
Публикация является частью публикации:
oxford exam support
 Upper-Intermediate
Student's Book
Upper-Intermediate
Student's BookWords app
Words on the go!
Tim Falla, Paul A Davies OXFORD
Solutions 2nd edition
Upper-intermediate Words app
 |
 test
knowledge of
test
knowledge ofinto contextual how words are used
 |
Think about your progress as you work through Solutions 2nd edition Upper-Intermediote. After completing Skills Round-up read each statement and write the number Of ticks (V) that is true for you. DO the same again after Skills Round•up I —10.
![]()

![]() I need more practice. I
sometimes find this difficult. NO problem!
I need more practice. I
sometimes find this difficult. NO problem!
|
In English I tan |
Skills Round-up |
Skills Round-up 1-10 |
|
|
Listening |
|
||
|
Bl |
understand the main points of speech about familiar topics and follow the main points Of an extended discussion. IA. 2C, IOC |
|
|
|
B2 |
understand extended discussions on familiar topics and identify speaker viewpoints. SC. 6C, 8A |
|
|
|
B2 |
understand and react to current affairs radio programmes. 4A. 5C.6C |
|
|
|
B2 |
follow complex lines of argument on familiar topics. 2C, 'C, SC, 6C |
|
|
|
B2 |
understand detailed and linguistically complex descriptive and narrative passages. IC, 5D, 9C |
|
|
|
|
understand a wide range Of broadcast material and identify finer points of detail. 3B, 8A.9A |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Bl |
understand the description Of events and feelings. 1C. ID. 3D.90 |
|
|
|
B2 |
scan quickly through long and complex texts. locating relevant detail. 50.60. ID, 80.90 |
|
|
|
B2 |
understand magazine articles about current issues in which writers adopt particular viewpoints. 2C, |
|
|
|
2 |
understand factual
articles and reports. |
|
|
|
Cl |
understand long and complex factual and literary texts. 40, 60, 7D, 80 |
|
|
|
Speaking |
|
||
|
Bl |
express personal views on familiar topics. IA, 2A. 2E, 6F |
|
|
|
|
give detailed accounts Of events, real or imagined. 5E, 7E, 8B |
|
|
|
B2 |
present detailed descriptions on a variety Of familiar topics. SD, 7A |
|
|
|
B2 |
take an active part in a discussion On familiar topics. 1B, 2B.3D |
|
|
|
B2 |
develop a clear argument, Supporting my views at some length With relevant examples. 1 G, 2D.4A, 9E |
|
|
|
B2 |
explain a viewpoint on a topical issue giving the advantages and disadvantages. 3C, 7C, 8A, I OG |
|
|
|
Cl |
formulate ideas and Opinions and present them skilfully and coherently to Others. 5E, 6A, 6C, ID |
|
|
|
Writing |
|
||
|
BI |
Write accounts Of experiences, describing feelings and reactions in a simple text. 5G, 9G |
|
|
|
Bl |
write detailed descriptions on a range of familiar subjects. IG, 66. IOG |
|
|
|
B2 |
writea review of a film, book or play. 7G |
|
|
|
B2 |
write detailed descriptions of real or imaginary events in a clear connected text. 2G, 5G, 9G |
|
|
|
B2 |
write an essay which develops an argument. giving reasons in support Of Or against a particular point ofview. 3G, 86 |
|
|
|
B2 |
write an essay Which develops an argument, explaining the advantages and disadvantages of various options. 3G |
|
|
|
Cl |
expand and support Views With subsidiary points, reasons and examples. 8G |
|
|
|
CI |
write formally correct letters. 4G |
|
|
Check
your progress O
Oxford University Press ![]()
 THIS UNIT INCLUDES
THIS UNIT INCLUDES
Describe the photos. What mental qualities do adjectives?
|
the people need for doing these activities? Which of those |
|
|
|
qualities do you have, in your opinion? |
5 |
|
|
2 |
|
best describe you, in your opinion. Explain your choices to your partner. |
|
Why? |
6 |
|
|
Personality traits ambitious argumentative assertive |
|
Which question is each person answering? Whose answer |
|
calm considerate conventional creative dedicated |
|
surprises you most? |
|
eccentric immature organised outgoing responsible |
|
Which personality trait: |
|
selfish sensible serious sociable stubborn |
|
a do you find most annoying? Wtv,'? |
|
unconventional |
|
b do you most admire? Why? c would you like but don't have? Give reasons. |
|
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 1.1:
PAGE 134 |
|
d would you prefer not to have? Give reasons. |
|
3 Complete the sentences With adjectives from exercise 2. |
|
e is the most important to become rich? Why? f is the most important in a friend? Why? |
|
I My brother is so |
7 |
1.02 Listen again and complete the compound |
|
loses at a game. |
|
|
|
2 My aunt is very . If a conversation isn't about |
|
adjectives I —6. |
her, she isn't interested.![]() •motivated
•motivated![]() •tempered
•tempered
3 You're so If
I give an opinion, you always![]() •mean•ng
•mean•ng![]() -skinned
-skinned
|
disagree with it! |
|
|
|
4
suppose I'm quite |
8 |
|
|
5 My best friend is very |
|
exercise 6. Give your own ideas and reasons. |
|
work late, she looks after her little brothers. |
|
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 1.2:
PAGE 134 |
I Out
Of the ![]()
Complete each sentence
people need to climb mountains?
2 Read the text and find the name, age and nationality Of the person it is describing. Then give your own answers to the two questions at the end Of the text.
AT FIRST GLANCE, Jordan appears to be a typical American teenager, but for the past three years he has not been leading an ordinary life. Since he was ten. he's had a single goal: to climb the highest mountain on every continent in the world.
Now thirteen, Jordan has already climbed seven ot the eight mountains on his list including Mount Everest he is due to climb the last, Mount Vinson in Antarctica. next month. He's been using Facebook and Twitter to publicise his climbs arui raise money. And recently, Jordan has been giving motivational talks to schoolchildren around the world via an online link. Tve learned a lot about setting goals. healthy eating and living and Of Course climbing mountains: He has also tpen appearing on TV chat shows.
But some experts have been voicing concerns about the climbs. Have Jordan and his family been consldering the risks? Or have they been thinking more about the publicity?
3 Read the Learn this! box. Then underline all the examples Of the present perfect continuous in the text in exercise 2 and match them With uses 1, 2 and 3.
|
Present perfect simple and present perfect continuous I We use the present perfect continuous form for an action in progress and, the simple form for a completed action. I've been learning Russian, but / can't speak it well. I've learnt a new piece On the piano. / can ploy it now. 2 We use the continuous form for something which has been happening recently and repeatedly: / haven 't been doing my homework this term. But we use the simple form for one occasion or an exact number Of Occasions: I haven't done my proiect/my last three projects. 3 We can use the simple or continuous form with for or since to say how long a Current action has been in progress. The continuous form is more frequent: I've been waiting/"ve waited for hours! |
|

 D
GRAMMAR BUILDER 1.1: PAGE 115
D
GRAMMAR BUILDER 1.1: PAGE 115
Out of the ordinary
simple and continuous. Explain the difference.
(read) the new Stephenie Meyer novel.
2 We (not play) football for a long time. 3 She (do) well in her exams this year. (finish) his science homework.
My parents (go) to the new gym. 6 You (eat) my crisps!
LOOK OUT!
State verbs are verbs which describe States, whereas dynamic verbs describe actions. We do not use State verbs in continuous tenses.
![]() X I've always hated
dogs. Some verbs can be State or dynamic verbs, depending on the meaning: e.g.
taste is a dynamic verb when it means try.
X I've always hated
dogs. Some verbs can be State or dynamic verbs, depending on the meaning: e.g.
taste is a dynamic verb when it means try.
We've been tasting different cheeses.
Is.üt.tastinyttrrmy?x Does it taste funny?
![]()
5 Read the Look out! box. Then find a verb in the text in exercise 2 which is used once as a state verb and once as a dynamic verb. What is the difference in meaning?
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 1.2: PAGE 115
6 Complete
the sentences about Jordan using the present perfect continuous, affirmative or
negative. or the present perfect simple form when the continuous is not
correct. ![]() His dad and Step-mum
His dad and Step-mum ![]() (help)
him.
(help)
him.
2 He (like) mountain-climbing since he was
(climb) the highest mountain in Australia.
(not climb) the highest mountain in
(not go) to school very regularly this year. (appear' on TV a lot recently.
7 Look at the prompts and write questions using the present perfect continuous if possible. If it is a State verb, use the present pertKt simple
I what / you / watch on TV / recently?
2 how long / English?
3 vou / work hard / recentty?
4 how long you / teacher?
5 your best friend seem I happy / recently?
6 how much / it / rain / this month?
7
 What time / / goto bed / recently?
What time / / goto bed / recently?
understand this grammar lesson?
|
|
8 Ask and answer the questions in about adolescents. HOW many can you think of in three minutes?
2 1.03 Listen to a radio programme about two writers. Think Of at least two things they have in common.
|
EXAM |
TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
When you do a multiple choice listening task, mark the answers you know after the first listening. When you listen again, focus mainly on the answers you still need. |
||||||
3 Read the Exam tip and mark the answers Which you think you know for questions 1—5. Then listen again and choose the best answers. 1 The novelist l. D. Salinger went to university but a was asked to leave.
b received poor grades in his first year. c left before finishing the first year.
d did not regard getting a degree as •success'.
2 Salinger's famous novel about adolescence was a popular mainly because it was controversial. b only popular with younger readers. c extremely popular but condemned by some people. d not taught in many schools at first.
3 Because Salinger refused to be in the public eye, a people stopped asking him for interviews. b nobody was even sure What religion he was. c he was rarely talked about.
d his fame actually increased.
4 Harper Lee's education was a not as successful as she had hoped. b more successful than Salinger's. c not as successful as Salinger's. d very similar to Salinger's.
5 How did Harper Lee find time to write herfirst novel? a A friend paid for her to take a year off work. b A friend got her work as a songwriter in New York. c She couldn't find a job in New York.
d She wrote slowly for ten years in total.
![]() Complete
the chart using a dictionary to help you if necessary. Which four religions did
J. D. Salinger follow during his life, according to the radio programme?
Complete
the chart using a dictionary to help you if necessary. Which four religions did
J. D. Salinger follow during his life, according to the radio programme?
|
Religion Christianity Hinduism Islam Judaism |
Adjective Buddhist
Sikh |
Follower Buddhist
|
narrated by a girt called Scout. find two separate implications in the text that Aunt Alexandra will be staying for a long time.
'Put my bag in the front bedrcÄMn, Calpurnia,' was the first thing Aunt Alexandra said. 'Jean Louise, stop scratching your head,' was the second thing she said. Calpurnta picked up Aunty"s heavy suitcase and opened the door. 'I'll take it,' said Jem, and took it. I heard the suitcase hit the bedroom floor with a thump. The sound had a dull permanence about it. 'Have you come for a visit, Aunty?' I asked. Aunt Alexandra's visits from the Landing were rare, and she travelled in state. She owned a bright green square Buick and a black chauffeur, both kept in an unhealthy State of tidiness, but today they were nowhere to be seen.
'Didn't your father tell you?' she asked.
Jem and I shook our heads.
' ProbÖ• he forgot. He's not in yet, is he?' 'Nome, he doesn't usually get back till late afternoon,' said Jem,
'Well, your father and I decided it was time I came to stay with you for a while. '
 'For
a while' in Maycomb meant anything from three days to thirty years, Jem and I
exchanged glances. 'Jem's growing up now and you are too,' she said to me.
"We decided that it would be best for you to have some feminine influence.
It won't be many years, Jean Louise, before you become interested in clothes
and boys.
'For
a while' in Maycomb meant anything from three days to thirty years, Jem and I
exchanged glances. 'Jem's growing up now and you are too,' she said to me.
"We decided that it would be best for you to have some feminine influence.
It won't be many years, Jean Louise, before you become interested in clothes
and boys. ![]() I could have made several answers to
this: Cal's a girl; it would be many years before I would be interested in
boys; [ would never be interested in clothes but I kept quiet.
I could have made several answers to
this: Cal's a girl; it would be many years before I would be interested in
boys; [ would never be interested in clothes but I kept quiet.
6 Find evidence in the text Which implies that:
1 Aunt Alexandra is bossy.
2 Jem is considerate.
3 Scout and Jern•s father is absent-minded. 4 Scout is a tomboy.
7
![]() Work in pairs. Choose one book, film or
W show
Work in pairs. Choose one book, film or
W show
from your list in exercise I. Give an example Of how it deals With one or more of these topics:
• friendship
and arguments between friends. ![]() the relationship between teenagers and
adults.
the relationship between teenagers and
adults. ![]() rebellion and breaking the rules.
rebellion and breaking the rules.
• becoming
an adult and taking responsibility for your life. 1 Outofthe ![]()
I can understand and react to a text about a high achiever.
BAD SCHOOL LIVES
Work in pairs. Discuss the quotation below. What personality adjectives could you use to describe this person? Does it sound like you?
I'm desperate to achieve. I'm desperate to get high margs. I'm too hard on m•fself_
Cameron Thompson, fourteen•gear-old mathsprodigy
2 1109 Read the text opposite about Cameron Thompson. DO you think the adjectives you chose in exercise I are accurate? What Others could you add to your description? Justify your answer with evidence from the text.
|
EXAM TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
When you do a multiple choice reading task, read the options carefully and choose the one which matches the text in terms of information. DO not be distracted by specific words or phrases. focus on the meaning. |
||||
3 Read the Exam tip. Then choose the correct answers for the questions (1—5).
I Between the ages Of four and ten, Cameron a demonstrated outstanding ability in maths. b allowed his passion for numbers to dominate his life. c excelled at various school subjects.
d didn't really fulfil his promise at maths.
3 Cameron's problems With communication a have been getting worse recently.
![]() b
haven't been affecting his popularity at school. c are irrelevant when he's
doing maths, d have been interfering With his ability to do maths work.
b
haven't been affecting his popularity at school. c are irrelevant when he's
doing maths, d have been interfering With his ability to do maths work.
4 Cameron met a boy at his new school who a has something in common with him.
b has even more severe problems With communication. c is even better at maths.
d took a strong dislike to him from the first day.
4 Professor Leader thinks Cameron should a continue With his degree.
b have a temporary break from his degree. c give up maths completely for a few years. d try to increase the speed Of his progress.
5 Recently. Cameron has noticed a a deterioration in his relationship with his parents. b a loss of ambition academically. c an improvement in his social life.
d a sudden improvement in his school life.
Out ofthe ordinary
Teachers first noticed Cameron Thompson's talent for numbers when he was four years old and at pre-school. Throughout primary school, Cameron Thompson's best subject was maths. Then. When he was eleven, he took a maths test prior to entering secondary school. The test was Out of 140; Cameron scored 141. 'l broke the system,' he recalls.
Since then. he has continued to progress quickly. He passed two GCSEs (maths and further maths) at the age Of eleven and then got the highest grade in his maths A-Ievel before the end Of that same academic year. He is now fϥrteen years Old and studying for a degree in maths, a remarkable achievement bearing in mind his age.
But his academic achievements have not always been matched by social Success. 'I have the social ability Of a talking potato,' he admits. In other words. he feels more at ease with numbers than among Other teenagers. 'Most people my age do despise me. rve been like this for years.'
Communication is not one of Cameron's strong points and, aside from the problems this causes socially. it is now beginning affect his marks in mathematics. This is because. at undergraduate level, he is expected to give
|
|
4 |
I considering 5 before 9 because of 2 together with 6 apart from 10 regarding 3 about 7 past/furtherthan 4 with 8 right through |
|
|
5 |
2 Doing a hobby usually means spending more time about / among people your own age.
4 It's essential to develop non-academic skills prior to / regarding starting your career. |
|
reasons for his answers alongside the answers themselves. |
|
|
|
Cameron's difficulty is that he Often doesn't know how he |
|
considering / Owing to a lack of facilities. |
|
has arrived at the answers, even though the answers are |
|
6 Doing hobbies can help develop useful skills among / |
|
usually correct. |
|
aside from the ones you need for the hobby itself. |
|
Cameron and his family have recently moved house and |
6 |
|
|
Cameron is due to start at a new school. He regards it as |
|
activities which would be best for developing a person's |
|
a chance to make a fresh start and make some friends. |
|
social skills. Give reasons for your choices. Use the activities |
|
gut his mother, Alison, has a few worries concerning his lack Of social skills. While she describes Cameron as •very |
|
below or your own ideas. |
|
sensitive', she also acknowledges that he is socially naive |
|
Extra-curricular activities doing drama doing karate |
|
and often oblivious to signals from Other people. |
|
doing yoga going dancing going shopping |
|
The new school specialises in dealing with students |
|
joining a choir jogging learning an instrument |
|
who, like Cameron, excel academically but find it difficult |
|
playing basketball playing computer games |
|
to relate to other students. And indeed, on his first day. |
|
watch ing sport |
|
Cameron did make a new friend — a boy called Tim — mainly |
7 |
|
|
oning to a shared dislike Of lustin Bieber's music. |
|
|
|
Recently, a maths professor from Cambridge University |
|
Student A: You are a teenager who, like Cameron, has poor |
|
has been looking at Cameron's work. His advice to |
|
social skills. You want advice on how to improve them. |
|
Cameron is perhaps surprising. professor Imre Leader |
|
Student B: You are giving Student A advice on how to |
|
thinks Cameron should slow down. Stop taking maths |
|
improve his/her social skills. Suggest activities to achieve |
|
exams, and wait until he is eighteen before doing a degree. |
|
this. |
|
•There's quite an important distinction,' he explains, |
8 |
|
|
•Between taking lots of exams as fast as you can, and |
|
should agree on one activity for Student A to try. Use the |
|
relaxing and enjoying the level that you are at — What we call enrichment.' Professor Leader believes Cameron Will |
|
expressions below to help you. |
|
do better in the long run if he Stops trying to progress so |
|
Su stin |
|
.uickly_ And although Cameron does want to finish his |
|
How about taking up ? It's realty good for (building |
![]()
Since turning fourteen, Cameron's feelings towards girls 0b ectin
|
being disgusted by them.' He's even been on a first date — without his parents. And in general, he feels less isolated and unusual than he did before. 'There are other people me — high maths abilities, bad school lives — I am not Spooky. ' |
be my thing/would suit me). Maybe you've got a point./That's not a bad idea./l could try it, I suppose./l might give it a go. |
Save changed. As he puts it, 'I started to like them instead TO be honest, I don't realty like not that keen on ...Il don't feel happy about don't think (would
1 9
Work in pairs. Discuss how strongly you agree With this Statement: I prefer to be in the background than in the The verbs remember, forget, stop and try can be followed
spotlight. Give it a mark between 5 (strongly agree) and 0 (strongly disagree).
2 Work in pairs. DO questions 1—3 Of a personality quiz. Are the results So far similar to your ideas in exercise I?
Fitting in or STANDING OUT: Which do YOU prefer?
Take the personality quiz and find out!
More a's than b's? You like to stand out!
Do you let your friends to-row your clothes?
Sure - ant I hen them choose! b No W3/!
If you want your decorated do you invite friends to come tor a Dainting ;nrty•? decide to paint it yourself one weekend?
If a stranger seems tabe upset in the street doyou ,offet to help immediately?
b avoid helping because you teel shy?
3 Read the Learn this! box. Complete the second example of each pattern With phrases from the quiz in exercise 2.
|
|
Verb pattern S I verb + infinitive a They failed to finish the race. 2 verb + •ing form a / gave up doing karate school.
3 verb + Object + infinitive a They forced him to get into the Cor.
4 verb + Object * infinitive without to a She made me wait outside her office.
5 verb + Object + past participle a Let's get your bike repaired tomorrow.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4
find
three more examples Of verb patterns in questions ![]() Of
exercise 2. Which pattern does each one belong to?
Of
exercise 2. Which pattern does each one belong to?
5 Can you remember if the verbs below are followed by (A) an infinitive or (B) an •ing form? Label them A or B then check your answers in the Grammar Builder 1.3 on page 116.
![]()

 agree
avoid can't help can't stand consider deny enjoy feel like finish hope imagine
keep (on) miss practise pretend refuse risk spend (time) suggest
agree
avoid can't help can't stand consider deny enjoy feel like finish hope imagine
keep (on) miss practise pretend refuse risk spend (time) suggest
Outoftheordinary
by an infinitive or •ing form, but with different meanings: I remembered to vote. / / don't remember voting (but I did).
I'll never forget visiting the Tate. I forgot to visit the Tate. She's stopped smoking. / She stopped to light a cigarette. / tried to stand up but / couldn't. / tried standing up but / still couldn't see the stage.
The verbs see, hear,
watch and feel are followed by an Object ± -ing form for ongoing actions, or an
Object ![]() infinitive without to for completed
actions:
infinitive without to for completed
actions:
/ can felt him staring at me. / felt the ball brush mvarrn. / saw two cats fighting. / Did you see him steal the car?
![]()
6 Read the Look out! box. Then explain the difference in meaning between each pair Of sentences. 1 a heard my neighbour shout.
b heard my neighbour shouting.
2 a She tried smiling at the policeman.
b She tried to smile at the policeman.
3 a The busker stopped chatting With the crowd. b The busker stopped to chat With the crowd. 4 a You must remember to speak to Sam. b You must remember speaking to Sam.
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 1.3: PAGE 116 ![]()
7 Complete questions Of the quiz. Use the infinitive (With or Without to), past participle or •ing form Of the verb in brackets. Then answer the questions.
8 In pairs. write two more questions for the quiz.
Include at least one verb pattern from the Learn this! or Look out! box. Swap With another pair and answer their questions.
I can describe a photo and answer questions about it.
1 Look at the photo.
Choose three adjectives below to describe the couple's overall appearance. Then compare your ideas in pairs. Do you agree?
attention-seeking cool fashionable individual intriguing messy outlandish unattractive
2 Work in pairs.
Add the words below to the mind map. Then add as many other words as you can in two minutes.
bracelet crouching dyed eye-liner mascara moody piercing spiky tie tights
![]()
3 .06 Listen to a candidate describing the photo in exercise
1. How many of the words in exercise 2 does she mention?
|
EXAM |
TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
When you describe a photo, talk about what you can see and also what you can guess Or deduce. For guesses and deductions. avoid repeating think and instead use phrases like; should think they are Mavbe/Perhaps They look as if... They 100k like They look as though They are obviously I'd say they are They could be/may be/might be |
||||||||||
Read the first Exam tip. Then listen to the candidate again. Which of the phrases in the box does she use?
|
EXAM |
TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The examiner's first question in the picture description task usually asks you to interpret the picture, the second usually requires you to give a more general opinion. Listen carefully to each question and make sure you really answer them. |
|||||||||
5 Read the second Exam tip. Then read the phrases below and decide if each one would be more useful in answering question 1 or question 2 in the exam.
a Judging by , I reckon b By and large, c Looking at . I'd say that d Personally, I think„ e In my experience, f Jr s clear from the photo that
6 Look at the examiner's first two questions for the photo in exercise I. Discuss them in pairs and note down your ideas. Do you think the boy in the photo cares about his appearance? do you think so?
2 How much can you tell about a teenagers personality just from looking at their appearance?
7 1.07 NOW listen to the candidate answering the questions. Do you agree with her answers? Why?'Why not?
8 1.07 Listen again. Which phrases from exercise 5 does the candidate use?
9 In pairs, describe the photo below. Then take turns to ask and answer the examiner's first two questions. Include at least two phrases from exercise 5.
1 What impression do you think these women want to give other people?
2 Why do some young people want to dress in a way that older people find shocking?
unit
Read the saying below and its definition. DO you Match four adjectives from the words below With Connor
|
agree or disagree? Give examples to support your opinion. Opposites attract. |
|
and four with Bess. Justify your answers using phrases from |
|
||
|
People Who are very different tend to get on well together. |
|
conformist considerate dependable funny |
|
||
|
2 Read the text. Can you explain the title? |
|
outgoing shy unconventional unreliable |
|
||
|
|
4 |
Complete these contrasting pairs Of phrases |
|
||
|
CÐ/LZ and CHEESE |
|
for describing character and behaviour. Use the verbs below. Which phrases are in the text in exercise 2? count get give keep let look play take wear |
|
||
|
Describing character and behaviour |
||||
|
be up for anything/ it safe |
||||
|
(always) on the bright side expect the worst speak your mind your Opinions to yourself things in your stride / get stressed your heart on your sleeve / not much away never be lost for words / tongue-tied me down / I can't on you |
||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
|
|
Complete the second sentence So that it means the same as the first. Write 2—5 words, including the word in brackets. |
|
Connor and Bess are completely different from each other. |
|
She takes everything in her stride. |
|
They're both seventeen years old, but that's about all |
|
She about anything. (stressed) |
|
they've got in common! |
|
You can always count on me. |
|
For a teenager, Connor comes across as very confident. |
|
down. (never) |
|
He finds it easy to talk to people and is never lost for words. |
|
a Suddenly, I got tongue-tied. |
|
He's got a good sense of humour and really enjoys making |
|
was words. (lost) |
|
people laugh. |
|
He doesn't give much away. |
|
As far as clothes go, Connor dresses in quite an unusual |
|
He doesn't his sleeve. (heart) |
|
way and buys a lot Of his outfits in second-hand markets |
|
a I usually expect the worst. |
|
and charity shops. He Often changes his hairstyle too. Connor is really good fun to be With. He's up for anything, |
|
I rarely side. (bright) |
|
and when you go out with him, you end up doing some |
6 |
Read the Look out! box below. Find an example Of this use Of |
|
crazy things. Having said that, he isn't that reliable. We Often make plans to go out at the weekend, but he's always |
|
the present continuous in the text in exercise 2. |
|
phoning me at the last minute to change the arrangement. |
|
LOOK OUT! |
|
Unlike Connor, Bess hates being the centre Of attention |
|
We normally use the present simple for describing regular |
|
and isn't particularly interested in fashion. When it comes |
|
actions. However, we can use the present continuous with |
|
to clothes, Bess usually plays it safe. And Whilst Connor |
|
always or forever to express disapproval. |
|
regularly changes his hairstyle, Bess's hair has looked the |
|
Tom always goes home by bus. (fact) |
|
same since I first met her. |
|
Lucy is always asking me for money. (disapproval) |

![]() When
Bess is with close friends. she tends to be very talkative, but she often gets
tongue-tied in social 7 In pairs, discuss which
person in the text, Connor
When
Bess is with close friends. she tends to be very talkative, but she often gets
tongue-tied in social 7 In pairs, discuss which
person in the text, Connor
|
situations. However, she's a very good friend. She always thinks Of Others and she never lets you down. Connor and Bess are complete opposites. Nevertheless, I get on well With both of them — and surprisingly, perhaps, they get On well together. |
or Bess, is more like you, in your opinion. Who would you rather be friends with? Give reasons. |
Outofthe ordinary
You are going to do the following exam writing task. Look at
|
the list Of topics you might include in the description. Which ones are mentioned in the text on page 12? Write a description of two people you know Who are very different. Write 200—250 words. |
exercise 2. To make your writing more sophisticated, include four different ways to make contrasts from the Learn this! |
|
EXAM |
TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Make your descriptions ot people's personalities more subtle by using the phrases below: She tends to verb He has a tendency to verb She has a habit 4 •ing form He comes across as ± adjective People regard her os adjective People consider her + adjective Some people find her adjective She can be (adjective) at times. |
|||||||
annoying habits clothes hair hobbies likes and dislikes personal traits talents
2 Choose the two people you are going to write about. Make notes about them in the chart. Use four topics from exercise I or your own ideas.
 6 Read the Exam tip. Find two Of the phrases in the model text
6 Read the Exam tip. Find two Of the phrases in the model text
|
3 |
Read the Learn this! box below. Underline examples Of these words and phrases in the text on page 12. |
|
on page 12. Then suggest two other places in the text where you could use phrases from the tip. |
|
|
|
7 |
Rewrite these sentences in a more subtle way. Include the |
|
|
Contrast You can use a variety Of phrases for making contrasts, not just but and however. Unlike Sara, Jade is tall. In contrast to Sara, Jade is tall. Sara is short, but/whereas her sister Jade is tall. While/Whilst Sara is short, lade is toll. Sara is short. lode, on the other hand, is tall. lade is tall, and yet her sister Sara is short. Jade is tall. However, Sara is short. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
word in brackets.

