
Practical work # 4 on the topic " Solving experimental problems on the topic "Substances and their properties" " - SUBSTANCES AND their PROPERTIES - LESSON PLANS for CHEMISTRY 11 class-lesson plans-lesson plans-author's lessons-plan-lesson summary - chemistry
Objectives of the lesson: to improve practical skills and skills of performing chemical experiments, observing the rules of OT and TB; to teach to apply knowledge of the theory of the topic in solving experimental problems.
Equipment: set of reagents, S6H5OH, SN3Coos, Cao; unique indicator, alcohol lamp, test tubes, holder for prophet; sets for determining substances I, II, III, according to options.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment
Setting goals and tasks. Instruction on performing practical work on tasks in compliance with the rules of OT and TB: all reactions are recorded in molecular and ionic form; the work is paired.
II. Performance of tasks
|
Option I |
Option II |
|
1. Give the proposed compounds a name and classification characteristic: |
|
|
NCl and CH3COOH |
C6N5HE and H2SO4 |
|
To compare their reactivity in relation to the substances: |
|
|
a) Zn. b) Cao; |
a) R-ru I2 b) NaOH; |
|
2. To experimentally determine the substances to give the classification characteristic: |
|
|
sodium hydroxide of feno. aminoacetic acid |
hydrochloric acid potassium hydroxide acetic acid |
|
3. Experimentally confirm the amphotericity of zinc hydroxide and aminoacetic acid (glycine). |
|
III. Summarizing the lesson results
IV. Homework assignment
§ 21 № 6, № 7; § 22 № 5 (tasks).
Answers to practical work tasks
Option 1
1. HCl-hydrochloric acid, oxygen-free, monobasic, soluble, volatile, strong α → 1, stable.
NCSS — acetic acid, oxygen-containing, monobasic, soluble, volatile, weak α → 0, stable.
Experience:
![]() —
the reaction takes place without heating, with a high speed and heat release.
—
the reaction takes place without heating, with a high speed and heat release.
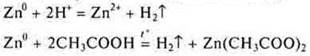
![]() —
without heating, the speed is very low; when heated, the reaction speed
increases.
—
without heating, the speed is very low; when heated, the reaction speed
increases.
Conclusion: HCl is an inorganic acid, strong.
CH3COOH-organic acid, weak.
However, both acids interact with the metal Zn and hydrogen is displaced from the acids. But because acids are different in strength, the reaction rates are different.
Experience:
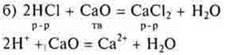
There is a complete interaction of the main oxide with the acid to form a transparent solution of calcium chloride.
![]()
There is an interaction of an organic acid with the main oxide to form a soluble salt, but here it would be necessary to heat it slightly, increase the reaction speed.
Conclusion: organic and inorganic acids interact with the main oxides.
2. Creating a table:
|
Reagents, appearance, smell |
sodium Hydroxide, NaOH |
Phenol With6H5IT |
is an Aminoacetic acid
|
|
Appearance of the solution |
Transparent |
Transparent |
Transparent |
|
Zagroin |
- |
Characteristic |
— |
|
Universal indicator |
Blue pH > 7 > alkaline medium |
Yellow-pink pH < 7 acidic medium |
Green pH = 7 neutral medium |
![]() — pH
alkaline, pH > 7. Universal indicator of color change > to blue under the
influence ofOH -.
— pH
alkaline, pH > 7. Universal indicator of color change > to blue under the
influence ofOH -.
S6N5IT is a phenol, pH acidic, pH < 7. Universal indicator of color change to yellow-pink under the influence of H+.
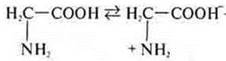 — a
solution is neutral, the bipolar ion
— a
solution is neutral, the bipolar ion
The universal indicator turned green.
The response must specify the number of test tubes for certain substances.
![]() -
sodium hydroxide, oxygen-containing base, monoacid, soluble, non-volatile,
strong α > 1, stable.
-
sodium hydroxide, oxygen-containing base, monoacid, soluble, non-volatile,
strong α > 1, stable.
![]() —
phenol, organic compound, oxygen-containing, monobasic as acid, soluble,
volatile, weak α → 0, stable.
