
Types of SQL Commands
The following sections discuss the basic categories of commands used in SQL to perform various functions. These functions include building database objects, manipulating objects, populating database tables with data, updating existing data in tables, deleting data, performing database queries, controlling database access, and overall database administration.
The main categories are
· DDL (Data Definition Language)
· DML (Data Manipulation Language)
· DQL (Data Query Language)
· DCL (Data Control Language)
· Data administration commands
· Transactional control commands
Defining Database Structures
Data Definition Language, DDL, is the part of SQL that allows a database user to create and restructure database objects, such as the creation or the deletion of a table.
Some of the most fundamental DDL commands:
CREATE TABLE
ALTER TABLE
DROP TABLE
CREATE INDEX
ALTER INDEX
DROP INDEX
CREATE VIEW
DROP VIEW
Manipulating Data
Data Manipulation Language, DML, is the part of SQL used to manipulate data within objects of a relational database.
There are three basic DML commands:
INSERT
UPDATE
DELETE
These commands are discussed in detail during Hour 5, "Manipulating Data."
Selecting Data
Though comprised of only one command, Data Query Language (DQL) is the most concentrated focus of SQL for modern relational database users. The base command is as follows:
SELECT
This command, accompanied by many options and clauses, is used to compose queries against a relational database. Queries, from simple to complex, from vague to specific, can be easily created.
Data Control Language
Data control commands in SQL allow you to control access to data within the database. These DCL commands are normally used to create objects related to user access and also control the distribution of privileges among users. Some data control commands are as follows:
ALTER PASSWORD
GRANT
REVOKE
CREATE SYNONYM
Data Administration Commands
Data administration commands allow the user to perform audits and perform analyses on operations within the database. They can also be used to help analyze system performance. Two general data administration commands are as follows:
START AUDIT
STOP AUDIT
Do not get data administration confused with database administration. Database administration is the overall administration of a database, which envelops the use of all levels of commands. Database administration is much more specific to each SQL implementation than are those core commands of the SQL language.
Transactional Control Commands
In addition to the previously introduced categories of commands, there are commands that allow the user to manage database transactions.
· COMMIT Saves database transactions
· ROLLBACK Undoes database transactions
· SAVEPOINT Creates points within groups of transactions in which to ROLLBACK
· SET TRANSACTION Places a name on a transaction

Creating a simple query including the sorting of information in ascending order
From the student table in the Access database a query can be created. A query is when the table is searched for specific data and when the query is run and processed by the program the information is presented.
A query is created by using the Query Design Wizard.
![]()
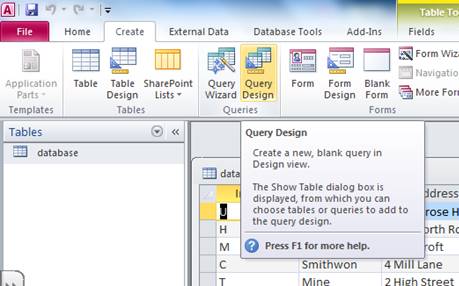
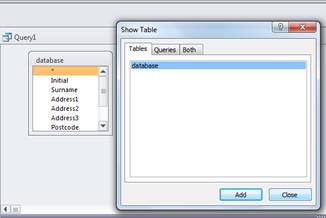
The table is then added from the menu so that the required information can be selected. The pop up window can then be closed, see example below.
![]()
![]()
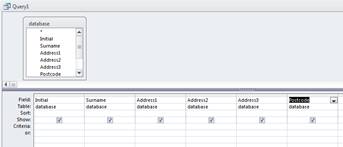
The information that needs to be contained in the query can now be selected from the table by double clicking with the mouse on each field. The field will then appear in the columns below.
![]()
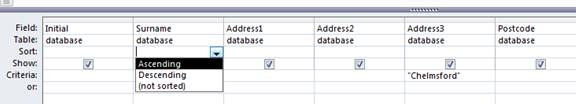
The query I will produce will show all those students that live in Chelmsford. I would also like the query sorted in alphabetically ascending order. The below screen shot demonstrates the criteria used.
![]()
![]()
![]()
The query is then run using the large exclamation mark on the menu ribbon.
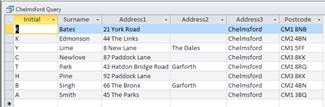
The resultant query is now displayed with those students who live in Chelmsford only and in ascending alphabetical order.
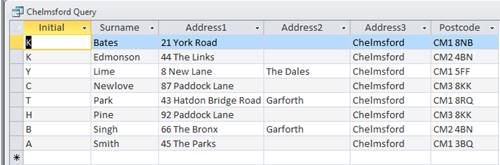
![]()
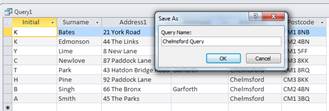
![]() The query has
subsequently been saved (using File, Save functions) with an appropriate file
name and printed off in a suitable format ensuring that it has a professional
layout.
The query has
subsequently been saved (using File, Save functions) with an appropriate file
name and printed off in a suitable format ensuring that it has a professional
layout.
![]()
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.