 |
2 My neighbour talks too much. (tendency)
![]() My friend George is an ambitious student. (regard)
My friend George is an ambitious student. (regard)
4 Lucy's brother offends people. (tends)
![]() My best friend is argumentative.
(find)
My best friend is argumentative.
(find)
6 My mum is unconventional. (can)
7 1'm trustworthy. (consider)
8 He says the wrong thing. (habit)
8 Do the writing task in exercise 1.
4 Choose the correct words in these sentences.
|
CHECK YOUR WORK Have you:
used different phrases for making contrasts? included phrases from the tip box? checked your spelling and grammar? |
I Luke is eccentric. unlike / whereas his sister is conventional.
2 Whilst / In contrast to my brother is hard-working, I'm quite lazy.
3 Ryan is very popular, and yet / while he's quite shy.
4 Sam is easy-going, but / however his brothers aren't.
5 Charlie is quite generous. His cousin, whereas / on the Other hand, is very penny-pinching.
1 Get Ready for your Exam
|
|
1 and decide which you would most like to attend. Then explain your choice to your partner.
a an intensive English course in the USA b a survival course in the Arctic c a meditation and martial arts course d a performing arts course (music, dance, drama, etc.)
2 DO the exam task.
91.08 You will hear information about various summer courses. Match each extract to the correct summary sentence (A—F). There is one extra sentence.
Speaking
4 Which Of a summer activity course are most important? put ideas below in order from Exercising your mind could be the answer to Vour I (most important) to 4 (least important). everyday problems.
a having the chance to mix and make new friends Join the fast track to personal safety.
b improving fitness and/or strength
C Go back to the beginning to discover the true c learning a new skill or improving an existing one meaning.
d having fun and avoiding boredom
D This year, exciting fun in the water is available to all.
If you know the basics, refine your skills and train 5 Do the exam task.

financial income repay save waste (v) Say if you agree or disagree, and why.
|
Mone for teens |
|
2 |
|
Tips for parents |
|
4
Don't
worry if your What might seem a poor decision to you can sometimes be a valuable lesson for the child. 5 Involve teenagers in family finances. Discuss big decisions (e.g. Can we to take a holiday this year?) and weekly or monthly like food and power bills. 6 Teach teenagers how to Wisely but allow them the freedom to make mistakes. |
1 ![]() You
get what you pay for. If something is
You
get what you pay for. If something is ![]() probably
isn't worth having.
probably
isn't worth having.
2 Friendship is
3 The more you are, the easier your life is. 4 Being will help you to get rich.
6![]() Listen
and match each speaker with a statement (A—E). There is one statement you don't
need.
Listen
and match each speaker with a statement (A—E). There is one statement you don't
need.
This person:
A won't spend money just to have nice things.
B ![]()

has
been raised to be careful with his/her money.
C should probably be more careful with his/her money.
D thinks that having a bank account isn't necessary.
E is good with his/her finances but likes spending, too.
7 ![]() Discuss in pairs. Give reasons and
examples.
Discuss in pairs. Give reasons and
examples.
1 Does money burn a hole in your pocket?
2 DO you keep some money back for a rainy day?
3 When you buy something, do you shop around?
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 2.1: PAGE 135 ![]()
3 Which two tips do you think are most useful? Give reasons.
• andpoor
|
|
|
Some Of these sentences are incorrect. Correct them. |
|
you think buying a lottery ticket is a good idea? Give reasons. |
|
1 Dan use to work in a bank. X |
|
2 Read the text and answer the questions. |
|
Dan used to work in a bank 2 1'm not used to wear glasses, butl do now. |
|
I Has Molly always been well Off? |
|
3 Did you use to have long hair? |
|
2 What was her life like in Bristol? |
|
4 MV dad would have a beautiful old sports car. |
|
3 Why didn't Molly check whether she'd won the lottery? |
|
5 Sally used to be a teacher for ten years. 6 Joe used to smoke. He'd smoke 30 a day. |
5 Complete the sentences with would, used to or the past LI.J@K'V simple. Sometimes more than one answer is possible.
1 My
dad![]() (have) a credit card. He (use)
it
(have) a credit card. He (use)
it
NUMBERS! for buying expensive things. But two
years ago he ![]()
(get) rid of it. The credit card company (charge) a
Molly Higgins is a very rich woman and the proud owner very high rate of interest and he (end) up deep in of a ten-bedroom mansion near London. But she didn't debt.
use to be rich. She used to live in a
small flat in a run• 2 My grandad ![]() (be) a factory worker. He
(be) a factory worker. He![]()
![]()
down
area of Bristol and get by on state benefits. Every (work)
in a car factory for 30 years. He ![]() (have
to)
(have
to)
![]()
Thursday evening Molly would buy a EuroMillions lottery work long hours and he (not earn) very much ticket. She'd always choose the same numbers but she money. But he (do) the lottery every week and didn't usually look at the winning eventually he (win) enough money to buy a car.
numbers the following evening. D
GRAMMAR BUILDER 2.1: PAGE 117 ![]()
![]() 'l never used to win anything, and I'd
sometimes forget to LOOK OUT!
'l never used to win anything, and I'd
sometimes forget to LOOK OUT!
look at the results,' says If we stress would, it suggests irritation and criticism. Molly. But one Friday, when In this case, we don't use the contracted form 'd.
she
checked the results He would wear those old jeans to school every
day. she couldn't believe her ![]()
1

eyes.
She'd won the jackpot 6 01.10 PRONUNCIATION Read the Lookout! box. Then - €10
million! listen, repeat. and say if the speaker is irritated.
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
3 |
Read the Learn this! box. Then underline all the examples Of |
|
including the word in brackets. |
|
|
used to and would in the text. |
|
I It was typical Of Sue to interrupt all the time! |
|
used to and would 1 We use usedto and would to talk about habits and situations that are now finished. We used to live in London. But now we live in Brighton. When I was at primary school I'd always play football after school. 2 We don't use wouldwith state verbs. I.wauldheve•c-cat X / used to have a cat. 3 We don't use used to or wouldto say how long a situation or habit continued. We use the past simple. Sh She worked in a bank for six years. 4 Never used to and would never are common negative forms.
He would never admit he was wrong. |
|
all the time! (would)
I was in the habit Of spending all my pocket money. all my pocket money. (used)
In the '90s my dad always drove to work.
In the '90s my dad ![]() work.
(would) 4 In the past was your hair much longer?
work.
(would) 4 In the past was your hair much longer? ![]() much longer hair?
(use)
much longer hair?
(use)
![]() There wasn't a bank at the end of the
street.
There wasn't a bank at the end of the
street.
There a bank at the end of the street. (never)
8 Work in pairs. Think about when you were younger. Using would or used to, tell your partner about: 1 something ridiculous you often wore when you were little.
2 something boring you did at weekends.
3 something you did that annoyed other people.
16 2 • and poor
HOUSE!
In July property developer lim Lock bought a large, detached.
|
be a nursing home, through a downstairs window that had been left open. The group, includes three small |
|
|
|
children, is sleeping on the floor in sleeping bags. There's |
4 |
Decide Which opinion is not expressed by the |
|
no heating or furniture. Mr Lock went to the police but |
|
squatter in the interview. Then listen again and check exactly |
|
they said they could do nothing. Squatting in commercial |
|
What she says. |
|
properties isn't a criminal offence in England squatters |
|
I Rented accommodation is too expensive. |
|
don't actually break into an empty property or cause criminal |
|
2 Property developers are wrong to leave houses empty |
|
damage. 'I was astonished that the police evict them,' |
|
and wait for prices to rise before selling them. |
|
said an exasperated Mr Lock. 'They're just a bunch Of lazy |
|
3 Private property is wrong. |
|
hippies. I'll have to go to court to get them evicted. It'll cost |
|
4 Everybody has the right to shelter. |
|
me thousands in legal fees.' |
|
5 Squatters are using something that would Otherwise go to waste. |
|
|
|
6 Squatters contribute to society. |
|
questions. |
5 |
|
|
1 Are there a lot Of homeless people in your country? What |
|
With the verbs in the box. |
|
about in your town Or city? 2 Why do people become homeless, do you think? |
|
become do get make make pay rent take |

ten-bedroom
building in Bath With plans to convert it into three luxury flats. He's
planning to sell the flats for £400,000 and expects to t _ a profit Of
about £250,000. However, before building work started. a group Of twenty
squatters moved into the house and claimed they were 'looking the empty
property. They climbed into the building, which

![]()
 possession
(of) 3 Think of five problems homeless people face.
possession
(of) 3 Think of five problems homeless people face.
maintenance
2 Choose the correct words (a, b, cimprovements or d) to complete the text. Then listen and check.evicted
2 a for b after C c bringat d d makeinto 6 Discuss this question in pairs: Who do feel 1 a do b take
3
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() a was to b would c used to d had to more sympathy with,
Jim Lock or the squatters? Give reasons. Then take a class vote.
a was to b would c used to d had to more sympathy with,
Jim Lock or the squatters? Give reasons. Then take a class vote.
4
![]() a that b Whichd whose
a that b Whichd whose
5 a as long as b although c as much as d apart from 7Work in pairs. prepare this role-play. Make notes. 6 a can't b shouldn't c didn't use to d wouldn't
Student A: You have been homeless for two years and have
3
![]() Listen to a radio reporter interviewing one Of the
recently joined a squat With some friends. Explain to the squatters. Are the
sentences true (T) or false (F)? owner Of the property Why you should be
allowed to stay there.
Listen to a radio reporter interviewing one Of the
recently joined a squat With some friends. Explain to the squatters. Are the
sentences true (T) or false (F)? owner Of the property Why you should be
allowed to stay there.
Listeners can hear the interview on the radio as it takes
Student 3: You are the property owner. Explain to place.
![]() The
squatters can't afford both rent and living expenses. the squatter
Why you think he/she should move Out immediately.
The
squatters can't afford both rent and living expenses. the squatter
Why you think he/she should move Out immediately.
3
![]() According the squatter, there aren't enough properties in
the UK to house everybody. 8Work in pairs. Have a conversation using your
According the squatter, there aren't enough properties in
the UK to house everybody. 8Work in pairs. Have a conversation using your
4
![]()
![]() The squatters were certain that the house was notes from
exercise 7. Include as many phrases as you can unoccupied When they first saw
it. from exercise 5. Student starts the conversation. The squatters have
improved the house since moving in.
The squatters were certain that the house was notes from
exercise 7. Include as many phrases as you can unoccupied When they first saw
it. from exercise 5. Student starts the conversation. The squatters have
improved the house since moving in.
6 The squatters won't move out under anv circumstances.
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 2.2: PAGE 135
2 •
READING How the other half live
I can understand and react to a story about millionaire philanthropists.
|
Look at the text title and the photos only. What is happening |
In the programme, millionaires go undercwer to deprived areas |
|
|
in the photos? What do you think the text Will be about? Then |
Of Britain, where they volunteer in the local community. For |
|
|
look quickly through the text to check your ideas. |
a fortnight they give up their affluent lifestyle and live with little money in substandard accommodation. Their experiences |
|
|
2 Read the introduction to the text and mark the sentences true |
Often prompt them to hand over life-changing sums Of money to deserving individuals and institutions. At the end, they |
|
|
I The people who meet the millionaires know that they are |
reveal who they actually are. |
|
|
rich straight away. |
There have been eight series Of the programme in the UK so |
|
|
2 The millionaires have to live differently for a While. |
far, with millions Of pounds being given away to good causes. |
|
|
3 The millionaires have to donate lots of money. |
While watching the programmes, it's sometimes hard to tell |
|
|
4 The socially disadvantaged people benefit more than the |
who is benefiting most from the relationship. All of the people |
|
|
rich people in the programme. |
involved have talked about how it has changed their lives. But |
|
|
5 The millionaires don't Stay in touch with the people they meet. |
interestingly. it seemed that it was the millionaires Who found their experiences the most rewarding. Some discovered that |
|
|
EXAM TIP |
there are more important things in life than making money, |
|
|
For multiple matching tasks, look quickly through the |
and forged lasting relationships with the people they met. |
|
|
texts to geta general idea of their meaning. Then read |
HILARY DEVEY, who, as a single mother. risked everything |
|
|
the questions that you have to match With them. It may |
to start up a now hugely successful transport company, lives |
|
|
be easier to work through texts A—D in order, matching |
on her Own in her enormous mansion. |
|
|
the questions to them as vou go, and underlining the |
She returned incognito to the place she |
A' |
|
relevant parts Of the text, rather than working through |
grew up in, and one of the projects she |
|
|
the questions in Order and searching through all four |
got involved in was a local community |
|
|
texts each time. |
support centre which was in danger Of |
|
closing.
Secret Millionaire is a reality TV show with a difference. The participants come on the programme to possibly give away thousands of pounds.
• and poor
The centre provides marriage counseling,
support for single ![]() parents
and homeless people and so on. She funded the centre
parents
and homeless people and so on. She funded the centre
below. They are all in the text.
![]() and
provided more facilities for it. Hilary is still a regular
and
provided more facilities for it. Hilary is still a regular ![]() visitor
to the centre, and feels she now has friends who value her for the person she
is, not her money.
visitor
to the centre, and feels she now has friends who value her for the person she
is, not her money. ![]()
![]() NICK
LESLAU is one of Britain's wealthiest property
NICK
LESLAU is one of Britain's wealthiest property ![]() tycoons
and lives in luxury With his family in London. He went to Glasgow and worked in
a poor area with severely disabled people. He was astonished at how friendly
and kind everyone
tycoons
and lives in luxury With his family in London. He went to Glasgow and worked in
a poor area with severely disabled people. He was astonished at how friendly
and kind everyone ![]() was, even though they didn't know
anything about him.
was, even though they didn't know
anything about him. ![]()
![]() Although
he has always donated money to various charities, he found it immensely
rewarding to get involved directly for
Although
he has always donated money to various charities, he found it immensely
rewarding to get involved directly for ![]() once.
He said he felt privileged to have met some Of society's genuine heroes —
people Who work tirelessly to help others.
once.
He said he felt privileged to have met some Of society's genuine heroes —
people Who work tirelessly to help others. ![]()
![]()
![]() KAVITA
OBEROI is a 38-year-old IT millionaire whose
KAVITA
OBEROI is a 38-year-old IT millionaire whose ![]() sole
interest in life, apart from her family, was making money.
sole
interest in life, apart from her family, was making money. ![]() views
completely changed when she went to a centre for
views
completely changed when she went to a centre for ![]() disadvantaged
girls in Manchester. She used to believe that
disadvantaged
girls in Manchester. She used to believe that ![]() people
were poor because they didn't try to improve their lives. When she got involved
with the girls' centre, she realised that people Often need help and support to
do their best. She realised that her Own mother had sacrificed a lot so that Kavita
could have a good education. Kavita became a director of the group and is
helping it to go national to support more young
people
were poor because they didn't try to improve their lives. When she got involved
with the girls' centre, she realised that people Often need help and support to
do their best. She realised that her Own mother had sacrificed a lot so that Kavita
could have a good education. Kavita became a director of the group and is
helping it to go national to support more young
![]() JAMES
BENAMORE, a tough financial dealer now worth
JAMES
BENAMORE, a tough financial dealer now worth ![]() £77
million. used to have a drug problem himself. He waved
£77
million. used to have a drug problem himself. He waved ![]() goodbye
to his wife and children and went to a crime-ridden area of Manchester. He
worked in a centre for teenagers who
goodbye
to his wife and children and went to a crime-ridden area of Manchester. He
worked in a centre for teenagers who ![]() excluded
from mainstream education and found that
excluded
from mainstream education and found that
![]()
![]() they
had no confidence in themselves, nor any belief that any effort they made would
make any difference. James donated
they
had no confidence in themselves, nor any belief that any effort they made would
make any difference. James donated
![]()
![]() money
to the centre so that children who worked hard earned rewards in the form of
trips and outings. He also offered some
money
to the centre so that children who worked hard earned rewards in the form of
trips and outings. He also offered some ![]() for
from in in in Of to to With
for
from in in in Of to to With

![]()
![]() I
benefit
I
benefit![]() 5 value
sb/sth
5 value
sb/sth ![]()
2
forge
a relationship![]() 6 donate money
6 donate money![]()
3
get
involved![]() 7 wave goodbye
7 wave goodbye![]()
4
be danger![]() 8
have confidence
8
have confidence![]()
5
![]() Work in pairs. Each choose one of the
millionaires. Read the relevant text again for one minute, then cover it and
tell your partner as much about the millionaire as you can remember.
Work in pairs. Each choose one of the
millionaires. Read the relevant text again for one minute, then cover it and
tell your partner as much about the millionaire as you can remember.
6
![]() What do you think about the programme?
Is it a good idea? Are there any bad aspects to it? Decide on at least
What do you think about the programme?
Is it a good idea? Are there any bad aspects to it? Decide on at least
two positive and two negative things with your partner.
7 Read the Learn this! box and complete the rule.
|
|
Second conditional I We use the second conditional to talk about unreal situations and events. If / was o secret millionaire, I'd visit a homeless charity. Perhaps he wouldn't be so stingy if he had more money. 2 We use the in the if clause and the base form Ofthe verb in the main clause. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 2.2: PAGE 117 ![]()
8

![]() Discuss this question in pairs: If you
had €50,000 to give away, who would you give it to, and why? Use the second
conditional. Agree on three good causes and make
Discuss this question in pairs: If you
had €50,000 to give away, who would you give it to, and why? Use the second
conditional. Agree on three good causes and make
9 Report your ideas to the class. The class votes on
tænagers a month's work experience at his company. He was
&lighted to see how their attitudes
changed, and has set up ![]() scheme permanently.
scheme permanently.
![]()
•
I can talk about actions and events and their consequences in the past.
1 Read the text. Underline the examples Of the past perfect and past perfect continuous.
1994, J.K. Rowling, creator Of the Harry
Potter books, was living in Scotland, and feeling a complete failure. She had just returned from Portugal, where she had been living for two years. She had been teaching English in Porto, and had married a Portuguese man there. But the marriage had only lasted for a few years, and she had moved back to Britain with her baby daughter. She hadn't been feeling well for months and was eventually diagnosed with depression. SO, there she was: a jobless, penniless, depressed single mother. She decided that the only thing she wanted to do was write a story that had been going around in her head for a long time. And the rest, as they say, is history.
2 Read the Learn this! box. Choose the correct alternatives to complete the rules. Then match an example from the text to each rule.
Past perfect simple and continuous
1 We use the past perfect simple / continuous fora completed action that happened before a specific time in the past.
2 We use the past perfect simple I continuous for an action in progress before a specific time in the past.
Th's Often shows the cause of something in the past.
3 With state verbs (know, be, like. etc.), we use the past perfect simple / continuous with for or since to say how long an action had been in progress.
4 With action verbs, we use the past perfect simple / continuous with for or since to say how long an action had been in progress.
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 2.3: PAGE 118
3 Choose the correct tense.
1 How long had you had / been having a credit card when you got rid Of it?
![]() The
road was flooded because it had rained / been raining for hours and showed no
sign of stopping.
The
road was flooded because it had rained / been raining for hours and showed no
sign of stopping. ![]() She had learnt / been learning English
for three years before she visited Britain.
She had learnt / been learning English
for three years before she visited Britain.
4 Had you ever eaten / been eating Japanese food before you visited Japan?
5
1
was thirsty because I'd run / been running all morning. ![]() Martin
told me that he hadn't seen / been seeing the Champions League final On IV. 20
2 • andpoor
Martin
told me that he hadn't seen / been seeing the Champions League final On IV. 20
2 • andpoor
Complete the sentences With the verbs below. Use the past perfect simple Or past perfect continuous. Say which use Of the tenses in the Learn this! box each sentence follows.
go out know learn not have wait work I The grass was slippery because
2 Ed to drive for two years when he took his test.
3 When JO finally arrived, we for Over an hour.
4 They each other for many years when they got engaged, but they only for a year.
5 1 was thirsty because I a drink for hours.
6 Sue's hands were muddy. She in the garden.
5 Complete the text with the verbs in brackets. Use the past perfect simple or past perfect continuous.
Now in his 70s, American designer Ralph Lauren is a multi-millionaire, but he wasn't born into fame and fortune. In 1967 Lauren was looking for a job in fashion, but he didn't have any qualifications at all. Earlier that year, he (drop Out) Of night school. He 2 (study) for a business degree in the evenings, but he (not finish) it. By day he (sell) glcwes, but he knew he had to make a change. As a child growing up in New York, fashion-conscious Ralph s_ (not have) much money for nice clothes, so he 6 always (work) after school in department stores. It was this experience that eventually led to his own huge clothing empire. In 1967 he started working for a tie maker, and by the end of 1968 he (start) his own tie design company. By the 1970s Lauren (design) his own ties for several years, and they were very popular. so he started designing suits to match.
6 Work in pairs. Think about the last time you were: delighted embarrassed exhausted irritated relieved soaking wet starving
Find out Why your partner felt that way. Use appropriate past

|
Because I'd been listening to some fantastic music. |
|
|
|
|
|
Photo description I can describe a photo and answer the examiner's questions. |
Work in pairs. Describe the photo. Use the words below to help you.
decoration dressing gown lid surprise
2 Workin pairs. What is the boy thinking and feeling, and Why? Make notes about your ideas.
3 Now listen to a candidate answering the question in exercise 2. Compare your ideas from exercise 2 With the candidate's ideas. How are they similar and different?
4 Which two extreme adjectives meaning surprised and happy did the student use?
D
VOCABULARY
BUILDER 2.3: PAGE 135 ![]()
|
EXAM |
TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In the picture description task, the examiner can ask you to talk about a personal experience. You will need to use narrative tenses, e.g. past simple, past continuous, past perfect and past perfect continuous, used to and would. |
||||||||
5 Read the Exam tip. Then listen to the candidate answering the examiners question. Which of the tenses mentioned in the tip does the candidate use?
6 Answer the questions.
I Why did the girl choose to buy her sister a hoodie?
![]() How does she think she came to select
the wrong size?
How does she think she came to select
the wrong size? ![]() Why didn't she see the hoodie herself
before giving it to her sister?
Why didn't she see the hoodie herself
before giving it to her sister?
![]() How did her sister react when she saw
the hoodie?
How did her sister react when she saw
the hoodie?
5 How did the girl feel then? Have her feelings changed?
|
Comment adverbs and adverbial phrases Comment adverbs give the speaker's opinion. Unfortunately, we can't afford a holiday this year. ro my surprise, he sold his motorbike. Some adverbs can be used as both comment adverbs and as adverbs Of manner. Frankly, / don't believe you. He spoke frank/v about his financial problems. We usually put comment adverbs at the Start Of the sentence, although they can go with the verb. Foolishly, left my wallet at home. / fochlishly left my wallet at home. |
7 Read the Learn this! box. Then complete the sentences with five Of the comment adverbs below. Listen again and check.
fortunately hopefully ideally luckily Obviously stupidly to be honest
1 1 found a great one on a website, but I ordered the wrong size.
didn't realise my mistake until she Opened the present on her birthday.
she saw the funny side.
, I didn't think it was very funny at the time. , Iwas able to return it.
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 2.4: PAGE 135
 pairs. Take turns to ask and answer the
examineds questions. Try to use some comment adverbs.
pairs. Take turns to ask and answer the
examineds questions. Try to use some comment adverbs.
1 What is the girl thinking and feeling, and why?
2 00 you like spending money on Other people? Why?/Why not?
3 Tell me about a really good present that you once received.
2 •
|
|
or found any money? When? Where? What happened?
2 Read the story. Where do you think the money came from?

