
Hydrolysis of organic substances-DISPERSED SYSTEMS. SOLUTIONS. PROCESSES OCCURRING in SOLUTIONS - LESSON DEVELOPMENTS in CHEMISTRY grade 11 - lesson developments-lesson developments - author's lessons - lesson plan-lesson summary - chemistry
The purpose of the lesson: to summarize information about the hydrolysis of organic substances; based on the concept of "hydrolysis" to show the unity of the world of organic and inorganic substances; to expand the understanding of the meaning of hydrolysis of organic substances in living nature and society.
Basic concepts: hydrolysis, esters, carbohydrates,proteins-biopolymers, adenosine triphosphoric acid, amino acids.
Equipment for the experiment: solutions of Na2, SO3, ZnCl 2 , So 3 salts in test tubes № 1 , 2,32, NaNО3; indicators: universal indicator, phenolphthalein, blue litmus, methyl orange.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment
The lesson combined. The lesson provides for a survey, an experiment of students at the time of a monologue answer. When studying a new material, you can work with a textbook, make a table in a notebook.
II. Checking students ' knowledge
1. Monologue response of students at the blackboard with the implementation of the experiment. Determine the reaction of the medium of solutions of salts Na2SO3; XnCl2;So 3indicators. Give a reasonable answer.
2. Homework # 3 (two salts).
3. Homework assignment # 4 (two salts).
All other students discuss completing task # 5.
At the end of the homework check, offer students a question on the use test:
1) Water solutions of which salt pair have the same reaction (acid, alkaline, neutral)?
![]()
2) Match the dissolved substance with the pH of the solution:
|
1. Slightly alkaline |
|
|
2. Highly acidic |
|
|
3. Neutral |
|
|
4. Weakly acidic |
|
|
5. Highly alkaline |
Answers to the knowledge verification questions
Task # 1. Experiment. Layout in the form of a table.
|
Na2SO3 |
ZnCl2 |
NaNO3 |
|
|
Acid |
is Weak, to-TA |
SIL. K-TA |
SIL. to-TA |
|
The Base |
Is Strong. the OSN-e |
is Weak. aboutSN-e |
Strong. main-e |
|
Compare to thed |
- To -d acid< Cd main |
Cd кислq > C> d main Q dд осн |
K acid= Kd OSN |
|
pH |
pH > 7> |
pH < 7 |
pH = 7 |
|
The Medium |
Is Highly Alkaline. |
Acidic |
Neutral |
|
Universal indicator |
Blue |
Pink |
Green |
|
Phenolphthalein |
Crimson |
- |
— |
|
Blue litmus |
Blue |
Red |
Purple |
|
Methylorange |
Yellow |
Pink-red |
Orange |
The teacher analyzes the correct execution and design of the experiment, warns that the next lesson will be a practical work on the topic "Hydrolysis.Ion exchangereagents".
Task # 2. salts formed by a weak base and a strong acid are subjected to Hydrolysis by cation. Among the proposed salts is Cu(NO3)2, NH4NO3, NiSO4:
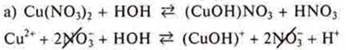
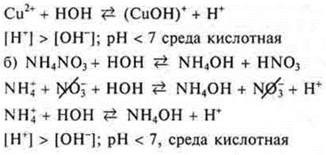
Task # 3.salts formed by a strong base and a weak acid are subjected to Hydrolysis by anion. Of the proposed salts, this is Na2SO3, K(NSOO):
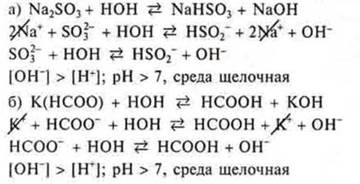
The task № 4
|
SrCl2 |
Rb2SiO3 |
Col2 |
Aug2 |
Fe(NO3)2 |
ALVR3 |
Li2CO3 |
Nal |
KNO3 |
|
|
K-TA |
is Strong. |
Weak. |
Strong. |
Strong. |
Strong. |
Strong. |
Weak. |
Strong. |
Strong. |
|
Basic Strength .-e |
Strong. |
Strong. |
Weak. |
Strong. |
Weak. |
Weak. |
Strong. |
Strong. |
Strong. |
|
pH |
7 |
> 7 |
< 7 |
7 |
< 7 |
< 7 |
> 7 |
7 |
7 |
|
Wednesday |
On natural hair.. |
Lye. |
КислNo problem . |
On natural hair.. |
КислNo problem . |
КислNo problem . |
Lye. |
On natural hair.. |
On natural hair.. |
|
Ins. litmus |
Fiol. |
Ins. |
Red. |
Fiol. |
Red. |
Red. |
Fiol. |
Fiol. |
Fiol. |

Salts formed by strong bases and strong acids do not undergo hydrolysis. The medium in these solutions is neutral.
