
Metal and hydrogen bonds. Unified nature of chemical bond - structure of SUBSTANCE - LESSON PLANS for CHEMISTRY 11 class - lesson plans-lesson plans-author's lessons-plan-lesson summary - chemistry
Lesson objectives: to consolidate knowledge of concepts of metallic and hydrogen bonds, to teach, to explain the mechanisms of their formation, to characterize the physical properties of these types of chemical bond; to give an idea of the reasons for the unity of all types of chemical bonding.
Equipment: Mendeleev PSCE, tables of chemical bond types; test for variants I-II; chemical glasses; water, ethanol, butanol equal volumes; aspirin, crystal lattices, codotransporants. "Principles of complementarity", HCl SL .Diss.
Basic concepts: metal bond, hydrogen bond, metal crystal lattice, molecular crystal lattice.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment
The teacher sets the goals of the lesson before the students, organizes students to check the studied material of the previous lesson. It is also necessary to collect the homework completed by students.
II. Conducting the test
|
Option I |
Option II |
|
|
1. A pair of elements between which an |
||
|
ionic bond |
is formed covalent polar bond |
|
|
a) C and S |
a) N and NB |
|
|
) K I O |
b) O and O |
|
|
in) Si and H |
in) N and O |
|
|
d) Li and N |
d) Na and F |
|
|
2. Formula of a compound |
||
|
with a covalent bond |
with an ionic bond |
|
|
a) NaCl; b) HCl; C) VAO |
a) Ca3N2; b) PH3; C) O2 |
|
|
3. Chemical bond |
||
|
is most polar |
least polar |
|
|
a) C-H |
a) H—S |
|
|
b) C-Cl |
b) H-O |
|
|
C) C-F |
C) N-H |
|
|
4. A covalent bond |
||
|
is the most durable |
to the least durable |
|
|
and) H2; b) N2; C) F2 |
a) O2; b) CL2; C) VG2 |
|
|
5. Is the statement correct? |
||
|
σ-coupling occurs as a result of lateral overlapping of orbitals |
π-bond arises from the lateral overlap of orbitals |
|
|
6. The schemes of overlapping orbitals are given: |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Select the correct answers: a) σ-connection; b) π-connection; C) σ - and π-connections |
||
|
7. The crystal lattice of |
||
|
ionno. |
nuclear |
|
|
power plants have: |
||
|
a) diamond b) potassium fluoride C) carbon monoxide d) sodium sulfide |
a) graphite b) sodium chloride C) iodine d) silicon oxide |
|
Answers to the test questions
(You should write down the answers on the hidden side of the Board and organize a self-check.)
|
Option I |
Option II |
|
1. b), d). |
1.a), C). |
|
2. HCl. |
2. Ca3N2. |
|
3. C—F. |
3. N-O. |
|
4. N2. |
4. VG2. |
|
5. No. |
5. Yes. |
|
6. σ-connection. |
6. π-link. |
|
7. b), d). |
7.a), d). |
II. Learning new material
Plan of presentation
1. Metal connection. Metal crystal lattice. Similarities and differences of a metal bond with an ionic and covalent one.
2. Hydrogen bonding:
a) the mechanism of hydrogen bonding;
b) intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bonding;
C) features of physical properties of substances;
d) the type of crystal lattice of compounds with a hydrogen bond;
e) the significance of hydrogen bonding in living nature; inanimate nature.
3. the uniform nature of all types of chemical bond. Mutual transfer of one type of communication to another, depending on the conditions.
4. Plan features type of chemical communication in connection:
a) type of connection (considering the EO of elements);
b) the mechanism of education:
C) methods of overlapping orbitals, σ-or p-bonds, their strength;
d) bond strength;
d) current of the crystal lattice;
f) possible physical properties of the substance formed by this compound.
All metals combine properties of a General nature, such as a relatively high melting point, the ability to reflect light, high thermal and electrical conductivity, and plasticity. It turns out that these features are due to the existence of a special type of chemical bond in metals — metal.