It was a day like any Other and Graham Hill was doing his normal round as a waste collector. He was putting bags Of rubbish onto his handcart, when he noticed something unusual in one of the dustbins. Leaning over the bin, he took a closer 100k and saw a filthy plastic bag with what looked like money inside. As he pulled it Out, he gasped. It was money. Inside the carrier bag were lots of banknotes! But they were all Cut into pieces! As soon as he realised What he'd found, Hill called the police, Who quickly arrived on the Scene. Having looked in the bag, they calculated that there must be about £10,000 in torn notes. The police thanked Hill and said that the money must have come from a robbery that had gone wrong. As they were leaving, the police told him they would find Out what had happened.
Six months later, Hill had forgotten all about the incident. Out Of the blue the police phoned with some unexpected and wonderful news. Surprisingly, after investigating for a long time, they had been unable to discover anything about the bag Of notes. There was no crime or robbery that they could link the money to. Apparently, under British law, the bag Of money now belonged to Hill. What's more, the Bank Of England said that for every note that he could put back together, Hill would receive a new one. He had been given the ultimate jigsaw puzzle!
3 Identify the following Stages in the story in exercise 2.
• background information that sets the Scene
• a first event, often a problem, that triggers the action
• later events that follow from the first event
• the final resolution or Outcome
22 2 • and poor
tenses. Then find examples Of each use in the Story in exercise 2.
![]()
LOOK OUT! Past simple and past continuous
![]() We can use the past continuous to set
the scene.
We can use the past continuous to set
the scene.
![]() (rain) and the Wind (blow).
(rain) and the Wind (blow). ![]()
![]() We
use the past simple for actions that happened one after another.
We
use the past simple for actions that happened one after another.
She (stand
up), (open) the door and ![]() (leave).
(leave).
3 We use the past simple for an action or event that interrupted a background event; we use the past continuous for the background event. While (read) my book, my phone (ring).
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 2.4: PAGE 118 ![]()
5 Read the Learn this! box. Find an example Of each type of sequencing clause in the story.
|
Sequencing clauses For an action which happens before another action, we can use: I ager + •ing After losing his wallet, he called the police. 2 having + past participle Having found the money, he took it to the police station. For an action Which happens at the same time as another action, We can use: 3 as + past simple As he put his hand in his pocket he realised his wallet was missing. the moment/os soon as + past simple The moment I Saw his face, / knew he'd been crying. 5 a present participle Looking up, she Saw a police Officer approaching. The subject of the participle clause and the main clause must be the same. Crossing the rood, she was hit byo car. Crossing-the.raadv-a-eerhit-trer: X |
6 Combine the pairs Of sentences into single sentences. Use the sequencing clauses in the Learn this! box. More than one answer is possible.
I •I've lost my wallet,' said Mary. At the same time, she closed her handbag.
![]() I
stepped outside. At the same time, it started to snow.
I
stepped outside. At the same time, it started to snow.
![]() He sat down. Then he opened the
newspaper.
He sat down. Then he opened the
newspaper.
4 I
walked to the shops. At the same time, thought about what my mum had just said.
![]() She had lunch. Then she went out.
She had lunch. Then she went out.
|
EXAM TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
In a Story. use a mix of long and short sentences. The short ones can make events more dramatic. The moment he arrived home, be made o cup Of tea and, sitting down on the sofa, turned on the television to watch the news. Suddenly, he jumped up. Somebody wCs in the room. |
|||||
![]() You
are going to do the following exam writing task. first think Of some ideas for
your Story. Use the questions below to help you.
You
are going to do the following exam writing task. first think Of some ideas for
your Story. Use the questions below to help you.
Wrlte a story with a happy ending about a character Who loses or finds something valuable. Write 200—250 words. 1 Does the character lose or find something?
|
|
2 Where does he/she lose Or find it? |
6 |
Find the following features which make the writing style |
|
|
3 If the character loses something, does he/she find it again? If the character finds something. does he/she get |
|
interesting in the Story on page 22. |
|
|
to keep it? |
|
1 two extreme adjectives |
|
|
4 How does the story end? |
|
2 two examples of comment adverbs 3 two examples Of reported speech |
|
2 |
Look again at the stages Of a Story in exercise 3 on page 22. |
|
|
|
|
Think how your ideas will fit into paragraphs. Use your ideas |
7 |
Write the middle paragraphs Of the story. Tell the later events |
|
|
from exercise I to make notes under paragraph headings. |
|
in a logical order. Remember to make the language dramatic |
|
|
|
|
and varied. Link events together to show time and sequence. |
|
Paragraph I |
|
Paragraph 2 |
|
Paragraph 3 |
|
Paragraph 4 |
|
CHECK YOUR WORK
written 200—250 words? used a variety of narrative tenses? used sequencing clauses and Other time expressions? used a mix of short dramatic sentences and longer Ones? included some extreme adjectives, comment adverbs, and/or reported speech? -included a last sentence that links to the title? |
8 
![]() Look
at the title and the last sentence of the Story on page 22. Think of a good
sentence to finish your story. Then write a title for your story which links
everything together.
Look
at the title and the last sentence of the Story on page 22. Think of a good
sentence to finish your story. Then write a title for your story which links
everything together.
9 Write the final paragraph of the story. Give the resolution or final outcome Of the Story. End With a good sentence.
3 Write the first paragraph Of the Story. Set the scene briefly With background information, then tell the first event Of the story. Remember to use appropriate narrative tenses.
•
1-2 Language Review
Complete the sentences With a suitable adjective. (More than one answer may be possible.)
I Lucy is very : she only thinks about herself.
2 MV dad is so : nothing gets him angry or excited.
3 1'm very : I want to be CEO Of a big company.
4 My dad is 42 but acts like he's 12: he's so
5 Ian is very : he writes songs and paints too.
Mark: _ 15
2 Complete the sentences With the present perfect simple or continuous Of five of the verbs below.
belong do go read remember stay want where you put the tickets?
The Hobbit; I'm about half way through
it. 3 My English teacher to England three times. ![]() 4
My parents at that hotel every year since it
4
My parents at that hotel every year since it ![]() -opened.
-opened.
5 Karen a horse since she was a little girl.
Mark: _ 15
3 Complete the email. Use the infinitive, the infinitive without to, the -ing form or the past participle of the verbs given.
I went into town this afternoon because 1 needed to get my phone (repair). The man at the shop said it would take an hour didn't feel like (stand) around, 50 decided
(go) toa coffee shop instead. saw some friends of
(play) cards, so I sat down with them, They let me
(join) the game and We played for ages. When I got back to the phone Shop, it was closed!
Mark:
Complete the dialogue With the words below.
could like say should though
|
|
Have you seen this photo of dad when he was young? |
|
|
NO, I haven't. Let me see! He looks he's feeling sick! |
![]() Boy NO, he doesn't. I'd 2 he's
just trying to look cool.
Boy NO, he doesn't. I'd 2 he's
just trying to look cool.
Girl He looks as he's getting ready to go out.
|
Boy |
How old do you think he is? |
|
Girl |
think he's about fifteen. |
5 Choose the best word (a, b or c) to complete each sentence.
A broken mirror is a priceless b worthless c mean My grandfather owns three shops, and the rentfrom those gives him a good a ncome b budget c allowance
3 The hotel isn't expensive; in fact, it's very a extortionate b pricey c reasonable
4 I wouldn't say I'm rich, but I'm certainly not _ a comfortably Off b affluent c hard up
I love that jacket. but I can't buy it — it's too a dear b valuable c precious
Mark: 15
6 Complete the sentences With the verbs below.
'd
didn't use to used to would wouldn't ![]()
I My grandmother![]() work.
but now she's got a job in
work.
but now she's got a job in ![]() a bookshop.
a bookshop.
2 1 be a football fan, but I prefer
basketball now. 3 We had somegreat parties in those days, but the neighbours
at-ways complain about the noise! ![]()
4
Every
time my uncle went abroad, he![]() buy a painting.
buy a painting.
5
She
bought a chocolate bar every day after school, but ![]() eat
it until she got home.
eat
it until she got home.
Mark: _ 15
7 Choose the best verb forms.
Elena 'had looked / had been looking forward to the day Of the garden pany for weeks. Now. finally. it 'had arrived / had been arriving. She Yhad got up / had been getting up early to give her more time for the preparations. Anxiously, she looked Out Of the Window to check the weather, Which 'had got / had been getting worse and worse each day, even though it was June. To her dismay. she saw that the apple tree by the back wall Shad fallen / had been falling down during the night.
![]() Mark: 15
Mark: 15
8 Write an extreme adjective Which means:
 1
very angry:
1
very angry: ![]() 4 very ugly: 2 very dirty:
4 very ugly: 2 very dirty: ![]() 5
very funny: 3 very clean:
5
very funny: 3 very clean:![]()
![]()
![]() Boy
Yes, I agree. He be getting ready to go on a
Boy
Yes, I agree. He be getting ready to go on a ![]() date
with Mum!
date
with Mum!
![]()
Language Review 1—2
|
|
|
|
|
Hi Anna, How are you? hope you're enjoying your job in Warsaw. HOW long have you been doing it now? It must be six months or so, reckon, because you'd been working there for a few days when I got back from backpacking holiday in Australia. Let me know hcwit's going and what the people there are like, DO you ever hear from Mike these days? Maybe YOU just want to forget about him and your time in Liverpool, He really wasn't right for I mean, it'5 OK to be ambitious, but he was just selfish. And there Was something Strange about him For example, why did he decide to Change his name from Jack to Mike? kncp,v we British people are supposed to be eccentric, but that'S just ridiculous! Stefan has been looking for a place to live, 1 think found one or two possibilities. We've loved having him here, and he's welcome to stay as long as he wants, but he's determined to find his own place, He'S Very single-minded, your brother, isn't he? I suppose pu are too, now 1 think about it, so maybe it n.'ns in the family! AnyAqay, I guess he can afford to rent somewhere nice, working in the financial sector — he must be on a good salary. (I've asked him what he earns, but he won't tell me!) I hope he won't get lonely, living on his Win, He isn't as outgoing as you are, so I don't think he'll meet people as easily. gut Still, everybody needs Company. He doesn't talk about people from work much, so 'guess he hasn't made many friends I've tried to persuade him to play basketball a few times, but he's refused. He Says he'S rubbish at ball games, but he might start going swimming when he's got more free time. That's better than nothing, I suppose — OK for keeping fit, but not a great way to meet Anyway, I shouldn't worry about him, I'm Sure he can look after himself. Please send me an email with your news— and some pictures of your new flat. You haven't in touch for |
||
![]()
![]() a is
very similar to Anna. b needs to be more Outgoing.
a is
very similar to Anna. b needs to be more Outgoing. ![]() c is
too single-minded.
c is
too single-minded.
d is similar to Anna in some ways but different in Others.
4 In Libby's opinion, swimming isn't the ideal hobby for Stefan because a it's something he'll do on his own. b it requires tCH) much free time. c it won't make him as fit as basketball. d he'll probably give up Soon.
4 1.17 Listen. Does Spikey sound more friendly or less friendly towards Stefan by the end Of their conversation? What is the reason for this, in your opinion?
5 I .17 Listen again. Are these sentences true (T) or false (F)?
1 Stefan is planning to buy or rent a flat.
2
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
3 Stefan started learning English ten years ago.
4 Spikey tells Stefan that he's sharing with seven or eight friends.
5 Spikey describes squatting as a criminal activity. 6 Spikey is not his real name.
6 Tell your partner about an occasion when you met somebody for the first time.
7 Imagine you are Stefan. Write an announcement to be put in a newsagent's Window to help you find a flat to rent. Include this information:
What you are looking for and when you
want to move in. some personal details about you: job, nationality, etc. Why
you would be a good tenant. ![]() the best way to contact you.
the best way to contact you.
![]() Skills
Round-up 1-2
Skills
Round-up 1-2
2 Get Ready for your Exam
I Talk in pairs about the following questions. Then report your ideas to the class.
1 Do you think you are influenced by advertising?
Give reasons for your answer.
2 What different marketing techniques do companies use to make us buy their products?
3 What do you think the term 'neuromarketing' might mean?
2 Do the exam task.
![]()
Complete the text with the missing sentences (A—EL There is one extra sentence that is not needed.
Big business has always wanted to see inside our heads. The marketing and advertising departments of the major corporations spend millions every year trying to work out what we want and then find ways to try and sell it to us. The more accurately businesses can predict What we, the consumers, are likely to buy and when and how much for, the more money they can get us to spend.
Understanding consumers has not been particularly easy. Marketing teams have watched what we buy in supermarkets, they have measured how we have responded to their various promotional campaigns. and they have carried Out endless Surveys asking us why we buy what we do. However, it is not by any means an exact science. 1 And even if they do, they do not always tell the truth.
This is where •neuro' or brain science steps in. For the first time researchers have begun to wire consumers up to MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) machines to watch what actually happens inside people's brains when they are faced With consumer choices. The researchers followed the areas of activity lighting up inside the shoppers' brains. Something Which is definitely Of interest to the marketing specialists.
This new area of science is called •neuromarketing•. Marketing departments Of companies say they won't need to watch us shopping or ask us what we'd buy, they'll just •read our minds'. This is good news for companies, as their massive marketing budgets can be used more effectively, but where's the benefit for us?
If businesses can know more about how we think than we do ourselves, they'll have the power not just to influence us, but also to manipulate us. so far, advertising regulations have merely restricted companies from making unsupported claims for their products. In future. they may have to go one step further and assess whether the marketers are having our behaviour as consumers altered in ways we cannot ourselves detect.
Get Ready for your Exam 2
Advertising will be cleverly deployedtOÞer4 us more accurately to buy the products on show.
They also need to keep in mind that increased activity in the brain doesn't necessarily mean increased preference for a product.
This Cannot be a good thing for the general public and something will have to be done about it.
It seems that people do not always know What they are thinking.
Eventually they found that they could predict
![]()
3 could buy in a jewellery shop. Which pair can write the most in two minutes?
4 Do the exam task.
SPEAKING exam task
Describe the picture. Then answer the questions.
Why do you think this couple is buying something in this shop?
What are the advantages and disadvantages Of having expensive possessions?
Tell me about the most expensive thing you have ever bought.
THIS UNIT INCLUDES
|
Vocabulary • relatins • interaction • phrasal verbs Grammar • question foms • comparison • question tags • Speaking • role-play |
Generations |
Writing • pros andtons
I can discuss relationships and behaviour.
Workin pairs. Find out as much information about each other's families as you tan in three minutes. Use the ideas below and add your own.
how many in immediate family? extended family? brothers / sisters / twins? (how many? ages? names?) Oldest / youngest family members? cousins / aunts / uncles / in-laws, etc.?
relatives living in your home / nearby / faraway / abroad?
2 In pairs, put the expressions below into two groups: negative and positive. (In some cases, it is a matter of opinion.)
Relating to people admire adore be on the same wavelength (as) be (very) close (to) be wary of despise envy feel sorry for have a lot in common (with) have nothing in common (With) 100k down on
100k up to not see eye to eye (with) respect trust
3 01.18 Listen to six people discussing members Of their family. Complete each summary with an expression from exercise 2 and a reason.
![]() arianna admires / trusts her mother,
because
arianna admires / trusts her mother,
because ![]()
2
Ryan
despises / doesn't see eye to eye with his father, because![]()
3
Sophia
is very close to / has a lot in common with her grandfather, because![]()
4
Isaac
envies / respects his cousin, because ![]()
![]() Ella
looks down on has nothing in common with her twin brother, because
Ella
looks down on has nothing in common with her twin brother, because![]()
6 David feels sorry for / is wary of his
uncle, because![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Find
out more about your partner's relationships with family and friends. Ask three
questions using expressions from exercise 2. Ask for reasons. v•lho do you
admire and *hi?
Find
out more about your partner's relationships with family and friends. Ask three
questions using expressions from exercise 2. Ask for reasons. v•lho do you
admire and *hi?
5 ![]() In
pairs, Check the meaning of the verbs below
In
pairs, Check the meaning of the verbs below ![]() using
a dictionary. Then test each other. Can you remember the translations?
using
a dictionary. Then test each other. Can you remember the translations?
Verbal interaction bicker (with sb) boast (to sb about sth) confide (in sb about sth) flatter (sb) flirt (with 5b) insult (5b) lecture (sb about sth) nag (sb about sth)
praise 6b for sth) tease (sb about sth) tell (sb) Off (for 5th) warn (sb about sth)
•a'hat mean? It means
6 Complete the questions With the correct prepositions.
1
Who
does Brianna bicker![]()
2
Who
can Ryan always confide ![]() 3 What does Sophia's mum nag her
3 What does Sophia's mum nag her![]()
4
What
does Isaac's cousin boast![]()
5
What
does Ella's dad tease her![]()
6
What
does David's aunt praise him![]()
7Listen to the extracts again. Answer the questions in exercise 6.
![]() 1.19 Listen to six monologues. What
is each speaker doing? Choose the best verb from exercise 5.
1.19 Listen to six monologues. What
is each speaker doing? Choose the best verb from exercise 5.
ipeaker l: praising: Speager![]()
9 01.19 Listen again. Write a one-sentence summary to describe What each speaker is doing.
ipeaker I is praising somebody for winning a tennis match.
prepare a monologue like the ones in exercise 8. Choose a verb from exercise 5 and invent your own situation.
![]() Perform your monologue to the class.
Can they describe what you are doing?
Perform your monologue to the class.
Can they describe what you are doing?
You're boasting to somebodi about esarn
results ![]() Yet. that" right.
Yet. that" right. ![]() NO,
tn again
NO,
tn again
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 3.1: PAGE 136
|
Tom 0K. fine. Ava Thank you. First, I need a few details about you. old you are? Tom I'm twenty. Ava you do? Tom I'm a web designer. you work for? Tom I'm self-employed. I work at home. Ava Great. so. question one. What do you argue about most in your family? Tom Er whose turn it is to use the car. Ava OK. Question two. Who cooks most of the meals in Tom We don't have family meals. We help ourselves. Ava And finally, question three. Who do you get With hest in your family? Tom My sister, definitely. We've got a lot in common. Ava That's all. Thanks very much for your help. Tom NO problem. I can ask you a question. Ava Sure. Go ahead. Tom you're free this evening. |
|
Can you tell me whether you share a bedroom? |
|
|
|
|
|
Subject and Object questions Questions with Who, What or Which can be subject Or object questions. Object questions include the normal interrogative form Of the verb. The answers are the object of the verb. What did you buy? (l bought a scarf.) Who did vou sit with? sat with Jack.) Subject questions include the normal affirmative form of the verb. The answers are the subject of the verb. Who bought this DVD? (Darren bought it.) |
3 Rewrite the six indirect questions from the dialogue in exercise as direct questions. 1 Could Nou spare moment?
D
GRAMMAR
BUILDER 3.1: PAGE 119 ![]()
4
Rewrite
the questions below as indirect questions. Use a different phrase from the
Learn this! box for each one. ![]() Do you share a bedroom?
Do you share a bedroom?
2 Who do you bicker with most at home?
3 Are you the only teenager in your home?
4 How often do you all have a meal together at home?
5 Who goes to bed first in family?
6 Are pu Often alone in your home? 7 Do you help with the housework?
5
![]() In pairs, ask and answer the indirect
questions in exercise 4. Add three indirect questions ofyour own.
In pairs, ask and answer the indirect
questions in exercise 4. Add three indirect questions ofyour own.
6
![]()
Read
the Learn this! box. Are the underlined questions in the dialogue in exercise
subject or Object questions?
D
GRAMMAR
BUILDER 3.2: PAGE 119 ![]()
![]() 01.20 Read, listen and complete the
dialogue. Does Tom like Ava? How do you know? 7 Write questions in the present
simple using the prompts below. Is each question a subject or Object question?
01.20 Read, listen and complete the
dialogue. Does Tom like Ava? How do you know? 7 Write questions in the present
simple using the prompts below. Is each question a subject or Object question?
2 Read the Learn this! box. Then look
again at answers ![]() in exercise 1. Which of these indirect
questions include a 1 Who / live / next door to you? question word and Which
include if or Whether? Who lives ne.xt door to •iou?
in exercise 1. Which of these indirect
questions include a 1 Who / live / next door to you? question word and Which
include if or Whether? Who lives ne.xt door to •iou?
2 What / you / have / for breakfast?
|
Indirect questions Indirect questions are more polite and more formal than direct questions. They use the same word order and verb form as a statement. They begin with a phrase like: Can / ask (you) ? Can/Could you tell me I'd like to know.„ I wonder Would you mind telling me ? These phrases are followed by a question word (what, how, etc.) or, in yes/no questions, by if or Whether. Can / ask where Emma lives? Do know if she's in? |
|
![]() Which letter / your surname / start
with?
Which letter / your surname / start
with?
4 Which month / have the fewest days?
![]() Which subject / you / have / first on
Mondays?
Which subject / you / have / first on
Mondays? ![]() Who / buy / your clothes?
Who / buy / your clothes?
7 What/ make / you laugh?
![]() Who / you / admire most / in the world?
Who / you / admire most / in the world?
![]() Who / have the most in common with you?
Who / have the most in common with you?
8
![]() In pairs, ask and answer the questions
in exercise 7.
In pairs, ask and answer the questions
in exercise 7.
3
I can talk about the elderly.
1 Work in pairs. Describe the photo opposite. Then agree on a definition Of elderly. Compare with the class.
2 In pairs, read the facts box and guess the missing numbers.
For the first time in history, there are more people in the UK aged over 65 than undert
Average life expectancy for people born today in the UK is about 78 for men and 2 for women.
Forty years ago, life expectancy was for men and 75 for women.
The retirement age for all UK workers will rise to probably by 2027.
3 Listen to the first part Of a radio interview and check your answers to exercise 2. What is the most interesting piece of information, in your opinion?
4 Listen to the whole interview. Choose the correct answer: a, b, c or d.
I Professor Clark believes people a don't like thinking about getting Old.
b don't mind the idea of getting old. c are frightened of the elderly. d cannot explain their own view Of Old age.
3 In Classical times, most people a died during infancy or childhood.
b died around the age of 28.
c died between 60 and 70.
d were ill for more than half their life.
4 Life expectancy has increased mainly because people a still go jogging when they're in their eighties.
b spend their State pension on food and exercise. c worry less about having poor health.
d have better healthcare and a healthier lifestyle.
5 Professor Clark's personal opinion is that a soon, most people Will reach the age Of 100. b the human lifespan has a natural limit.
c in
the future ![]() will be fitter than 80•year• olds
today.
will be fitter than 80•year• olds
today.
d people Will have to take up keep-fit in their fifties.
5 In Britain and North America, elderly people a have to work after the retirement age.
b are not treated as well as in most other places.
c are Often abandoned by their families. d prefer to live in nursing homes.
6 In modern cities in China and India, families are a taking better care of the elderly than they used to. b allowing elderly people to lead independent lives. C asking grandparents to 100k after children. d taking worse care of the elderly than they used to.
5 the two halves nouns and write them correctly as one word Or two. (All the nouns are in exercise 4.)
I life care
2 health homes
3 old c expectancy 4 elderly span nursing age retirement pension state age
8 life relatives
6 Complete the sentences using the compound nouns from exercise 5.
![]() continues
to rise, we won't be able to feed everyone.
continues
to rise, we won't be able to feed everyone.
2
Elderly
people should only live in ![]() if they have no families to look after
them.
if they have no families to look after
them.
![]() The average human
The average human ![]() could
be 200 years if
could
be 200 years if
scientists continue to make advances in ![]()
4 We won't have enough money to pay
retired people the ![]() if the number of elderly people
increases.
if the number of elderly people
increases.
![]() You can learn a lot by spending more
time With your
You can learn a lot by spending more
time With your
should be 75 or older.
7
![]() In
pairs, ask and answer about the Opinions in exercise 6. DO you agree or
disagree? Give reasons.
In
pairs, ask and answer about the Opinions in exercise 6. DO you agree or
disagree? Give reasons.

