therefore it was decided to build a sea port on the shore of never freezing Kola Inlet and to connect this port with Petrograd by railway.
Murmansk is famous for its two ports – the Fishing port and the Merchant port. The life of Murmansk is closely connected with the sea and the ocean. Many seamen and fishermen live here. They have their own Culture Centers. In July there is a special festival which is called Fishermen’s Day.
Many tourists visit Murmansk every year. They are attracted by such phenomena as the polar day, the polar night, the unforgettable northern lights, traditional festivals, interesting sightseeings.
In the square in front of the Regional Scientific Library, which was built in 1970, there is a monument to the Fathers of the Slavic alphabet, Cyril and Mephody. This monument is the second and last copy of the world’s famed monument by Vladimir Grinevski. It is a gift from Bulgaria. An original monument is in Sofia and the first copy of it is in Rome. The monument was erected on 22 May, 1990.
The building occupied by the Art Museum is the first brick building in Murmansk. It was built in 1927 and used as a department store and a restaurant before. Nowadays the Art Museum houses a collection of applied arts, an exhibition of drawings, pictures of modern painters.
The regional Museum of local lore has a permanent exposition describing nature and history of the region. The remarkable natural conditions in any season offer the best opportunities for fishing, hunting and gathering mushrooms, berries, herbs. On the shore of Semenovskoye Lake there is Children’s Palace.
Traditional Northern Festivals have been celebrated in Murmansk since 1934.Different kinds of winter sports are included in festival programs. The most popular sports are skiing, biathlon, reindeer races. Murmansk townspeople also celebrate the following festivals: New Year, Maslenitsa, Victory Day, Fishermen’s Day, the date of town foundation and religious holidays.
Murmansk is rather young but native people are proud of their beautiful, hospitable town.
Task 2. Answer the questions
1) Why was it decided to build a sea port on the shore of never freezing Kola Inlet?
2) What does the statue “Alyosha” symbolize?
3) How many terraces does the town spread on?
4) What is the life of Murmansk closely connected with?
5) Why do many tourists visit Murmansk?
6) What festivals do Murmansk townspeople celebrate?
Task 3. Say if the statements are true or false. If they are false give the right variant
1) Murmansk was founded on the 4th of October in 1916.
2) The foundation of the town is connected with World War 2.
3) Murmansk spreads on five terraces.
4) Many fishermen live in Murmansk.
5) The monument to Cyril and Mephody is in front of the Art Museum.
6) The most popular winter sports are skiing, biathlon, reindeer races.
Task 4. Ask at least 6 questions to the text. Let your partner answer them.
Task 5. Follow-up
Imagine you have a foreign friend in your town. Name the places you would advise him/her to visit. Give reasons for your choice.
Useful phrases:
2. What are you going to do during this weekend? — Что ты собираешься делать в эти выходные?
3. I think it’s a good idea to go on a guided tour. — Я думаю это хорошая идея поехать на экскурсию.
4. Do you have any preferences? — У тебя есть какие-нибудь предпочтения (пожелания)?
5. We could as well go…- Мы также могли бы сходить…
GRAMMAR. CONDITIONALS 0, 1, 2
!!!!Let’s revise Conditionals 0,1,2 and make the charts of grammar rules
Task 1. Zero Conditionals:
1.If I ( to think) about Murmansk, I (not to imagine) beaches and the sun.
2.If you (to be) at the Five Corners Square, you (admire) the unique atmosphere of this place.
3.Any tourist (to be able) to see polar nights and polar days if he (she) (come) to Murmansk.
4.If there (to be) a lot of people at the central square in July, so Fisherman’s Day (to be) celebrated.

5.What winter sports (to be) discovered if you (get) acquainted with our traditional Northern Festival?
Task 2. First or Second Conditionals:
1. I (to show) you all the memorials if you come to our town.
2.If I (to be) you, I (visit) the Regional Museum.
3.You (to enjoy) polar nights if you came in winter.
4.What I (to learn) if I go to the Art Museum?
5.My family (to be) fond of winter sports if we take part in the Northern Festival.
Task 3. Complete the sentences with Conditionals 1 and 2 talking about Murmansk:
1.If I were you,…….
2.If polar days come,……
3.If it is winter outside,…….
4.If you could visit our town,……
5.What would you see if……?
6.The sun wouldn’t set down behind the horizon if…….
7.It snows a lot if…..
8.What will you do if…..?
9.You wouldn’t be surprised if…..
10.If you had an opportunity to visit Murmansk ,……?
!!!!SPEAKING: make a report about one of the places of interest (monuments, famous persons, traditions) in Murmansk.
RUSSIA’S FAMOUS PEOPLE
All over the world Russia is famous for its cultural life. It is literature, music and art. Among Russia’s famous people there are writers, poets, artists, composers, scientists, sportsmen and others.
The best–known Russian writers and poets are Aleksander Pushkin (the 2d in the picture), Michail Lermontov, Sergey Esenin, Nicolay Gogol, Ivan Turgenev, Leo Tolstoy, Fyodor Dostoevsky, Anton Chekhov, Boris Pasternak and others. They are popular throughout the world.
The greatest Russian composers are Aleksander Borodin, Modest Musorgsky, Nicolay Rimsky-Korsakov, and Peter Ilich Tchaikovsky (the 3d in the picture).
The outstanding Russian artists and painters are Isaak Levitan, Repin, Vasnetsov, Shishkin, Surikov. Their pictures are exhibited in the Tretyakov Gallery, which is one of the most famous and well-known picture gallery in our country and in the world.
The first cosmonaut on the Earth, Yuri Gagarin (the 4th in the picture) was from Russia and he made his flight into space on the 12th of April in 1961.
The father of Russian science is Mikhail Lomonosov (the 1st in the picture). He was also an outstanding poet and the founder of Russian literature. He founded the first Russian university.
Text 1: Mikhail Lomonosov.
Key words:
Slav-Greek-Latin Academy
conditions of work - условия работы
neither ….. no……- ни….ни
capability-способность
curriculum – рабочая программа, учебный курс
mining – рудное дело
achievement - достижения
enlightenment - просветление
The Russian scientist Mikhail Vasilievich Lomonosov was born in 1711, in the village of Denisovka near the town of Kholmogory, Arkhangelsk Gubernia, in the family of fisherman.
As soon as he learned to read, little Mikhail read all the books he could get in his village. At the age of 17 he left his native place, and made his way to Moscow. In Moscow he successfully entered the Slav-Greek-Latin Academy, the only higher educational institution in Moscow at that time. Neither conditions of work nor material difficulties discouraged young Lomonosov. His brilliant capabilities and hard work enabled him to complete the seven-grade curriculum of the Academy in four years.
A year later he came to Petersburg, and then was sent abroad to study metallurgy and mining.
In 1741, after his return to Russia, Lomonosov became a Professor of Chemistry and a full member of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Lomonosov was a man of unusual abilities. He made great achievements in the spheres of physics, chemistry, astronomy, geology, geography, linguistics and history. Among the numerous discoveries of Lomonosov was the Law of the Conservation of Mass (закон сохранения энергии).
Lomonosov himself considered chemistry his “main profession”, but he was at the same time the first Russian physicist. He gave all his energy to the promotion of Russian science. In 1755 thanks to his efforts the Moscow University was founded. The university became a major centre of Russian enlightenment and science.
Mikhail Lomonosov was the most famous person in the 18th century. He died in 1765 at the age of 54.
Task 1. Answer the questions:
1) Where and when was Lomonosov born?
2) When did he leave his native place?
3) At what age did Lomonosov start to learn?
4) In what spheres of knowledge did Lomonosov make his achievements?
5) What was the “main profession” of Lomonosov?
6) What were the great discoveries of Lomonosov?
Text 2: Dmitri Mendeleev
Complete the text using the following words. Use the Passive voice where necessary:
Achievement, create, enormous, member, name, after, not discover, receive a degree, research, succeed, is known.
Dmitri Mendeleev is a great Russian scientist of the 19th century. He 1) _____________as a great chemist who 2) ____________ the periodic classification of the elements Dmitri Mendeleev was born in Tobolsk in 1834. At school, Dmitri 3)_____________ in mathematics, physics, and geography but was not good at languages. In 1855 he graduated from the Pedagogical Institute in St Petersburg with a gold medal for his 4)___________________.In 1856 , he 5) _______________in chemistry. Dmitri Mendeleev's contribution to the world's science was 6) ________________. He was the first 7) ______________the dependence of the qualities of the elements on their atomic weight. He forecast that the gaps in the table of elements would be filled in by elements which 8)___________________yet. Dmitri Mendeleev was greatly honoured as a 9) ___________________ of academies in many countries. Element No 101 10)_______________ him. It is called Mendelevium.
Text 3: Russian scientists.
Russia gave the world many outstanding scientists. Russian scientists made a great contribution to world science.
V.V.Petrov (176l-1834), the follower of Lomonosov in studying electricity, is called a pioneer of the world electrical engineering. He was experimenting with electricity and made many discoveries of great importance. He published a great number of articles on electricity. The electric arc discovered by Petrov became the first source of electric lighting. Petrov discovered the possibility of getting metals out of ores by means of electricity.
Academician E.Kh.Lenz (1804-1875) is one of the most prominent Russian physicists. He discovered the law of heat generation by an electric current and the law defining the direction of an induced electric current.
P.M.Yablochkov (1847-1894) is a prominent inventor and designer. He did much for using alternating current. He is famous for inventing the "Yablochkov candle"(arc lamp) known abroad under the name of the "Russian
Light".
A.S.Popov (1859-1906) is known for his invention of a radio. After demonstrating his device Popov was offered a lot of money for the commercial use of the radio abroad. But he was a true Russian patriot, he refused to leave Russia. He said that all his knowledge and his achievements belonged to his
native land.
Dolivo-Dobrovolsky (1862-1919) is a Russian engineer. He is the inventor of a three-phase generator and a three-phase transformer. He proposed а number of original designs of measuring instruments.
We know many other names of great Russian scientists and we are proud of them. Lobachevsky's non-Euclidean geometry[1] brought about a revolution in science. Mendeleev discovered the periodic law of elements. The world's first photoelectric cell was built by Stoletov. Lebedev succeeded in measuring the pressure of light experimentally. Zhukovsky and Chaplygin worked out the theory of flight and the principles of aerodynamics. Vernadsky laid the foundations of geochemistry- the science of chemical elements.
The first atomic power station and Yuri Gagarin's flight into space, lasers, semiconductors and many other achievements of modern science and technology have been created and discovered by such prominent Russian scientists as Tsiolkovsky and Kurchatov, Keldysh and Korolyov, Basov and Prokhorov and many others.
Task 1. Answer the questions:
1. What country gave the world many outstanding scientists?
2. Who is called a pioneer of the world electrical engineering?
3. What are the discoveries of academician Lenz connected with?
4. What is Yablochkov known for?
5. Popov was a true Russian patriot, wasn't he? Prove it.
6. What is Dolivo- Dobrovolsky famous for?
7. Whose name is non-Euclidean geometry connected with?
8. What field of science did Mendeleev and Vernadsky make great contribution to?
9. What scientists worked in the sphere of space flights?
10. A great number of achievements of modern science and technology have been created and discovered by prominent Russian scientists, haven't they? Name some of them.
Task 2. Make as many words combinations as you can use the words:
|
electric photoelectric electrical |
cell lightning current engineering |
Task 3. Read the “text 3” again and agree/disagree with the following statements. Use the speech patterns:
I think so. – Думаю, что да.
Most likely. – Весьма вероятно.
Of course not! – Конечно нет!
I doubt it. – Я сомневаюсь в этом.
Hard to say. – Трудно сказать.
1) Petrov is the follower of Lomosov in studying electricity.
2) The electric arc was the first source of electric lighting.
3) Yablochkov is known for his arc lamp.
4) Popov was offered a lot of money for the commercial use of radio in Russia.
5) It was non Euclidean geometry that brought about a revolution in science.
6) Lebedev measured the pressure of light experimentally.
7) Chemistry is a science of chemical elements.
Task 4. What questions can you make for these answers?
1) Yes, they did. Russian scientists made a great contribution to world science.
2) «Yablochkov candle» is called abroad the «Russian Light».
3) . . . because Popov was a true Russian patriot.