A metal bond is a bond between positively charged metal ions in a crystal (atoms-ions), which is carried out by the attraction of electrons freely moving in the crystal.
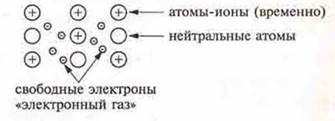
Metal atoms, in accordance with their structure at the external energy level, have from 1 to 3 electrons, less often — 4, and they are weakly bound to the nucleus of the atom, since the radius of metal atoms is relatively large. Electrons can easily break away from atoms, resulting in free electrons and ion atoms appearing in the crystal lattice.
In a crystal lattice, there is a great freedom of movement of electrons: some atoms will lose electrons, the resulting ions can take electrons from the"electron gas".
Free electrons are common to most metal ions in a crystal. This makes the metal bond different from a covalentbond , where the electron pair is shared by only two atoms. In the case of a metal bond, the electrons are evenly distributed over the crystal. This explains the plasticity of methyls, i.e. the ability to shift ions and atoms in any direction without breaking the bond. The energy of the metal bond is 3-4 times less than the energy of the covalent bond.
In the gaseous state (in the form of steam), metal atoms are also bound by unstable covalent bonds. Let us compare the binding energy in H2- 432 kJ/mol; Li2 - 104; Na22-104; Na 2 - 71.1; K22-49.6.
In a metal crystal, the bonds are much stronger than in the vapor state: Li-159; Na -106.
Hydrogen bonding is a kind of chemical bond. It occurs due to the mutual attraction of a positively charged hydrogen atom of one molecule (or part of it) and a negative charge of an atom of a more electronegative element or an unshielded electron pair of another molecule (or part of it).
The mechanism of hydrogen bonding is partly electrostatic, partly donor-acceptor.
Water molecule N2About polar covalent bonding:

Молекула The hydrogen fluoride molecule HF is a covalent polar bond:
![]()
The NH3 ammonia moleculeis a covalent polar bond:
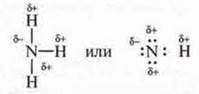
The molecule of alcohol:

In all cases, molecules have common electron pairs between hydrogen atoms and electronegative atoms such as oxygen, fluorine, nitrogen that are shifted in their direction. Hydrogen gets a partially positive charge, and an atom of a more electronegative element gets a partially negative charge. These electronegative atoms also have non-separated pairs of electrons. The molecules of these compounds are mutually attracted.
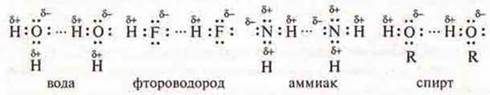
The hydrogen bond is shown by three points ( ... ), it is 15-20 times weaker than the covalent bond.
The presence of a hydrogen bond explains the fact that low-molecular-weight substances (for example, water, hydrogen fluoride, ammonia) are usually liquids or liquefied.
Hydrogen bonding can also occur between different molecules, such as water and alcohol.
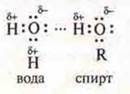
A
hydrogen bond formed between molecules is called an intermolecular bond. Water
molecules form associates (H2O)2; (H2O)3;
(N2O)4; alcohol - ![]() -
alcohol Association. This explains the increase in the boiling point of
alcohols in comparison with hydrocarbons. There is a good dissolution of
methanol and ethanol in water.
-
alcohol Association. This explains the increase in the boiling point of
alcohols in comparison with hydrocarbons. There is a good dissolution of
methanol and ethanol in water.
Experience.
In equal volumes of water, low-molecular-weight alcohols dissolve well, since an intermolecular hydrogen bond occurs. However, the greater the molecular weight of alcohol, the solubility of it in water decreases: such alcohols have much less partial negative and positive charges, hydrogen bonds with water molecules are formed weak.