of elderly people. Then share your ideas With the class. Try to include nouns from exercise 5.
|
3D READING Closing the generation gap I can talk about relationships between parents and teenagers. |
1 Read the quotation below and say ifyou agree or disagree. At what age do people become adults, in your opinion? Give reasons.
A boy becomes an adult three before his parents think he does, and about two pars after he thin" he
2 Read the title and the last sentence Of the text opposite.
Predict which sentence (a—d) best summarises the opinions
Of the text's writer.
a Parents should let their teenage children spend more time alone.
b parents should treat their teenage children more like adults.
c Teenagers should remember that their parents are trying their best.
d If teenagers want to be treated like adults, they should behave like adults.
3 Read the text, ignoring the gaps, and check your answer to exercise 2. Do you agree with Ellie's view? Why?'Why not?
![]()
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
5 Read the Exam tip. Match the gaps (1—6) in the text with the sentences below (A-H). There are two extra sentences.
A Why was it such a big deal?
B
Even
more worrying was the fact that my parents weren't talking to each Other. ![]()
![]() A few more rows later and written more
than 10,000 words Of advice for parents.
A few more rows later and written more
than 10,000 words Of advice for parents.
![]() D
But part Of being a teenager is feeling free to take Steps down new paths and
learning from our own mistakes.
D
But part Of being a teenager is feeling free to take Steps down new paths and
learning from our own mistakes. ![]() After
that. the arguments with my dad just got worse.
After
that. the arguments with my dad just got worse. ![]() lust
last week, for example, I persuaded Mum to buy me a pair of shoes that she had
said I couldn't have.
lust
last week, for example, I persuaded Mum to buy me a pair of shoes that she had
said I couldn't have.
G It makes me not want to confide in you.
H ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Surprisingly,
we all share similar views on What our
Surprisingly,
we all share similar views on What our ![]() parents
are doing wrong.
parents
are doing wrong. ![]()
3
HOW TO
BE A GOOD PARENT:
a teenager's guide
All adults think teenagers are a nightmare. According to them. we're moody, argumentative, rude and disruptive. But have any adults ever stopped to think that perhaps they are resmsible for the unpredictable and confusing way we behave?
![]() Take
me, for instance. I may be a teenage nightmare. but
Take
me, for instance. I may be a teenage nightmare. but ![]() this
is all to do with my parents, not me. With my mother, I stamp my feet. storm
out ot shops in the middle of arguments and moan until I get my own way.
C]But my father, On the other hand, turns me nto a shining example of teenage
perfection. I do as he asks, I dont answer and I happily
this
is all to do with my parents, not me. With my mother, I stamp my feet. storm
out ot shops in the middle of arguments and moan until I get my own way.
C]But my father, On the other hand, turns me nto a shining example of teenage
perfection. I do as he asks, I dont answer and I happily ![]() accept
that means no.
accept
that means no.
My parents have very different parenting styles. While my dad brino out the best in me, by being calm and reasonable and treating me like an adult. my mum, like so many other parents of teenagers, inadvertently makes me want to rebel by being combative and speaking to me as though I'm still a child. Last summer. after yet another row in a shop with my mother, I decided to start writing down the way I felt about things. 2 C]
In
December, having contacted uarious publishers, I signed a book deal. My
parenting book, HOW Teenagers Think. is going to be published next year, the
firstot its type actually written by a teenager. Much of my book is based on my
own ![]() experiences, but I've also interviewed my
friends about their
experiences, but I've also interviewed my
friends about their ![]() patents. s C] And it usually comes down
to the fact that our parents care too much about us and don't want to let us grow
patents. s C] And it usually comes down
to the fact that our parents care too much about us and don't want to let us grow
For example, mum drove me crazy a few weeks ago when she kept worrying I'd broken my neck after I fell off my bike, Yes, my neck hurt. but I'd been to the doctor and he'd told me I was fine, so why did she want to take me to hospital?
HOW n
TEENAGERS
jellyellie
Instead of fussing around teenagers like we're small children,
—entS could be using Our desire to feel grown-up to their Eantage, If were behaving badly, why not tell us straight an that we don't deserve to be treated like an adult? Then try to earn your And why not reward us when behave maturely? Recently, I wanted to take a train
•Portsmouth to see a friend - a journey rd done with Mum W.e. Dad was fine with the idea of me going alone, but it Æeks Of arguments before Mum agreed.
need to learn to trust teenagers, And when parents
— wried about us, there is no point becoming angry - that things worse. A few months ago, Mum lost her when I told my parents I'd been receiving emails from rd met in a chatroom. She instantly banned me trom S-€tne Internet and we ended having a huge row. But rm
Most teenagers know talking to strangers online is a pod idea. so I'd told them What was happening - I don't get abducted, just as much as they don't want me to.
S: be angry with me. Mum? Surely its better for won't be angry, so I can talk to you?
of my friends feel the same way. They end up not parents What they're up to because theVII be cross.
I interviewed for my book bved the idea Of being to their parents, Despite the way we behave, we relationships with our parents. We also all know that our parents usually do know best. s Our ha•e to unwrap the cotton wool they place around us what is just a natural phase ot lite.
6 Work in pairs. Listen and check your answers to exercise 5 and say Which words helped you to work out the
7 Match the phrasal verbs highlighted in the text with the definitions below.
change; transform
2 gradually become an adult 3 do something Without interruption
4 can be explained by
5 arrive at a situation (often unintentionally)
6 cause a certain type of behaviour in somebody
7 leave quickly and angrily
8 reply impolitely to somebody in authority
8 Explain the meaning Of the underlined phrases in these Sentences from the text. Rewrite the sentences using different words.
1 All adults think teenagers are a nightmare.
2 1 moan until I germeown_way.
3 Mum a few weeks ago.
4 Why was it
5 Part of being a teenager is feeling free to take steps down
9 Match the two parts of the words to make adjectives from the text. Which adjective best describes (a) most teenagers? (b) most adults? (c) you? Compare your ideas in pairs.
|
I mood |
able |
|
2 argument |
able |
|
3 respons 4 unpredict 5 confus 6 reason |
ative |
|
7 combat |
ing |
Work in pairs. HOW could relationships between teenagers and their parents be improved? Think of three things that (a) parents and (b) teenagers should do. Use the ideas below to help you.
communication courtesy friends holidays housework independence money privacy respect schoolwork stress trust understanding
Present your ideas to the class. Include as many words and phrases from exercises 7—10 as possible. Use the phrases below to structure your presentation.
|
e first thini i teenageþþþogld do is |
|
||
|
|
. in my opinion parents/ teenagers should |
||
|
nallý, it would help if parents teen tense) |
|
||
|
|
|
||
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 3.2: PAGE 136 HOW do you and your friends speak compared with Read the Look out! box. Then complete the sentences with a
people Of your parents' generation? Discuss the ideas below in pairs and decide on the biggest difference.
grammar pronunciation slang speed vocabulary
2 Read the text. HOW many comparative and superlative forms can you find? Are they adjectives or adverbs, regular or irregular?
![]()
![]() Although
teenagers in the UK generally understand about 40,000 different words, the
number Of words they actually use is far smaller than you might think —
sometimes only 800 words. An inability to distinguish between formal and
informal language is almost as worrying. Ever since the 1950s, speaking correct
English has been nowhere near as important for teenagers as sounding cool. But
experts are worried that today's teenagers are even worse at talking in formal
situations than previous generations were.
Although
teenagers in the UK generally understand about 40,000 different words, the
number Of words they actually use is far smaller than you might think —
sometimes only 800 words. An inability to distinguish between formal and
informal language is almost as worrying. Ever since the 1950s, speaking correct
English has been nowhere near as important for teenagers as sounding cool. But
experts are worried that today's teenagers are even worse at talking in formal
situations than previous generations were.
The language that teenagers use is nothing
like as varied as,vou would imagine, With the twenty commonest words ![]() representing
about a third Of all words spoken. And if you 100k at younger age groups, the
situation is just as worrying: children are developing speech problems more and
more frequently. Children watch a lot of IV. as do adults. This creates
background noise; and the noisier their surroundings. the harder it is for
babies to hear conversations around them.
representing
about a third Of all words spoken. And if you 100k at younger age groups, the
situation is just as worrying: children are developing speech problems more and
more frequently. Children watch a lot of IV. as do adults. This creates
background noise; and the noisier their surroundings. the harder it is for
babies to hear conversations around them.
![]()
3 Read the Learn this! box. Find at least one example in the text in exercise 2 for each point (1—5) in the box.
|
Comparative structures I We can qualify comparatives using far, much, even. a little or no: She's no better at swimming than her sister. 2
We
can qualify comparatives with as 3 Comparatives often have a clause after than. She's less argumentative than she used to be. It's much hotter today than realised. 4 We can use double comparatives for changes: He's getting taller and taller/more and more handsome. 5 We can use the following Structure to say that two things change together because they are connected: The faster he works, the more mistakes he makes. |
|
LOOK OUTI
We can use a clause beginning with os an auxiliary or modal verb or the correct form Of be to show similarity.
![]() Pay
attention to the word order:
Pay
attention to the word order:
![]()
She's a great singer, as is her
father.
clause to show similarity. Use the words in brackets. I I love Lady Gaga, do friends. (my friends)
2 We've sold our house, . (our neighbours)
3 She can speak Russian, . (her dad)
4 The school will be closed, . (the pre-school) 5 She loved the film, . (her boyfriend)
5 Match the two halves of the comparative sentences.
![]()
![]() I
speak far more clearly
I
speak far more clearly
2 1'm much more intelligent 3 The harder you work, 4 I love sport.
![]() I'm nowhere near as moody
I'm nowhere near as moody
6 This dessert is even more delicious
7 She's getting more and more confident, 8 This exercise isn't nearly as difficult
![]() than everyone thinks I am.
than everyone thinks I am.
![]() as do most of my friends. c as some
people I know.
as do most of my friends. c as some
people I know.
![]() than used to.
than used to.
e than I thought it would be.
![]() as
the next one.
as
the next one.
g the more successful you'll be. as are most teenagers.
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 3.3: PAGE 120
6 Write new beginnings for in exercise 5.
a far more stubborn than everyone thin" I am.
7 Rewrite sentences below using a different comparative or superlative form. Include the word in brackets and do not change the meaning. There is more than one possible answer. I Nobody in my class is as Outgoing as I am. (most) I'm the mott outgoing person in class.
2 lack is far more talkative than Sam. (nowhere)
3 Getting online is becoming easier and easier. (less)
4 My sister drives badly. My dad drives badly too. (as)
5 Everybody in the class sings better than I do. (singer)
6 He plays football much better than he thinks. (badly)
7 The town centre is much emptier than it used to be. (busy)
8
![]() In pairs, think of an appropriate way
to finish each sentence. Then compare your ideas with the class.
In pairs, think of an appropriate way
to finish each sentence. Then compare your ideas with the class.
![]() The longer people live,
The longer people live,![]()
![]() It's getting more and more difficult to
It's getting more and more difficult to
![]()
![]() The hardest thing about being a
teenager is
The hardest thing about being a
teenager is![]()
![]() The
world is getting more and more
The
world is getting more and more![]()
![]() The quickest way to improve your
English is
The quickest way to improve your
English is![]()
busy / quiet cheap / expensive exciting / relaxing formal / informal noisy / peaceful trendy / Old-fashioned
|
2 01:26 Read the role-play task and listen to a student doing the task with an examiner. What conclusion do they reach for each Of the four issues? Complete the chart below. A teenage foreign friend is coming to visit your town with |
4 5 |
his/her grandfather. Talk to your friend about the visit, remembering to make plans and arrangements Which are suitable for both visitors. Cover these issues:
![]() where
they should Stay
where
they should Stay
![]() a
recommended place to eat out
a
recommended place to eat out
![]() a
daÝtrip or excursion that both would enjoy
a
daÝtrip or excursion that both would enjoy
![]() the
best wayto getaround
the
best wayto getaround
|
place to stay |
|
|
day-trip |
|
|
getting around |
|
|
eating out |
|
Complete the phrases using the words below. Check you
•derstand the expressions. 6
I Suggesting a course of action could got idea know Other think
Why don't we ? 7
Here's
an : . Let's it. How about ? we should always 8 thing we should do is![]()
Listen to the role•play again. Which of the phrases in exercise 3 do they use?
Read the Learn this! box and complete the examples. Then listen and check.
|
Question tags turn statements into questions. We use affirmative tags after negative verbs and negative tags after affirmative verbs. Tags include a modal verb or auxiliary pan of a verb form (have, do, did. etc.). Your grandfather is coming too, You haven't got a big flat, Thai food is spicy, Everybody likes Italian food, / should 100k online, Let's decide later, Don 't forget, |
D GRAMMAR BUILDER
3.4: PAGE 120 ![]()
![]() Listen
and repeat the sentences in exercise 5. Does the intonation go up or down at
the end Of each one? HOW does that affect the meaning?
Listen
and repeat the sentences in exercise 5. Does the intonation go up or down at
the end Of each one? HOW does that affect the meaning?
In pairs, prepare to do the role-play task from exercise 2. Decide which part you will each play and what conclusions you will reach. Make a chart like the one in exercise 2 and write your ideas in it.
![]() Do the role-play task in pairs. Make
sure you include some question tags.
Do the role-play task in pairs. Make
sure you include some question tags.
Ask and answer these questions in pairs.
I DO you think you have enough freedom and independence from your family?
2 What are the positive effects of giving teenagers more freedom and independence?
3 What are the negative effects?
2
![]() Work in pairs. Read the task below and
agree on one advantage and one disadvantage.
Work in pairs. Read the task below and
agree on one advantage and one disadvantage.
Many teenagers spend time looking after themselves at home while the adults are away. Write an essay which presents the advantages and disadvantages Of being 'home alone' When you're a teenager.
3 Read the essay. Does the candidate mention your ideas from exercise 2?
Scme parents happy to their teenage chilWen in the tE:ause they trust ttHn to ttunseh,es. There can drawbacks. Exit situation can also out the best r.
Firstly. itk a to hcw to favcx_rite c:nüne ftÿ, say.
c.cuk:in't it means ncbody is there to nag tell What to do. Which — even thCROh you may two little things. Thirdly, not acuts arcond is a chance to prcyve that you can inc8Jendent and even deal with difficult situaticns occasionally.
other hand, there we definitely cisadvantages to at WNe your parents are away. Although sceparing yCMr own fcod may fun, Will end up eatrg k)ts ot snacks and no meals.
![]() Secondly,
it your parents arent there to renind you, forget something impœtant. a
doctor S apçnntn-ult. Thny, wthout your parents at home, you need to
Cc*ye With any domestic emergenciœ yourself. For example, f the bathrocyn
roods, ytl' næd to it Out!
Secondly,
it your parents arent there to renind you, forget something impœtant. a
doctor S apçnntn-ult. Thny, wthout your parents at home, you need to
Cc*ye With any domestic emergenciœ yourself. For example, f the bathrocyn
roods, ytl' næd to it Out!
![]() Ov•erall,
I the advantages fix teenagers Ot sÇmding a tine home ame the
Ov•erall,
I the advantages fix teenagers Ot sÇmding a tine home ame the
Despite risk 0t its an part of grcywing up.
|
EXAM |
TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Make sure your essay is divided into paragraphs and has a clear and logical Structure. For example: Paragraph 1: (introduction) Rephrase the question and / or give an example of the situation it describes to show that you have understood it. Paragraph 2: (pros) List two or three advantages. Include examples. Paragraph 3: (cons) List two or three disadvantages. Include examples. Paragraph 4: (conclusion) Sum up the most important points and / or give your own opinion. |
|||||||||
4 Read the Exam tip. Answer the questions in relation to the essay in exercise 3.
I Does the essay follow the structure in the tip?
2 How many different (a) advantages and (b) disadvantages does the candidate mention?
3 Underline all the places where the candidate gives examples. How are the examples introduced?
4 What phrase does the candidate use to introduce a personal opinion in the conclusion?
|
|
Concessions We can use although Or even though to introduce a concession clause. He won the race even though he'd hurt his foot. Although he'd hurt his foot, he won the race. Despite and in spite Of also express concession but are followed by a noun or •ing form. not a clause. Despite/ln spite Of his injury, he won the race. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Read the Learn this! box. Underline all the examples Of concession in the essay in exercise 3.
6 Rewrite the sentences without changing the meaning. Include the word in brackets.
I Even though they get on well, they're splitting up.
(despite)
Despite getting on well, theft-e splitting up.
2 Even though they're friends, they often argue. (despite) Although we tease each other, we're actually very close.
(in spite on
4 In spite of the rain, they walked home together.
(although)
5 Many parents watch too much TV, despite lecturing their children about the same thing. (even though)
6 She doesn't respect her dad, even though he's got a well• paid job. (in spite on
7 In pairs, discuss the conclusion Of the essay in
exercise 3. Do you agree or disagree? Give reasons.
![]()
I can analyse and express the pros and cons of a situation.
|
|
Write an essay which presents the advantages and |
|
|
|
disadvantages of going on holiday With friends your own age rather than with your family. |
5 |
|
2 |
Plan your essay in pairs. Student A: Think Of as many advantages as you can. |
|
|
|
Student B: Think Of as many disadvantages as you can. Make notes using the ideas below to help you. be on the same wavelength eat unhealthy food get ill get lost get mugged make mistakes make new friends |
6 |
|
|
miss your family run out ot money stay up all night stay in hostels |
7 |
|
3 |
Paragraph I: introduction Paragraph 2: advantages |
|
You are going to do the following exam writing task. Read the task and discuss Some ideas for advantages and disadvantages with your partner.
8
|
|
|
Paragraph 3: disadvantages
|
Point I: Point 2: point 3: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Paragraph 4.• conclusion
In pairs, translate the underlined phrases in the sentences below. Think about how you could use the phrases in your essay. Which section of the essay might they belong to?
You might live on junk food for the entire holiday.
Ifyou comedown with food poisoning, find a doctor.
It's important to stick together.
Your family are only a phone call away.
Holidays can be a bonding experience.
Teenagers can be anvasytarget for criminals.
If things go wrong. you may need to grow LID overnight. It could be the holidav Of a lifetime.
In pairs, write the introduction to your essay by completing the outline below.
Some teenagers have the opportunity to go on
hol"day with friends their own age. Although this can be it can also![]()
Agree on a conclusion with your partner. Do the advantages outweigh the disadvantages, or vice versa? Make a note of your opinion and the reasons for it.
Look back at the essay in exercise 3 on page 34 and complete these three different ways Of expressing the idea Of being
![]() is a
chance to prove you can be independent
is a
chance to prove you can be independent ![]() there
are definitely disadvantages to being at home
there
are definitely disadvantages to being at home
, you need to cope With any domestic emergencies yourself.
Do the writing task in exercise I. Follow the essay plan you made With your partner in exercises 3—6.
|
CHECK YOUR WORK
given your essay a clear and logical structure? used at least one concession clause? included some expressions from exercises 2 and 4? rephrased the wording Of the task in different ways? written 200-250 words? your spelling and grammar? |
•
|
Get Ready for your Exam |
spend your weekends:
alone or with company? With friends or family? indoors or outdoors? being active or relaxed?
|
LISTENING exam task |
2 DO the exam task.
You Will hear five people talking about how they spend the weekend. Match each sentence in the table to the correct speaker(s). Which speaker
loves to expand his/her wardrobe?
spends his/her weekend glued to the screen?
loves to chill Out?
has an expensive hobby?
has a hobby which annoys his/her family?
doesn't mind getting dirty?
9 has a role model? appreciates nature?
|
spends weekends with a |
3 Do the exam task.
USE OF ENGLISH exam task
Read the text. Choose the correct answer (A, B, C or D) for each gap to create a logical and grammatically Correct text.
LIK life expectancy has risen quite dramatically, despite concerns over Obesity and its attendant health problems. reports published this month, average life expectancy has risen 80 years Old, eight years higher than in the 1970s. What has made the most difference to the population's health? Has it been increasing the government budget for hospitals, staff and medical equipment? Has it been the in medicine with exciting breakthroughs in new treatments for tackling disease? Has it been the fact that we're more conscious Of staying healthy these days? These factors have obviously contributed to the health Of the nation. But one thing in particular has been an enormous contributing
Get Ready for your Exam 3
factor — it was a simple public health campaign about the dangers of smoking.
In 1971, many thousands of men in their early 60s died 3 smoking-related heart disease. 2000 the figure for this age group had halved, while for cancer the number had gone down by a third, and strokerelated deaths had fallen by two-thirds. The dramatic fall in these numbers can be attributed to the first generation Of non-smokers arriving at Old age.
But what is the likelihood of life expectancy increasing? Health professionals are concerned that this trend by the time today's youth reach old age. Smoking has been replaced by the equally unhealthy habit Of over-eating, and unless a similar public health campaign takes soon, who knows what the future may bring?
Due to B According to C Based on
D Apart from growth B acceleration C improvement
D advances on B from C at D for
4 A Since B In C By D After is reversing B has been reversed
C Will be reversed D reverses
6 A effect B result C action D control
4
better at as they get older? What do they get worse at? In pairs, make two lists.
5 DO the exam task.
SPEAKING exam task
DO you agree or disagree With this Statement? Give reasons.
In Our society, we do not attach enough value to the wisdom and experience Of the Old.
Look at the four politicians in the photos. a What nationality are/were they? b Name one thing they are famous for.
Name three members of the government in your country.
3 How old do you have to be to vote in your country?
4 How many countries are there in the EU? Who is the current a President of the US? b British Prime Minister? c President of the EU Commission?
Work in pairs. DO the political awareness quiz. HOW well-informed are you?
2 Complete the text with the correct form Of the verbs below. Then listen and check.
call for change gauge influence join launch sign tackle take part write e-petitions
3 In pairs, check the meaning Of the collocations in red. Then test each other. launch? a campaign
DVOCABULARY BUILDER 4.1: PAGE
137 ![]()
4 Listen to five teenagers being interviewed about their attitude to politics. Match the statements (A—F) with the speakers. There is one statement that you don't need.
A I don't think that politicians ever listen.
B I believe people have a duty to get involved in politics.
C I want to have a say in who governs the country.
D I don't believe that young people care enough to vote.
E I don't think our voting system produces fair results. F I'll never change my attitude to politics.
5 Listen again. Identify one reason that each teenager gives to explain their attitude.
6 What's the meaning Of these political terms?
How many can you explain?
general public / general election mainstream politics / single-issue politics electoral system I political system left-wing / right-wing public opinion / public Office
7 Work in pairs. Say whether you agree or disagree with the opinions in exercise 4. Give reasons.
don't agree that politicians never lislen. They have to listen in order to get elected.
DVOCABULARY BUILDER 4.2: PAGE 137
1 01.31 Read and listen to the dialogue. Answer the questions.
I Who are Sandy and Ryan?
2 What's happening and why?
|
Ryan Hey Sandy, move it! Hurry up! Grab a placard and some water. Chances are we'll be Out all day. Sandy OK. Where are we off to? Ryan The university library. Thousands of students will be heading there right now. Hurry! Sandy OK, OK. Blimey, there are loads Of us! People must be wondering what's going on. Ryan That's the idea! Come on! Sandy What's the plan then? Ryan Well, at least a hundred students are likely to occupy the library. The rest of us could march to the Town Hall, or it might be better to Stay in the centre of town to protest there. Either way. people are bound to sit up and take notice. Crowd No to student fees! No to student fees! Ryan And the TV cameras should be here today as well! The Government can't ignore us any longer. Come on! No to student fees! No to student fees! |
2
![]()
Read
the Learn this! box. Underline in the dialogue all the modal verbs and phrases
that express probability.
|
|
Talking about possibility I We use will to make predictions about the future. / don't think the President Will be re-elected. 2 We use the future continuous and the future perfect to make assumptions about the present. It's 8.00. Carolyn Will be driving to work. think Emily Will have left the Office by now. 3 We use must to conclude that something is certain. Dad isn't at home. He must be at work. 4 We use can't to express impossibility. He can't be at work. His car's outside. 5 We use may, might and could to talk about the possibility Of something happening. Where's Max?' 'He could be doing his homework. • It may rain later, so we might not play tennis. 6 We use should to say that something will probably happen, in our opinion. Spain should beat England. 7 We can use Other phrases to express probability. It's so cold. It's bound to snow tonight. certain) Chances are it'll rain tomorrow. very probable) Are you likely to go to Jeff's party? |
|
|
|
|
|
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 4.1: PAGE 121 ![]()
3 Choose the correct answers. Where more than one answer is possible, explain the difference in meaning.
I This exercise shouldn't / mustn't / won't take you too long to complete if you've read the learn this! box.
2 'It's freezing in here. The window must / could / should be open.'
![]() 'Where's Aidan?' 'I'm not sure. He
might / should / will be playing football.'
'Where's Aidan?' 'I'm not sure. He
might / should / will be playing football.'
![]() The plane left London for Paris six
hours ago. It Will arrive / have arrived / be arriving by now.
The plane left London for Paris six
hours ago. It Will arrive / have arrived / be arriving by now.
5 You shouldn't / mustn't / can't be
listening to the teacher if you are whispering to the student next to you. ![]() Emma
has revised very hard for her exams so she should / may / won't do well.
Emma
has revised very hard for her exams so she should / may / won't do well.
7 Bring warm clothes to the barbecue next Saturday. The weather mustn't / can't I might not be as warm as it's been recently.
4
![]() Rewrite the sentences using the words
in brackets. Keep the meaning the same.
Rewrite the sentences using the words
in brackets. Keep the meaning the same.
![]() The phone's ringing. think it's Tom.
(Will)
The phone's ringing. think it's Tom.
(Will)
The phone.@ ringiny It'll be Torn
![]() I'm
certain that the Government will be defeated. (bound)
I'm
certain that the Government will be defeated. (bound) ![]() I
rang Liam at home but there was no answer. There's no way that he's at home.
(can't)
I
rang Liam at home but there was no answer. There's no way that he's at home.
(can't)
4 DO vou think that lash will arrive soon? (likely)
5 1 really don't expect Sam Will fail his driving test.
(shouldn't)
6 Fran is probably lying. (chances)
7 It's one o'clock. I assume she's having lunch. (will)
5
![]() Work in pairs. Describe the photo.
Discuss What is happening now and what might happen. Use language from the
Learn this! box.
Work in pairs. Describe the photo.
Discuss What is happening now and what might happen. Use language from the
Learn this! box.
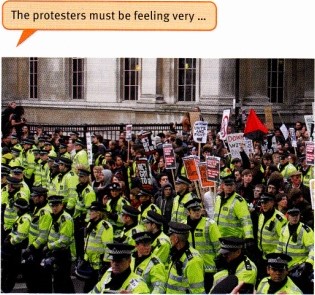
adjectives (un)armed violent
![]()
![]() unrest 5
armed
unrest 5
armed
nouns
barricade riot rioter shield weapon verbs riot protest demonstrate 3
paramilitary![]()
3 I .32 Read the text. What is the significance Of these 6 I .33 Listen to two teenagers talking about Northern Ireland. Choose the correct answer. dates?
a 1922 c 1969 e 1998 a Neither of them wants a united Ireland. b the 1960s d 1985 b One Of them wants a united Ireland.
c Both Of them want a united Ireland. Read the text again. Answer the questions.
7 Listen again. Are the sentences true (T) or false (n?
1 What proportion of the population of Northern Ireland is
1
Protestant? William has some happy childhood memories.
2 Why did the Catholic community feel aggrieved following 2 TWO Of William's relatives were killed by terrorists.
the partition of Ireland? 3 William can't help thinking Of Catholics as enemies. C]
4
![]() Niamh thinks the IRA made a mistake when it gave up its
armed struggle.
Niamh thinks the IRA made a mistake when it gave up its
armed struggle.
5 Approximately 90% Of children in Northern Ireland go to faith schools.
6
![]()
Niamh
will probably send her children to a Catholic
independence in 1922. the North, united again and started killing British soldiers. The British government of the population were Protestants. remained part Of the UK. For acknowledged the Catholics' grievances, but insisted that Northern after, the minority Catholic population in the North felt badly Ireland would remain part of the UK as long as that was what the
|
f•ated. They ware less well off and were often excluded from public Most of them wanted an end to British rule in Northern Ireland. b the some Protestants reacted violently to Catholic demands L and civil rights, and police used force to break up Catholic —onstrations. Rioting and civil unrest followed and in 1S9the Brmsh ETV was sent into restore law and order. Catholic and Protestant groups started planting bombs and murdering people. •mag that they were •protecting their communities'. One of these the Provisional IRA (Irish Republican Army), wanted Ireland to be |
majority Of its people wanted. The British government was unable to Stop the violence, Which lasted for nearly 30 years. This period saw a number at failed peace initiatives, an attempt by the IRA in 1985 to murder Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher, and the deaths Of aver 351 people, including 1,100 British soldiers. But people in both communities were tiring of the spiral of violence and IRA agreedto give up its armed struggle and seek to achieve its goal by peaceful means. Northern Ireland is still part Of the UK, butnow has its own government, made up of Catholics and Protestants. |
I can understand a text about freedom of speech.
Freedom of speech and information
how much should we have?
SIMON WILSON - libertarian
We libertarians believe that the Gwetnment should interfere in peoplek lives as little as gnssible That means that peoples right to free should not law unless what they are saying is certain to incite violence, I tvlie•e that extreme right-wing or left•aing views and extreme religious views should all be allowed even though most people find them abhorrent This is the es§ence of a free society. Extreme views should be expressed That the only wav to defeat them
JASON ROMFORD - comedian
Its difficult to be polite in comedy because you are usually making tun Of people. so you're to offend somebody at some point. But just somebody is OffeMed doesrft mean they are right. I believe that have right to Offend you. and if you are offended. thats rot a problem. That doesn't mean that I try to offensive. don't I tri/ to be funny. try to be honest try to make people think. If sœneone feels Offerded at something I say. that's too bad That's their ;yoblem. JANE SIMMONS - politician
Governments have the right to cansot information and restrict free speech in the interests Of national secu:ity, for yeservinç public safety. or for the prevention of disorder or crime. For example. its a crime to incite people to carry Out acts of terrorism Most geople agree that this is sensibla However. there is a danger that governments will use •the defence Of national security' as an excuse to silence legitimate protests and stifle to their polities Ifs imgœtant therefore that l*ople are able to challenge the limits ot free speech in a court 0t law
PETER GREENWOOD - civil rights activist
There's a danger that people can use tree speech to undermine the human rights of others. Liberalism is a good thing. butwe should limit people's to express racist. sexist. ageist or homophobic views There are lessons we must learn from history If had been no free speech for the Nazi pan,' in Germany during the early 20s. it is possible that fascism may not have grown in power and influenca The lesson is: be intolerantot intoleraxe.
SARAH MATTHEWS - online activist
Contribute to a website called Wikileaks, where anonymous volunteers leak confidential government information hack into government cunøuler files worldwide and put them on the Internal. GD•ærnments say Our actions are dangero•as. I think they just want to conceal their tram us. I want expose the truth. people have tt-æ right to know everything that their Weernment is doing I'm absolutely opposed to censorship Of the
I Have you or someone you know ever signed a petition or demonstrated against something? If So, why? If not, would you? Give reasons.
2 2.01 Read through the texts quickly. Decide who believes that there should be limits to freedom of speech. Which keywords/phrases helped you decide?
Simon Wilson — M: unless incite violence interfere as little as possible ntrme views be allowed
EXAM TIP
Skim read the text before you read the multiple choice questions in Order to get the general meaning. Then read each question and identify the part of the text that contains the information you need.
Reject any options that are clearly wrong and identify the correct answer by looking carefully at the relevant part of the text.
If you are unsure which of two answers is correct, make an intelligent guess.
ANNIE THATCHER - journalist The press must not invade peoples privacy. nor can say things which hurt a personS reputation without clear evidence ttk2t they are true. But is it fair to investigate the private lives of figures? Journalists tend to justify their intrusion into the lives Of famous mple claiming that certain information is 'in the public interest' las opposed ta something the public is interested ink For example. thew argue. if the captain Of the England football team is having an affair. the public should know atX)ut it as he is in a position of authority and respect and a role model tor young boys. Ultimately. though. some of the press will print anything that sells newspa¥.rs — if they can get away with it
3 Read the Exam tip on page Then read the texts again and choose the best answer.
I Simon Wilson says that a libertarians don't believe in government.
b everybody has extreme views.
c governments cannot ever restrict free speech. d we should fight against extreme views.
3 Jason Romford a always tries to be polite.
b thinks that comedians are always offensive.
c is upset When he thinks he has offended someone. d wants to entertain people.
4 Jane Simmons thinks that a we need to be able to restrict free speech to guard people's safety.
b governments are always right to restrict free speech.
c people are free to carry out terrorist acts.
d people shouldn't question any government's actions.
4 Peter Greenwood a wants restrictions On what people say about others. b thinks that we have learned something from history. c says that the Nazi party restricted free speech.
d thinks that people have become more intolerant.
5 Sarah Matthews wants a governments to conceal confidential information. b to reveal what governments are doing.
c everyone to hack into government computer documents.
d everyone to read the Wikileaks website.
6 Annie Thatcher believes that a the press isn't allowed the right to freedom of speech. b the press always reports information responsibly.
c journalists have the right to Say What they like about celebrities.
d the press generally argue that they print What the public needs to know.
|
The suffixes -ism and -ist 1 We often use the suffix -ism for beliefs, ideologies and behaviour (Buddhism, Marxism). 2 We often use -ist for people who have those beliefs and ideologies (a Buddhist, a Marxist) and for adjectives GMarxist ideology, a Buddhist temple). 3 There are exceptions. liberalism (n. belief), a liberal (n, person), liberal (adj) criticism (n, behaviour), a critic (n, person), critical (adj) 4 We also use •ism and •ist for some occupations. (Journalism, a journalist) |
|
![]()
the texts and find the suffixes for these words. Which category does each one belong to?
1 activ 5 age_
7 ![]()
![]() journal_
journal_
8
terror![]()
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 4.3: PAGE 137 ![]()
5 Read statements A—F. On your own, score them from I (z disagree strongly) to 5 agree strongly). Think of reasons for each opinion.
A We should know everything the Government is doing or plans to do.
B It is right for hackers to try to access government files.
C We have the right to know everything about celebrities' lives.
D Comedians should be careful What they make jokes about.
![]() People should be allowed to express any
opinion, however extreme.
People should be allowed to express any
opinion, however extreme.
![]() Racist. sexist. ageist. anti-religious
and homophobic views should not be tolerated.
Racist. sexist. ageist. anti-religious
and homophobic views should not be tolerated.
6
![]() Work in small groups. Compare your
scores for exercise 5. Justify your opinions and give examples to back them up.
Work in small groups. Compare your
scores for exercise 5. Justify your opinions and give examples to back them up.
 Work in pairs. Discuss these questions.
Is John
Work in pairs. Discuss these questions.
Is John
Lennon's vision (a) worth striving for? (b) realistic and achievable? Give reasons for your opinions.
|
|
|
Future continuous We can use the future continuous to make enquiries. Will you be voting in the election? |
|
|
||
1 Read the flyer. What sort Of things do you think the School
Council does? Do you have a group like this at your school?
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 4.2: PAGE 122 ![]()
*out NEEDS*OU!School Council 4 Read the Learn this! box and rephrase the questions using
the future continuous to make polite questions.
I What time are you leaving school?
2 What do you plan to do this evening?
Helping to improve your school 3 Who are you going to see at the weekend?
4 Where will you go for your next holiday?
By the end Of this week we'll have been running 5 What are you intending to wear to school tomorrow? your new School Council for a whole term.
We've already had an impact on the way the 5Ask and answer the questions in pairs. Use the future continuous in the questions. school is run. We asked to have a say in the new school uniform and the teachers agreed. 6 2.04 Listen to the conversation. What Will have Next term, we'll all be wearing a uniform happened by tomorrow afternoon?
![]()
designed
by you. 7 2.04
Complete the Sentences with a verb in the correct
And by the end Of the year we'll have made tense. Then listen again and check. our school even better. We'll be meeting more
![]() We'll
We'll![]() in
Birmingham soon.
in
Birmingham soon.
regularly next term. Come along With ideas on 2 By the time I arrive home I'llfor eight hours.
![]()
how
to improve our school. 3
Will you ![]() something to eat when you arrive?
something to eat when you arrive?
SEE YOU THERE! 5 By five O'clock, be hungry. we'll
I'll down to a lovely meal. 4 NO, I won't ![]()
![]()
8 Complete the predictions. Use the future continuous or the future perfect of the verbs below.
![]() find
go live melt speak spread
find
go live melt speak spread
2 Find four examples Of the future continuous, future perfect and future perfect continuous in the text. Then match each example With a use in the Learn this! box.
|
Future continuous, future perfect and future perfect continuous 1 We use the future continuous to: a talk about something we expectwill happen. b talk about an action in progress in the future. 2 We use the future perfect to talk about a completed action in the future. 3 We
use the future perfect continuous. usuallywith for |
3 Explain the meaning Of these sentences. Translate them into your language.
I At 4 p.m. we'll watch the film.
2 At 4 p.m. we'll be watching the film.
3 By 4 p.m. we'll have watched the film.
4 By 4 p.m. we'll have been watching the film for an hour.
![]() 2.06
Complete the phrases with the words below. Check
2.06
Complete the phrases with the words below. Check
help you. you understand the expressions. Then listen again. Which phrases don't they use?
advantage don't it maybe persuadin
![]()
![]()
![]() The bigof (my idea) is
The bigof (my idea) is
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Wouldn'tbe better to ? you think that ?
Wouldn'tbe better to ? you think that ?
![]()
![]() , but I still think
, but I still think
![]() agree
decided persuaded right
agree
decided persuaded right
OK, you've
0K. Let's
That's s
![]() PRONUNCIATION
How is the noun protest (in exercise 6) pronounced? How would it be pronounced
if it were a verb?
PRONUNCIATION
How is the noun protest (in exercise 6) pronounced? How would it be pronounced
if it were a verb?
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 4.4: PAGE 137
Work in small groups. You are planning to launch a campaign. Follow the instructions.
![]() •
Decide which issue you are going to protest about. Choose from the ideas in the
box below or think of your own.
•
Decide which issue you are going to protest about. Choose from the ideas in the
box below or think of your own.
Discuss What form Vour protest Will take and agree On three types of action. (See exercise 6.)
|
the building of a new road through a rural area popular With tourists a plan to build a nuclear power station near your town
|
![]()
![]()
![]() Discuss
and decide Who Will be responsible for each.
Discuss
and decide Who Will be responsible for each.
Takingastand
![]() banner
chant (v) demonstration demonstrator march (v) megaphone placard protest (v)
slogan
banner
chant (v) demonstration demonstrator march (v) megaphone placard protest (v)
slogan
2 Work in pairs. Imagine there are plans to build a massive car park in the centre Of a small town near you. Brainstorm reasons Why you might object to this.
3 ![]() 2.05
Listen to two teenagers, Ollie and Emma, discussing their Objections to the car
park. Compare your ideas With theirs.
2.05
Listen to two teenagers, Ollie and Emma, discussing their Objections to the car
park. Compare your ideas With theirs.
![]() 2.05
Complete the lines from the conversation With the verbs in brackets. Use the
present continuous, the present simple, going to and Will. Then listen and
check.
2.05
Complete the lines from the conversation With the verbs in brackets. Use the
present continuous, the present simple, going to and Will. Then listen and
check.
They (build) a massive car park in the town centre.
|
The council (meet) in a month's time so we need to mcwe quickly.
|
8 |
2
![]() 9
9
5 Match the sentences (1—4) in exercise 4 With the descriptions
|
D
GRAMMAR BUILDER 4.3: PAGE 122 2.06 Listen to Ollie, Emma and Jane discussing What form their protest Will take. Which Of these do they decide to do? Which do they reject, and why? |
a an arrangement b a timetabled event c an intention d an instant decision
I draw up a petition 2 hand out leaflets 3 organise a march make placards
6 write a letter Of protest
7 put up posters
8 contact the media
|
set up a website |
9 hold a rally
![]() HOW
would the beginning and the end Of the letter be 3 different if June
didn't know the name of the person she was writi ng to?
HOW
would the beginning and the end Of the letter be 3 different if June
didn't know the name of the person she was writi ng to?
![]()
![]()
![]() Mary
Jones
Mary
Jones
4 April 2013
![]() r Mrs
Jones,
r Mrs
Jones,
I am writing to protest against the planned Of the public library in the centre Of Greenford. I understand that it is to Close at the end of the year.
![]() am
particularly about the primary and secondary
am
particularly about the primary and secondary ![]() students
who currently use the library to research
students
who currently use the library to research
homework assignments and It is to tha t the library is Of crucial importance to people in
In
addition, many elderly and less well-off people might not ![]() able
to affcmå to buy many The fact is the Closure
is bound to adversely affext such people Who rely on the library as their
only source of reading matter.
able
to affcmå to buy many The fact is the Closure
is bound to adversely affext such people Who rely on the library as their
only source of reading matter.
Furthermore, the library Serves as a social centre Where people dmp in to read the papers and meet their friends. The consequences of the Will be Very damaging to people who use the library tn this way. 4
It is for these reasons that think the should reconsider its decision and keep the library open for the benefit of all the citizens o f Greenford.
1100k forward to response.
Yours sincerely,
Tune Knight 5
June![]()
![]()
Find and underline in the letter nine phrases from the list below.
![]()
Useful
phrases for a tetter of protest opening the letter
I am writing to protest against ![]()
![]() wish
to register my opposition to
wish
to register my opposition to ![]() I am writing to express my concern about
I am writing to express my concern about![]()
introducin ur reasons for
rotestin ![]() am very worried about/that
am very worried about/that![]()
I am particularly concerned about![]()
' fear that (it) Will lead to „ It is clearly
unfair to/that ![]() In addition ...'Furthermore
In addition ...'Furthermore![]()
making a point forcefulÿ
It 's important to recognise that![]()
The
fact is that What you don't seem to realise is that![]()
describinz ill effects ![]() will
do serious damage to
will
do serious damage to![]()
„ will lead to the
collapse:'destruction/death etc. of ![]()
„ is bound to adversely affect ![]() The
consequences Of will be very damaging
The
consequences Of will be very damaging![]()
![]()
requesting_aqggon
It is for these reasons that I think...
Please
put immediate) Stop to ![]()
Please do everything in your power to![]()
Add one of these phrases to each group in exercise 3.
a It is/l find it
unacceptable that ![]() b I would like to point out that
b I would like to point out that ![]() c I
wish to object in the strongest possible terms to
c I
wish to object in the strongest possible terms to ![]() d I
urge you therefore to reconsider your decision/proposal
d I
urge you therefore to reconsider your decision/proposal
(to ![]() e will
have a devastating effect on
e will
have a devastating effect on![]()
Complete the Exam tip. Find the features in the letter. Check you understand the key features of formal letters.
|
EXAM TIP at the top on the right, address just below on the left and below that. • Start and end the letter correctly: Dear Madam / name Yours faithfully / Avoid s language and , direct questions and marks. At the end, sign yours , then print it underneath. |
2 Read the letter. Answer the questions.
I What is the council planning to do, and when?
2 How many objections does June raise in her letter? 3 How do many students currently use the library?
4 HOW Will the closure affect elderly and less affluent people?
5 How else do people use the library, apart from to borrow books?
6 What action does June request?
Describe the photo. Do you or your town retail parks? Why?/Why not?
|
|
5 |
Work in pairs. Choose two reasons for Objecting to the |
|
2 Read the newspaper article. Answer the questions. |
|
proposed retail park from the list below, or think of your own |
|
1 What does the council have to decide? |
|
ideas. Expand the two ideas and make notes. |
|
2 Who is paying for the new retail park? |
|
Possible objections |
|
3 HOW big Will it be and how much will it cost? |
|
effect on shops/toss Of jobs in the town centre |
|
4 What two possible advantages of the plans are |
|
increased traffic |
|
mentioned in the text? |
|
destruction of a beautiful rural area |
|
5 What two possible disadvantages are mentioned? |
|
effect on wildlife |
|
|
6 |
Write the second and third paragraphs ofyour letter, using |
|
£20M RETAIL PARK |
|
the notes you made in exercise 5. Use phrases from exercise 3 on page 44. |
|
FOR AYLESMARSH |
7 |
Work in pairs. Decide What action you would like the council to take. Choose ideas from the list or thinkofyour own. Expand the ideas and write notes. |
|
AYLESMARSH COUNCIL are the centre Of town to the park. —Eing next June to decide The plans are likely to be |
|
Possible actions |
|
*ether or not to approve plans Controversial. Councillor Mike |
|
find an alternative location |
|
a 200-hectare retail park on Nesbit. Who is in favour of the |
|
abandon the proposal |
|
outskirts of the town. The development. said it would |
|
hold an enquiry and consult local traders |
|
will include department a massive boost to the local •es. clothing Outlets, media economy. creating hundreds Of |
|
build new shops and a car park in the town centre |
|
computer and electrical jobs and attracting major retailers |
8 |
Write the fourth paragraph Of your letter, using the notes you |
|
to the new park. However. local Hærington the traders are reported to be upset .ith plans to develop the at the effect the retail park Bill |
|
made in exercise 7. Use phrases from exercise 3 on page 44. |
|
CHECK YOUR WORK structured your letter following the task in exercise 3? included some phrases in each section from page 44? used a polite, formal style? used the correct layout and language to start and finish letter? Written 200—250 words? your spelling |
site, that the have on town centre shops, will cast £20 million A and environmentalists say it spokesperson said. 'The will destroy fields and ancient
![]()
Unit 4 Taking a stand
I Read the sentences. Describe what is happening using the verbs below and correct prepositions.
boasting confiding praising telling warning
1 •Rover, sit! Good boy, Rover!' said Joe.
Joe
was![]() his dog obeying him.
his dog obeying him.
2 •I can play football better than any of you.' Brandon said. Brandon was his friends.
![]() 'You can't swim here, there are rocks,'
said the lifeguard.
'You can't swim here, there are rocks,'
said the lifeguard.
The lifeguard was the rocks.
4 'Actually, I'm scared Of cats,' Kurt said to his son.
Kurt was his son his fear Of cats.
5 'Tom! Put those crisps away!' said the teacher.
The teacher was Tom off eating in class.
![]() Mark: _ 15
Mark: _ 15
2 Write the missing questions.
![]() Keira went to Spain with her sister.
Keira went to Spain with her sister.
Q: ? A: Her sister.
They stayed in a hotel for two weeks. ? A: Two weeks.
They were unhappy about their room.
Q: ? A: Their room.
4 They complained to the hotel manager.
? A: The hotel manager.
5 He told the maid Off for not cleaning the room.
? A: For not cleaning the room.
Mark: _
3 Complete the text. Write one or two words in each gap.
Thanks to technology, it's getting harder for teenagers to experience independence. In the past,
travelling abroad without your parents was
one Of ![]() effective ways Of learning survival
skills. But today, going
effective ways Of learning survival
skills. But today, going
abroad is nowhere liberating as it used to be
because teenagers can stay in touch via texts, as ![]() their
parents. The more connected the world becomes,
their
parents. The more connected the world becomes, ![]() easy
it is for teenagers to find space to grow.
easy
it is for teenagers to find space to grow.
4 Add question tags to the dialogue.
Boy Let's go out for dinner this weekend.
![]() Girl
Good idea. We should book somewhere,
Girl
Good idea. We should book somewhere,
Boy Yes. I'll do that. How
Girl You haven't been there before, 3
Boy NO. Nobody said anything bad about it,
![]()
![]()
![]() Girt OK! Don't forget to ask about vegan food,
Girt OK! Don't forget to ask about vegan food,
Language Review![]()
5 Complete the sentences With the verbs below.
gauge influence launch tackle take part in
1 Did
you![]() the demonstration last night?
the demonstration last night?
2 Online
surveys are a good way to public opinion. ![]() Local
politicians have done nothing to vandalism
Local
politicians have done nothing to vandalism
in this city.
4 Can you government policy by donating money to political parties?
![]() The Government plans to
The Government plans to![]() a
new antismoking campaign focusing on teenagers.
a
new antismoking campaign focusing on teenagers.
|
|
|
6 Complete the dialogue with the words below.
bound chances might must won't
Boy Where's our taxi? It 1 be at least half an hour since I called.
Girl are it's stuck in traffic. It is rush hour.
Boy The gig starts at 7.30. We ' miss the beginning
Girl Don't worry. There's to be a support act on first. We s miss the main band.
Mark: _ 15
7 Choose the correct verb forms, a or b.
![]() gone
to bed yet. it's only 9 p.m. a won't have gone b won't have been going
gone
to bed yet. it's only 9 p.m. a won't have gone b won't have been going ![]() I
can't text you tomorrow afternoon, I an exam. a 'Il have done b 'Il be doing
I
can't text you tomorrow afternoon, I an exam. a 'Il have done b 'Il be doing
3 Sue's
on holiday. She![]() a great time, I expect. a 'Il have had
b 'Il be having
a great time, I expect. a 'Il have had
b 'Il be having
4 They![]() together
for a year this December.
together
for a year this December.
a 'Il have gone out b 'Il have been going out
5 You
need to say it again. He ![]() a won't have heard b won't have been
hearing
a won't have heard b won't have been
hearing
Mark; —
8 Complete the dialogue With suitable words.
Boy Here's an t . Why don't write a letter to the newspaper?
Girl I'm not about that. They probably won't
print it. I ' we should launch a campaign on Facebook. It's easy and effective.
We always get our friends to join ![]()
Boy I sees you're saying that, but
Will anyone notice a campaign on Facebook? 
Find Out if your partner prefers shopping in small, local shops or giant superstores. Agree on two pros and two cons for each type Of shop.
2 2.08 Listen. Where does the conversation take place? Choose one, two or three Of the places below.
in a superstore in the squat outside a shop
3 2.08 Listen again. Choose the correct answers. I Why does Stefan assume Daisy is not English? a Her English is worse than his. b Her appearance is not typically English.
c She doesn't seem to know anyone.
2 Daisy lives a in the same squat as Spikey. b in a flat on Western Avenue. c with her Spanish mother.
3 When Spikey tells Stefan he shouldn't buy bananas, Stefan a suggests Spikey has got his facts wrong. b agrees not to buy any bananas.
c does not understand how not buying bananas Will make a difference.
4 Daisy left home because a she didn't like living with a capitalist.
b she had a big argument with her father. c she wanted to live with Spikey.
![]() Read
the text. What is it from? Choose from a—d.
Read
the text. What is it from? Choose from a—d.
|
b a leaflet |
d a magazine article |
D CHECK YOUR PROGRESS:
PAGE' |
|
|
S-O-S- SAVE |
OUR SHOPS! |
a a newspaper report c a formal letter
in exercise 4?
Wesley's are planning to build a car park next to an existing row of shops.
![]() An Official decision to allow the
development has already been made.
An Official decision to allow the
development has already been made.
3 Letters Of complaint should focus on the fact that local people were not asked to discuss the plans.
4 The supermarket chain has already bought a playing field from the local council.
![]() There are already traffic problems in
the area.
There are already traffic problems in
the area.
6 Imagine you are planning a protest for the campaign against
Wesley's. Which Of the options below Will you choose and
![]()
![]()
Why?
Why are you rejecting the other options? Take turns to