4) The periodic law of elements was discovered by Mendeleyev.
5) Many achievements of modern science and technology have been made by prominent Russian scientists.
Task 4. Use the information and complete the table:
|
Inventor |
Invention |
Field of science |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Speak about the Russian scientists` achievements.
EDUCATION IN RUSSIA
Words for the text:
1) academic subjects – учебные предметы
2) competition – зд. конкурс
3) fierce — жесткий
4) public — государственный
5) bachelor’s degree – диплом бакалавра
6) specialist’s degree – диплом инженера
7) master’s degree – диплом магистра
8) higher education — высшее образование
9) institutions of higher education — высшие учебные заведения
All Russian children have the right to education, but it is not only a right, it is a duty, too. Education in our country is compulsory and now lasts eleven years. It consists of primary education and secondary education.
Primary education starts at the age of 6 or 7 and continues for four years. After finishing primary school pupils go on to secondary school. The school year starts in September and ends in May. Generally there 4 school terms with holidays up to 10 days between them. The summer holidays last from June to September.
Most schools in Russia are comprehensive, which take pupils of all abilities without entrance exams. As a rule, students go to school 5 days a week. But there are also specialized schools, lyceums and gymnasiums, which give profound knowledge in various academic subjects. In lyceums and gymnasiums students study 6 days a week.
After finishing the 9th form students must take 4 examinations. Then young people can choose to stay at school, enter a college or a technical school. But to enter a university they have to study for two more years (either at school or at college).
Higher education in Russia.
There are many colleges and universities in our country, but it is not easy to enter a university or college as the competition is rather fierce. Most of the colleges and universities are public and students do not have to pay for their education.
After 4 years of study students can pass examinations and get a bachelor’s degree, after 5 years a specialist’s degree and after 6 years a master’s degree.
There are a lot of institutions of higher education in our country:
1) the Moscow State University (Московский Государственный Университет)
2) the Linguistic University, known as Maurice Thorez Institute of Foreign Languages (Лингвистический Университет, известный как Институт иностранных языков имени Мориса Терезы)
3) People’s Friendship University of Russia (Российский Университет Дружбы Народов)
They are well-known not only in Russia but also abroad.
Task 1. Retell the text to make sure that you have remembered the words:
1. study academic subjects
2. there is a fierce competition
3. take entrance exams
4. enter a university
5. get profound knowledge
6. get a bachelor’s degree
7. get higher education
8. various institutions of higher education
Task 2. Write a letter to your friend.
… Recently I have moved to a new flat. I like my new school. We can choose subjects to study. I have chosen Maths and Physics. I like them because I am good at solving problems. And what about you? Do you like your school? What subjects are you good at? I hope you’ll write a lot of interesting things.
…
Best wishes,
John
Task 3. Answer the following questions:
1. What is your favourite subject? Why?
2. What subjects are you bad at? Why?
3. What do you think is the biggest problem of school life? Give your reason.
4. What can you say about the school building?
5. Do you find your classmates easy to get on with?
Task 4. Complete the text

RUSSIAN HOLIDAYS AND TRADITIONS
1.
Shrovetide or Pancake Day.
holiday — 1. выходной день 2. праздник
2. festival — праздник
3. holidays – каникулы (мн.ч.)
4. day off – выходной
5. family holiday – семейный праздник
6. religious holiday – религиозный праздник
7. public holiday = national holiday = state holiday – государственный праздник
8. pagan holiday — языческий праздник
Russians enjoy their holidays and celebrate them with a lot of food, presents
and in big companies of relatives and friends.
There are three types of holidays in Russia: family holidays, state or public
holidays and.
Family holidays include birthdays, weddings, anniversaries and other family
celebrations. Different families have different traditions of celebrations.
State
or public holidays in Russia include
Constitution Day, New Year's Day, the International Women's Day, May Day,
Victory Day and Independence Day. State organisations, banks and companies do
not work on these days. People spend holiday time with their families and
friends; they go to theatres or exhibitions, or go to city centre where there
are usually folk festivals and concerts in the open air and celebrate with
other people.
Russian religious holidays include Christmas, Easter and some others.
There is also a pagan holiday - Shrovetide or Pancake Day.
New Year's Day is the major family holiday for many Russians. It is
a national holiday in Russia, on which most businesses and public offices are
closed. Schools and universities are closed as part of their winter holidays at
this time of the year.
New Year's dinner usually starts late on December 31 and includes Russian
salad, dressed herring, sparkling wine and other national food. Five minutes
before the clock strikes midnight people watch the president's speech on TV and
raise a toast to the chiming of the Kremlin clock. After that Russians
congratulate each other and exchange presents. Some people go outside to play
snowballs, make a snowman or light fire crackers.
Some Russians celebrate this day at their friends' houses or attend the
fireworks displays in their city. Celebrations for children include a decorated
fir tree and Grandfather Frost, the Russian equivalent of Santa Claus who is
believed to bring presents. Grandfather 'Frost often comes with his
granddaughter, Snegurochka (Snow Girl).
Victory
Day celebrated on May 9 is a very important historic holiday
which marks Germany's surrender to the Soviet Union in 1945, ending one of the
bloodiest wars in Russia's history. Public offices, schools and most businesses
are closed for the celebrations. There may be changes in public transport
routes due to parades and street performances.
A lot of people attend a local military parade and watch the fireworks display
at night on this day. The biggest parade is in Moscow's Red Square, showcasing
Russia's military forces. Veterans wear their medals as they head to the parade
or an event organised by local veteran organisations. Another tradition is to
give red carnations to veterans and to lay wreaths at the war memorial sites.
Schools usually have concerts and performances, sing wartime songs and read
poetry. At home, families gather around a festive table to honor surviving
witnesses of World War II and remember those who passed away.
Orthodox Christmas is both a national and religious holiday in
Russia so banks and public offices are closed on January 7th. Russians
celebrate it by having a family dinner, attending a Christmas liturgy and
visiting relatives and friends.
For many Russians, Christmas Day is a family holiday but it is not as important
for many families as New Year's Day. Many people visit friends and relatives,
as well as give and receive presents. Prior to Christmas Day, there is
Christmas Eve, which marks the start of an old Slavonic holiday, Svyatki,
during which young women used a mirror and candles to see the image of their
future husbands.
Maslenitsa, also known as Pancake Week or Shrovetide, is a Russian pagan holiday celebrated during the last week before Great Lent (the seventh week before Easter). Maslenitsa is an ancient Slavonic holiday, dating back to the pagan culture. This is a festival, celebrating the approach of the spring, warmth and renovation of the nature. During the week Russians eat pancakes, have celebrations and every day of the Pancake Week has its own name and traditions.
For example, Sunday is
called the Forgiveness Day when everybody should ask for forgiveness. Young
married couples usually visit their relatives, give presents to parents and
friends, pay visits to their godparents to give presents to them, too.
When asking for forgiveness people usually bow and normally hear the reply, God
will forgive you. All the food that is left needs to be eaten up, followed by a
piece of rye bread and salt, as a reminder of the upcoming Lent. This is also
the last day of the week when pancakes are eaten.
Sunday evening is the
time when Maslenitsa straw doll has to be burnt; after it has turned to ashes,
young people walk over the fire, marking the end of the Maslenitsa festivities.
Nowadays foreign celebrations are becoming more and more popular in Russia. The
most popular ones are Halloween and St.Valentine's Day.
Task 1. Answer the
questions:
1. What holidays do the Russians have?
2. What are the three types of Russian holidays?
3. What days are included in family holidays?
4. What celebrations are state or public?
5. What do religion holidays include?
6. When is New Year's Day celebrated?
7. What are the most popular traditions on this day?
8. How do you usually celebrate New Year's Day?
9. What is Victory Day and why is it important for the Russians?
10. What are the traditions and activities on Victory Day?
11. When is Christmas celebrated in Russia?
12. What are the Christmas traditions?
13. What is Maslenitsa? What other names does it have?
14. What are the traditions of this pagan holiday?
17. What foreign celebrations appeared in Russia?
18. Do you celebrate any of them?
19. What are your favourite Russian holidays?
20. Why do you like them?
21. What do you and your family usually do on these days?
22. Do you think holidays are important? Why (not)?
Task 2. Complete the text about Russian holidays.
Another Russian ______ is Maslenitsa. It used to be a ______ holiday. Now it becomes a _____ to celebrate it. This holiday is loved by everybody. People celebrate it at the ____ of February or at the beginning of March. It lasts for a week. During this holiday people ____ the winter ____ and greet spring. In old times people usually cooked _____, had fires, burnt scarecrows of winter, sang songs and danced. _____, which are round and hot, symbolize the Sun. Now it is a merry holiday when people dance, sing songs and cook pancakes. Usually this holiday is ______ in parks.
The most important _____ holidays are Christmas and Easter. In Russia Christmas is celebrated on the 7th of January but in Europe and in the USA on the 25th of December. On that day Christians celebrate the birth of _______, though the actual date of his birth is not known.
The tradition to decorate Christmas tree came from Germany. In Russia this tradition was _____ by Peter the Great. It is a custom to decorate Christmas tree with candles, coloured lights and balls. The _______ Christmas colours are red and green. The traditional Christmas food is a roast turkey with vegetables and a Christmas pudding.
Task 3. Вы проводите информационный поиск в ходе выполнения проектной
работы. Определите, в каком из текстов A — F содержатся ответы на интересующие Вас
вопросы 1 — 7. Один из вопросов останется без ответа.
1. Who
do we worship on July, 8?
2. What do Russians traditionally cook during
Butter Week?
3. What
are the two most popular holidays in Russia?
4. Why
is the celebration in St. Petersburg called ‘Scarlet Sails’?
5. What
do we usually do during the first week of each year?
6. Why
do Russian students have parties on January, 25?
7. When
do people jump over a bonfire?
A. Of
all the public holidays in Russia New Year is the first in popularity. Russian
New Year traditions resemble those of the Western Christmas including Christmas
Tree, Father Frost and family celebrations. Another popular family winter
holiday is Old New Year which is New Year according to the Julian Calendar. It
ends the New Year holiday cycle which also includes Christmas.
B. On
January, 25 the day of Saint Tatiana is celebrated. On this day in 1755 the
Russian Empress Elizabeth signed a decree establishing Moscow State University.
So, Saint Tatiana was declared the patron saint of students, and St. Tatiana’s
Day has come to be celebrated as Students’ Day. This day usually coincides with
the end of examinations when students may go out partying all day long and all
night through.
C. One
of the Russian folk holidays is Maslenitsa or Butter Week which is celebrated
during the eighth week before Easter. During this week people arrange snowball
fights, go sledding and take part in some other activities. In Slavic mythology
it is a celebration of the coming end of winter. The shape of pancakes, which
are made on this day, is the praise to the sun. Pancakes are still the most traditional
food of Maslenitsa.
D. The
night of Ivan Kupala is celebrated by joyful rituals, songs and bonfires.
People believe that the highest jumper over a bonfire is the luckiest. In the
past Mothers used to burn the shirts of their sick children in those bonfires
to put an end to their diseases. Fern was believed to bloom at midnight. No man
could pick up this flower, but if you saw it any wish would come true.
E. The
Russian analogue of Valentine’s Day is Peter and Fevronia Day which is
celebrated on July, 8. It focuses, however, on family love. Peter and Fevronia
are historical figures. Peter was the Murom prince who married a peasant woman
after she had cured him of a disease. They were deeply in love with each other.
They died on the same day and they were buried together.
F. Scarlet
Sails Tradition which began in the late sixties of the 20th century is a famous
event of the White Nights Festival. It is associated with a love story told by
the Russian writer Alexander Green in the book with the same title. You can see
a ship with scarlet sails navigate along St. Petersburgh’s main waterway.
Together with fireworks and concerts it symbolizes freedom from “schools and
rules” and entering “an adult life”.
Task 4. Speak about your favorite holiday.
THE UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN AND NORTHERN IRELAND
GEOGRAPHICAL POSITION OF THE UNITED KINGDOM AND NORTHERN IRELAND
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is situated on the British Isles. The British Isles consist of two large islands, Great Britain and Ireland, and above five thousand small islands. Their total area is over 315 000 square kilometers. The United Kingdom is made up of four countries: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. Their capitals are London, Edinburgh, Cardiff and Belfast respectively.
