
Annex 1
We have two powerful tools at our disposal: PHP scripting language and MySQL database engine. It is important to understand how they will be combined with each other.
The basic idea of a database-driven website is to provide the
ability to host site content in a database and dynamically retrieve that
content from the database to create web pages that users can view using a
normal web browser. So, at one end of the system, you have a visitor to your
site who uses a web browser to request a page and expects to receive a standard
HTML document in return. At the other end, you have the content of your site
that is in one or more tables in a MySQL database that only understands how to
respond to SQL queries (commands).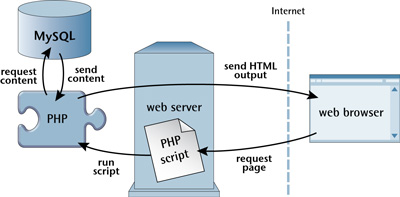
As shown in the figure above, the PHP scripting language is an intermediary that speaks both languages. It processes the page request and retrieves the data from the MySQL database and then dynamically displays it as an HTML page with good formatting.
* A visitor's web browser requests a web page using a standard URL.
* Web server software (typically Apache) recognizes that the requested file is a PHP script, so the server runs a PHP interpreter to execute the code contained in the file.
* Some PHP commands (which will be the focus of this Chapter) connect to a MySQL database and request content that belongs to a web page.
* MySQL database responds by sending the requested content to a PHP script.
* A PHP script stores content in one or more PHP variables and then uses echo statements to output the content as part of a web page.
* Finally, the PHP interpreter passes a copy of the HTML code it created to the web server.
* The web server sends HTML to the web browser as a normal HTML file, except that instead of coming directly from the HTML file, the page is the output provided by the PHP interpreter.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.