7 Stún. Write a letter, in an appropriate Style, to in
• thank her for letting stay.
• describe 'Our new flat.
![]() invite her to visit your new flat.
invite her to visit your new flat.
• describe Spikey and Daisy.
chain are planning demolish a row Of shops in Williams and build a new, massi Ve superstore underground car park in the same
They have already received planning permission for the development the local council, Who own the land, we believe it is not too late to stop it, campaign — write and complain! asking people to write to their ICRaI of to development , and in particular, the lack with local residalts
We feel the decision to appmve
the plan was taken without considering its negative impact on the environment and the community. Fiv e good reasons to the developmen t:
The site for the new superstore includes a 10,mOm: playing field which the local government plans to sell off Our Children need spaœs for Sports and exercise!
2 Unlike Shops, the profit from a big superstore goes to its shareholders, who do not live locally. The money is not reinvested in area _
3 from all
around world. which causes polluticm and is Our small,
Shops produce Whenever
4 Parking and traffic are already a big -prc&m in this part Of London. A new superstore will make it worse, especially as park is small for the expected number of customers.
5 Large keep their p I ow by exploiting workers in developing countries Many banana-growers, for example. earn less than El a day.
Skills Round-up
4 Get Ready for your Exam
pairs:
1 What are androids?
2 Will they be part Of our lives in the future?
Why? / Why not?
3 Do you think the future looks bright or bleak for the human race?
2 DO the exam task.
![]()
READING exam task
![]()
Read the extract from Do Androids Dream Of Electric Sheep? by Philip K Dick. Complete the text With the missing sentences (A—E). There is one extra sentence that is not needed.
In a great empty apartment building far from the centre Of San Francisco a single television played. There were few people left to miss them.
Nobody reallv remembered why the war had started or who, if anyone, had won. The radioactive dust that covered the Earth had come from no country and nobody had planned it. Under United Nations law each person Who left was given an android to work for them. It became very easy to go and difficult to Stay. The few thousands who remained moved into areas where they could live together and see each other. There were only a few Odd individuals who stayed alone in the suburbs. John Isidore, listening to the television as he shaved, was one of these.
'Let's hear from Mrs Maggie klugman,' the television presenter was saying. •She emigrated to Mars a short time ago. MrsKIugman, how does your exciting life in New New York compare with the difficulties of your previous life on Earth?'
There was a pause, and then a tired middle-aged voice said, •3 And before we left, my husband and I were always worried that we might become specials. NOW Our worries have gone for ever.'
For me too, John Isidore thought, and I didn't have to emigrate. He had been a special now for over a year. Snce he had failed even a basic intelligence test, the popular name for him and Others like him was 'chickenhead' — but he survived. He had a job driving a truck for a false-animal repair company, and Mr Sloat, his boss, accepted him as a human being. There were chickenheads who were much more stupid than Isidore.
Isidore had finished shaving, and turned the television off. Silence. • He experienced the silence with his eyes as well as his ears. It almost felt alive.
Get Ready for your Exam 4
A After the war the animals had died, the sun had stopped shining and most people were encouraged to emigrate.
B Before World War Terminus the building had been well looked after, but now the owner Of this and Other apartments had died or emigrated to other planets.
C It came from the walls. the floor. the ceiling and from all the machines in the apartment that had stopped working years before.
D Life used to be so easy and carefree and leaving Earth behind was such an ordeal.
Oh, it's wonderful have an android that you can depend On.
3 Do the exam task.
![]()
Complete each gap in the text with a word formed from the word in brackets.
The number Of people Without jobs in the UK has risen by 28,000 to 2.67 million during the three months to January, according to the (LATE) figures, Which the government says show signs Of stabilising. It is the lowest rise in over a year, but 8.4% Of the population is still affected. (EMPLOY) amongst the female population accounted for most of the rise in the number (JOB) people. They have been most s (SEVERE) hit, making up nearly 80% Ofthe increase. The figures also underlined the extent to Which the increase in the number Of part-time jobs is masking the problem. They are Often (ADEQUATE) paid and therefore cannot replace the full-time (EARN) that people generally require. Meanwhile, the government continued to emphasise that despite the latest Cuts in public sector jobs, more jobs were being created in the private sector. However, there is some (COURAGE) data for the UK economy. (SURPRISE), retail sales rose by an unexpected 0.9% in January, as fears of a recession disappeared.
Vc-zabulary • comm.tins: phrases and useful verbs • components • crime
Grammar • active and pa"ive • passive; all forms • participle clauses Technology
• future in the past
Speaking • stimulus description
Writing • story
Look at the photos. Which of these websites do verbs below. Then use some
you visit regularly? What do you do there?
2 Complete the chart using the verbs below. Then in pairs.
translate all the phrases. Which words are the same in your Own language?
|
Computing: edit or |
phrases your profile/ status/ personal details/ contact details/ preferences |
(on Facebook/ MMSpace/Amazon, etcJ |
|
|
sign in or |
to Faceb00k/H0tmail/your account,
|
||
|
|
a comment/an entry |
(on YouTube/a blog/ an Internet forum) |
|
|
|
a chat/a Wi-fi network, etc. |
||
|
|
an app/a film/a file, |
(from iTunes/the Internet, etc.) |
|
|
|
a video/a photo, etc. |
(to YouTube/ Facebook/Flickr, etc.) |
|
|
|
music/video |
(to your phone/TV/ computer. etc.) |
|
3 Listen to five conversations. Describe what the people are doing using phrases from exercise 2.
to complete the sentences from the conversations. Computing: useful verbs browse cancel click/double-clitk delete enter highlight key press (a key) scan scroll up/down search swipe tap zoom in/out
I Let's![]() and
see what they've written underneath,the video.
and
see what they've written underneath,the video.
2 What were we going to for?
3 1 don't need to in my card details.
![]() on that button.
on that button.
![]() so we can see him more clearly.
so we can see him more clearly.
6
Just![]() from
left to right, then
from
left to right, then![]() the red button with your finger.
the red button with your finger.
7
Use
the cursor to![]() the name of the film and then
the name of the film and then ![]() the
return key.
the
return key.
8 We can't wait that long. HOW do wethe download?
![]()
5 Listen again. Check your answers to exercise 4.
6 Work in pairs. Using the language in exercises 2 and 4 to help you, explain to your partner how to:
I add a new contact to your phone.
2 domload a song from the Internet. 3 find and watch a video clip Online.
First, you need to open the address book app by tapping the icon. Then you tap the plus sign.
you key in the name and address
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 5.1: PAGE 138
5
Choose one or two words from below or your own
|
(can / try on) without having to undress or even find the items in the store. The mirror is in fact a computer screen. Stand in front of it and your body (scan / instantly). An image Of yourself (display) on the screen and your measurements (calculate / automatically). Once this (do), items of clothing (can / choose) from the on-screen menus. These 9 (superimpose) onto your Own image. Shoes and accessories (may / add) to complete the outfit. And because a second opinion (often / need), your new look (can share / instantly) With your friends: ifyou click on an icon, it (post) on Facebook a few seconds later. At the moment, magic mirrors (not find I often) in independent clothes shops, but they (introduce / quickly) in larger stores across the country. |
|
|
in pairs and give reasons. |
|
put them immediately before the past participle: |
|
|
Trying
things on when you go shopping for clothes is |
|
The results Will be thoroughly checked. |
|
|
a chore embarrassing essential exciting fun |
|
In compound tenses, adverbs of frequency usually go |
|
|
inconvenient oft-putting uncomfortable |
|
between the auxiliary and be or been: They'll never be told. She's often been warned. |
|
2 |
Complete the sentences With the words below. |
|
Prepositions which belong with the verb go immediately after the past participle: |
|
|
bought closed done introduced returned tried 1
About Of clothes which have been |
|
Will she be listened to? MV laptop is being looked at. |
|
|
|
5 |
Read the Look out! box. Then complete the text with the |
|
|
2 The advantage of high
street clothes stores is that the clothes can be |
|
passive forms Of the verbs in brackets. Use the correct tense. |
3 New technology is being to stores to make shopping easier.
4
![]()
![]()
![]() By 2025, most shopping Will beonline and many high street
stores will have been
By 2025, most shopping Will beonline and many high street
stores will have been
3 Study the sentences in exercise 2 and say:
|
|
Passive: all forms 1 We can form the passive of any tense by using that tense of the verb be plus the past participle. Wi•Fi has been/is being/will be installed at school. 2 We use the past continuous and present continuous forms of the passive, but we don't use Other continuous forms because they are very clumsy. I'm being watched. Someone has been watching me. 3 We can use the passive with present and past forms Of modal verbs. Shoes must be worn. This puzzle can 't be solved. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 1
which different tenses the passive forms are in. 2 which passive form includes
a modal verb.
1
which different tenses the passive forms are in. 2 which passive form includes
a modal verb.
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 5.1: PAGE 123
4
![]() Read the Learn this! box. Then rewrite the sentences in
the passive, unless they contain a tense not used in the passive.
Read the Learn this! box. Then rewrite the sentences in
the passive, unless they contain a tense not used in the passive.
A giant asteroid might destroy the earth.
![]() They're
testing our theories about the universe at CERN.
They're
testing our theories about the universe at CERN.
![]() The
Chinese mav have invented gunpowder.
The
Chinese mav have invented gunpowder.
|
|
|
|
|
they hold the Olympics. |
6 |
|
|
6 Someone had been reading all my emails, I realised. |
|
sentence. Then compare your ideas With the class. |
|
7 If they'd received your complaint, they would have |
|
1 Shopping could be made easier by (t -ingform) |
|
notified you. |
|
2 If
all shopping was done Online, 3 Apart from clothes shopping, a magic mirror could be |
![]() You
can join the Wi•Fi network free of charge.
You
can join the Wi•Fi network free of charge.
![]() used for
used for
5
In pairs, complete the definition using the words below.
embryo engineering fertilisation genes implanted
 baby born after IVF (in vitro
baby born after IVF (in vitro
Some people see designer babies as a step forward in technological development. However, many people see it as a negative step for technology.
2 Listen to five people talking about designer babies. Is each speaker generally for or against them? Write F (for) or A (against).
3
 below. Translate the other four words.
below. Translate the other four words.
Science advance (n, v) diagnosis DNA experiment (n, v) injection laboratory laser patent (n, v) procedure side effects technicians test tube
I I don't think a technological is the same as progress.
2 The rich will pay to genetically improve their babies.
3 I think all babies will be created in a one day.
4
We
shouldn't![]() With human embryos.
With human embryos.
![]() We could accidentally change human forever.
6 I think it's just a medical , like any Other.
We could accidentally change human forever.
6 I think it's just a medical , like any Other.
![]() Listen
again. Check your answers to exercise 3.
Listen
again. Check your answers to exercise 3.
Workin pairs. Find out whether your partner agrees Or disagrees With the sentences in exercise 3.
|
Do you agree thatwe shouldn't |
? |
|
|
|
|
|
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
|
|
b ensure |
c certify |
d convince |
|
2 a keep |
b allow |
c go on |
d continue |
|
a warn |
b risk |
c threaten |
d endanger |
|
4 a regard |
b think |
c imagine |
d 100k |
|
|
b by |
c for |
d up |
|
6 a already |
b just |
c yet |
d ever |
|
|
b so |
|
d exactly |
|
8 a Better |
b Rather |
c Sooner |
d Instead |
We
now have the ability to that children are born free Of any one Of
hundreds of serious genetic disorders. from cystic fibrosis to early-onset
cancers, aut children to be born with these diseases. All would-be
parents should be offered screening to alert them to any genetic disorders they
![]() passing on to their children. Those at
risk should then be offered IVF with tests to ensure embryos are healthy before
they are implanted. Why isn't it happening? Because most people still attempts
to influence Which genes our children inherit as taboo. But fears of •designer
babies' are misplaced. You cannot select for traits the parents don't have. and
the scope for choosing specific traits is very limited. aut you can make sure
children do not end 5 With disastrous genetic disorders.
passing on to their children. Those at
risk should then be offered IVF with tests to ensure embryos are healthy before
they are implanted. Why isn't it happening? Because most people still attempts
to influence Which genes our children inherit as taboo. But fears of •designer
babies' are misplaced. You cannot select for traits the parents don't have. and
the scope for choosing specific traits is very limited. aut you can make sure
children do not end 5 With disastrous genetic disorders.
Nearly 150 years after Darwin unveiled
his theory* of evolution, we have to grasp one of its most unsettling
implications: having diseased children is ![]() natural
as having healthy ones. Thanks to technology. we are no longer entirely at the mercy
Of this callous process. 8
natural
as having healthy ones. Thanks to technology. we are no longer entirely at the mercy
Of this callous process. 8 ![]() than regarding this ability With
suspicion. we should be celebrating it and encouraging its use. But instead. we
continue to allow children to be born with terrible diseases because of our
collective ignorance and superstition.
than regarding this ability With
suspicion. we should be celebrating it and encouraging its use. But instead. we
continue to allow children to be born with terrible diseases because of our
collective ignorance and superstition.
•an opinion or idea that somebody believes is true but that is not proved
![]()
7 Which sentence best sums up the text in exercise 6? a We shouldn't select traits for babies even though we have the technology to do so.
b We should use all the technology we have in Order to prevent diseases in babies.
c We shouldn't use technology unless we know that a child has a serious genetic disorder.
![]() In pairs, discuss the opinions in
exercise 7. Do you agree or disagree? Give reasons.
In pairs, discuss the opinions in
exercise 7. Do you agree or disagree? Give reasons.
5
Computer hackers rarely show their faces in public, allowing the
d three hi-tech companies.
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
![]()
3 ![]() Read
the Exam tip. Then match the gaps (1—6) in the text With the sentences below
(A—H). There are two extra sentences.
Read
the Exam tip. Then match the gaps (1—6) in the text With the sentences below
(A—H). There are two extra sentences.
A That
is easily enough to cover his computer science education so far at the
University of Georgia. ![]() He mowed people's lawns near his home in
Peachtree City, Georgia, to earn money to buy the parts for a computer he was
building.
He mowed people's lawns near his home in
Peachtree City, Georgia, to earn money to buy the parts for a computer he was
building.
![]() C
Apple was apparently so impressed with his jailbreaking skills that it
persuaded him to join the company instead. D Without those, it was impossible
to develop software for any of these devices.
C
Apple was apparently so impressed with his jailbreaking skills that it
persuaded him to join the company instead. D Without those, it was impossible
to develop software for any of these devices.
![]() His introduction into the world Of
jailbreaking was
His introduction into the world Of
jailbreaking was ![]() accidental.
accidental.
![]()
![]() However, many Other former hackers have
taken up
However, many Other former hackers have
taken up![]()
![]()
positions with software companies.
G That's something you can't do if you are an
official![]()
![]()
developer.![]()
![]()
![]()
5
stereotype Of the socially awkward loner sitting in the dark in front of a computer screen to flourish. But the reality is rather different - at least when it comes to jailbreaking. Jailbreakers do not commit criminal acts like hacking into government computer
systems or writing malicious viruses. Instead, they write code which removes the manufacturers' restrictions On everyday devices like smartphones and games consoles. A 'jailbroken' device can run unofficial software and be used in ways which the manufacturer did not intend. Some of the big technology companies have taken legal action against jailbreakers but with little success.
James Whelton, a smooth-talking twenty-year-old from Cork, started messing around With computers at the age Of nine, and began programming soon afterwards. It happened when he won a pink iPod Nano. 'Basically I was on a plane and I was bored. so I just started tinkering with it and found something interesting,' he explained.
He discovered a vulnerability in the iPod's software that could possibly be exploited to jailbreak the device. Within a few days he was contacted by another hacker known as DarkHalIoc - in reality a sixteen year old from Wales called Joshua Tucker. He introduced Whelton to Other hackers — big names in the hacking scene like chronic and ih8snOw. Chronic - a teenager from the United States called Will Strafach — is the founder of a jailbreaking team called Chronic Dev, while ih8snOw, a sixteenyear-old called Steven from Canada, is the developer of several well-known jailbreak-ing tools.
Instead Of taking up a place at university earlier this month, Whelton decided to use the exposure that his jailbreaking activities have earned him to help get investors for a software company called Disruptive Developments that he founded in June. 'I did my final exams on a Friday, and became a chief executive on the Monday.'
Aaron Ash is another hacker-turned-entrepreneur. When Mr Ash was fourteen he got his hands on a calculator which he
|
|
4 |
Answer the questions. Why are jailbreakers less likely to end up in prison than some Other types of hackers? 2 How did jailbreaking help James Whelton to Start a business? Why did Aaron Ash start writing apps for jailbroken |
|
programmed to do his homework. After teaching himself to |
|
phones? |
|
program it. he worked on video games before getting an Apple |
|
4 Why hasn't Aaron Ash earned millions Of dollars from his |
|
iPhone and turning his attention to that. |
|
highly successful apps? |
|
The young Mr Ash wanted to write apps for his phone, but |
|
5 Why is Aaron Ash thinking Of leaving full•time education? |
|
it turned out that at seventeen he was too young to sign up |
|
6 In What way has the jailbreaking scene •lost' many Of its |
|
to Apple's Official iPhone development program. That left him with no alternative but to become a hacker and write apps for jailbroken phones. 'This was actually even cooler to my mind, it let me |
|
senior figures? |
|
|
|
noun — the activity |
noun — someone who does it |
|
|
|
||
|
|
hacking |
|
|
|
to jailbreak |
|
|
|
|
to pirate |
|
a pirate |
|
|
actually paid for it is now about one in a hundred,' he said. |
|
|
|
Despite the rampant piracy Ash has earned over 5100.000 from his applications. The problem he faces now is that he |
|
VOCABULARY BUILDER 5.2: PAGE 138 |
|
knows more than most Of the teachers. Tm actually considering |
6 |
Work in pairs. Read the descriptions of cybercrime and put |
|
leaving uni and starting a software contracting company with a |
|
them in order from the most to the least serious, in your |
|
friend met in the jailbreaking scene.' |
|
opinion. Give reasons. |
|
Going straight' at an early age certainly seems to be the |
|
a stealing somebody's identity and using it to buy goods |
|
pattern in the jailbreaking world, and the scene has lost several |
|
on eBay |
|
Of its senior figures to the lure Of business. George Hotz, the |
|
b selling pirated copies Of films and computer games from |
|
22•year-Old hacker known as Geohot who was responsible for |
|
a market stall |
|
programs that jailbreak Apple's devices as well as Sony's PS3, |
|
c leaving racist comments On a Facebook page |
|
left the jailbreaking scene earlier this year to take up a full-time |
|
writing •malware' — software designed to damage |
|
job wlth Facebook. And Nicholas Allegra - the nineteen-year-old |
|
people's computers |
|
jailbreaking guru better known in the hacking world as Comex |
|
e sharing all your music, films and IV shows online via an |
|
- also found an alternative career. It seems that the Old notion Of poacher turned gamekeeper still exists, even in our |
|
illegal site |
|
technology-oriented world. |
7 |
Compare your ideas from exercise 6 with the class. Can you agree on one order between you? |
|
|
8 |
In pairs, choose one Of the topics below for a short presentation. Make notes. a Cybercrime is just as serious as other forms of crime and should be punished. b Cybercrime Often has no victim and should not be compared with other forms of crime. |
|
|
9 |
Present your ideas to the class. |
because write programs that change the way the iPhone works,' he said,
Mr Ash started selling his programs, called Barrel and Multiflow. but at this point he Came face to face with the darker side of the jailbreaking Scene. 'My Barrel app is being used by three and half million people, but the proportion of people who
5
4 Today, more than 450.000 servers around the world store 2 focuses mainly on Steve lobs?
Google'sin formation.
3
contains
mainly passive verbs? ![]() People have criticised
Google for storing too much
People have criticised
Google for storing too much
4 contains mainly active verbs? information about the public without their consent.
|
Apple Computers was |
Steve Jobs helped design |
adults named Google as the company thev would most like to work for. |
|
founded by Steve lobs and |
the first Macintosh |
|
|
Steve Wozniak. |
computer. |
|
LOOK OUT! |
|
n the 1980s, the company |
Jobs left Apple in 1985 after |
|
Verbs like give, Offer, send, award, show, etc. Often have |
|
was run by John Sculley. |
a dispute with Sculley. |
|
two Objects: a person and a thing. The person is usually |
|
Sculley was sacked by |
Jobs bought a small |
|
the indirect object. |
|
Apple's directors in 1993 |
computer graphics company |
|
They Offered Harry a job. (They offered a job to Harry.) |
|
because market share was |
and transformed it into |
|
We usually make the indirect Object (i.e. the person) into |
|
being lost. |
Pixar, the company behind rov Story. |
|
the subject of the passive. |
|
The iMac was launched in |
Jobs earned Only $1 a |
5 |
Read the Look out/ box. Underline the indirect Object in these |
|
1998, after lobs had been |
year as CEO of Apple, |
|
|
|
reappointed CEO, and it was |
although he was already a |
|
sentences. Then rewrite them in the passive. |
|
an instant success. |
multi-billionaire. |
|
I My uncle gave a phone for Christmas. |
|
Will the company's |
Millions first learned Of |
|
I was given a phone for
Christmas bi my uncle |
|
reputation for creativity and |
Jobs's death in 2011 on |
|
2 Her grandfather left her some money in his will. |
|
innovation be maintained |
a device Which had been |
|
3 My cousins taught us to ski. |
|
now that Jobs's personal |
invented by lobs himself. |
|
4 Somebody has sent me a really funny video clip. |
|
input has been lost? |
|
|
5 The computer shop has lent my dad a laptop. 6 Somebody had told my neighbours about the party. |
![]()
![]()
![]() 6 In a survey for Business Excellence magazine, British
6 In a survey for Business Excellence magazine, British
|
Active and passive voices I We use the passive when we want to describe an action but do not know who or what performed it. Our car window had been smashed. 2 We sometimes choose to use the passive even when we do know who or what performed the action. because it allows us to change the focus Of the Sentence. Jonathan Ives designed the iMac when he was 30 years Old. (focus On Jonathan Ives) The iMac was designed by Jonathan Ives and was available in six colours. (focus on the iMac) |
|
6
![]() Make notes about:
Make notes about:
• the funniest email you've ever been sent.
•
the
coolest app you've ever been shown. ![]() the
first phone you were given.
the
first phone you were given.
• a gadget you were once lent.
7
![]() Talk to your partner and find out the
information in exercise 6. Use the questions below and your Own ideas.
Talk to your partner and find out the
information in exercise 6. Use the questions below and your Own ideas.
3 Read the Learn this! box. use the information to explain your answer to the questions in exercise 2.
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 5.2: PAGE 124 ![]()
5
Listen to a different student doing the task in
nouns components face masks factory instruments production line protection tools
2 In pairs, discuss which of the factories in exercise I you would rather work in for a holiday job. Try to think of three different reasons.
3 Listen to a student doing the task below in relation to the photos in exercise I. Does he choose the same factory as you? Are his reasons the same Or different?
You're going to apply for a holiday job working in a factory. Which factory will you choose and why? Why are you rejecting the Other option?
EXAM TIP
Make sure you say clearly which picture you are choosing and why you are rejecting the other option(s). Use the phrases below to help you: so, I'd opt for the , mainly because
I think the would be the better/best option because so my choice would be the That's because
'wouldn't choose the because
The reason / wouldn't go for the is that wouldn't pick the simply because
![]() Read the Exam tip. Find three verbs which are synonyms
for exercise 3. Which factory does she choose and what is her main reason for
rejecting the other one?
Read the Exam tip. Find three verbs which are synonyms
for exercise 3. Which factory does she choose and what is her main reason for
rejecting the other one?
7 Complete the phrases With the words below. Then listen again and tick the phrases the student uses.
chances imagine likely possible say seems though about a photo
There to be
|
It looks (to me) as It's quite that I should |
/ as if |
|
Judging by , I'd are (that) More than not |
that |
8 Write five sentences speculating about the photos in exercise 1. Use five different phrases from exercise 7.
9 Work in pairs. Look at the photos and read the task. Choose a language school, then agree on two reasons for your choice and two reasons for rejecting the Other one.
You're going to apply for a short course at a language school. Which course Will you choose and Why? Why areyou rejecting the Other Option?
|
5
|
In pairs, take turns to do the task in exercise 9. Include your reasons. Make sure you include phrases from the Exam tip and exercise 7.
|
A WEEKEND IN THE COUNTRY |
|
|
•I hate these narrow country roads,' said Zena. trying u:' make out the landscape in the darkness as her husband Alex drove. Having worked hard all week, Zena and Alex were looking forward to their weekend away, It was a long drive for a Friday evening, but they would soon arrive at the holiday cottage. Mr Martin, the farmer who owned the cottage, was to meet them there With the key. 'After 50 metres. turn left.' ordered the satnav. Zena frowned. looking out of the window. 'I'm sure we should go right,' she muttered. But Alex didn't hear her. Turning the the wheel sharply to the left, he put his foot down. The car bumped loudly on a rock. There was a splash, and the car swerved before coming toa halt. •l knew the satnav was wrong! • exclaimed Zena. Alex tried to Start the car but the engine was dead. What were they going to do? They couldn't even open the car door because the water would rush in. Zena took her phone out Of her pocket and tried to call Mr Martin. There was no signal. At that moment, there was a loud tap on the window. Zena screamed and dropped her phone. A smiling face appeared at the window. •Mr and Mrs Henderson? I'm Mr Martin. I've been expecting you. Most visitors from London follow their satnav into the river!'
|
|
3 In pairs, divide the story in exercise 2 into four sections.
1 setting the scene (characters, background, etc.)
2 the first event; a problem arises
3 efforts to solve the problem
4 how the problem is finally resolved
5
Read the Learn this! box. How many examples of future in the past can you find in the Story in exercise 2?
|
Future in the past When we talk about the future from a point ofview in the past we can use these verb forms; It was Monday. Dod Iwas coming home the next day. We were Sure he 'would be happy With the changes we were making to the house. But 'were we going to finish them on time? These three verb forms are the past equivalents Of (I) present continuous for future arrangements OR present simple for future scheduled events (2) Will future (3) going to future. In written English.
we can also use the expression was/ were My aunt arrived early on Saturday morning. She was to spend the weekend with us. |
|
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() D GRAMMAR BUILDER 5.3: PAGE 124
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 5.3: PAGE 124 ![]()
|
EXAM TIP There are several good ways to begin a story: 1 Set the scene: was a warm evening in August and / was on holiday in Thailand With my parents. The sun was going down and the insects were coming out. 2 Start with dialogue: Wow! look at this place!' said my dad as the taxi stopped Outside the Grand Palace Hotel in phuket, Thailand. 3 Start by looking back: / Often think back to the first foreign holiday I went on with my parents and how it changed my relationship With them. |
Read the Exam tip. Which type of beginning (1—3) does the Story in exercise 2 contain? Write alternative beginnings for the same story using the other two types.
6 Rewrite the story opening below. Change it from dialogue to a paragraph setting the scene. Include Some future in the past.
•The
summer holidays start soon!' exclaimed Anna. 'And ![]()
Jacqui is coming to Stay with us for two whole weeks!' •l know. I'm really excited about that,' said Harry, who always enjoyed having their cousin Jacqui to Stay. 'We'll go to the beach every day. We'll teach Jacqui to surf.' 'We'll have a great time,' agreed Anna.
For Anna and the
summer holiåav![]()
In pairs, compare your answers to exercise 6 and check each Other's work for mistakes. Can you take ideas from your partners version to improve your own?
headings below.
1 Background: when/where the events happen:
Main character(s):
2 Item of technology involved:
What problem it causes and how:
3 What happens as a result: 4 How the Story ends:
![]() In pairs, 100k at each Other's plans
and ask three questions about them. Think Of answers and add them to your
plans.
In pairs, 100k at each Other's plans
and ask three questions about them. Think Of answers and add them to your
plans.
|
EXAM |
TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Include a mix ot direct speech and ordinary narrative in your stories. TO make your writing more vivid. you can use a variety of speech verbs after direct speech: mutter, shout. joke, sob, moan, insist, urge, etc. Direct speech needs inverted commas around the words spoken and a comma, question mark or exclamation mark before the closing inverted commas. Study the examples: 'By that time, ' she joked. q.ve'll all be dead!' 'Leave now!' she insisted, getting to her feet. |
|||||||||
7
![]()
Rewrite
these sentences with correct punctuation and an appropriate speech verb in the
past simple.
1 You must tell her he before it's too late.
2 What is he doing here she , spinning around.
3 Look out Gloria he . It's heading straight for us.
4 The worst thing she is not knowing.
5 1 hate this film he . It's worse than you said it was.
8 Decide how to begin your story. Look back at the three types Of beginning in the tip on page 56. Write the opening lines.
9 Write the rest of your story. Follow the plan you made in exercises 3 and 4. Write 200—250 words in total.