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is situated on the British Isles. The larger island is Great Britain and the smaller is Ireland. The country consists of four parts: England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. England, Wales and Scotland occupy Great Britain. Northern Ireland is situated in the Northern part of Ireland. Southern Ireland, now called the Irish Republic, is independent of the UK.
The British isles are separated from the European continent by the North Sea and the English Channel, which is between Great Britain and Ireland. Great Britain is separated from the continent by the English Channel which is 34 kilometres wide in its narrowest point. The western coast of Great Britain is washed by the Atlantic Ocean and the Irish Sea.
The surface of Great Britain varies greatly. The northern and western parts of the country are mountainous and are called the Highlands. There are mountain chains in Scotland, Wales and North-West England, but they are not very high. Ben Nevis is the highest mountain. (1343) The north of Scotland is mountainous and is called Highlands, while the south, which has beautiful valleys and plains, is called Lowlands. North-West England is famous for its beautiful lakes. All the rest territory is a vast plain which is called Lowlands.
The rivers are not long, too. The longest river is the Severn, while the Thames is the deepest and the most important one, on which stands London.
The mountains, the Atlantic Ocean and the warm waters of the Gulf Stream influence the climate of Great Britain. The climate of the British Isles is generally mild; it is seldom cold in winter and never too hot in summer. This is due to the warm current of the Atlantic Ocean, Gulf Stream. Britain was always known as the country of fogs, but now it is not quite so because of the climatic changes: there is maybe less fog than in any other European country.
The territory of the United Kingdom is about 2444,000 square kilometers. The population is more than 57 million. About 80% of the population is urban. The capital of the country is London.
Geographically, the UK has a very convenient position, being located on the crossroads from Europe to America. This is one of the reasons why Britain was (and is up to the present time) one of the leading world powers. The capital of the country is London. It is situated on the river Thames.
|
1 |
Location |
|
|
1 |
Boarders |
|
|
2 |
Surface |
|
|
3 |
Water resources |
|
|
4 |
Mineral resources |
|
|
5 |
Climate |
|
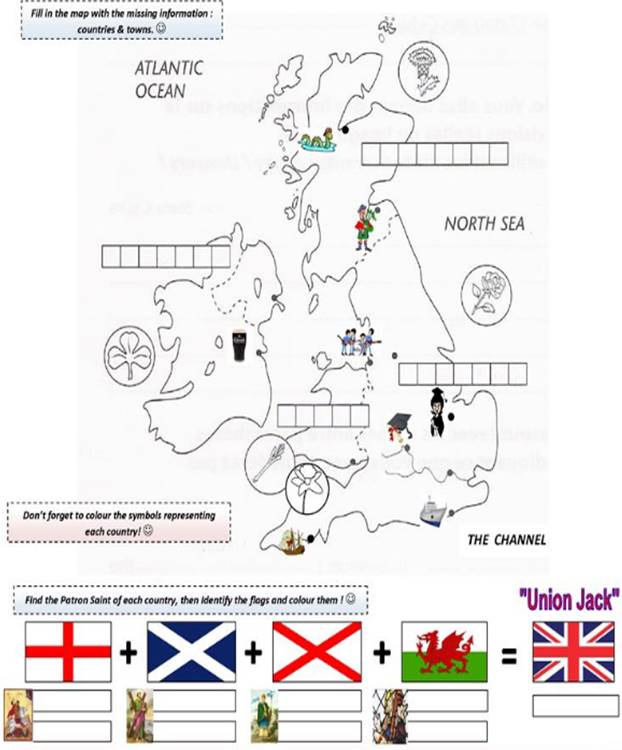
THE POLITICAL SYSTEM OF THE UK. THE ROYAL FAMILY. THE NATIONAL SYMBOLS.
1. POLITICAL SYSTEM OF THE UK.
Pre-reading.
What kind of state is the UK?
Who is the head of the state in the UK?
What are the Houses of the British Parliament?
Read the text and check your answers.
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is a constitutional monarchy. It means that the sovereign reigns but does not rule.
Britain does not have a written constitution, but a set of laws.
Parliament is the most important authority in Britain. Technically Parliament is made up of three parts: the Monarch, the House of Lords; and the House of Commons. In reality the House of Commons is the only one of the three which has true power.
The monarch serves formally as head of state. But the monarch is expected to be politically neutral and should not make political decisions.
The present sovereign is Queen Elizabeth II. She was crowned in Westminster Abbey in 1953.
The House of Commons consists of Members of Parliament. There are 650 of them in the House of Commons. They are elected by secret ballot. General elections are held every five years. The country is divided into 650 constituencies. All citizens aged 18 and registered in a constituency, have the right to vote. But voting is not compulsory in Britain. Only persons convicted of corrupt and certain mentally ill patients don't take part in voting.
There are few political parties in Britain thanks to the British electoral system. The main ones are: the Conservative Party, the Labour Party and the Liberal / Social Democratic Alliance.
Each political party puts up one candidate for each constituency. The one who wins the most votes is elected MP for that area.
The party which wins the most seats in Parliament forms the Government. Its leader becomes the Prime Minister. His first job is to choose his Cabinet. The Prime Minister usually takes policy decisions with the agreement of the Cabinet.
The functions of the House of Commons are legislation and scrutiny of government activities. The House of Commons is presided over by the Speaker. The Speaker is appointed by the Government.
The House of Lords comprises about 1,200 peers. It is presided by the Lord Chancellor. The House of Lords has no real power. It acts rather as an advisory council.
It's in the House of Commons that new bills are introduced and debated. If the majority of the members are in favour of a bill, it goes to the House of Lords to be debated. The House of Lords has the right to reject a new bill twice.
But after two rejections they are obliged to accept it. And finally a bill goes to the monarch to be signed. Only then it becomes law.
Parliament is responsible for British national policy. Local governments are responsible for organizing of education, police and many others.
Task 1. Answer the following questions:
1. What are the names of the islands situated to the west of the continent of Europe?
2. What parts does the island of Great Britain consist of?
3. How many parts is Ireland divided into?
4. What is the official name of Great Britain?
5. Name the seas and oceans the country is washed by.
6. How large is the territory of the UK?
7. How are the people living in the UK called?
8. Why is the climate of the British Isles moderate?
9. What is the highest mountain in the UK?
10. What are the longest and most important rivers in the UK? 11. What is the capital of the country?
12. Prove that the UK has a very convenient position.
Task 2. Open the brackets and use the adjective in the corresponding degree of comparison.
1. The (large) island is known as Great Britain, the (small) is Ireland.
2. The (high) mountain in Scotland is Ben Nevis.
3. The (long) river in Great Britain is the Severn, the Thames is (important).
4. The arctic zone has (cold) climate.
5. The (narrow) part of the English Channel is called the Strait of Dover.
6. Among the Russian lakes (deep) is the Baikal.
Task 3 . Read the text again and fill in the gaps.
1) In the UK there is no president, the Queen is ___________of the __________________.
2) There are two Houses in the Parliament: _______________and _______________.
3) People who sit in the _____________Commons are called _________________.
4) People who sit in the _____________Lords are called ______________ .
5) British people ________________for MPs at a general _________________ .
6) The party which wins a general ______________forms the ________________and their leader becomes __________.
7) After the Queen approves the bill, it becomes ____________.
Task 4. Decide if the sentences are true, false or not stated.
1. British Constitution is one of the oldest in the world.
1) True 2) False 3) Not stated
2. The House of Commons has the real power in the country
1) True 2) False 3) Not stated
3. The Monarch was responsible for political decisions till the 20-th century.
1) True 2) False 3) Not stated
4. The present Monarch was crowned in Buckingham Palace.
1) True 2) False 3) Not stated
5. Members of the House of Commons are elected every five years.
1) True 2) False 3) Not stated
6. Citizens have the right to vote at the age of 18.
1) True 2) False 3) Not stated
7. The Conservative Party has the majority in the Parliament.
1) True 2) False 3) Not stated
8. The Prime Minister is the leader of the party which wins the most seats in Parliament.
1) True 2) False 3) Not stated
9. The Speaker is chosen by the Members of Parliament.
1) True 2) False 3) Not stated
10. The House of Lords acts as an advisory council.
1) True 2) False 3) Not stated
11. A bill becomes law after it is accepted in the House of Lords.
1) True 2) False 3) Not stated
Task 5. “The political numbers” Find this numbers in the text and answer the questions
1) What period are the Members of the House of Commons elected for?
2) When did Elizabeth II come to the throne?
3) How many constituencies is the country divided into?
4) How many members are there in the House of Lords?
Установите соответствие между заголовками 1–8 и текстами A–G. Запишите свои ответы в таблицу. Используйте каждую цифру только один раз. В задании есть один лишний заголовок.
1. The House of Commons
2. Parliamentary Procedure
3. The House of Lords
4. Westminster
5. The System of Government
6. Parliamentary Committees
7. Whitehall
8. The Crown
A. Her Majesty’s Government, in spite of its name, derives its authority and power from its party representation in Parliament. Parliament is housed in the Palace of Westminster, once a home of the monarchy. Like the monarchy, Parliament is an ancient institution, dating from the middle of the thirteenth century. Parliament is the seat of British democracy, but it is perhaps valuable to remember that while the House of Lords was created in order to provide a council of the nobility for the king, the Commons were summoned originally in order to provide the king with money.
B. The reigning monarch is not only head of state but symbol of the unity of the nation. The monarchy is Britain’s oldest secular institution, its continuity for over a thousand years broken only once by a republic that lasted a mere eleven years (1649-60). The monarchy is hereditary, the succession passing automatically to the oldest male child, or in the absence of males to the oldest female offspring of the monarch. In law the monarch is head of the executive and of the judiciary, head of the Church of England, and commander-in-chief of the armed forces.
C. The dynamic power of Parliament lies in its lower chamber. Of its 650 members, 523 represent constituencies in England, 38 in Wales, 72 in Scotland and 17 in Northern Ireland. There are only seats in the Commons debating chamber for 370 members, but except on matters of great interest, it is unusual for all members to be present at any one time. Many MPs find themselves in other rooms of the Commons, participating in a variety of committees and meetings necessary for an effective parliamentary process.
D. Britain is a democracy, yet its people are not, as one might expect in a democracy, constitutionally in control of the state. The constitutional situation is an apparently contradictory one. As a result of a historical process the people of Britain are subjects of the Crown, accepting the Queen as the head of the state. Yet even the Queen is not sovereign in any substantial sense since she receives her authority from Parliament, and is subject to its direction in almost all matters. This curious situation came about as a result of a long struggle for power between the Crown and Parliament during the sixteenth and the seventeenth centuries.
E. Her Majesty’s Government governs in the name of the Queen, and its hub, Downing Street, lies in Whitehall, a short walk from Parliament. Following a general election, the Queen invites the leader of the majority party represented in the Commons, to form a government on her behalf. Government ministers are invariably members of the House of Commons, but infrequently members of the House of Lords are appointed. All government members continue to represent “constituencies” which elected them.
F. Each parliamentary session begins with the “State Opening of Parliament”, a ceremonial occasion in which the Queen proceeds from Buckingham Palace to the Palace of Westminster where she delivers the Queen’s Speech from her throne in the House of Lords. Her speech is drafted by her government, and describes what the government intends to implement during the forthcoming session. Leading members of the Commons may hear the speech from the far end of the chamber, but are not allowed to enter the House of Lords.
G. The upper chamber of Parliament is not democratic in any sense at all. It consists of four categories of peer. The majority are hereditary peers, a total of almost 800, but of whom only about half take an active interest in the affairs of the state. A smaller number, between 350 and 400, are “life” peers – an idea introduced in 1958 to elevate to the peerage certain people who rendered political or public service to the nation. The purpose was not only to honour but also to enhance the quality of business done in the Lords.
|
Текст |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
|
Заголовок |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Task 7. Speaking. Speak about the political system of the UK using the cluster. Compare the British and Russian political systems. Who has more power the Queen of Great Britain or the President of the Russian Federation?