Let's recall the formula of organic acid-salicylic:
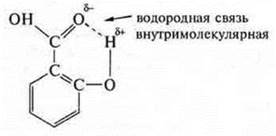
It
was created due to the presence of an O in the group—ОH of hydrogen with a
partial positive charge and a of the carboxyl group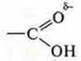 of
oxygen, which has unshielded electron ions, with a partial negative charge.
of
oxygen, which has unshielded electron ions, with a partial negative charge.
The greatest importance of intramolecular hydrogen bonding is in the formation of the natural structure of biopolymers: the secondary structure of protein, the double helix of DNA.
DNA is a biopolymer that contains the genetic information of living organisms. The biopolymer of DNA is composed of nucleotides, which are located in the polymer chains in a strict order. When forming a double helix, hydrogen bonds arise between them and the principle of complementarityis observed : A—T, G—C.
Large purine bases with small pyrimidine ones form hydrogen bonds, which is energetically and spatially advantageous.
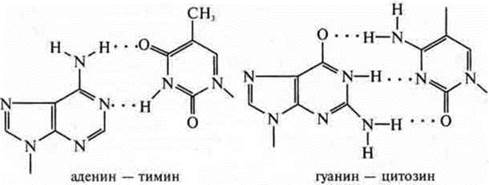
It is recommended to use colotransporants, where the data of nucleotide formulas are presented and how they form intramolecular hydrogen bonds.
All substances that form hydrogen bonds, by their physical properties — gases that easily pass into liquids and, conversely, are easily vaporized-have a low melting point.
Crystal lattice by type molecular. Example: "dry ice" - CO2; water-ice.
Having studied all types of chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, metallic, hydrogen-it should be noted that they have a single nature of origin. There is an electron-nuclear interaction of atoms, accompanied by the release of energy.
Ionic bonding is an extreme case of covalent polar bonding. The degree of ionicity of the bond gives an indication of which type of bond prevails.
Example: LiF is the degree of ionization of 80%, therefore, in this compound 80% is an ionic bond, 20% is covalent polar. In the series of hydrogen halides (polar covalent bond) H—F, H—Cl, H—VG, H—I, the polarity of the bond decreases and at H—At it becomes almost nonpolar, because the difference in EO decreases.
![]()
A metal bond combines a covalent bond — there are generalized electrons and an ionic bond-there is a mutual attraction of generalized electrons and ion-atoms.
Most substances have several types of bonds.
Example: the base is NaOH. Between the oxygen atom and the hydrogen atom of the hydrox group — a covalent polar bond, between the sodium cation and the anion of the hydrox group-an ionic bond.
If we consider the salts of oxygenated acids, the acid residue occurs polar covalent bond between the oxygen atoms and the Central nonmetal atom, and between the metal cation and the acid anion balance of ion bond.
Peroxides: K2O; Na2O2; between oxygen atoms — covalent nonpolar bond, between metal and oxygen-ion bond.
Depending on the conditions, you can switch one type of communication to another. When electrolytic dissociation of compounds with a covalent polar bond occurs, the molecules are polarized by strongly polar water molecules and the bond becomes ionic.
Totransport:
Scheme of electrolytic dissociation of a polar hydrogen chloride molecule into hydrated ions
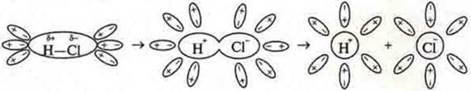
When metals evaporate, the metal bond turns into a covalent nonpolar bond.
In organic chemistry, the covalent nonpolar bond of the Vg2 halogen2becomes ionic when it interacts with unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Conclusion: based on the study of the theory of chemical bondtypes . мwe need to be able to determine the type of chemical bond in the compounds and characterize this compound according to a certain plan.
1. Types of chemical bonds (taking into account the EO of elements).
2. Mechanisms of their formation. What are the connections σ -, π -, multiplicity of the connection.
3. the Corresponding type of crystal lattice, physical properties of this substance.
IV. Homework assignment
§ 6. № 3, 4, 6, prepare for a seminar lesson and independent work.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.