
Formative assessment test.
|
Learning objectives |
10.1.2.2 – to understand the law of universal gravitation and describe the motion of spacecrafts. |
|
Descriptors |
describe motion of spacecraft; analyse circular orbits in inverse square law fields by relating the gravitational force to the centripetal acceleration it. |
|
Criteria |
Knowledge with Understanding Applying and Evaluating Information. |
Name……………....................................................class………………………………………..Date………
A. matches the curve of planet Earth. B. results in a straight line.
C. spirals out indefinitely. D. is within 150 kilometers of Earth’s surface
A. circle. B. ellipse. C. oval that is almost elliptical. D. square.
3. A satellite in elliptical orbit about Earth travels
A. fastest when it moves closer to Earth.
B. fastest when it moves farther from Earth.
C. slowest when it moves closer to Earth.
D. at the same rate for the entire orbit.
4. Energy is conserved when an Earth satellite travels
A. in either a circular or elliptical orbit.
B. in only an elliptical orbit.
C. away from Earth.
D. toward Earth
5. When a projectile achieves escape speed from Earth, it
A. forever leaves Earth’s gravitational field.
B. outruns the influence of Earth’s gravity, but is never beyond it.
C. comes to an eventual stop, eventually returning to Earth at some future time.
D. has a potential energy and a kinetic energy that are reduced to zero.
The orbital path of a satellite is shown in the sketch. Use the sketch to answer question 7-9

6. In
which of the positions A through D does the satellite have the
most KE?
7. At what point does the satellite have most PE?
8. At what point does it have highest total energy?
A. Point B B. point A C. point D D. total energy is the same everywhere in the orbit
9. For a satellite in a parking orbit round the earth ( geostationary satellite), calculate:
(Use radius of the Earth = 6.4x106, mass of the Earth = 6.0x1024 kg, G = 6.7x10-11N m2 kg-2)
a. the radius of orbit
b. the height above the Earth
c. the speed in this orbit
10. Determine the escape velocity from the Earth. (G = 6.67 ´ 10-11 N m2 kg-2, mass of the Earth = 6.0 ´ 1024 kg, Radius of the Earth, RE = 6.4 ´ 106 m)
ANSWERS
1. A
2. A
3. A
4. A
5. B
6. A
7. C
8. D
9. a)
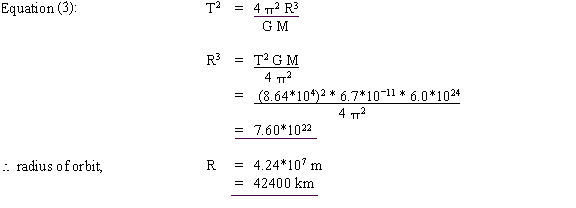
b) height above the Earth = 42400 - 6400 = 36000 km
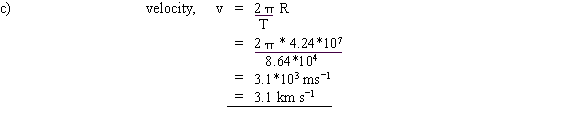
10.
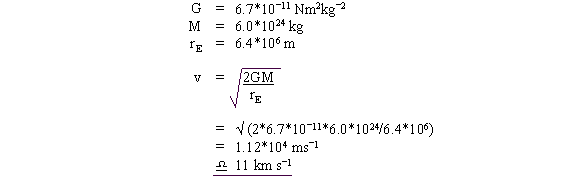
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.