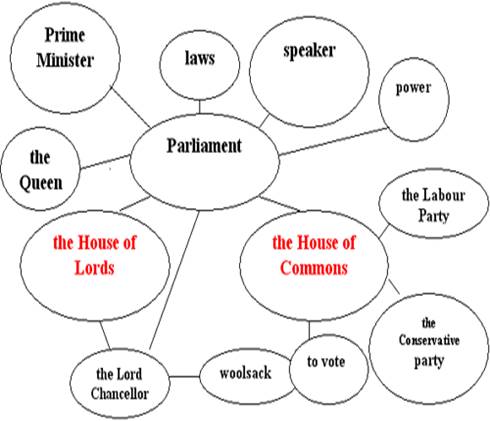
Task 8. Read the text below. Use the words given in brackets to form a word that fits the space:

The UK Political System
1. The UK is…
a) a constitutional monarchy
b) a presidential republic
c) a monarchy
2. The official head of the state in the UK is …
a) the Queen
b) the Prime Minister
c) Parliament
3. The Queen … the bills.
a) signs
b) votes on
c) passes
4. The Government of the UK represents the… branch of power.
a) legislative
b) representative
c) executive
5. … makes laws in the UK.
a) the House of Commons
b) the House of Lords
c) the Cabinet
6. The members of the House of Lords are …
a) elected
b) non- elected
c) appointed
7. The British Prime Minister is the leader of the party with the majority seats in …
a) The House of Lords
b) the House of Commons.
8. The House of Commons is made up of … elected MPs.
a) 100
b) 1000
c) 646
9. Which are Britain's two main political parties?
a) Democratic, Republican and Conservative
b) Conservative and Democratic
c) Labour and Conservative
10. The official residence of the Prime Minister is at … Downing Street in central London.
a) 7 b) 10 c) 55
2. THE BRITISH ROYAL FAMILY.
Read the words.
1. Royal - королевский
2. Monarch (king or queen) - монарх
3. Heir -наследник
4. Throne - трон
5. Coronation -коронация
6. To sign state papers- подписывать госудаствен ные бумаги
7. Duties -обязанности
8. To support –поддерживать
9. Charity organizations - благотворительные организации
10. Travel abroad -ездить за границ
11. To be well-known (to be famous) -быть хорошо известным
12. To hold honorary rank - проводить торжественное вручение наград
13. To carry out-выполнять, нести
14. Oil painting –живопись
15. Environment-окружающая среда
16. To be interested in (to be fond of) –интересоваться
17. Horse racing- скачки
18. Duke -герцог
Task 1. Read the following text:
At
present the British royal family is headed by Queen Elizabeth. The Queen was
born on the 21st of April 1926, in London, England. Her father was King George
VI and her mother was Queen Elizabeth (the late Queen Mother.) Her father
became king in 1936. Elizabeth and her sister Princess Margaret were taught at
home by tutors. Elizabeth studied history and law, art, music, learned to horseback ride. ![]()
Queen
Elizabeth II has got a large family. Their surname is Windsor. Elizabeth
married Lieutenant Mountbatten in Westminster Abbey on November 20, 1947.
Prince Philip was the son of Prince Andrew of Greece and a great-great-grandson
of Queen Victoria. The Queen's husband, Duke of Edinburgh, was born in 1926 and
served in the Royal Navy. Prince Philip supports the Queen in her Royal Duties:
gives interviews, works with lots of charity organizations, travels around the
UK and abroad with the Queen and alone.![]()
Prince Philip is interested in environment, wildlife, science, technology, sports. He also likes sports.
Elizabeth
and Prince Philip have four children: Prince Charles, The Prince of Wales
born on November 14, 1948, Princess Anne, now The Princess Royal born on
August 15, 1950, Prince Andrew, the Duke of York was born on February
19, 1960, and Prince Edward, the Earl of Wessex born on March 10, 1964. ![]()
The
Queen's heir is Charles, Prince of Wales, married Lady Diana Spencer and has
two children, Prince William and Prince Harry. The Prince of Wales is
well-known as a keen promoter of British interests. In recent years he has
become outspoken on such controversial topics as modern architecture, violence
in films and on television, and the standard of English teaching in schools.
His wife Diana, Princess of Wales (often called in mass media Princess Di), won
the affection of many people by her modesty, shyness and beauty. Unfortunately,
she died in a car accident in August, 1997. ![]()
Prince Andrew, Duke of York, served as a helicopter pilot in the Royal Navy. In 1986 he married Miss Sarah Ferguson (Fergie, for short) and has two daughters, Eugenia and Beatrice.
Prince Edward is keen on the theatre. This interest began while he was at university. He quit the Royal Marines, and is now pursuing a career with a theatrical company. His wife `s name is Sophie. They have got 2 children, a son and a daughter
Task 2. Answer the following questions:
1) By whom is the British royal family headed at present?
2) What did the Queen Elizabeth study as a child?
3) Who was the Queen’s father? What is his name?
4) When was the Queen’s husband born?
5) How many children does the Queen have?
6) Whom did Prince Charles marry?
7) What are the names of the Queen’s other children?
8) Who is the youngest Queen’s child?
9) How many daughters does the Queen have?
10) Who is the Queen’s heir?
Task 3. Complete the sentences using the words in the box:
|
monarch, royal heir, throne, reigns, Prince (x2), charity organizations, was crowned, Princess, became, oil painting |
1) The present … is Elizabeth II.
2) The eldest son … Charles, the … of Wales is the … to the …
3) Elizabeth … the sovereign in 1952 when her father, King George VI died.
4) She … but doesn’t rule the country.
5) Elizabeth II … …. in 1953.
6) Prince Philip likes … .
7) The Queen’s children and husband help her working with …
Task 4. Say is it TRUE or FALSE
1) Queen Elizabeth was born on April 21, 1952
2) Prince Philip is the Queen’s husband.
3) Prince Philip and Queen Elizabeth II have got five children.
4) Prince Charles is the eldest son of the British Royal Couple.
5) Prince Philip is the Prince of Wales.
3. THE NATIONAL SYMBOLS.
It is a well-known fact that British flag is often called the Union Jack. Its name derives from the use of the Union Flag on the jack-staff of naval vessels. It represents the emblems of three countries under one Sovereign. There are several emblems that appear on the Union Flag. They are of three crosses patron saints. A red cross on a white background is a cross of St George, a patron saint of England. A white diagonal cross on a blue background is a cross of St Andrew, a patron saint of Scotland. A red diagonal cross on a white background is a cross of St Patrick, a patron saint of Ireland.

In 1801 appeared the final version of the Union Flag, it followed the Union of Great Britain with Ireland, and it included the cross of St Patrick. The cross still remains on the flag, though only Northern Ireland is now a part of the United Kingdom.
You won't find Wales on the Union Flag, because it is not represented there. When the first version of the flag appeared, Wales was already united with England. The national flag of Wales is a red dragon on a field of white and green. It dates from the 15th century.
The red rose was the emblem of Lancastrians, the white rose
that of the Yorkists, the two Houses fighting for the English throne n the War of
Roses. But their struggle ended by marriage of Henry VI, the Lancastrian with Princess Elizabeth,
the Yorkist.The red rose has since become the emblem of ![]()
England.
The thistle is the national emblem of Scotland.
It happened in very old times when Norsemen
wanted to settle
in this country. They came close to the Scots
camps in the night and wanted to
kill them in their sleep. ![]()
That's why they took off their shoes so as to
make no noise. But one of the Norsemen
stepped on a thistle and screamed. The Scots woke up and put the enemy to flight.
The leek is the emblem of Wales. ![]()
Welshmen all over the world celebrate their
national holiday St David's Day by wearing
leeks. They do it because they believe St Davidhave lived for several years on bread and wild
leeks. Daffodils naturally appear in early spring around the time of St
David's Day - depending on the weather that year.![]()
Irishmen wear their national emblem on St Patrick's Day. It's a small white clover with three leaves on the stem. It is called a
shamrock.
The British National anthem is a patriotic song, which was first performed in 1745. On official occasions it is usual to sing the first verse only. Here are the words of this verse:
God save our gracious Queen!
Long live our noble Queen!
God save the Queen!
Happy and glorious,
Long to reign over us
God save the Queen!
QUESTIONS
1. What is the name of the British flag?
2. What does it represent?
3. When did the final version of the flag appear?
4. Why is Wales not represented on the Flag?
5. When was first British national anthem performed?
VOCABULARY
vessels - судна
patron saint - святой покровитель
background - фон
anthem - гимн
gracious - славный
noble - благородный
to reign - править
LONDON. THE CAPITAL OF THE UK.
London is the capital of the UK. It was founded in the first century A. D. by the Romans. One in seven of the population of the United Kingdom is a Londoner.
London draws people from all over the world. Some come on business, some come to study, to work or on holiday. London is naturally a very English city and it is very cosmopolitan, containing goods, food and entertainment, as well as people, from many countries of the world. London spreads its influence over much of the southern areas of England; it gives work to millions of people who live not only in the inner city areas but in surrounding districts.
There is much in London which fascinates visitors and inspires the affection of Londoners: the splendour of the royal palaces and the Houses of Parliament, the Tower of London, the dignity of St. Paul’s Cathedral and many monuments and beautiful parks. London shows examples of buildings that express all the different areas of its history. Buckingham Palace is the official London residence of the Sovereign. The palace was built in 1703 by the Duke of Buckingham. Piccadilly Circus has become an important meeting point. At its heart there is a bronze fountain topped by a figure of a winded archer, known as Eros, the pagan god of love. This area is now famous for its theatres, clubs and shops. Whitehall is a street in central London running from Trafalgar Square to the Houses of Parliament and containing many important buildings and government offices, such as the Treasury, Admiralty and others. In the centre of the roadway stands the Cenotaph, the memorial to the fallen of both world wars. The Prime Minister’s residence at No. 10 Downing Street is directly connected to Whitehall.
London is always full of life. The streets are crowded with traffic. High ‘double-decker’ buses rise above the smaller cars and vans.
London is a city of great contrasts. Its West end is the richest part of London. The East End is the district inhabited by the workers and the poor. The heart of London is the City – its commercial and business centre. The city of London today is the financial powerhouse of the country and one of the chief commercial centres of the western world. The city has its own Lord Major, its own Government and its own police force. Here the medieval buildings stand side by side with modern glass high-rise offices.
The parks of London provide a welcome contrast to the great built-up areas. St. James’s Park, Green Park, Hyde Park, and Kensington Gardens are linked together. They form 313 hectares of open parkland in the heart of London.
Task 1: Match the words with their definitions
|
1. cosmopolitan |
A. the power of persons or things to affect others, seen only in its effects |
|
2. influence |
B. to cause to be encircled on all or nearby all sides |
|
3. to surround |
C. to have in it: hold, enclose, or include |
|
4. to contain |
D. common to or representative of all or many parts of the world |
|
5. inner city |
e) the quality of being worthy of esteem or honour; worthiness |
|
6. to spread |
f) to come together in a large group |
|
7. splendour |
g) the sections of a large city in or near its centre, esp. When crowded or blighted |
|
8. dignity |
h) to dwell or live in |
|
9. to crowd |
I) to distribute over a surface or areas |
|
10. to inhabit |
j) great luster or brightness; brilliance |
Task 2: Fill in the prepositions.
|
in (3), by (2), on (2), of (3), to (2), from, over (2), at, for, with (2), above |
1) London was founded … the first century A. D. … the Romans.
2) London draws people … all … the world.
3) Some come … business, some come to study, to work or … holiday.
4) London spreads its influence … much … the southern areas … England; it gives work … millions … people.
5) Buckingham Palace was built … 1703 by the Duke of Buckingham.
6) The Prime Minister’s residence … No. 10 Downing Street is directly connected Whitehall.
7) Piccadilly Circus is now famous … its theatres, clubs and shops.
8) The streets in London are crowded … traffic. High ‘double-decker’ buses rise … the smaller cars and vans.
9) In the city the medieval buildings stand side … side … modern glass high-rise offices.
10) The parks of London form 313 hectares of open parkland … the heart of London.
Task 3: Find in the text the sentences with the Passive Voice and translate them into Russian. Choose the right variant and explain your choice.
1) This bridge … in 1867.
A. was building B. were built C. was built
2) Such modern glass high-rise offices … here in 3 or 5 years.
A. will construct B. will be constructed C. were being constructed
3) The East End … by the workers and the poor.
A. inhabited B. will inhabit C. is inhabited
4) The bronze fountain topped by a figure of a winded archer … as Eros, the pagan god of love.