—
phenol, organic compound, oxygen-containing, monobasic as acid, soluble,
volatile, weak α → 0, stable.
 —
alpha-aminoacetic acid, amphoteric compound, monoacid — monobasic, soluble,
non-volatile, weak, stable.
—
alpha-aminoacetic acid, amphoteric compound, monoacid — monobasic, soluble,
non-volatile, weak, stable.
3. Experience: sediment white, gelatinous:
a) Zn(OH)2-base insoluble; amphoteric inorganic compound.
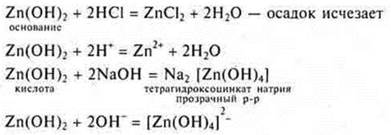
Experience:
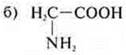 —
aminoacetic acid; an amphoteric organic compound
—
aminoacetic acid; an amphoteric organic compound
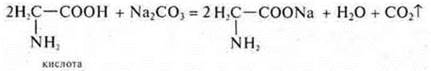
Gas is released and water is formed:
![]()
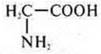 —
aminoacetic acid-base
—
aminoacetic acid-base
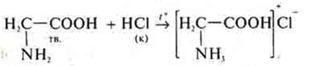
The formation of a transparent salt solution is observed.
When cooling, crystals fall out.
Option II
1. S6N5IT is a phenol, an organic compound, has acidic properties as a monobasic, oxygen-containing, soluble, volatile, weak, stable acid.
H2SO4-sulfuric acid, inorganic acid, oxygen-containing, dibasic, soluble, non-volatile, strong α → 1, stable:
a) p-p I2; phenol interacts, there is a substitution along the aromatic ring;
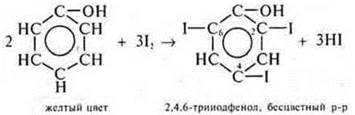
H2SO4(p-p)does not react with I2.
b) R-R NaOH
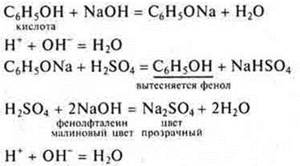
Output: C6N5IT is an organic compound that exhibits acidic properties, since an undivided pair of electrons of an oxygen atom comes into contact with the 6E-π cloud of the aromatic ring, resulting in an oxygen atom of the group-OH will mix the common electron pair with the hydrogen atom in its direction, making it mobile. Phenol is an acid that is weaker than carbonic acid.
H2SO4is an inorganic, strong acid.
2. Creating a table:
|
Reagents appearance, smell |
Hydrochloric acid HCl, solution |
The hydroxide is potassium Hydroxide KOH, solution |
Acetic acid CH3COOH |
|
Appearance |
Transparent |
Transparent |
Transparent |
|
Smell |
No |
No |
Yes, characteristic sharp |
|
Reagent-a universal indicator |
Pink pH < 7 medium strongly acidic |
Blue pH > 7 medium alkaline> |
Yellow-pink pH < 7 среда кислая |
NSl gives a strong acidic reaction.
![]() — the
indicator color change to pink is influenced by H+.
— the
indicator color change to pink is influenced by H+.
![]() the
solution is alkaline, pH > 7. the Universal indicator has changed color >
to blue under the influence ofOH -.
the
solution is alkaline, pH > 7. the Universal indicator has changed color >
to blue under the influence ofOH -.
CH3COOH is acetic acid, the solution is slightly acidic, pH < 7
![]()
The universal indicator changed color to yellow-pink under the influence of H+.
The response must specify the number of test tubes for certain substances.
![]() —
hydrochloric acid, oxygen-free, monobasic, soluble, volatile, strong α
→ 1, stable.
—
hydrochloric acid, oxygen-free, monobasic, soluble, volatile, strong α
→ 1, stable.
![]() —
potassium hydroxide, base oxygen-containing, monoacid, soluble, non-volatile,
strong, stable.
—
potassium hydroxide, base oxygen-containing, monoacid, soluble, non-volatile,
strong, stable.
![]() —
acetic acid, organic acid, oxygen-containing, monobasic, soluble, volatile,
weak α → 0, stable.
—
acetic acid, organic acid, oxygen-containing, monobasic, soluble, volatile,
weak α → 0, stable.
3. The response is the same as in option # 1.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.