5 |
5 Get Ready for your Exam
the compound nouns.
|
scientific |
creatures b sledge |
|
marine |
station |
|
research |
d change |
|
ice |
e research |
|
6 dog |
cap |
|
7 climate |
g biology |
2 DO the exam task.
|
LISTENING exam task |
Listen to an interview with a scientist. For each sentence, select the correct ending: A, B, C or D.
I At the beginning of the programme, the radio presenter says that
A Elaine comes from a family of scientists.
B Antarctica is appealing to scientists because it's untouched by civilisation.
C it's difficult to explore Antarctica because it's so vast.
D many scientific discoveries have taken place in
Antarctica in the last 70 years.
2 Ata young age, Dr Glover
A dreamed Of studying insects at university.
B was never interested in social sciences.
C collected sea creatures because she lived by the
D paid little attention to making friends with other kids.
3 Dr Glover says that scientists working in Antarctica have to learn
A how to use appropriate forms of transport.
B how to relax when not at work.
C not to get distracted.
D to think Of the research station as their home. 4 When asked about the future. Dr Glover says that
A her group needs new maps of the area they're interested in.
B the ice in Antarctica may sometimes prove too thick to drill for data.
C more pictures of the whole area are needed for further studies.
D the studies will involve cooperation with specialists
3 DO the exam task.
USE OF ENGLISH exam task
Complete the text with an appropriate word in each gap. In ten years' time, robots will be used in every home, according technology experts and manufacturers. At the Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas, all Of domestic robots were unveiled. them were robots which are linked into the home's broadband service and Which act home organisers. These are capable responding to the family's voice commands in the house and at the time can be operated by mobile phones outside the house. In the future, robots these Will be responsible for operating the household's domestic appliances, as washing machines, alarm clocks, heating, lighting, music players and TV sets. effect, they Will act as household managers and Will even be able to activate smaller cleaning and vacuuming robots. ••0 of these types - the managing robot and the cleaning robot — will be able to provide security surveillance. As they travel round the house, an on-board camera will send pictures to your office laptop.
could be done by a robot and three that could not. Discuss your ideas with the class.
5 DO the exam task.
![]()
Discuss how new kinds of robots might affect everyday life in the future. Talk about:
robots in the workplace robots at home robots in leisure and entertainment possible dangers Of super-intelligent robots
from Other fields.
Get Ready for your Exam 5 Work in pairs. Discuss this question: Ifyou could Listen to customers complaining in a restaurant.
choose any meal in a restaurant, What would it be?Think Of starters, main courses and desserts.
2
![]() Divide the words below into two groups:
those that describe taste and those that describe texture.
Divide the words below into two groups:
those that describe taste and those that describe texture.
Describing food bitter bland chewy creamy crispy crunchy crumbly disgusting dry fresh fruity greasy juicy mild mouth-watering peppery raw rich ripe runny salty smoky smooth sour spicy stale sticky stodgy Strong Sugary sweet tasteless tasty tender tough unpleasant unripe
3 Which adjectives have a negative connotation for you? HOW many opposites or near opposites can you find?
4 Complete the adjectives in these sentences. Then translate them.
I Ripe pears are very j![]()
2 1 don't like much milk on my breakfast
cereal. I prefer ![]()
![]() Strong coffee without sugar tastes
quite b_ .
Strong coffee without sugar tastes
quite b_ .
4 These crisps are really s_. They make me thirsty.
![]() Lean over the plate when you're eating
your biscuits.
Lean over the plate when you're eating
your biscuits.
They're rather .
6 This steak is fantastic. It's really t_.
7 This peach is It's hard and s_.
5 Describe the foods in the photos. Use the adjectives in exercise 2 to help you.
Write the name of the food or dish they are talking about and the adjectives used to describe it.
7 Listen to three teenagers talking about food they like and don't like. Write the correct initial: J Genny), E (Ed) or R (Rosie).
I Who completely changed his/her mind about a certain food later in life?
![]()
3 Whose parents made him/her eat something he/she didn't like?
![]() Who helped Someone else deal with
something he/she didn't like eating?
Who helped Someone else deal with
something he/she didn't like eating?
5 Whose parents stopped buying the food he/she really loved?
![]() Whose parents used to love the food
that he/she couldn't stand?
Whose parents used to love the food
that he/she couldn't stand?
8 Complete the sentences With the verbs below. Then listen and check.
adored bear detested found got had loathed mind stand
I I
really couldn't![]() the texture.
the texture.
![]() the smell Of it unpleasant, never
the smell Of it unpleasant, never ![]() taste.
taste.
3 1've![]() to
like a few types of cheese now.
to
like a few types of cheese now.
![]() cauliflower - yuck! - and my brother
absolutely
cauliflower - yuck! - and my brother
absolutely ![]() Brussels sprouts.
Brussels sprouts.
He couldn't even the smell ofthem.
6 Asa kid I a passion for baked beans. the smooth texture of the beans.
9 Work in pairs. Tell your partner about two or three foods that you (a) hate or used to hate, (b) love or used to love. Try to give reasons for your answers. Use the sentences in exercise 8 to help you.
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 6.1: PAGE 139 ![]()
6 • Of |
I can use advanced passive structures.
DO the food quiz. Then listen and check your
It is believed that ice cream was invented in a China in about 650 b Italy in about 1500 c the USA in about 1850.
Wheat is first thought to have been cultivated in Turkey in about a 1000 BC b 4000 BC c 9000 BC. The potato is known to have originated in a North America b South America c Africa. a Saffron b Vanilla c Cardamom is considered to be the most expensive spice in the world. Until the 19th century, a oranges b apples c tomatoes were thought by many people to be poisonous.
O In the 17th century it was thought that bathing in a milk b sea water c Wine would cure most ills. There are known to be over 7,500 types Of a apple b banana c strawberry.
2 Read the Learn this! box. Find examples Of each passive structure in the quiz.
|
|
Passive with know, believe etc. WIth verbs like know, believe, think, etc., we Often use: 1 passive (present or past) ± that It is known that too much junk food is bad for you. It used to be thought that eating honey cured hay fever. 2 there ± passive (present or past) + to be/to have been There are thought to be about 5, 200 varieties of potato. 3 subject passive (present or past) to do/to have done something Until about 1850, bleeding was believed to cure fevers. If we are expressing a present belief about a past event, we use the present simple passive followed by a perfect infinitive (to have done something): rhe Mayans in Central America are thought to have used tobacco. |
|
|
3 Change the examples in the quiz using alternative passive structures from the Learn this! box.
I Ice cream is believed io have been
![]()
5
6
7
Complete the second sentence so that it means the same as the first. Start With the words in brackets.
For centuries it was thought that mercury wasn't poisonous. (For centuries mercury wasn't )
2 It is known that the universe is about 13.7 billion years
Old. (The universe is )
3 It is thought that there are fewer than 500 Siberian tigers living in the wild. (There are )
4 In 16th century England taking a bath was considered to be unhealthy. ('n 16th century England it was )
The Chinese are thought to have invented tea. (It is )
Passive modals, gerunds and infinitives
1 We can use passive structures with modal verbs. The sauce should be stirred continuously.
2 Verbs that are followed by an infinitive or gerund can also be followed by a passive infinitive or gerund: My dad hopes to be promoted. (hope ± infinitive) hate being photographed. (hate •ing)
Read the Learn this! box. Complete the sentences with the correct passive form. Use the verb in brackets.
If you continue to behave badly at school you'll end up (expel).
Everybody wants (love)!
The grammar reference for this lesson can (find) on pages 124—5.
4 Put on this cream to avoid (bite) by mosquitos.
Tables must (book) in advance.
6 I hope (choose) for the school football team. These books should (handle) with care. 8 Can you imagine (tell) you'd won the lottery?
Work in pairs. Decide if the verbs below take a gerund, an infinitive or both. Then add them to the correct group.
agree expect imagine remember can't stand vertvgerund avoid. be used to, can't face, don't mind, end
![]() arrange, hope, refuse, want,
arrange, hope, refuse, want,![]()
yerþ_gerundor infinitive continue,
prefer,![]()
![]() Work in pairs. Make as many different
sentences as you can using verbs from exercise 6 followed by passive gerund or
passive infinitive forms Of verbs below.
Work in pairs. Make as many different
sentences as you can using verbs from exercise 6 followed by passive gerund or
passive infinitive forms Of verbs below.
arrest call criticise film give ignore invite involve keep waiting laugh at photograph rob tease tell treat watch Most people can't stand being ignored,
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 6.1: PAGE 124
formed from the words in brackets. play in people's health. smoking.
3 Explain What information is linked to these numbers from the tell people what to do.
text. Were any pieces Of information in your list above?
a 30 c 34 e 147 billion b 75 d 28
Answer the questions.
I HOW do people put on weight?
2 How has the American diet changed?
3 What things can prevent people in the US from getting enough exercise?
4 Why is the Government trying to improve the situation?
5 What has caused the obesity epidemic to stabilise in the last decade?
5 Listen to three young people talking about whether the Government should be doing more to promote a healthy lifestyle. Which person do you most agree with?
common (know) that obesity figures in the USA have (drama) over the last 30 years. 75% of American are now overweight, with 34% classed as obese, rmnlng are dangerously overweight. But why is this epidemic czcurñrm Weight gain occurs through a straightforward energy imbalance. t don't use up in energy all the calories that you have then your body stores the rest in your fat cells. There are factors in the USA that have contributed to this imbalance.
F'Stty, people eat differently now. Too much sugar in the diet
—es it harder for the t»dy to burn fat Snack foods high in sugar, salt are widely 3 (advert) and heavily marketed in the
Valding machines selling these snacks are found in schools the country, and calorific fast fwd' is cheap and available. Furthermore, portion sizes are famed tor being
![]() It is
therefore easy to eat too much of the wrong food
It is
therefore easy to eat too much of the wrong food
4 The Government should take a harder line with food manufacturers.
5 An early education in healthy living is the answer. 6 Healthy food is an important issue.
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 6.2: PAGE 139 ![]()
7
![]() Work in pairs or small groups. Discuss
these points in detail and make notes.
Work in pairs or small groups. Discuss
these points in detail and make notes.
1 Do you think your town/country has a problem With an increasingly unhealthy lifestyle?
2 Do you agree or disagree with the opinions in exercise 6?
Give reasons.
3 Decide on three initiatives that your government could implement to tackle the problem.
8 Present the results Of your discussion to the class. Speak for a maximum of two minutes.
Changes in the way of ffe have also contributed greatly.
(commune) are built ways that make it difficult to be physically active. Americans can drive evermfiere, tilt fiM it harder to anything else, sate rwtes for be rmexistent. A sedentary lifestyle has develoçz' at hcgne with the average young American child (watch) b 28 Furs cd TV a week
In the USA, obesity is therefcwe to be a (nation) epidemic, with serious cmsetWEes for individual health and medical expenditure. The meócal care costs of obesiÿ are staggering — around $147 billion — US wvernment has been trying to combat the problem.
The obesity trend to sbwing cbwn owing to government initiatives md public (aware). Over the last ten years (bæity eveis æern to tave levelled But Donna Ryan, president of Ot— to level off at 34% obesity is no great (ahieve). tt's stNl very, very (alarm)
6
I can understand a text about the origin ofdrinks.
|
Work in pairs. Look at the photos ofthe three drinks: tea, coffee and Coca-Cola. Discuss these questions and make notes. 1 Where did each drink originate? 2 What facts do you know about the three drinks? 2 Quickly read the three texts. Were you right about where the drinks came from? Were any Of your ideas from exercise I in the texts? If so, tell the class. 3 Read the texts and choose the correct statement. I All three drinks became popular partly as an alternative to alcohol. 2 All three drinks became popular through clever advertising. 3 All three drinks became popular because of royal connections. EXAM TIP With a multiple-matching task, read the Whole text once and then read the questions. Match any questions that are immediately obvious, and underline the relevant parts Of the text. Then carefully read each section Of the text again and 100k for the answers to the remaining questions. 4 Read the Exam tip. For questions 1—9, choose the correct drink. coffee Coca-Cola tea Which drink: I doesn't have a legend attached to it? wasn't immediately popular in Britain? led to the establishment Of special places Where it was dru nk? was used by a government as a means Of raising money? wasn't endorsed by someone high up in society? is the second most popular drink in the world? was at first unpopular with religious authorities? 8 is the world's second most important commodity? 9 became popular following a big advertising campaign? 5 Write nouns formed from these verbs. The nouns are all in the texts. 1 discover 5 prohibit operate 2 know 6 consume 10 argue 3 approve 7 succeed 11 endorse 4 converse 8 advertise 12 invent |
6 Work in pairs. Answer the questions, giving reasons where appropriate. Which Of the three drinks do you like most/least? Put them in order, and explain your reasons to your partner. NOW put them in order Of unhealthiest first and compare them again. What do you like to drink, and when? What is the healthiest drink you have? Is there any drink you think you have too much Of? HOW much water should we drink and why? Do you drink enough water? 4 If there were one drink you could ban in the world, what would it be? Why? Drink Coffee Coffee was first discovered in Ethiopia several centuries ago. There is a legend surrounding its discovery, and there is probably some truth to the tale. It is said that a goatherd called Kaldi noticed that his goats became very excitable after eating the berries from one particular bush. Kaldi reported this discovery to the Abbat of the local monastery, who made a drink from the berries and found it kept him awake through the long hours of evening prayer. This knowledge of the energising effects of these berries began to spread east towards the Arab world. The Arabs were the first people to cultivate coffee and also to trade it. Coffee quickly became popular with Muslims who were forbidden by their religion to drink alcohol. By the 16th century, coffee had spread to Persia, Egypt and Turkey. All over |
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 6.3: PAGE 139
| •
the Middle East, new public coffee houses sprang up as places of social activity.
By the 17th century, coffee had finally found its way into Europe, where religious leaders initially condemned it as the devil's drink. However, the Pope at that time decided to taste the new beverage himself, and liked it so much that he gave it papal approval. By the mid.
17th century there were coffee houses in all the major cities of Europe. In London alone there were 300. People gathered in them to engage stimulating conversation over a cup of the hot, dark, revitalising drink. Coffee has established itself as one of the most valuable crops in the world, and is the world's second biggest tanmodity, after oil.
The worlds most popular fizzy drink was awented in Georgia,
ISA 1886 as a health drink. Dr John Pemberton, a pharmacist,
-axed the secret formula a big kettle in his backyard. He
...s prompted by a new prohibition law, which forbade the ard consumption of alcohol Pemberton's previous health had contained Wine, so he carne up With a new recipe.
bookkeeper, Frank Robinson, gave the refreshing new drink ts rm-e because, until 1905, it contained extracts of cocaine
•e' as the caffeine-rich cola nut. Mr Robinson also wrote
E."ulty, and is his original lettering that we can still see on today.
1 businessman Asa Candler bought the formula from and very twickly turned it into one of America's most soft drinks. At that time people went to ice cream parlours a drink. Tt-Be were often attached to pharmacies and ap»ular meeting place. Coke was sold as a health &ink,
*Scess was due mot only to its new taste but also to advertising. bought full-page advertisements With girls' inviting you to 'pause and refresh' _ In 1931, Ft-er Christmas was used to sell the product, and the of a round, jolly, white-bearded man dressed in the iconic mage of Father Christmas.
"My hat* off
The story of tea begins in China in 2737bc. According to legend, the emperor Shen Nung was sifting under some trees wtlile his servant boiled water to drink. Some leaves from the Camellia sinensis tree blew into the water, and the emperor tried the resulting beverage, True or not, tea certainty originated in China many, many centuries ago.
It wasn't until the 16th century that tea arrived in Europe, brought by the Portuguese and Dutch. The British were slow to take to the new drink, but that changed in 1662 when King Charles Il married a Portuguese princess, Catherine of Braganca, who was a lover of tea. She made the drink fashionable among the wealthy. Tea was quickly introduced into the cities' coffee houses and British drinking habits were altered forever. The country began to nwort tea for tself and later started growing it
In the 1 7th and 18th centuries, the British Government used the poplÅarity of tea to generate revenue and taxed it so higmy that a huge smuggling operabon sprang up. Soon, more tea was being smuggled Into Britain than inported legauy, so in 1784 the Government finally abolished high tea taxes.
At the Same time there was a great debate about wt'ether tea was good for your health. This argument was finally brought to an end Wtlen religious groups decided that tea was much better for people than alcohol. With lower prices and a health endorsement, there was now nothing to stop everybody from drinking tea.
Meanwhile, Britain had Û1troduced tea to America and the 19th century America introduced the rest of the world to its invention — the teabag. This invention has helped tea to become an important commodity in world trade, and the world's second most widely consumed drink, after water.
|
We use few/ little instead Of a |
the text. Then listen and check.
FIGHT!
tThe / - Food is central to most festivals in Ithe / - Spain. But it isn't always for eating! Once la the year in •a / the small town of La Pobla del Duc, about 100 kilometres from Valencia, up to 90 tonnes of grapes are brought in by lorry from 'the I — surrounding countryside and dumped in Othe / — corner of the market square. What happens next is la / the massive food-fight as the inhabitants Of the town hurt grapes at each other. 'A The fight, which marks the end of e grape harvest and Of Summer, can last all day!
3 Complete these rules with Clan, the or no article and match each answer in exercise 2 with a rule. Check all the rules in the Grammar Builder on page 125.
![]() We often use when we mention
something for the first time, but when we mention it again.
We often use when we mention
something for the first time, but when we mention it again.
![]() We use
We use![]() when
there is only one of something.
when
there is only one of something.
c We use![]() for
continents and most countries.
for
continents and most countries. ![]() We use
We use![]() When
we talk about something in general.
When
we talk about something in general.
![]() We sometimes use to mean per; ror each.
We sometimes use to mean per; ror each.
![]() We use with some general expressions
that refer to the physical environment.
We use with some general expressions
that refer to the physical environment.
g We sometimes use![]() when
we refer to one of several similar things or people and we don't need to be
more definite.
when
we refer to one of several similar things or people and we don't need to be
more definite.
D
GRAMMAR
BUILDER 6.2: PAGE 125 ![]()
4 Look at the use of articles with other nouns in the text in exercise 2. HOW many Other rules can you identify?
'bN — •We don't use an article with 'bf we are talking about means Of transport.
Quantifiers
Examples of quantifiers are: all. both, many, each, every, several, some, few, no, a lot, a little, etc.
Most quantifiers can be followed by of:
![]()
Most
Of the peaches are ripe. A few of them are unripe. However, no and every cannot
be followed by Of; instead, we say none of and every one of:
I've rung all my friends but none of them are at home.
6 •
smallness Of the number or quantity. Compare: There are a few good restaurants in town. Let's eat out.
There ore few good restaurants in town. Let's eat at home.
5 Read the Learn this! and Look out! boxes. Then choose the correct words to complete the sentences.
1 She
was so hungry that she ate each / whole / most of the cake Within a few/ a
little / some minutes. ![]() •There's no / any / none use-by date on
this yoghurt.'
•There's no / any / none use-by date on
this yoghurt.'
'Put it back and choose other l' another /
any one, then.' 3 1 take my tea With a little / much a few milk. ![]() 'Are
you both / each / either going to town?' 'NO, both / either / neither Of us
is.'
'Are
you both / each / either going to town?' 'NO, both / either / neither Of us
is.'
5 He finished off all I each whole of the chips himself! There were any / no / none left for me!
D
GRAMMAR
BUILDER 6.3: PAGE 125 ![]()
6 Number the expressions Of quantity from 1—9: I the least, 9 the most.
a
![]() a few of/ a little of t:] f none
a few of/ a little of t:] f none
b
![]() all
of
all
of![]() g nearly all c hardly any (Lh some of
g nearly all c hardly any (Lh some of
![]() i
i
e
mostof![]()
7
![]() Work in pairs. Find out this
information about your partner. Use expressions from exercise 6 in your
answers.
Work in pairs. Find out this
information about your partner. Use expressions from exercise 6 in your
answers.
![]() how many of his/her friends are on
Facebook
how many of his/her friends are on
Facebook ![]() how many Of his/her friends live within
about one kilometre of him/her
how many Of his/her friends live within
about one kilometre of him/her
3 how many of his/her classmates he/she sees at weekends
4 how much of his/her money he/she spends on snacks and drinks
5 how many of his/her friends he/she would trust With an important secret
6 how much Of his/her time in the evening is spent using a computer
7 how many Of his/her friends share the same taste in music