A. is known B. will know C. was knowing
5) This old monument … at the moment.
A. is reconstructed B. is reconstructing C. is being reconstructed
SUPPLEMENTARY TEXTS
Big and famous cities in the UK (part 1).
There are many big and famous cities of the United Kingdom, such as Birmingham, Glasgow, Liverpool, Manchester, Edinburgh, Belfast and others. Birmingham is long famous as an international business centre. It has developed into a modern and exciting city, which buildings and shops are second to none. Birmingham is at heart of Britain's motorway system. Massive post-war development brought exciting new buildings, but the best of the old ones have been preserved. The city's museum and art gallery has some of the finest examples of European painting. Birmingnam's ultra-modern library is one of the largest and best stocked in Europe and includes the Shakespeare Memorial Library with 40,000 books in 90 languages. The city possesses several interesting churches and two cathedrals.
Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland, is also a great city of more than half a million inhabitants. The city is built of stone, not brick. The houses look hard and solid. Some people would call them grim, especially on a wet day, but when the sun shines beautifully in the city the city looks fine. Its many bookshops, taverns, and clubs some of world-famous people visited at different times. Among them were Dr. Johnson and Robert Burns. One of the famous avenues in the world is the Prince's Street in Edinburgh. It is the finest street and a shopping area of the city.
Glasgow is the third largest city of Great Britain. You may feel its industrial energy everywhere in the city. The city extends along both banks of the river Clyde. With each phase of its development it has stretched, until its outskirts now lie several miles from the city centre. It is, by far, the largest and most populous city in the whole of Scotland. Glasgow is known the world over for its ship-building. Glasgow-built locomotives run in every part of the world. Today Glasgow is of such a size that it extends far over both banks of the river Clyde and bridges are as essential for the conduct of activities as are the people themselves. Within a distance of a mile there are 7 bridges. They carry road and rail traffic in and out of the city. No other city of Scotland has or needs as many river crossings as Glasgow.
Task 1. Answer the questions:
1) What is Edinburg famous for?
2) What is Birmingham famous for?
3) What are the places of interests in Birmingham?
4) What industries is Glasgow famous for?
5) Where is Glasgow situated?
Task 2. Say is TRUE or FALSE:
1) Birmingham is not an international business centre.
2) Edinburgh is known the world over for its ship-building.
3) Glasgow-built locomotives run in every part of the world.
4) Edinburgh is also a great city of more than half a million inhabitants.
5) Glasgow extends along both banks of the river Clyde.
6) One of the famous avenues in the world is the Queen's Street in Edinburgh.
Big and famous cities in the UK (part 2).
Cardiff, the capital of Wales, lies near the mouth of the river Taff. In the days of our great-grandparents Cardiff was a tiny village. Today there are about a quarter of a million people living there. Cardiff is now the largest town in Wales and is noted for its coal. There is also a delightful park in the city which everyone tries to see. This is Cathay's Park. Few towns in the world have such fine public buildings as Cardiff. The Law Courts, City Hall and University buildings in Cathay's Park are worthy of any city in the world. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland have many other cities and towns, that attract thousands of people from all over the world either on business or private visit.
Brighton is one of the most popular seaside resorts of Britain. It has mild climate, warm sea and wonderful beaches. a city of ancient origin. By the 17th century it was great commercial city, a centre of textile industry. Now engineering along with clothing manufacture are most important industries there. Sheffield, situated in South Yorkshire, produces almost two-thirds of the country's alloy steel, it is famous for its-tools and cutlery. Other industries include paper making machinery and food processing. In North Yorkshire the largest town is York. Its leading industries are engineering and manufacture of confectionery. York attracts many tourists because of its famous medieval city walls.
Task 1. Answer the questions:
1) Where is Cardiff situated?
2) York has leading industries are engineering and manufacture of confectionery, has not it?
3) Where is Sheffield situated?
4) Brighton is one of the most popular seaside resorts of Britain, is not it?
5) What is the largest city in North Yorkshire?
6) What is Cardiff famous for?
7) Why did Brighton became a popular seaside resort?
8) What are the places of interests in Cardiff?
Task 2. Say is TRUE or FALSE:
1) Cardiff is the smallest town in Wales and is noted for its oil.
2) Manchester was a centre of textile industry in the 17 th century.
3) Brighton has mild climate, warm sea and wonderful beaches.
4) Sheffield is famous for its-tools and cutlery.
5) Cardiff attracts many tourists because of its famous medieval city walls.
6) Cardiff lies near the mouth of the river Taff.
Task 3. Complete the table.
|
Birmingham |
|
|
Edinburgh |
|
|
Glasgow |
|
|
Cardiff |
|
|
Brighton |
|
|
Manchester |
|
|
Sheffield |
|
|
York |
|
EDUCATION IN BRITAIN
Key words:
1. stage — ступень
2. grammar school — гимназия
3. national exam — государственный экзамен
4. General Certificate of Secondary Education — Аттестат об общем среднем образовании
5. 6th form — шестой класс (соответствует 10-11 классу в российской системе образования)
6. further education — дальнейшее образование
7. accept — принимать
8. graduate from — заканчивать
9. private school — частная школа
10. provide education — предоставлять образование
11. boarding school — школа с проживанием
12. Oxford and Cambridge — старейшие британские университеты
13. public school — английская частная школа для аристократии
14. Eton — известная частная элитная школа
15. assessment — оценивание
Education in Britain is compulsory from 5 till 16. The first stage is primary school (5-11). Children start primary school at 5 and continue until they are 11. In primary schools pupils are taught the so-called three “R”: reading, writing and arithmetic.
The second stage is secondary school, which children start at 11. Secondary schools are called comprehensive, they are free and take children of all abilities, without entrance exams. There are also grammar schools which take children who pass the 11 plus exams. At 16 pupils take a national exam called GCSE (General Certificate of Secondary Education or “O” level (Ordinary) and they can leave school if they wish and start working. This is the end of compulsory education. Some 16-year-olds continue their studies in the 6th form ( at school or at a sixth-form college). The 6th form prepares pupils for a national exam called “A” level (advanced) at the age of 18. You need “A” level to enter a university. If you don’t enter a university you can go to college of further education to study more practical things such as hairdressing, typing, cooking etc.
The third stage is further education at university or college. Universities and colleges of higher education accept students with “A” levels. Most students graduate at 21 or 22 and are given their degree. Generally universities award two kinds of degree: the Bachelor’s degree and the Master’s degree. Altogether in Britain there are about 100 universities. The oldest and the most famous of them are Oxford and Cambridge.
In Britain there are also private schools. They are expensive but considered to provide a better education and good job opportunities. Private schools are boarding schools, where the children actually live in the school.
The most famous private schools are called “public” schools and they have a long history and traditions. Children from wealthy and aristocratic families often go to the same public schools as their parents and grand parents. The best known of these schools is Eton.
Some more facts about education in Britain:
1) The academic year in Britain usually begins in September runs to early July; it has three terms, divided by the Christmas and Easter holidays. In addition all schools have a “half-term” holiday lasting for a few days or a week, in the middle of each term.
2) Compulsory education is free.
In Britain education is compulsory, but schooling is not. It means that parents have right to educate their children at home if they wish. But the authorities have no right to enter people’s homes or make routine checks on children’s progress. The responsibility rests on the parents.
Children learn in different ways and at different times and speed and that is the main reason that some parents choose home education for their children. Some other reasons are:
1. distance from school — расстояние от школы
2. religious beliefs — религиозные убеждения
3. dissatisfaction with the system — неудовлетворенность системой
4. bulling — запугивание
5. child’s unwillingness or inability to go to school — нежелание или неспособность учиться
6. special educational needs — особые образовательные потребности
Подведем итоги информации про систему образования в Великобритании:
1. There are three stages of education in Britain:
● the first stage is primary education (5-11). There are infant schools (5-7) and junior school (7-11). In primary schools pupils are taught the so-called three “R”: reading, writing and arithmetic.
● the second stage is secondary education (11- 18) Two last years (6th form) may be spent in a separate sixth-form college, which concentrates on career training.
● the third stage is further education at university or college.
2. There is the National Curriculum (государственный учебный план), which was introduced in Britain in 1988. It tells pupils what subjects they have to study, what they must learn and when they have to take assessment tests.
3. There are three types of state
secondary schools in Britain:
1) grammar schools (for the most intelligent children)
2) modern schools (for less intelligent children)
3) comprehensive schools ( for children of all abilities, without entrance
exams)
Grammar schools lead towards higher education, the others give general education to prepare students for employment.
Task 1. Answer the questions:
1) What are the main types of schools in Britain?
2) What do grammar schools offer?
3) What is the aim of the National Curriculum?
4) How is pupils’ progress in subjects measured?
5) What are the main standards for entrance to university?
6) What does the private sector include?
7) What kind of students study in public schools?
Oxford and Cambridge compared
Oxford and Cambridge are the most prestigious universities in the English-speaking world. You never say Cambridge and Oxford; Oxford always comes first. They are often called Oxbridge.
Oxford and Cambridge universities consist of a number of colledges. Each college has its own name and its coats of arms. On the territory there is usually a chapel, a dining hall, a library, rooms for undergraduates, fellows and the master, and also rooms for teaching.
Oxford is one of the oldest universities in Europe. It is situated at a distance of 100 km from London. It is the second largest one in Britain after London University. It dates in chronicles from 911 AD. Most colleges are made of grey stone. They have stood there for many centuries. Oxfords is an aristocratic university. Now there are 27 colleges for men, 5 for women and another five which have both ones. All the students at Oxford talk in a very superior way known as the Oxford accent, which is a bit like the BBC accent.
Cambridge is situated at a distance of seventy miles from London. It is one of the most beautiful towns in England and looks more like a country town. The Cambridge University started during the 13th century (1284). It has more than twenty nine colleges. A college is a group of buildings which form a square with a lawn in the centre. The colleges line the bank of the river Cam. They have beautiful college gardens with green lawns and lines of tall trees. A lot of famous people studied at Cambridge. They are Sir Isaac Newton, Oliver Cromwell, John Milton and Sir Charles Darwin. In Trinity College, which is a very famous, there is a statue of Sir Isaac Newton, the greatest scientist in the world.
Sport is a part of students life at both universities. There is a great rivalry between the universities and they play all sorts of games between each other like cricket and rugger (rugby football). Also they compete at punting and rowing, which are the most popular sports. The Oxford team wear dark blue uniform and the Cambridge team wear light blue one.
Task 1. Answer the questions:
1) Are Cambridge and Oxford the oldest universities?
2) What does Oxbridge mean?
3) Where is Oxford situated?
4) When was it founded?
5) Who was studied in Oxford firstly?
6) When was Cambridge founded?
7) How many colleges are there in Cambridge?
8) Where is Cambridge situated?
9) What were famous people who studied at Cambridge?
10) Does sport have a large part of students` lives in both universities?
Task 2. Complete the sentences using the Passive Voice:
1) Oxford (situate) at a distance of 100 km from London.
2) Oxford (found) in 911 AD.
3) Oxford and Cambridge (call) Oxbridge.
4) Cambridge (situate) at a distance of seventy miles from London.
5) Cambridge (found) in 1284.
Task 3. Fill in the gaps.
|
self-governing; independent; organizes lectures, arranges exams, grants degrees; life; maintain discipline; more than 400; 300 years before scholars began to resort to it; New; rowing and punting; rich; gowns. |
1. Only . . . people send their children to
Ox-bridge.
2. Each college is . . . and ….
3. The University is an administrative body,
which ….
4. Chancellor is elected for ….
5. Proctor’s job is to ….
6. The largest colleges have . .. students.
7. Oxford as a city had existed for at least . .
. years.
8. The first regular quadrangle had . . .
College.
9. The most popular sports are ….
10. All the students have to wear ….
SUPPLEMENTARY TEXTS
Task 1. Read the texts (1—6) about the oldest universities in the UK and match them with the statements (a—g) There is one...
1) The text says that this university educates students in subjects referring both to the past and present.
2) The text says that this university educates scientists and authors better than any other in the country.
3) The text says that this university appeared in the middle of the 15th century.
4) The text says that the library of this university has no rivals in a central part of the UK.
5) The text says that at this university only 2 students out of three are British citizens.
6) The text says that this university’s graduate made his alma mater a generous gift.