Tasks for the unified state exam tests
1. Aqueous solutions of substances of vapor No. 1 have a neutral reaction of solutions, since they themselves are formed by a strong base and a strong acid. There is no hydrolysis. KNO3( CON, HNO3), NaCl(NaOH, HCl). If we consider pairs:
No. 2. Na2CO3, FeCl3, then in solution:
Na2CO3-alkaline medium,
FeCl3-acidic medium.
№ 3. Na2SO4, Cu(NO3)2:
Na2SO4-neutral medium,
Cu(NO3)2— the acidic environment.
No. 4. Aug2, АlВr3:
Vavg2-neutral medium,
ALVR3-acidic medium.
2. Weakly alkaline-NH3 solution; 1-G;
Strongly acidic-solution H2SO4; 2-D;
Neutral — a solution of Ba(NO3)2; 3-In;
Weak acid-solution NH4Cl; 4-B;
Strongly alkaline-a solution of KOH; 5-A.
III. Learning new material
Students 'work with the text of § 16 p. 158-161 and completing the table "Hydrolysis of organic compounds and its practical significance".
Thus, hydrolysis is also characteristic of most organic substances — this is their most important organic property. However, in these cases, water is a reagent, and not necessarily one of the products — a weak electrolyte, as in the hydrolysis of inorganic substances, and the solution medium does not always change.
Hydrolysis of organic substances is also a reversible process, the onset of chemical equilibrium is possible, and it is necessary to know the conditions for its displacement according to the Le Chatelier principle.
It should be remembered that the study of the theoretical foundations of hydrolysis requires knowledge not only of previously studied questions of the chemistry course, but also questions of the biology course, especially metabolism in a living organism.
IV. Homework assignment
§ 16, preparation for practical work, repetition § 15, № 7, 8, 11, 12.
|
Organic compounds |
Equation of hydrolysis |
Practical application |
|
of Haloalkanes |
|
Getting alcohol. The presence of alkali shifts the balance to the right, there is a binding of HCl |
|
esters |
The medium is acidic (inorganic acid). To shift the balance to the right, hydrolysis is carried out in the presence of an alkali with the formation of a salt of carboxylic acid and alcohol
|
.in industry |
|
, the Fat ester of higher carboxylic acids and glycerol are oxidized. 1811 By E. Chevrel |
In a living organism, fat hydrolysis is an enzymatic process. |
Soap and glycerine production
In a living organism, fat is synthesized, corresponding to this body, and then participates in the metabolic process. |
|
Carbohydrates. Starch
Carbohydrate metabolism (see the biology textbook): |
In a living organism, hydrolysis is enzymatic. Scheme 4, p. 161 of the textbook.
|
Glucose is the most important energy material in a living organism
In industry, the products of the hydrolysis of dextrins, maltose and glucose. Molasses is a mixture of dextrins, maltose, and glucose. Confectionery prom-t. Dextrins have a gluing effect. They are associated with the appearance of crusts on bread, fried potatoes; when starching and Ironing linen-a dense film |
|
of cellulose (logging waste): sawdust, shavings; non-food raw materials-waste from processing agricultural crops: straw, husks, etc. |
|
Glycerin, ethylene glycol, feed yeast are obtained; sorbitol, ethyl alcohol |
|
Biopolymers — proteins (protein exchange; see the biology textbook) |
|
In the body, hydrolysis to amino acids, which participate in the synthesis of proteins peculiar to this body. Energy source in the body |
|
Hydrolysis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) |
|
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.