1 HOW often do you eat out?
2 HOW Often do you get a takeaway or a home delivery?
2 Read the exam task belch". Then listen to two students doing the exam task. Which options do they choose and why?
Your cousin, Who is the same age as you, is coming to spend the weekend at your house. What kind Of meal Will you have With him/her on Saturday evening? Choose one Of the options in the photos. Justify your choice and Say why you rejected the other suggestions.

below to help you.
So, I'd opt for the , mainly because![]()
I think the would be the better/best option because
![]()
So my choice would be the . That's because
![]()
I wouldn't choose the because
![]()
The reason I wouldn't go for the is that „![]()
I wouldn't pick the simply because![]()
4 Complete the useful phrases with the words below.
argued arguing clear feel hand having mind Of opinions sure then time view Expressigg a firm opinion
To my 1 ![]() In
my
In
my ![]()
![]() the opinion that
the opinion that ![]()
![]() fairly
strongly that
fairly
strongly that![]()
It seems to me that
![]()
![]()
Expressing
a tentative opinion
I don't have any Strong s about
I'm not
![]() It
could be
It
could be
There might be a case
for that![]()
Introducing a Counter-argument
On the other![]()
![]()
5 Read the Exam tip below. Listen to a candidate answering the examiner's questions. Tick the phrases in exercise 4 that she uses.
|
EXAM |
TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
It's important that you do not give single-sentence answers to the examiner's questions. You should develop your ideas With examples. supporting statements and, if you like. counter•arguments. |
||||||
6 DO you agree With the candidate? use phrases from exercise
4 in your answer.
7
![]() Work in pairs. Ask and answer the
questions below. Use phrases from exercise 4.
Work in pairs. Ask and answer the
questions below. Use phrases from exercise 4.
I DO you think a vegetarian diet is healthier than a diet that includes meat?
2 DO you think that men should do more cooking at home?
8
![]() Work in pairs. Turn to page 144. Do the
exam task.
Work in pairs. Turn to page 144. Do the
exam task.
Read the model text below. Put these things in the order that 2 Read the Exam tip. Then 100k at the task below and underline they are described. Which thing is not described?

|
EXAM TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
It's very important to read the exam question very carefully two or three times so that you fully understand the task. It's a good idea to underline the verbs that tell you What you have to do, e.g. describe a teacher, recommend a film, present advantages and disadvantages, justify your opinion. etc. |
|||||||
Describe a restaurant which, because Of its location, atmosphere and value for money, you would recommend as an ideal place for teenagers to meet and eat.
3 What are the key elements that must be included in the description in exercise 2? Hint: look at the nouns in the instructions.
Description of a restaurant — by Becky
There's a new Pace in town trying a slightly different approach to sewing and thatS the latest restaurant in Fore Street conveniently Situated fm both the town centre and the unjverStty. The great thjng is that it's very reasonable compared Other r&5Caurants in that serve similar food You can get courses and a drink for under £20 When I Rent in was immediately st.•uck by the decor its modern with lots glass and steel and it feels bright and trendy The atmosphere is very lively - Chere am lots and lots ofyoung and always plenty Of funky background music The staff struck me as young friendly and nelcoming. and styW5h in their T-shirts,
6 • Of
![]() 5
Which Of these plans has the writer followed? Discuss the merits Of all four
plans. (They are all acceptable.)
5
Which Of these plans has the writer followed? Discuss the merits Of all four
plans. (They are all acceptable.)
![]() She
described things as you would encounter them if you visited the restaurant for
a meal (location, first impressions, decor. etc.).
She
described things as you would encounter them if you visited the restaurant for
a meal (location, first impressions, decor. etc.).
![]() She
described what she particularly liked about the restaurant followed by any
minor complaints or reservations.
She
described what she particularly liked about the restaurant followed by any
minor complaints or reservations.
![]() She described different aspects of the
restaurant, one after the Other, with the most important first.
She described different aspects of the
restaurant, one after the Other, with the most important first. ![]() She
described different aspects Of the restaurant, one after the other, with the
most important last.
She
described different aspects Of the restaurant, one after the other, with the
most important last.
But I found most apæ/ing is the way they %rve the It ordered from the you get It yaurseIÐ Ys styíed like an upmar*ct cafeteria The cdd section a wide variety Ofde!Þci0L'5 5aiad5 freshly made and quickb' mp/enj5hed The rniååle Section offers a varied selecnbn Of hot dishes several meat dishes, one or two spicy fish dishes, and vegetarian Options Final'ÿ they have a mouthwateriwg
Of cakes aru desserts. art co die The 5t.ic.ky toffee pudding was out Of and pear Cart had a wondsrfu/ çturnbb' pastry made Mth almonds which vas amazing:'
/ recommend you check th,J5 rvstaurant Out next time you In town, evenjust for coffee and cake'

![]() Use the words below to complete the
chart.
Use the words below to complete the
chart.
![]()
attentive
central conveniently located lively mouth•watering old-fashioned pricey
reasonable relaxing trendy varied welcoming
![]() 10 Of the words in the chart in exercise
1 in the model
10 Of the words in the chart in exercise
1 in the model ![]() page 66.
page 66.
3
the
atmosphere and decor Of the restaurants in the ![]() on
page 66 using words from the chart in exercise 1.
on
page 66 using words from the chart in exercise 1.
|
|
TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
zescribing nouns, try to avoid uninteresting adjectives. Think about the particular you are trying to describe and think Of —8ting Synonyms, e.g•: — seeable. extensive, large, broad. — *asant, enjoyable. friendly, sympathetic. pretty, delicious. |
||||||||
4 Read the Exam tip. Then replace the underlined adjectives in the text below With more interesting alternatives. There are many possible answers. Use a dictionary to help you.
The
restaurant is in a lovely square near the river. It has two ![]() dining
areas, one downstairs and One on the first floor, from where there are great
views of the city. It has a good atmosphere and the staff are nice. Most
importantly, the food is good. I always have a great time When I
go there.
dining
areas, one downstairs and One on the first floor, from where there are great
views of the city. It has a good atmosphere and the staff are nice. Most
importantly, the food is good. I always have a great time When I
go there.
5 Find three Of the phrases below in the model text on page 66. Check that you understand all Of the phrases.
Recommendin
![]()
![]()
![]()
|
CHECK YOUR WORK Have you: read the instructions carefully and asked for? included some interesting or more to make your writing more precise? included some words and phrases and 5? written 200-250 words? your grammar and spelling |
|
included unusual from |
exercises |
adjectives |
|
|
everything 1 |
|
1 Complete the sentences with suitable verbs in the past tense. 5 Write adjectives for describing food which mean the opposite
iTunes. 1 mouthwatering 4 tasteless 2
11
on to my account this morning, but there were 4
We s_ the film from a website to the TV so everyone
2 It is believed that birds evolved from dinosaurs. |
2
Complete
the sentences with the correct passive form of the verbs below. ![]()
build damage repair steal tell off
![]() 1
Yesterday. the children for being late.
1
Yesterday. the children for being late.
2 The new stadium over the next three years.
3
Oh
no! I think my password![]()
4 I haven't got my phone; it at the moment.
5 We saw houses that _ by the earthquake.
![]() Mark:
Mark:
3 Rewrite the sentences in the passive.
1 They will send us invitations to the wedding soon.
2 They
didn't teach us Latin at school. ![]()
3 They may have stolen my credit card.
4 They had warned me about the dangers.
5 They can't offer him the job because he's too young.
Mark:
![]()
Complete the dialogue With the words below.
![]() imagine
likely say seem though
imagine
likely say seem though
Boy DO you fancy going to this holiday camp? ![]() Girl
There t
Girl
There t ![]() to be a lot of young children. What's
to be a lot of young children. What's ![]() the
age range?
the
age range?
![]() Boy It's 10—18. But looking at them, I'd most
Of these kids are under 14.
Boy It's 10—18. But looking at them, I'd most
Of these kids are under 14.
![]() This
other camp looks as it's aimed at older
This
other camp looks as it's aimed at older
therve got a
![]()
![]() Mark:
Mark:
| Language Review![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Birds
Birds![]() from dinosaurs.
from dinosaurs.
![]() 3 It was thought that tomatoes were
poisonous.
3 It was thought that tomatoes were
poisonous.
Tomatoes![]() poisonous.
poisonous.
4 It is known that there are many Other solar systems in our galaxy.
There ![]() many Other solar
systems in our galaxy.
many Other solar
systems in our galaxy.
5
It
was believed that snake oil cured various diseases. ![]()
Snake Oil![]() various diseases.
various diseases.
Mark: — 15 ![]()
7
![]() Choose the best options (a—c) to complete the text.
Choose the best options (a—c) to complete the text.
Although 'Arriba!' calls itself a Mexican restaurant, 1 its dishes are authentic; are American variations
![]() on Mexican food. Having said that,
nearly the food we tried was tasty and fresh. The service was fast, but that
was • surprise: we arrived early and had
on Mexican food. Having said that,
nearly the food we tried was tasty and fresh. The service was fast, but that
was • surprise: we arrived early and had ![]()
![]() restaurant
to ourselves!
restaurant
to ourselves!
a many c very
few of ![]() a much b most C many Of
a much b most C many Of ![]() a
much of b most Of c all
a
much of b most Of c all ![]() a
none b no c a little
a
none b no c a little
5 a the Whole b all Of c all
![]() Mark.
Mark.
8
Write
the missing words to complete the comments. 'To rnv ' , French food is more
interesting than Italian food. At the same , Italian food is verytasty.' ![]() •There
might be a for arguing that the British prefer ethnic food. But again, they
love their fish and
•There
might be a for arguing that the British prefer ethnic food. But again, they
love their fish and
![]()
|
chips!' |
|
|
'I'm Ofthe s |
that Scandinavian food is rather bland.' |