7) The text says that this university was reorganized.
A. The University of Cambridge is proud of its museum. The museum was founded by Richard, seventh Viscount Fitzwilliam of Merrion in 1816 and is called after him. The founder presented his famous art collection and library to the University (where he had taken his degree nearly fifty years earlier).He also gave the University ? 100, 000 to provide a building for his collection. Many of the best paintings we can see at the Fitzwilliam Museum used to belong to the outstanding man.
B. Oxford is the oldest university in the English-speaking world. There is no clear date of its foundation, but we know for a fact that teaching existed at Oxford in some form in 1096 and developed fast from 1167 when Henry II banned English students from attending the University of Paris. In 1878 Oxford opened its doors for women. Nowadays the university’s student population is over 20, 000. It consists of students from than a hundred and forty countries and territories. Over the third comes from the outside the UK.
C. The University of Aberdeen is one of the ancient universities. It was founded in Old Aberdeen, Scotland. It is the fifth oldest university in what is now the United Kingdom. It started as King’s College in February 1495, but in April 1593 the second university, Marischal College, was founded in the city. It was highly unusual at the time to have two universities in one place. In 1860 the two colleges were finally united into the University of Aberdeen.
D. St Andrews is Scotland’s first university and third oldest in the English-speaking world. It was founded in 1413. Over six centuries it has established reputation as one of centres for teaching and research. The academic schools and departments of the university include: Art, History, Biology, Chemistry, Classical Studies, Ancient History, Greek, Latin, Economic & Finance, Computer Studies, English, Geography and Geostudies, Modern Languages and many others.
E. The University of Edinburgh was founded in 1583. It has the largest library in Scotland that includes more than a million books, about 600, 000 electronic books and 20, 000 e-journals. It has 20 laboratories. Many of its graduates are well known all over the world. Some of them are Charles Darwin, a scientist, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, a write, Joseph Black, a chemist.
F. The University of Glasgow is located in the west end of the city. This university was founded in 1451 and is the fourth oldest university in the United Kingdom. It is also one of the country’s most prestigious. Its library is one of the oldest in Europe and has about 2 million volumes. The University has about 16 thousand students, 2000 of which from abroad.
HOLIDAYS AND TRADITIONS
Listen to the text:
Every country and every nation has its own holidays. In the United Kingdom there are two types of them — bank and public holidays. Bank holidays are the days, when all people in the UK have a day off and celebrate a national event. Those days are: New Year’s Day, Good Friday, Easter Monday, Early May, Spring Bank holiday, Summer Bank holiday, Christmas and Boxing Day.
Public holidays are special occasions like «Guy Fawkes Night», «Mother’s Day», «Remembrance Day», «Valentine’s Day» and so on. People usually celebrate them but do not have a day off on these events, unless they falls on weekends.
Each holiday is good, but there are some of them that are really special and more popular than others.
New Year’s Day (December 31 – January 1) is a bank holiday. Like many nations around the world, British people celebrate it by hosting parties with their friends and families to await the countdown to the New Year. In Scotland they call it Hogmanay and celebrate it by having a party with friends and setting fireworks off. In many cities there are free celebrations that anyone can join.
Valentine’s Day (February 14) is celebrated in many countries around the world, although it is not a public holiday in most of them. This day has a Catholic origin and has been associated with romantic love since it was mentioned in one of Geoffrey Chaucer’s poems. Nowadays, it’s the day of anyone who is in love. On the Valentine’s Day people usually give to the person they love some sweets, a traditional heart-shaped card (“valentine”) and say, “Be my Valentine”.
Halloween (October 31) also known as All Hallow’s Eve, or All Saint’s Eve, is a yearly celebration observed in a number of countries on October 31. It is the time in the liturgical year dedicated to remembering the dead. On this day children will dress up in costumes and go ‘trick or treating’ around the neighborhood. “Trick or Treating” involves knocking on someone’s door and saying ‘Trick or Treat’. That person gives them a treat (usually sweets). Children enjoy the holiday because they go home with a bag of sweets!
Guy Fawkes Night (November 5) is a firework festival associated with the tradition of celebrating Guy Fawkes’s failed attempt to blow up the Houses of Parliament in 1605. It is an annual event dedicated to bonfires, fireworks and celebrations.
Christmas (December 25) is the most important holiday for British families. This is the day that people spend with their families. There are many Christmas traditions, but the most important one is about presents. Family members prepare their gifts and put them under the Christmas tree. In the evening they sit down around the table and enjoy the meal. Then they watch the Queen’s speech on the television as she delivers her traditional Christmas message to the people of the United Kingdom. After that, family eats the Christmas cake and goes to sleep. In the morning all the family members wake up and gather around the tree to find the presents that were prepared for them.
Boxing Day (December 26) is based on the tradition of giving gifts to poor people after celebrating Christmas. The word “boxing” refers to gift boxes, and has nothing to do with the sport.
There are also a few uniquely British holidays, such as Burns Supper in Scotland, dedicated to the poet Robert Burns, or the Queen’s Birthday, but these are the most important and popular holidays in the United Kingdom.
Task 2. Match the sentences with he names of holidays:
a) Christmas Day
b) Queen’s Birthday
c) Pancake Day
d) May Day
e) St. Patrick's Day
f) St. Valentine’s Day
g) April Fool’s Day
h) Boxing Day
i) Halloween
j) Guy Fawkes
k) Easter
1)
It is celebrated on February 14th. On this day
people send special cards and get presents from their sweethearts.
On this day people play jokes and tricks on each
other.
It is celebrated in spring. People usually make
special buns which are marked with a cross on top. On this day the Church marks
Jesus Christ’s resurrection from the dead.
2) It is a cultural and religious celebration held on 17 March.
3) It is celebrated in the UK on November 5th. British people mark this day by burning a dummy made of straw and old clothes on a bonfire.
4) It is celebrated on December 26th. It comes straight away after Christmas Day.
5) This official public holiday holiday is celebrated on the first Monday of the last spring month. People celebrate the coming of spring.
6)
It is celebrated on April the 21st. All the
newspapers, radio and TV channels congratulate her.
Shrove Tuesday is the last day when you can eat
and do everything before the fasting of Lent. It has this popular name because
many people traditionally eat blini on this day.
7) A holiday that is on October 31st. The most memorable symbol connected to this holiday is a lantern made of a pumpkin.
8) It is celebrated on December 25th. This holiday symbolizes the birth of Jesus Christ.
FAMOUS PEOPLE
Text 1. Alexander Fleming
Key words:
1) Bacteriologist - бактериолог
2) discovery of penicillin – открытие пенициллина
3) influenza - грипп
4) mould – плесень
5) staphylococci germ – стафилококк
6) immunology - иммунология
7) chemotherapy - химиотератпия
Alexander Fleming (1881-1955) was bacteriologist and Nobel Prize winner, best known for his
Alexander Fleming was born on 6 August 1881, the son of a farmer. He moved to London at the age of 13 and later trained as a doctor. He began research at St Mary's Hospital Medical School at the University of London under Sir Almroth Wright, a pioneer in vaccine therapy
In 1928, while studying, Fleming noticed that mould had developed on a set of culture dishes being used to grow the staphylococci germ. The mould had created a bacteria-free circle around itself. Fleming experimented further and named the active substance penicillin. At first supplies of penicillin were very limited, but by the 1940s it was being mass-produced by the American drugs industry.
Fleming wrote numerous papers on bacteriology, immunology and chemotherapy. He was elected professor of the medical school in 1928 and professor of bacteriology at the University of London in 1948. In 1945 Fleming, Florey and Chain shared the Nobel Prize in Medicine. Fleming died on 11 March 1955.
Task 1. Answer the questions:
1) What was Alexander Fleming?
2) How did he do his invention?
3) What is the result of his discovery?
4) What germs did he use to grow bacteria?
5) Do we use penicillin in our modern life?
William Gilbert (1544 - 1603)
Key words:
1) Physician - врач
2) lodestone (magnetic iron ore) магнит (магнитная железная руда)
3) a prosperous family – зажиточная семья
4) BA (Bachelor of Arts), MA (Master of Arts) and MD (doctor of Medicine)
5) magnetic phenomena – магнитные явления
6) distinguish – выделять
7) polarity – полярность
8) plague - чума
Gilbert was an English physician and scientist, the first man to research the properties of the lodestone (magnetic iron ore).He also invented the term 'electricity'.
William Gilbert was born on 24 May 1544 into a prosperous family in Essex. He was educated at Cambridge University, where he received, after which he became a senior fellow. He practised as a doctor in London for many years and in 1600 became president of the Royal College of Physicians. He served as physician to Elizabeth I in the last few years of her reign.
was published in 1600 and was quickly accepted as the standard work on electrical and magnetic phenomena throughout Europe. In it, Gilbert distinguished between magnetism and static (known as the amber effect). He also compared the magnet's polarity to the polarity of the Earth, and developed an entire magnetic philosophy on this analogy.
Gilbert died on 30 November 1602, probably of the plague.
Task 1. Answer the questions:
1) What did Gilbert get his education?
2) What did he invent?
3) How did his invention influence to people1 s life?
4) What did he research firstly?
5) What is 'De Magnete'?
James Watt (1736 - 1819)
Key words:
1) renowned for - славится
2) shipwright – корабельный плотник
3) hopelessly inefficient – безнадежно неэффективный
4) a separate condensing chamber – отдельная конденсационная камера
5) the rotary engine – роторный двигатель
Watt was a Scottish inventor and mechanical engineer, his improvements in steam engine technology.
James Watt was born in Greenock on 18 January 1736. His father was a prosperous shipwright. Watt became interested in steam engines.
In around 1764, Watt was given a model engine to repair. He realised that it was hopelessly inefficient and began to work to improve the design. He designed a separate condensing chamber for the steam engine that prevented enormous losses of steam. His first patent in 1769 covered this device and other improvements on Newcomen's engine.
By 1790, Watt was a wealthy man and in 1800 he retired and devoted himself entirely to research work. He patented several other important inventions including the rotary engine, the double-action engine and the steam indicator, which records the steam pressure inside the engine.
Watt died on 19 August 1819. A unit of measurement of electrical and mechanical power - the watt - is named in his honour.
Task 1. Answer the questions:
1) Where was Watt born?
2) What was his father?
3) What did he design?
4) How did his invention influence to people` s life?
Michael Faraday (1791-1867)
Key words:
1) electromagnetic induction – электромагнитная индукция
2) electromagnetic rotation – электромагнитное вращение
3) induction ring – индукционное кольцо
4) a steady electric current – постоянный электрический ток
5) a horseshoe magnet – подковообразный магнит
Michael Faraday was British physicist and chemist, best known for his discoveries of electromagnetic induction and of the laws of electrolysis. His biggest breakthrough in electricity was his invention of the electric motor.
He was born in 1791 to a poor family in London. He read every book that he bound, and decided that one day he would write a book of his own. He became interested in the concept of energy, specifically force. He became a chemist and physicist.
Michael Faraday built two devices to produce what he called electromagnetic rotation: that is a continuous circular motion from the circular magnetic force around a wire. Ten years later, in 1831, he began his great series of experiments in which he discovered electromagnetic induction. These experiments form the basis of modern electromagnetic technology.
In 1831, using his "induction ring", Michael Faraday made one of his greatest discoveries - electromagnetic induction: the "induction" or generation of electricity in a wire by means of the electromagnetic effect of a current in another wire. The induction ring was the first electric transformer. In a second series of experiments in September he discovered magneto-electric induction: the production of a steady electric current. To do this, Faraday attached two wires through a sliding contact to a copper disc. By rotating the disc between the poles of a horseshoe magnet he obtained a continuous direct current. This was the first generator. From his experiments came devices that led to the modern electric motor, generator and transformer.
Michael Faraday continued his electrical experiments. In 1832, he proved that the electricity induced from a magnet, voltaic electricity produced by a battery, and static electricity were all the same. He also did significant work in electrochemistry, stating the First and Second Laws of Electrolysis. This laid the basis for electrochemistry, another great modern industry.
Task 1. Answer the questions:
1) Where was Faradey born?
2) What experiments did he do?
3) What was he interested in?
4) How did his invention influence to people` s life?
III. THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
THE GEOGRAPHICAL POSITION OF THE USA
The USA is one of the largest countries in the world. It is situated in the central part of the North American continent. The area of the USA is over nine million square kilometers. Its oceans are the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic.
The population of the United States is nearly 250 million people.
The official language of the country is English. The capital of the country is Washington. It was named in honour of the first President, George Washington. As the USA is a large country, the climate is different in different regions.
There are many mountains in the USA. For example, the highest peak in the Cordillera in the USA is 4,418 metres.
The country’s main river is the Mississippi but there are many other great rivers in the USA: the Colorado in the south and the Columbia in the north-west. There are five Great Lakes between the USA and Canada.
There are many big cities in the country. They are Washington, New York, Boston, Chicago, San Francisco, Los Angeles and Philadelphia.
The USA is a federal republic, consisting of fifty states. Each of these states has its own government.
The President is the head of the state and the government.
A) Read the text again and complete the table.
|
Country |
|
|
Geographical position |
|
|
Area |
|
|
Population |
|
|
Official language |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Climate |
|
|
Mountains |
|
|
Rivers |
|
|
Cities |
|
|
Kind of state |
|
|
Head of the state |
|
B) Speaking: look at answers and try to ask questions for them

C) Grammar. The definite article with the geographical names.
Look through the text and complete the chart using the geographical names
|
Geographical names |
The |
Zero/0 article |
|
Rivers |
|
|
|
Mountains |
|
|
|
Cities |
|
|
|
Oceans |
|
|
!!!!!!!! So let’s make the conclusion and make your grammar rule – when we are to use the definite article and in what cases we are not to use it.
D) SPEAKING
Look at the map and tell the class about the geographical position of the USA, you may use the previous tables as the prompts
THE POLITICAL SYSTEM OF THE USA
The United States of America is a federal union, consisting of fifty states, with the District of Columbia as the seat of the national government. Each state has its own government and the state governments follow much the same pattern as the federal government. The present constitution was proclaimed in 1787 in Philadelphia. Since then, the basic document has not been changed.
The president is the head of state, of the federal government and he chooses its ministers, called ‘cabinet leaders’. He is chosen in a national election for a four- year term of office. The president must be a native-born citizen at least 35 years old. The president and his administration represent the executive branch. The Administration includes the secretaries who are heads of the executive departments. Each department is responsible for a specific area. The president appoints the secretaries but the Senate must approve his appointments.
He is elected directly by the people and he is not the member of the American parliament, Congress.
Congress is the legislative branch of power and it consists of two houses, the House of Representatives and the Senate. Congress makes laws and each house of Congress can introduce a new project. Each can vote against the project passed by the other. If both hoses agree the project becomes the law.
Elections to the House of Representatives take place every two years. The house has 435 members. A member must be an American citizen for more than seven years and at least 25 years old.
Each of the 50 states elects two Senators to the Senate. There are 100 members in the Senate. They are elected to serve for a period of six years, but every two years elections to the senate take place when one third of its members may be changed or re-elected.
A Senator must be over 30 years old and a citizen of the USA for at least nine years.
The legislative and the executive branches are involved in the system of checks and balances.
Election day is always in the month of November, on the first Tuesday after the first Monday.
In the USA there are two main political parties, the Democratic Party and the Republican Party. The Democratic Party is the oldest of the two. Its history began back in the 1820s. The Republican Party was organized in the 1850s.
The judicial branch is headed by the Supreme Court, which is the only court specifically was created by the Constitution. In addition, the Congress has established 11 federal courts of appeal and 91 federal district courts. Federal judges are appointed for life and can only be removed through the process of impeachment and trial in the Congress.
Vocabulary
1. national government - национальное правительство
2. pattern - образец, модель
3. to be proclaimed - быть провозглашенным
4. a four-year term of service - 4-летний срок службы
5. native-born - местный житель, уроженец
6. the House of Representatives - Палата Представителей
7. the Senate - Сенат
8. serve - служить, находиться на посту
9. re-elect – переизбирать
10. executive –исполнительный
11.legislative –законодательный
12.to appoint –назначать
13.to approve –одобрять
13.to exercise –осуществлять
14. judicial – судебный
15.court of appeal –апелляционный суд
16.trial – судебное разбирательство
Task 1. Answer the questions
1. Why do we call America a federal union?
2. Where is the seat of the national government?
3. How often is the president elected in the USA?
4. Who can be the president of the country?
5. Who can be elected to the House of Representatives?
6. How many senators are there in the Senate?
7. What is the period of service for a senator?
8. Who can be a senator?
9. When is the Election Day in the USA?
10. Can you name the main political parties in the USA?
Task 2. Test on the Political System of the USA
1). In America , the _________________ is the Head of State.
1. Congress
2. Parliament
3. President
2). The President of the United States is_______________ every four years.
1. examined
2. elected
3. changed
3). The President makes the most important decisions and chooses the members of his ________.
1. council
2. court
3. cabinet
4). In other words, the President ______________the heads of the most important departments in the Administration.
1. appoints
2. delays
3. opposes
5). The president __________the United States on official occasions.
1. controls
2. declares
3. represents
6). The President cannot act without the Senate’s __________
1. approval
2. appointment
3. opposition
7). Congress is the_____________ branch of the federal government.
1. democratic
2. political
3. legislative
8). The President’s policies must be approved by the House of Representatives and the Senate before they become ________________
1. constitution
2. law
3. democracy
Task 3. Speak about the political system of the USA.
Read the text and answer the questions: 1.What kind of state is the USA?
2. Who is the head of the state?
3. Who is the head of the executive branch in the USA?
4. Which officials are elected and which are appointed?
5. Is the head of state elected directly by the people?
6. Can the people of the USA exercise their power through their representatives?
7. What activities are the two branches of power involved in?
8. Is the role of the head of state in the USA ceremonial like in Great Britain?
TASK: complete the sentences:
1. The United States of America is a …
2. The President is elected directly by …
3. The legislative branch of the federal government is …
4. Congress is made up of …
5. Congress makes … and can introduce …
6. The President and his Administration represent …
7. The Administration includes …
8. The President appoints … but the Senate must …
9. The legislative and the executive branches of government are involved in the system of …
TASK: make the chart of the political system of the USA
THE WHITE HOUSE
The White House is the official office and residence of the President of the United States of America. Many year ago it was known as the Presidential Palace or the Executive Mansion.
It is situated in Washington DC facing Lafayette Square. The White House was built from 1792 to 1800, at the time when Washington DC itself was being built. Originally the house was grey, but after the reconstruction it became white. The building has quite simple but graceful looks. The White House with its landscapes occupies about 18 acres of land.
The only president who didn’t reside here was George Washington (1789-1797) – the first president of the country. He lived in New York and Philadelphian residences. However, it was him who chose the place for the new city.
The first person who lived in the White House was John Adams – the second president of the United States. He lived there with his family but in fact his wife didn’t like her new house. It was always cold there and even 50 fireplaces couldn’t warm three-storey mansion. In 1814 many buildings in the USA were burned by British invaders and the White House was among them. Thus, James Hoban, the architect, had to rebuild the president’s house.
Today, the White House is one of the most popular places for tourist in the USA. Only 5 rooms are open to public and every year more than a million people go through them.
Vocabulary:
Mansion – особняк
To reside –жить
Landscapes –ландшафт
Graceful – грациозный
Task 1: read the text and find the forms of Passive Voice
Task 2: ask questions to the underlined words
Task 3: make a list of the key words which help you to retell the text
Task 4: retell the text using the key words
THE SYSTEM OF EDUCATION IN THE USA
Education in the United States of America is compulsory for children from the age of 6 till 16 (or 18)/ It involves 12 years of schooling. A school year starts at the end of August or at the beginning of September and ends in late June or early July. The whole school year is divided into three or four terms. American students have winter, spring and summer holidays which last 2 or 3 weeks and 6 or 8 weeks, respectively. The length of the school year varies among the states as well as the day length. Students go to school 5 days a week.
The American education system consists of 3 basic components: elementary, secondary and higher education. There is also such a notion as preschool education. At the age of 4 or 5 children just get acquainted with the formal education in a nursery school. The preschool education programme aims to prepare children for elementary school through playing and help them to acquire the experience of association. It lasts for one year. Then they go to the first grade.
Elementary education starts when pupils are 6 years old. The programme of studies in the elementary school includes the following subjects: English, Arithmetic, Geography, History of the USA, Natural sciences, Physical Training, Singing, Drawing, wood or metal work. The education is mostly concentrated on the basic skills (speaking, reading, writing and arithmetic). Sometimes children also learn some foreign languages, general history and such new subjects as drug and sex education. The main goal of elementary education is the general intellectual, social and physical development of a pupil.
Secondary education includes middle school and high school. When children are 12 years old they begin their middle school, from the 6th grade till the 8th grade. There are public and private schools among them as well as among elementary schools. The secondary school curriculum is built around specific subjects rather than general skills. The students have an opportunity to learn some elective subjects, which are not necessary for everybody. After middle school they can select subjects according to their professional interests. The electives are to be connected with the students’ future work or further education at university or college.
High school starts from the 9th grade and lasts till the 12th, from the age of 14 up to 17 years old. Every high school has a special teacher – a guidance counselor who helps the students to choose these elective subjects. Moreover, he helps them with some social problems, too. The elective courses are different in various schools. Members of each grade in high school have special names: students in the 9th grade are called freshmen, 10th graders are called sophomores, 11th graders are juniors and as for 12th graders, they are seniors. At the end of the secondary education pupils have SAT, Scholastic Aptitude Test, a national examination in the US.
After graduating from high schools the majority of the Americans go on studying at higher education establishments. If students study at colleges they can get only a bachelor’s degree in arts or science. Universities offer a master’s degree and a doctorate degree besides a bachelor’s one. Students have to study for 4 years to get a bachelor’s degree. In order to get a master’s degree, they must study 2 years more and, besides, be engaged in a research work.
Vocabulary:
Elementary –начальный
Secondary –средний
Compulsory –обязательный
High school –старшие классы
Higher education –высшее образование
Elective – факультативный
Freshman – новичок
Sophomores –второкурсник
Guidance counselor – методист, консультант
Education establishment – образовательное учреждение
Scholastic Aptitude Test- экзамен на проверку школьных
знаний
Bachelor’s degree – степень бакалавра
Master’s degree – степень магистра
To be engaged – заниматься
Research - исследование
TASK: let’s make two teams and make up as many sentences with new words as possible, the team who makes more sentences than its rival will be the winner
TASK: work in pairs and make a crossword but don’t forget about the questions for the words of the crosswords, after that give your crosswords to your neighbours.
TASK: create the chart with the key words of the system of US education
HOLIDAYS AND TRADITIONS IN THE USA
American holidays are different in origin and show surprising similarities in the manner of their celebration. No matter what the holiday’s origin is, they all seem to be the same thing. A holiday has simply become, for most Americans, a day off from work, though some (for example, Thanksgiving and Christmas) retain some individuality.
The major holidays in the USA are:
New Year’s Day, January, 1st:
People stay awake until after midnight on December 31st to “watch the Old Year out and the New Year in”. Many parties are given on this night. Theatres, night clubs, restaurants are crowded.
When midnight comes, they greet the New Year: people gather in the streets of big cities, they ring bells, blow whistles and automobile horns, some shoot off guns and firecrackers.
Valentine’s Day, February 14th:
It is not a national holiday. Banks and offices do not close, but it is a happy little festival in honour of Saint Valentine, patron of sweethearts and lovers. It is widely celebrated among people of all ages by the exchange of “valentines”. A “valentine” may mean a special greeting card or a little present. The greeting cards are often coloured red, have red trimmings and pictures of hearts.
Washington’s Birthday, February, 22nd:
In addition to commemorating the birth of the United States’ first President, it’s a great day for shoppers. The department stores of Washington D.C., stated a national tradition of sales marked by unusual bargains.
It is not a national holiday. Many schools, offices and banks close for this day, some stay open. The US Congress observes the birthday of George Washington with speeches and readings from his works.
Easter:
Easter is in memory of the Resurrection of Jesus Christ. It falls on the first Sunday after the first full moon between March, 22nd and April, 25th. The 40 days before Easter are called Lent. Just before Easter, schools and colleges usually close. The students have a week or 10 days of spring vacation.
Easter is a church holiday, and many churches have an outdoor sunrise service.
People give each other presents of coloured or even decorated eggs which are the symbol of new life. There is a popular belief that wearing three new things on Easter will bring good luck throughout the year.
Memorial Day, May. 30th:
It is a national holiday. Schools, banks, offices close for the day. On that day Americans honour the servicemen who gave their lives in past wars. Schools, clubs and churches decorate the cemeteries. They put up the flags on the graves of the army, navy and airmen. They hold memorial services in churches, halls, parks and cemeteries.
In addition to solemn services Memorial Day is often marked by other, more joyful ceremonies: colourful parades, sports competitions.
Independence Day, July, 4th:
On this day, in 1776, America signed the Declaration of Independence. It is a national public holiday celebrated with fireworks and speeches praising “Americanism, democracy, free enterprise”.
Labor Day, the first Monday in September:
It is a holiday of recreation. It marks the end of summer and the beginning of autumn. Vacation time is over. Resorts, camps and beaches close…. Parents go to summer camps and take their children back to school.
Halloween, October, 31st:
Halloween is the day or evening before all Saints’ Day. Halloween customs date back to a time when people believed in devils, witches and ghosts. They thought that evil spirits could do all kinds of damage to property. Some people tried to ward off witches by painting magic signs on their barns. Other tried to scare them away by nailing a piece of iron, such as a horseshoe, over the door.
Now children dress up as witches and ghosts and go out into the streets to beg. They go from house to house and say “Trick or treat” meaning “Give me a treat or I’ll play a trick on you”. People give them candy, cookies and apples.
A favourite custom is to make a jack-o-lantern. Children scrape out a pumpkin and cut the outlines of eyes, nose and mouth in its side. They light a candle inside the pumpkin to scare their friends. This custom refers to a man named Jack who still wanders around the earth lightning his way with a pumpkin lantern.
Thanksgiving Day, the fourth Thursday in November:
It is a national holiday. It was first celebrated in 1621 by the Pilgrims fathers after their first good harvest. It is a family day, all members of a family gather at home of their parents. The family eats a large traditional dinner, usually with turkey, cranberry sauce and pumpkin pie.
Christmas Day, December, 25th:
It is usually a one- day official holiday, but it is preceded and followed by festive parties, and marked by special church services, gift-giving and feasting.
Christmas is a family holiday. People stay at home and spend time with their families. People send cards or Christmas greetings to family and friends away from home. Every family tries to have a Christmas tree, which is beautifully decorated. Santa Claus comes from the North Pole in his sleigh, dressed in a red cap and jacket, entering the house from the chimney. He has gifts of whatever kind you may wish for.
Vocabulary:
Whistle – свисток
Firecracker –фейерверк
Festival – празднество
Trimming –украшение
To commemorate – чтить память
Bargain – выгодная покупка
To observe – соблюдать
Resurrection –воскрешение
Lent – великий пост
To honour – почитать, чтить
Serviceman –военнослужащий
Cemetery –кладбище
Solemn –торжественный
Americanism –приверженность к американской культуре
Free enterprise – свободное предпринимательство
To ward off –держать на расстоянии
Barn –амбар
To nail –пригвоздить
Outlines –контуры
Lantern –фонарь
Pilgrims –пилигрим, приезжий
Harvest –урожай
Cranberry –клюква
Feast –пир
Chimney –дымоход
TASK: true or false
1) Theatres, night clubs, restaurants are not crowded on New Year’s Day.
2) Valentine’s Day is not a national holiday.
3) Washington’s Birthday is great day for sellers.
4) Easter is a church holiday, and many churches have an outdoor sunrise service.
5) On Memorial Day Americans honour the servicemen who gave their lives in past wars.
6) Independence Day is celebrated on June, 4th.
7) On Labor Day children go to school.
8) On Halloween people make jack-o-lanterns.
9) Thanksgiving Day is a family day with a large traditional breakfast.
10) On Christmas the Americans prefer going to restaurants.
TASK: fill in the right preposition
1) People stay awake_____ after midnight on December 31st.
2) It is widely celebrated_____ people of all ages by the exchange of “valentines”.
3) The department stores of Washington D.C., stated a national tradition of sales marked ____ unusual bargains.
4) Schools, banks, offices close ____ the day.
5) On this day, in 1776, America signed the Declaration _____ Independence.
6) Now children dress _____ as witches and ghosts and go out into the streets to beg.
7) Santa Claus comes ____ the North Pole ____ his sleigh.
TASK: fill in the missing words
1) Many _____ are given on this night.
2) It is a happy little festival in honour of Saint Valentine, ______ of sweethearts and lovers.
3) The greeting cards are often coloured red, have red _____ and pictures of hearts.
4) People give each other presents of coloured or even ______ eggs which are the symbol of new life.
5) Memorial Day is often marked by other, more joyful ceremonies: colourful _______, sports _______.
6) Independence Day is a national public holiday celebrated with ____ and speeches praising “Americanism, _______, free enterprise”.
7) On Labor Day parents go to _____ camps and take their children back to ______.
8) They go from house to house and say “____ or ____”.
9) Thanksgiving Day was first _____ in 1621 by the Pilgrims fathers after their first good ____.
10) Every family tries to have a Christmas ____, which is beautifully decorated.
TASK: ask questions to the underlined words
TASK: make a list of key words for each holiday and retell them.
FAMOUS AMERICANS
1. George Washington, the first President of the United States of America, was born on a plantation in Virginia, on February 22, 1732. At the death of his father, George, who was then only eleven years old, was left along with his brothers and sisters in the care of his mother.
Washington was only 16 years and had some knowledge of surveying but he was employed to go over the mountains and measure the land and establish the boundary lines. Washington did his work so well that the Governor of Virginia afterward employed him as public surveyor for the colony. At the age of 23 George was made colonel and commander of all Virginia’s forces.
In 1774Washington was chosen one of the Virginia’s delegates to the First, and in 1775 to the Second Continental Congress. When the War for Independence began, Washington was appointed commander-in-chief of all the colonial forces. He managed to build up a strong army, which won the victory in the war.
In 1789 George Washington was elected the President of the United States of America and served two terms. He died in 1799 and in his honour the newly-built capital of the country was named Washington.
2. Samuel Langhorne Clemens, known to the world as Mark Twain, was the son of a small town lawyer. He did not like school but he had a lot of friends and was their leader. As Mark Twain said later, many events in “The adventures of Tom Sawyer” really took place and the characters were taken from real life. At the age of 11 his father died and he had to start working as there were four children in their family. At first he worked as a printer then as a pilot on a boat travelling up and down the Mississippi.
He began to write humorous stories and sent them to newspapers under the pen-name Mark Twain. The publishers liked his stories and he was invited to work as a journalist for a newspaper.
Many professions that he had tried gave Mark Twain a knowledge of life and people and helped him to find his true profession – the profession of a writer.
3.Thomas Alva Edison was an American hero in his own times. He was a self-made man. He taught himself most of what he knew. And his inventions made life easier for people everywhere.
As a boy, he never stopped asking questions about how different things were made or how they worked. For every question he made experiments to find the answer. By the time he was 12, he was an expert in chemistry and physics.
Edison invented an electric bulb, improved early models of the telegraph, telephone, film camera and projector. His most unusual invention was the phonograph.
Edison was interested in many subjects. Throughout his life he studied literature, medicine and music, as well as science.
Vocabulary:
Surveying –геодезия
Surveyor –геодезист, землемер
To employ – нанимать на работу
Boundary lines –границы
To establish –устанавливать, создавать
Governor –губернатор
Colonel –полковник
Commander-in-chief – главнокомандующий
To manage – удаваться
Printer –работник типографии
Pilot –лоцман
Pen name –литературный псевдоним
Self-made- добившийся успеха своими силами
Bulb – электрическая лампа
Film camera – пленочный фотоаппарат
Phonograph –патефон, граммофон
TASK: Translate the sentences into English
1.Его интересовала геодезия.
2.Я учусь и хочу стать геодезистом.
3.Меня взяли на работу три дня назад.
4.Когда были установлены границы государства?
5. Его назначили губернатором.
6.Когда он стал полковником?
7.Он был командиром, но ему не удалось
стать главнокомандующим.
8.Его приняли на работу лоцманом.
9.Пленочные фотоаппараты не пользуются спросом
в наши дни.
TASK: Complete the sentences:
1) George Washington, the first President of the United
2) States of America, was born on...........
3) 2.Washington was only 16 years and had some knowledge
4) of surveying but he was employed…….
5) 3.At the age of 23 George was made …….
6) In 1789 George Washington was …….
7) Samuel Langhorne Clemens, known to the world as Mark Twain, was……. 6.Many events in “The adventures of Tom Sawyer” really took place and the characters……..
8) At the age of 11 his father died and he had to start working as......
9) He began to write humorous stories and sent……
10) Thomas Alva Edison was an American…..
11) 10.As a boy, he never stopped asking…….
12) 11.Edison invented….
TASK: fill in the correct preposition
1) Washington did his work so well that the Governor ____ Virginia afterward employed him as public surveyor ___ the colony.
2) In 1774 Washington was chosen one of the Virginia’s delegates ____ the First, and in 1775 ___ the Second Continental Congress.
3) When the War _____ Independence began, Washington was appointed colonel.
4) He began to write humorous stories and sent them to newspapers _____ the pen-name Mark Twain.
5) Many professions that he had tried gave Mark Twain a knowledge ____ life and people and helped him to find his true profession – the profession of a writer.
6) As a boy, he never stopped asking questions ____ how different things were made or how they worked.
7) ___ the time he was 12, he was an expert in chemistry and physics.
8) Edison invented an electric bulb, improved early models ____ the telegraph, telephone, film camera and projector.
TASK: answer the following questions:
1) Where and when was George Washington born?
2) What happened to Washington when he was 11 years old?
3) What happened to Washington when he was 16?
4) What did Washington manage to do during the War for Independence?
5) Who was Samuel Clemens?
6) What professions did Clemens try?
7) Where did Clemens send his stories?
8) What kind of man was Edison?
9) What did Edison invent?
10) What did Edison study besides science?
Список, использованной литературы:
1) "Across cultures" (Longman)
2) «Страноведение: учебное пособие» ; Попова Т. В. , Тюлькова Л. А. , Вдовюк Л. Н.
3) Britain: the country and its people — James O'Driscoll 2003 [Oxford]
4) Englishelp.ru – английский язык для всех! Https://www.englishelp.ru/
5) History of britain and ireland
6) Богородицкая В.Н., Хрусталева Л. В. Мир Британии. М., 2003 г.
7) Власова Е. Л. Focus on the USA. С - П., 1992 г.
8) Все сдали!//Https://vsesdali.com/topic/britain/87.html
9) Голицинский Ю. Б. Великобритания. С - П., 2003 г.
10) Голицинский Ю. Б. Соединенные Штаты Америки. С - П., 2002 г.
11) Голицынский Ю.Б. Great Britain: пособие по страноведению
12) Изучение английского языка самостоятельно или с преподавателем // Https://englishinn.ru/ The English Inn
13) Кауфман К. И., Кауфман М. Ю. Страницы Британской истории.Обнинск, 1998 г.
14) Колодяжная Л. Н. Познакомьтесь: Великобритания. М., 1999 г.
15) Ощепкова В. В. США. География, история... М., 1998 г.
16) ОщепковаВ. В. О Британии вкратце. М.,1998 г.
17) Павлоцкий В. М. Знакомимся с Америкой. С - П., 1997 г.
18) Павлоцкий В. М. Знакомимся с Британией. С - П., 1997 г,
19) Пособие по подготовке к викторинам и конкурсам по страноведению Великобритании на английском языке. Гаврилова Е.А., Рунова Е.А., Экарева И.Л. 2021// https://www.book.ru/book
20) Салина И. А. Все о Лондоне. М., 1996 г.
21)
Сатинова
В. Ф. Читаем и говорим о Британии и британцах. Минск,
1999 г.
22) Страноведение США: история и современность. Банина Н.В. 2020 // https://www.book.ru/book/940336
23) Страноведение. США: география, история, экономика, культура / Country studies. USA: geography, history, economy, culture Тюмень: Тюменский государственный университет, 2011
Скачано с www.znanio.ru
[1] non-Euclidean geometry – неэвклидова геометрия
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.