1-6 Skills Round-up
Work in pairs. Discuss the best place to go on a first date. Choose from the venues below or suggest your own idea.
an art gallery a café a cinema a museum a shopping centre a restaurant the beach
2 Work in pairs. Describe the photo. Then ask and answer the questions below.
1 Do you think the couple are enjoying their food? Why do you say so?
2 What are the advantages and disadvantages of eating outside, in your Opinion?
3 ![]() Tell
me about a recent occasion When you had food
Tell
me about a recent occasion When you had food ![]() Outside.
Outside.
3 Read the texts. Which restaurant would you (a) most like to, and (b) least like to eat in? Give reasons.
Match the restaurants in the text (1—5) with five Of the sentences below (A—B. There is one extra sentence.
A The service here is particularly fast.
B The food at this restaurant is European.
C You can get large portions Off00d here without spending too much money.
D Most of the dishes are very tasty. but rather expensive.
E None ofthe dishes here contain meat or fish.
F Some of the food on offer here is extremely spicy.
5 2.27 Listen. Which restaurant from the text in exercise 3 are Daisy and Stefan at? How do you know?
6 2.27 Listen again. Are these sentences true or false (B?
1 Daisy and Stefan are eating out because there wasn't much to eat at the squat.
2 Daisy feels the other people at the squat need to respect her opinions more.
3 Spikey is not particularly easy-going. according to Daisy.
4 Stefan has visited Daisy at the squat only once before.
5 Daisy thinks that seeing Stefan is making Spikey jealous.
6 Spikey and the group are planning to put their propaganda on a supermarket website.
7 Imagine you have had the worst meal of your life at a
restaurant. Write a formal letter Of complaint to the mana". Include the following information:
When you visited the restaurant.
• what you ordered and what was wrong with it.
What the service was like.
• What you expect the manager to do about the situation.
|
q"ide eatinq out I
CHEZ DIDIER; As the name Suggests. tnis restaurant serves Frenc:-. tc»od in
cos'. informal surroundings. It specialises in fish and seafood dishes. and
claims to use only the freshest ingredients bought each morning from the
nearby London food markets. The dishes can be a little he-a". With
plenty Of rich. creamy sauces, so it you were looking for a light lunch. this
might not be the best placa But 2 THE RICE BOX: This canteen•styte restaurant otters simple. affordable fr:uxt in bright clean surroundings Meals are ordered at the counter. then brought to the table — usually within five minutes' More a place for quick retuelling than a leisurely feast. making it an ideal choice if time is limited — for example. The number of regular Chinese customer's the facd is very authentic It' certainly very tasty! 3 THE STEAKHOUSE: Although the menu includes one or two vegetarian dishes, this is a place for serious meat-eaters, with eight different twes of steak on Offer as well as ribs and burgers The American-style dishes are large. tasty ard not wet-priced. The has an American feel too. |
Witn sports memorab•lla and pnotCS Of Hollywood service is friendly and efficient. finish Off your watering desserts 4 KO SAMUI: If you love the exotic taste Of Thai definitely the plate to come, It is believed ta the country. The range Of dishes on the you are notan eXWt on oriental cuisine. When ate here. we ordered about dishes the dishes were very tastV. although a [file on problem with chilli. some of dishes should are extremely hot! 5 CAFÉ SPICE: This is a vegetarian restaurant ct southern India. Not only is the and attractive —the set meal for four people •s you areni a fan of suzer•spi7/ Indian food — quite mid Some English disfTes. like egg and Our humble opinion. you'd be mad to Order them! |
Skills Round-up 1—6 69
6 Get Ready for your Exam
1
Then compare your ideas with the class.
2 Do the exam task.
|
READING exam task |
Read the text and answer the questions.
Eating disorders are so common in many developed countries that two out Of every hundred teenagers Will be struggling with one of them in any given year. Anorexia and bulimia are the most recognised disorders. However, there is a newer disorder which is becoming more common — orthorexia. Orthorexia nervosa is an unhealthy Obsession with healthy eating. Unlike its relation, anorexia. sufferers are primarily concerned with quality, rather than quantity. It's not about feeling thin, but about feeling 'pure' and healthy. Healthy eating is, Of course, seen as a good thing, but when taken to extremes, malnutrition, severe weight loss and even death can occur as a result.
Dr Steven 3ratman MD coined the phrase from the Greek 'ortho' meaning •accurate' and orexis, which means •appetite'. He feels that the medical profession remains largely unaware Of this very modern condition. He himself realised that he was a sufferer after a year Of his own extreme dieting. He began to view other people as greedy and animalistic, eating sugar-laden, fatty foods With no restraint or regard for their health. He says, 'Because it requires considerable willpowerto adopt a diet that differs radically from the food habits Of childhood and the surrounding culture, few accomplish the change gracefully. Most must resort to an iron selfdiscipline bolstered by a hefty dose Of superiority Over those who eat junk food.' TWO Of the questions asked on his website are: 'Does your diet socially isolate you?' and •DO you care more about the virtue Ofwhat you eat than the pleasure you receive from eating it?' If the answer to both Of these is yes, then Dr Bratman feels you may have a problem.
Simon Wheeler. a self-confessed mild orthorexic, talks about what it is like to have this particular form of illness. He says, 'I started out small, and then got more and more carried away. First I gave up caffeine, when I read that the plant world uses it as an insecticide. Then I gave up dairy products. After that I stopped eating sugar. And so On. Exaggeration turning into obsession, this is What you need to 100k out for.' And how has it affected his life? Well, none Of my friends plan all their meals in advance, and keep a food diary With the calorific breakdovffl of each meal in it. None of them look at the ingredients Of every single packet in the supermarket,
Get Ready for your Exam 6
checking for additives, sugar, saturated fats, colourings, and sodium. Only I go to the local markets to buy fresh, local produce in paper bags, and organic wherever possible. And Only I suffer from extreme guilt if So much as consume a single gram Of chocolate. It's no wonder that they don't invite me out so much any more. They find it really stressful, but I can't help it.'
What is the difference between anorexia and orthorexia?
According to Dr Bratman, hcrw does radically changing your diet alter your Opinion Of Other people? How can you tell the difference between orthorexia and a normal desire to have a healthy diet?
4 What was Simon Wheeler's first Step on the road to orthorexia?
5 In what way has Simon Wheeler's social life suffered as a result Of his Orthorexia?
3 food which include a lot Of:
a fat d vitamins b salt e fibre c sugar f protein
DO the exam task.
SPEAKING exam task
Describe the photo and answer the questions.
How healthy do you think your diet is? Give examples. HOW could teenagers be encouraged to eat healthier foods?
Why do you think teenage girls are particularly at risk from eating disorders?
![]() • •
headline language • verbs
• •
headline language • verbs
Grammar • speech • • indefinite
Speaking • describinga photo
Writing •
VOCABULARY AND LISTENING
Describe the photos. What is happening?
2 Can you explain the difference between:
I a news programme, a news story, a news flash and rolling news?
2 a tabloid newspaper and a broadsheet newspaper?
dictionary to help you.
breaking news correspondents live broadcasts
Communication
![]()
![]()
![]() I
can talk about the news.
I
can talk about the news.
6
news flashes news programmes rolling news channels satellite phone
TV news Most people in the UK follow the news on television. IV stations broadcast regular t as well as quick to cover important broadcast news 24 hours a day. With the advent Of the 'digital age', news can make 6 from anywhere in the world using just a laptop and a 7 articles broadsheet columns editorials front-page headlines human-interest tabloids
|
on topics like economics and politics; and popular |
4 |
2.28 Listen to four teenagers talking about the news. |
|
, that have some news but are more interested in |
|
Which person is (a) most interested (b) least interested in the |
|
gossip and entertainment and are full Of 11 stories. |
|
news? |
|
All newspapers have , Which give opinions and reflect the paper's political point of view, and regular |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
readers with exciting or important stories and |
|
teenagers pay no attention at all to the news. |
|
snappy
|
|
|
|
censorship citizen journalism eyewitness accounts |
|
|
|
news blogs online editions the press |
|
4 Becky needs to keep up With the news daily. |
|
Online news With the spread of fast broadband, many |
|
6 reads the headlines in the daily |
people now prefer to subscribe to of newspapers Sophie paper.
![]() orto
download the whole newspaper onto an ebook reader. 6Work
in small groups. Answer the questions.
orto
download the whole newspaper onto an ebook reader. 6Work
in small groups. Answer the questions.
![]() Another
recent development iswhen ordinary 1 How much attention do you pay to the news?
Why? people report and spread news. They do this by means Of
Another
recent development iswhen ordinary 1 How much attention do you pay to the news?
Why? people report and spread news. They do this by means Of
2 How do you find out about the news?
(web pages updated regularly With news), Twitter. 3 Put these news media in the order Of most importance for and Of important events posted online, Often With you personally and explain your reasons.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() photos
and videos. Citizen journalists can play an important a newspapers b radio c TV
d the Internet e Twitter in countries where there is strict4 Do you prefer
•hard' news or •soft' news? Why?
photos
and videos. Citizen journalists can play an important a newspapers b radio c TV
d the Internet e Twitter in countries where there is strict4 Do you prefer
•hard' news or •soft' news? Why?
VOCABULARY BUILDER 7.1: PAGE 140D VOCABULARY BUILDER 7.2: PAGE 140
7
I can report what people have said and asked.
1 Complete the reported speech. Identify the tense change in each example (if there is one).
1 'My brother's a news correspondent.'
She told me that her brother wat' a news correspondent. present simple past simple
2 'He works for a newspaper in our home town.' She says that he for a newspaper in their home town.
3 "He's going to Afghanistan tomorrow to report on the war.' She said he to Afghanistan the next day to report on the war.
4 'He'd better call me next week.'
She said that he call her next week.
5 'He'll be there for three months.'
She's told me that he there for three months.
2 Read the Learn this! box below and find examples in exercise 1 of the two rules.
Tense changes in reported speech We don't change the tense when:
1 the reporting verb is present or present perfect.
2 we are reporting a past perfectverb, would, could, should or had better.
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 7.1: PAGE 126
3 Study the examples in exercise I. What happens to
(a) personal and possessive pronouns? (b) time expressions?
LOOK OUT!
Reported speech With say and tell
1 Ifwe mention who is spoken to. we usually use tell. We don't use to before the person spoken to.
2 We use tell With the infinitive to report instructions.
3 After Say, we don't have to mention who is spoken to.
4 After say, if we do mention who is spoken to, we put to before the person.
4 Read the Look Out! box. Make up a Simple example to illustrate each point.
5 Change the direct speech to reported speech. Use the reporting verb in brackets. (The people are/were speaking to you.)
I Linda: 'I haven't seen the news.' (says)
![]() Kate: •I'll buy a tabloid tomorrow.'
(told)
Kate: •I'll buy a tabloid tomorrow.'
(told)
3 'I had never visited a news website before.' (said)
4 Ed: •you'd better 100k smart for your interview.' (told)
![]() Naomi: •I'm going to buy a broadsheet.'
(says)
Naomi: •I'm going to buy a broadsheet.'
(says)
6
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Marcus: 'I'll be flying to Paris this time tomorrow.'
(told)
Marcus: 'I'll be flying to Paris this time tomorrow.'
(told)
72 •
6 Read a report Of a conversation. Match each question With a sentence in the report.
Jake asked me Whether I had bought a newspaper that day. I said I had. Then he asked me which one I'd bought. I told him I'd bought The Daily Mail. He asked me if he could borrow it. I told him he could. He asked me when I wanted it back. I said I didn't.
'When do you want it back?' 'l don't.' 2 "Which one did you buy?' 'The Daily Mail.'
3 'Can I borrow it?' Yes. you can.'
4 'Have you bought a newspaper today?' 'Yes, I have.'
Answer the questions about reported questions. I Are the tense changes the same as in reported statements?
2 Is the word order in reported questions different from the word order in direct questions?
3 Which word do we add when we report yes/no question?
(two answers)
4 What are the rules for reporting short answers?
8 Report the conversation using past simple reporting verbs. Ben asked pat if she had seen his MP3 pat said she hadn't.
Ben Have you seen my MP3 player?
No, I haven't. Why are you asking me?
Ben Did you use it yesterday?
Yes, I did, but I put it back in your room.
Ben Well, it isn't there anymore.
Pat Have you looked properly?
Ben Yes! Will you help me look for it?
Pat I can't right now. I've got to go out.
Ben Where are you going?
Pat Why do you want to know? Ben I'm just curious. Is it a secret?
pat NO, it isn't a secret. But I'd rather not tell you.
9 Complete the second sentence so that it has a similar meaning to the first sentence. Use the words given.
![]() 'Can I borrow your scarf?' Rob asked me.
(in
'Can I borrow your scarf?' Rob asked me.
(in
![]() Rob
asked me if he could borrow zarf
Rob
asked me if he could borrow zarf
![]() 'I'll phone you tonight,' Ann said to
Fred. (that night) b Ann told
'I'll phone you tonight,' Ann said to
Fred. (that night) b Ann told ![]()
![]() a 'Has Sue ever been skiing?' 10 asked
me. (whether)
a 'Has Sue ever been skiing?' 10 asked
me. (whether) ![]() 10 asked me
10 asked me![]() skiing. 4 a 'Have you had lunch yet?' Dan asked Will. (had) b Dan asked Will
skiing. 4 a 'Have you had lunch yet?' Dan asked Will. (had) b Dan asked Will ![]() yet.
yet.
![]() a 'I want to know What you're doing,'
Ditold Ed. (asked) was doing.
a 'I want to know What you're doing,'
Ditold Ed. (asked) was doing.
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 7.2: PAGE 127
I can understand and react to a text about Twitter.
TwitterTwitter can be as part social networking site, part 'micro-blogging' site.
It allows users to say what they are doing, or what they are seeing or hearing, by posting messages on the Twitter website that their friends or 'followers' can see. The messages, called •tweets', cannot exceed 140 characters 2 which is the defining characteristic Of the service. Tweets are displayed on the user's profile page and on the home page Of each Of his or her followers. At first most people used Twitter to Stay touch With their friends and family; like other social networking sites, it was just broadcasting
![]() where
you are, what you are doing, what you are feeling and thinking. But it has s developed
into a place where people share information, opinions and advice, and it
resembles a blog. 7 purpose it serves, it is incredibly popular and used by a
huge number Of influential people such as politicians, journalists and
celebrities.
where
you are, what you are doing, what you are feeling and thinking. But it has s developed
into a place where people share information, opinions and advice, and it
resembles a blog. 7 purpose it serves, it is incredibly popular and used by a
huge number Of influential people such as politicians, journalists and
celebrities.
Work in pairs. What do you know about Twitter?
4 In order to gauge the truth Of a Story on Twitter, Maggie a tweets the same message to lots Of Other people. Read the text. Choose the correct options b checks the writer's background.
c asks the writer if he Or she is a journalist.
![]() 1 a
expressed b reported c described d explained 5 One disadvantage of Twitter is
that a long b in length c longer d in long a it can't be used by serious
journalists.
1 a
expressed b reported c described d explained 5 One disadvantage of Twitter is
that a long b in length c longer d in long a it can't be used by serious
journalists.
a on b to c at d in b important events can't be described in few words.
![]() 4 a
a way to b a means Of c in order to d a process of c anybody can use it so
there are too many different a since b formerly c still d soon opinions.
4 a
a way to b a means Of c in order to d a process of c anybody can use it so
there are too many different a since b formerly c still d soon opinions.
![]()
![]() 6 a
in respect b as regards C in that d for that of respect matter 6Complete
the collocations from the interview. 7 a However b What c Whatever d Which Context
events impact misinformation news picture 3 Listen and check your
ideas from exercise I.
6 a
in respect b as regards C in that d for that of respect matter 6Complete
the collocations from the interview. 7 a However b What c Whatever d Which Context
events impact misinformation news picture 3 Listen and check your
ideas from exercise I.
![]()
![]() 1 build up a4 democratise the
1 build up a4 democratise the
4
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 02.30 Listen to an interview with a journalist who 2 have
an (on) 5 spread uses Twitter. Does she think that the advantages Of Twitter 3
give the6 analyse outweigh the disadvantages?
02.30 Listen to an interview with a journalist who 2 have
an (on) 5 spread uses Twitter. Does she think that the advantages Of Twitter 3
give the6 analyse outweigh the disadvantages?
7Work in pairs.
5 Listen again and choose the correct answers. Student A: summarise two advantages of Twitter. 1 first thing in the morning, Maggie Student B: summarise two disadvantages. a adds breaking news stories to Twitter.
b looks for new stories on Twitter. 8Work in pairs. Ask and answer the questions.
c contacts about 1,000 Other journalists via Twitter. DO you have a Twitter account? If so, What do you use it
|
a to spread news and to ask about news. |
|
2 If not, would you like one? Why, and What would you use |
|
b just to find interesting news stories. |
|
it for?/Why not? |
|
c just to request information from Other journalists. |
|
3 DO you or does anyone you know have (a) a blog? (b) a |
|
3 Twitter has helped Maggie |
|
Facebook (or other social networking) account? What do |
|
a to use lots Of very short words. b to include lots of important information in every tweet. |
|
you/they use if for? |
|
c to write more economically and accurately. |
9 |
Visit an English-language news website (e.g. BBC |
2 Maggie uses Twitter
News, CNN, Yahoo News). Choose an interesting news Story and write a summary of it in no more than 150 words.
7 73
I can understand a text about the postal service.
I Lookat the pictures. Ask and answer the questions.
I What is happening in the painting? HOW do you think the girls are feeling?
2 What are the people doing in the photo?
2 Read the text. Which sentence (a—d) best
Summarises the main idea?
a A postman's job has changed greatly over the past 200
b The postal service was revolutionised in the mid• nineteenth century and has brought many benefits to the average British citizen. c Roland Hill persuaded the Government to allow him to change the Royal Mail.
d The average working person in Britain could no longer afford to pay to receive a letter so stamps were invented.
YOU'VE GOT MAIL!
With instant messaging and social networking, sending a message by post may not be something that you would automatically think Of. However, until very recently the post was the main means of communication and many people today still look forward to the postman's arrival every morning.
By contrast, in the 1800s the knock of the postman was something to dread. At that time. the person receiving a letter had to pay for it. The cost was dependent upon the distance the letter had travelled and the number of pages it consisted Of. Most ordinary people couldn't afford to receive a letter. So how had this situation come about?
In 1516 King Henry VIII the Royal Mail for royal communications and reasons of national security. From there a demand arose for a public postal service due to an increase in literacy amongst the general population and for business requirements. By the mid-nineteenth century the British had to a very complex, expensive postal service.
Roland Hill, a young enthusiastic Victorian man, wanted to reform it. His intention was to make postage accessible to all citizens by introducing much cheaper
7 •
|
charges. Hill's new |
|
3 |
Mark the sentences true (T) or false |
|
idea was to charge |
|
|
In the nineteenth century, the postal service was |
|
a universal single |
|
|
essentially for the use Of royalty and government. |
|
rate Of postage. This would reduce at one |
|
|
2 At the beginning of the 1800s, the post office had a simple method Of calculating the cost of a letter. |
|
stroke the complicated |
|
|
3 Roland Hill didn't find it easy to convince the government |
|
calculations necessary |
|
|
and post office of the value of his ideas. |
|
to organise payment of a letter, and make the |
|
|
4 The British public had no problem at all in adapting to |
|
post office efficient. He |
|
|
Roland Hill's new ideas. |
|
argued that his reforms |
|
|
Hill's argument that cheaper postage would improve |
|
would result in more |
|
|
people's lives was proved to be true. |
|
|
|
|
With the new postal service the British public quickly |
|
people sending more letters, which in turn |
tr• aæoncour |
|
found more reasons for writing letters. |
|
would lead to wider social |
|
4 |
Match the highlighted phrasal verbs in the text |
|
benefits and increased |
|
|
with the definitions. |
|
profits. Hill bombarded the |
|
|
I continue for a very long time 2 establish |
|
Government with his ideas. At first they were not well |
|
3 think Of an idea for |
|
|
received by anyone in a position Of power, but eventually |
|
4 make a decision On something |
|
|
the Government agreed to set up an enquiry. During this enquiry ministers from all over the country reported what their constituents had told them. They said that ordinary people felt terribly burdened by high postage costs and told stories of poor people having to sell furniture to receive a letter from their loved ones. Ministers reported that post office fees had placed an intolerable burden on the working classes. People had to go away to find Work, but could not afford to stay in touch with their families. The debate for months but finally Hill was given two years to reform the British Post Office. First, he needed to — a way Of showing that the letter was pre-paid. He experimented with various kinds of envelopes, a type of •stamp'. But what could he put on it that was instantly recognisable and difficult to forge? The answer was staring out at him from the coins in his hand - the head of the Queen, Victoria. On 1 May 1840, the world's first postage stamp was put on sale. At first no one wanted to lick a stamp - and the idea of licking the Queen seemed quite impolite! — but the idea eventually To this day British stamps are the only ones that do not bear the name of the country. Shortly after, another invention became necessary, as people now needed a letterbox at home. At first, many people objected to having a hole cut in their front door, but again this new idea soon became commonplace. Overnight the post office was revolutionised. People started writing more and more letters to each other, and the postman was no longer feared, but became a local hero. For the first time, Britain had a fair, cheap and efficient postal service and this had a profound impact on Ordinary people's lives. Businesses flourished. Children wrote to parents. families to relatives across the world. lovers to each Other. Valentine, Christmas and birthday cards were invented. Nowadays, we write far fewer letters than we used to, but the post office is still very busy — |
|
5 become popular |
|
6 endure or tolerate
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 7.3: PAGE 140
5 Explain the meaning Of the underlined phrases in these sentences from the text.
in the 1800s the knock Otthe postman was something
2 Hill
3 post office fees had placed an intolerable burden on the working classes.
4 The debate draggeWon for months.
. again this new idea soon becameçommonplaçe.
6 Britain had a fair, cheap and efficient postal service and this had a profound imaact on ordinary people's lives.
6 Find three indefinite pronouns in the text, one beginning With any", one With no- and one With Some•.
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 7.3: PAGE 127
7 Work in pairs. Ask and answer the questions.
1 DO you like writing or receiving letters? If so. how often? And who to/from?
2 What was the last thing that you sent or received in the post?
What is the most common way that you and your friends communicate? HOW Often?
In what circumstances would you write a letter rather than use some other form Of communication?
delivering goods ordered online!
7
Listen to the interview. Who does the politician Read the sentences. Then complete the Learn this! box With
blame for the state of the economy? What specific measures does she promise to carry out?
2 Complete what the minister said in her interview. Use the reporting verbs below. Listen again and check.
agreed announced denied reminded warned
1 The
minister![]() that the economy had not been performing
well.
that the economy had not been performing
well.
2 She that it was the Government's fault.
3 She the interviewer that the previous government left the nation's finances in a mess.
4 She![]() that
increasing public spending would be very dangerous.
that
increasing public spending would be very dangerous.
5 She that the Government was going to Cut taxes and create jobs.
|
|
Reporting verbs We can use Other verbs instead Of say and tell when we report statements, e.g. explain, deny, insist, agree, persuade, convince. repeat, beg, assure, etc. stole a TV,' he said. also stole a DVD player.' He admitted that he had stolen a TV. He added that he had also stolen a DVD player. He convinced me that he was telling the truth. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 Read the Learn this! box. Then report the sentences using One of the verbs in brackets. More than one answer is possible.
![]() Matt said to Sue, 'The film starts in
ten minutes.'
Matt said to Sue, 'The film starts in
ten minutes.'
(remind / admit warn) ![]() Jessica
said, 'I've already done my homework.' (point out / announce / warn)
Jessica
said, 'I've already done my homework.' (point out / announce / warn)
![]() Ross
said, 'I was tired because hadn't slept well.' (promise I explain I assure)
Ross
said, 'I was tired because hadn't slept well.' (promise I explain I assure) ![]() lim
said, 'I wouldn't have crashed ifthere hadn't been ice On the road.' (argue I
explain I persuade)
lim
said, 'I wouldn't have crashed ifthere hadn't been ice On the road.' (argue I
explain I persuade) ![]() Mandy said, 'Sally lost my gloves!'
(deny / complain / announce)
Mandy said, 'Sally lost my gloves!'
(deny / complain / announce)
![]() Beth said to Emma, 'You're wearing my
scarf!' (claim I insist I assure)
Beth said to Emma, 'You're wearing my
scarf!' (claim I insist I assure)
![]() Listen and match the speakers (1—6)
with the reported speech (a—n.
Listen and match the speakers (1—6)
with the reported speech (a—n.
a She admitted that she'd stayed out late.
b She begged her parents to allow her to Stay out late.
c
![]() She assured her parents that she wouldn't stay out late.
She assured her parents that she wouldn't stay out late. ![]() She
insisted that she was staving out late. e She repeated that she would be
staying out late. f She denied that she'd got home late.
She
insisted that she was staving out late. e She repeated that she would be
staying out late. f She denied that she'd got home late.
![]()
76 •
the base form of the reporting verbs in blue.
I Freddie denied hitting the police officer.
2 Martha insisted on going out without a coat.
3 The minister refused to give an interview.
4 teacher suggested that I should study law at university.
5 Jonty reminded me to post the letter.
6 Dad congratulated me on passing my driving test. 7 She insisted that he wear a tie.
|
|
Other reporting structures We can use Other structures When we report Offers, promises, requests, commands, suggestions, etc. verb + infinitive With to agree, offer, promise, , threaten verb + Object + infinitive With to advise, ask, beg, encourage, forbid, instruct, invite, order, , tell, warn verb gerund admit, , recommend, suggest 4 verb * preposition gerund apologise for, boast Of, confess to, verb * object preposition + gerund accuse shot, s , warn sb against 6 verb
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 7.4: PAGE 127 ![]()
6 Complete the sentences with a preposition if necessary and the correct form Of the verbs below.
buy copy go ground lose show sit Stay
Out ![]() My parents threatened me for the
weekend if I didn't keep my bedroom tidy.
My parents threatened me for the
weekend if I didn't keep my bedroom tidy.
![]() Our
teacher warned us essays from the Internet.
Our
teacher warned us essays from the Internet.
![]() My
dad forbade me after midnight.
My
dad forbade me after midnight.
4 Tim insisted me lunch, even though I tried to pay.
![]() The
police Officer requested that I her my ID.
The
police Officer requested that I her my ID.
6 Sally ordered her dog ![]()
![]() recommend
to see the new Johnny Depp film. 8 Jo apologised her temper.
recommend
to see the new Johnny Depp film. 8 Jo apologised her temper.
7
![]() Work in pairs. Using reported speech,
tell each other about something:
Work in pairs. Using reported speech,
tell each other about something:
1 that your parents ask you do.
2 that your parents forbid you to do.
3 that you were accused of doing.
4 that you promised to do.
alcohol and drugs being untidy clothes computers and TV homework and schoolwork parents treating siblings differently 4 Read the Learn this! box and make sentences using must/ parents treating teenagers like young children might/can 't (have) and the Sentences in exercise 3. Add a staying Out late reason for your Opinion. wasting money The boy mutt have Just arrived home
because the front door is open and he's still unring his 5 Complete the useful phrases with the words below. explain kind know mean moment question say see something thought what words Asking for clarification I'm not sure what you Could you what you mean, please? Paraphrasing I'm not sure how to ' it in English.
Let
me think about that for a • I
haven't given that a great deal Of
|
I The bov has just arrived home.
2 It's late at night.
3 He stayed out too late.
![]() He's been to a party.
He's been to a party.
5 He told his mum he'd be home earlier.
![]() He's feeling Sorry for his
behaviour.
He's feeling Sorry for his
behaviour.
7 His mum is telling him off.
8 She's been staying up to wait for him to get home.
9 She's happy with his behaviour.
10 She expected him to arrive home late.
6
 Read the Exam tip. Listen to a
candidate the examiner's second question. Tick the phrases in exercise 5 that
he uses.
Read the Exam tip. Listen to a
candidate the examiner's second question. Tick the phrases in exercise 5 that
he uses.
7
![]() Work in pairs. What's your opinion? DO you think young people should be
allowed to Stay out late? Why?{Why not?
Work in pairs. What's your opinion? DO you think young people should be
allowed to Stay out late? Why?{Why not?
8
![]() Work in pairs. Do the picture description exam task on page 144.
Work in pairs. Do the picture description exam task on page 144.
7 77
I can write a film review.
Work in pairs. Ask and answer.
1 Do you enjoy going to the cinema? Why?/Why not? O I recently Saw the comedy Bruce Almighty. Made
2 When was the last time you went to the cinema? What in 2003, it was directed by Tom Shadyac and Stars did you see? Jim Carrey, one of my favourite actors. However,
3 Think of your favourite film. it received mixed reviews from the critics, and my
• What kind Of film is it? friends weren't impressed by it, so I wasn't sure if
• Who stars in it? enjoy it. Despite my initial doubts, however, I have to
• Why do you like it? sav I was pleasantly surprised.
2 What kinds of information would you expect to find in a film O The protagonist is Bruce Nolan, a TV reporter who review? covers local interest stories. My friends maintain that
Carrey gives an unconvincing performance in the 3 Read the Exam tip and questions below. Identify the leading role, but I couldn't disagree more. He comes particular angle or point Of view that you need to adopt in across to me as very well-rounded and extremely
|
each question. |
funny. The Other main character is God. played by Morgan Freeman. Freeman is a fine actor and the |
|
EXAM |
TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In the exam you will not be asked simply to write a straightforward review Of a film, book, magazine, etc. that you liked or disliked. You will have to approach the task from the particular angle or point Of view specified in the task. 1 Write a review of a film that got rave reviews but which you were disappointed by. 2 Write a review of a film that you didn't think you would like, but Which you really enjoyed. 3 Write a review of a film that you really liked but which your friends didn't enjoy. |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
comedy; it's also thought•provoking. And in spite Of |
|
|
Read the introduction to the film review. Which of the |
|
the views Of my friends and the critics, I thoroughly |
|
|
questions in exercise 3 is it answering? |
|
enjoyed the film and would recommend anyone to See it. |
|
5 |
Read the whole review. I Underline phrases and sentences in the review where the writer reports Other people's opinions of the film. 2 Find where the writer contrasts these opinions With his/ her own views. |
|
|
|
6 |
In Which paragraph does the writer mainly talk about (a) the characters? (b) the plot? |
|
|
|
7 |
Which tense does the writer use in the review to describe the characters and What happens in the story? |
|
|
|
8 |
Find eight Of the following adjectives in the review. Adjectives to describe a plot or Story entertaining exhilaG3ting far-fetched fast-moving hilarious gripping intricate light-hearted moving predictable |
|
|
|
|
scary serious thought-provoking upsetting |
9 |
Think Of films and film characters you know that could be |
|
|
Adiectives to describe characters clichéd complex convincing familiar fascinating two-dimensional |
|
described using adjectives from exercise 8. |
|
|
uninteresting unconvincing rounded |
10 |
|
perfect complement to Carrey.
![]() The
story is set in a TV station and begins when Bruce complains to God that He is
making his life miserable. In response. God gives Bruce all His powers for a
week and tells him to do a better job! There are some hilarious moments and
very witty lines. Some critics were ofthe opinion that the story was
far-fetched and silly, but I think they are missing the point. By becoming God.
Nolan learns the importance Of helping Other people. That's the serious message
of this entertaining comedy. O To sum up, Bruce Almighty isn't just a
light-hearted
The
story is set in a TV station and begins when Bruce complains to God that He is
making his life miserable. In response. God gives Bruce all His powers for a
week and tells him to do a better job! There are some hilarious moments and
very witty lines. Some critics were ofthe opinion that the story was
far-fetched and silly, but I think they are missing the point. By becoming God.
Nolan learns the importance Of helping Other people. That's the serious message
of this entertaining comedy. O To sum up, Bruce Almighty isn't just a
light-hearted
7 •
wasn't as good as I had anticipated.
3
Although
I didn't expect to enjoy it, Iwas ![]() surprised
by both the story and the quality Of the acting.
surprised
by both the story and the quality Of the acting.
4 In spite Of the glowing , I was very disappointed with many aspects of the film.
![]() Despite what others said, the film
wasn't as bad as had been
Despite what others said, the film
wasn't as bad as had been![]()
6 Notwithstanding my low was thoroughly entertained.
7 Although I had to enjoy it, I was bored from start to finish.
8 Even though my friends about the film, I found it dull and predictable.
7 Make notes for a concluding paragraph. Summarise whatyou think Of the film, contrasting Other people's opinions with your own. Use some Of the phrases in exercise 6 and those below to help you.
Summing up a review
All alt,
_![]()
In conclusion, ![]()
TO sum up. „![]()
8 Now write your review using the notes you made.
|
CHECK YOUR WORK ve you: approached the Of view specified explained other them with your own? used the present characters? written 200-250 used some of the and plot?
|
task in words? |
from the particular the task? people's Opinions simple to describe useful phrases to and grammar? |
and the |
angle contrasted plot describe |
or and character |
|
|
|
you went to see it.
2
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
find
Out some background information about the film. Make notes On Some of these
things:
|
I Title? Type of film? Main theme? Part Of a series? Made when? Based on a book or a true story? Famous around the world? |
|
|
|
2 Director: Nationality? Has he/she won any prizes? Any other interesting information about him/her? |
|
|
|
3 Main actors: Nationality? Have they won any prizes? Any other interesting information about them ? |
|
|
3 Make notes about What happens in the film. Use some of the phrases below and the adjectives in exercise 8 on page 78 to help you.
Talking about the plot
The film is set in (where/when?) At the start
Of the film, ![]()
The Story begins when In the
course of the film ![]() It's the story of By the end of the
film
It's the story of By the end of the
film ![]()
The plot revolves around There's a twist at the end.
4 Make notes about the characters in the film. Use the nouns below and the adjectives in exercise 8 on page 78 to help
Types Of charatter]rOJe action hero anti-hero comic actor extra hero/ heroine leading role protagonist romantic lead side-kick Star supporting actor supporting cast villain
• 79
7 Get Ready for your Exam
In pairs, discuss which Of these types of show you would like to see most, and why.
a musical a classic drama stand-up comedy a mime show a piano recital
2 Do the exam task.
![]()
LISTENING exam task
![]()
93.04 Listen to descriptions Of five performances. Match each event (I —5) with the appropriate summary sentence (A—F). There is one extra sentence that is not needed.
A Get in line to be dazzled by a legend.
B Sing along and be part Of this amazing show.
C You won't get a second chance for such a laugh!
D Act quickly to see a great dance show free Of charge. Stand up for this unusual performance where actors don't speak.
F It's literature on Stage but, unlike the book, it's never the same thing twice.
3 Do the exam task.
![]()
USE OF ENGLISH exam task
![]()
Read the text. Choose the correct answer (A, B, Cor D) for each gap to create a logical and grammatically Correct text.
For a generation brought up on reality TV shows, 1 their accompanying public humiliation of fame-hungry volunteers. the film The Hunger Games Will not appear too far-fetched. This futuristic fantasy thriller explores the theme which has violent and fatal results. Directed by Gary Ross, it is based on the 2008 bestselling teen novel by Suzanne Collins.
The action is in a future North America with a population suffering chronic food shortages under a totalitarian government. The outlying districts of the evil Capitol once attempted to rebel against this government, but were cruelly suppressed. punishment, all twelve rebellious provinces have to provide young people every year, one girl and one boy each. to take part in a televised gameshow in which they must fight to the death. As in the times of Roman gladiator fights. only one survivor is allowed.
Get ReadVforyour Exam 7
The main protagonists are tough, practical Katniss
(actress Jennifer Lawrence) and softer peeta (Josh Hutcherson). When Peeta his feelings for Katniss, the TV ratings shoot up. Now the bloodthirsty audience tunes in eagerly to watch the two lovers fight each Other to the death.
The Hunger Games is at a clever satire on today's reality TV shows and an exciting thriller. It is
the big screen.
|
1 A for |
B having |
C with |
D including |
|
2 A placed |
B set |
C located |
D put |
|
3 A ln |
B Like |
|
|
|
4 A confesses |
B tells |
C confides |
D owns up |
|
5 A having to |
B had to |
C must |
D to have to |
|
6 A time |
B once |
C first |
D utmost |
4 you had to audition for a talent show.
5 Do the exam task.
![]()
Describe the picture. Answer the questions below.
What kind of show do you think this woman is auditioning for? Would you like to audition fora TV talent show?
Why / Why not?
Do you enjoy watching TV talent shows? Why / Why not?
do you know about them?
I global warming 2 renewable energy 3 fossil fuels
2 ![]() Complete
the word sets with the words below.
Complete
the word sets with the words below.
Use a dictionary to help you.
biofuel coal Oil solar tidal wave
Sources
|
of power power |
power |
power |
|
natural gas |
shale gas |
|
|
|
renewable energy |
|
|
hydroelectric power |
nuclear power |
Wind power |
![]()
mine
panel power pylon rig turbine
Listen again and check.
nuclear waste your carbon footprint renewable energy energy wind turbines or solar panels the atmosphere and oceans natural resources carbon emissions fossil fuels
![]()
![]() I
invest in
I
invest in ![]() 4 conserve
4 conserve![]() 7
cut
7
cut
2
dispose
of![]() 5 pollute
5 pollute![]() 8
rely on
8
rely on![]()
3
reduce![]() 6 install
6 install![]() 9 use up
9 use up![]()
5 ![]() Describe
the photos. Discuss these questions.
Describe
the photos. Discuss these questions.
I How is electricity generated in your country? 2 What are the advantages and disadvantages of a fossil fuel energy? c renewable energy? b nuclear energy?
warming.
![]() It's
impossible to persuade people to live •greener' lives. g We should rely more on
nuclear power.
It's
impossible to persuade people to live •greener' lives. g We should rely more on
nuclear power. ![]() If we are serious about stopping
climate change, we should Stop eating meat.
If we are serious about stopping
climate change, we should Stop eating meat.
![]() We should adapt to climate change, not
try to prevent it. statements in exercise 3? Give reasons for your opinions.
We should adapt to climate change, not
try to prevent it. statements in exercise 3? Give reasons for your opinions.
|
tha — That's because |
|
|
|
|
D VOCABULARY BUILDER
8.1: PAGE 141 ![]()
-8V
|
|
to ability. |
|
a similar meaning to the first. Use the word in brackets. |
|
|
|
I If developing countries don't cut carbon emissions, we |
|
I JO was able to find a job when she left school. (managed) |
|
|
|
won't be able to prevent climate change. |
|
10 |
|
|
|
2 New York's first power station, built in 1882, could |
|
2 Perhaps
I can ring you after work. (might) 3
It annoys me that I can't drive. (able) I don't like |
|
|
|
supply electricity to only 59 customers. The biggest wind turbines can generate enough electricity to power more than 2,000 households. |
|||
|
|
4
|
We managed to Cut our fuel bill by insulating the loft.
|
|
4 Susan was able to get a place at Oxford. (succeeded) Susan at Oxford. 5 Iwas
ill so I wasn't able to goto school. (couldn't) |
|
|
6
|
George W. Bush bought an Oil company in Texas, but they couldn't find any Oil and went bust. As we approached the factory, we could smell the fumes from the chimneys. |
|
6 The house was visible
through the trees. (see) D
GRAMMAR BUILDER8.1: PAGE 128 |
|
|
|
The Government isn't able to cut carbon emissions. |
5 |
Describe the photo. What is the person doing, and Why? Then |
|
2 |
Match each sentence in exercise 1 With a rule in the Learn this! box. |
|
read the text in exercise 6 and check your ideas. |
|
|
|
|
I Present ability • We normally use can to talk about ability in the present. • However, it's also correctto use the present tense of be able to, but it's less natural. 2 Ability in the past • We only use couldfor general ability in the past. • When we're talking about one occasion, we use a different expression, such as managed to do or succeeded in doing. • However, we use the negative couldn't whether we are talking about general ability or one occasion. • We use could With verbs Of perception, like see, smell, hear, taste, feel, even if it's one occasion. 3 Ability in the future • We normally use Will be to talk about ability in the future. • We Can use can talk about future arrangements. |
![]() 6 Complete
the text with the correct tense and form Of can, could, be able to, manage or
succeed. Sometimes there is more than one possible answer.
6 Complete
the text with the correct tense and form Of can, could, be able to, manage or
succeed. Sometimes there is more than one possible answer.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Jason Edwards has been involved in eco-protests for as
long remember. 'One of the most memorable was in 2010,' says Jason. were trying
to prevent them from building a bypass through some ancient woodland. We
Jason Edwards has been involved in eco-protests for as
long remember. 'One of the most memorable was in 2010,' says Jason. were trying
to prevent them from building a bypass through some ancient woodland. We ![]() dig
tunnels under the route of the road and we hid in them. For two months the
police find us. But despite our best efforts we . In the end, the police
dig
tunnels under the route of the road and we hid in them. For two months the
police find us. But despite our best efforts we . In the end, the police
|
3 |
Choose the best answers. Sometimes both answers are |
|
|
|
|
acceptable. |
|
Some friends of mine are
going to take direct action to Stop them building a new airport near London.
I hope I'll s |
|
|
I I couldn't hear / didn't hear the radio so I turned it up. |
|
get involved in that too. This time we might 7 prevent |
|
|
2 Can you / Are you able to play the piano? 3 1 don't manage to / can't type very fast. |
|
the project from going ahead.' |
|
|
4 1 was short Of money so I couldn't / wasn't able to goto |
7 |
|
|
|
the cinema with my friends. |
|
|
|
|
5 1'm having a party on Saturday. Can you / Will you be |
|
|
|
|
able to come? |
|
in doing) last year. |
|
|
6 After three attempts I managed to / could pass my |
|
3 two things that you have tried to do in the past but |
|
|
driving test. |
|
couldn't. 4 something that you don't like not being able to do. |
821 Unit8
more productive crops. and crops with ncreased vitamins. Anti-GM ¾0testers worry about health risks and damage to other plants that grow near the GM crops,
Vertical farming
Another answer could be to grow food in buildings.
Solthng the
CRISIS
Every night, almost one billion go to bed hungry. How can we feed all these undernourished people? Farmers all Over the wœld have to contend with weather. insects, and natural disasters, which are capable Of destroying crops and
nine billion by 2050. Here are four possible solutions.
GM crops
Proponents of genetically modified crops (GM crops) claim that they Will hugely increase food production. Scientists have developed drought-resistant and disease-resistant crops,
Work in pairs. Discuss these questions. Read the text and check your ideas.
I What causes food shortages?
2 What are some Of the arguments against GM crops? 3 Are people generally eating more or less meat?
2 What do these refer to, according to the text?
![]() one
billion 4 Seven kilos/one kilo
one
billion 4 Seven kilos/one kilo
2 the year 2050 5 6.7 million tannes
3 5 hectares/l hectare
3
![]() Read the Learn this! box. Find examples
of the three prefixes in the text.
Read the Learn this! box. Find examples
of the three prefixes in the text.
|
Some prefixes give adjectives, nouns and verbs a particular meaning. anti against anticapito/ism under not enough underpaid multi many multimillionaire |
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 8.2: PAGE 141 ![]()
4
![]()
![]() Listen to Dr Samuel Friedman talking
about the advantages Of vertical farming. Which countries does he mention and
why?
Listen to Dr Samuel Friedman talking
about the advantages Of vertical farming. Which countries does he mention and
why?
Advocates of vertical farming are Suggesting we construct multi-storey, farm buildings in the heart of Our cities. One indoor hectare Of land would be equivalent to about five hectares Outdoors, so we could grow year-round crops that would easily feed whole cities. Opponents point to the cost, the increased energy use and the effect on farmers.
Eat less meat
Others say the solution lies not in new technologies. but eating less meat. It takes about seven kilos of corn to pro-du* kilo Of That quantity of corn Will keep more people alive than that quantity Of But this is a rrwssage the world doesnt want to hear Meat Consumption is rising
Increase aid
Rich countries have far more food than they need and waste vast amounts Of — 6.7 million tonnes a year in the UK alone. We can afford to send surplus food to people who desperately need it, We could also simply give more to developing countries, So they can buy food. Critics say that this makes people dependent on rich countries and s only a short-term solution.
5 Listen again. Are the sentences true or false I The idea of vertical farming is definitely more than 50 years old
2 At the moment there's a shortage of farmland.
3 Food would not have to be transported long distances.
4 Vertical farming would encourage other industries to develop and increase employment.
5 The climate in the vertical farm buildings would match the climate outside.
6
![]() Work in pairs. Develop these possible
arguments against vertical farming:
Work in pairs. Develop these possible
arguments against vertical farming:
cost energy use variety Of food effect on farmers effect on shops and supermarkets effect on world trade vulnerability in a war
7
![]() Work
in pairs.
Work
in pairs.
Student A: Argue for vertical farming.
Student B: Argue against it. Use the phrases below.
I See your point, but I still think![]()
You have to admit that![]()
There may be some truth in that, but![]()
|
•READING The final dumping ground I can understand a text about space junk. |
Work in groups. Look at the photos and the title. What do you understand by the term space junk and Why might it be a problem?
2 Read the text quickly, ignoring the gaps. Check your ideas from exercise 1.
3 Read the text again and match the sentences (A—G) with the gaps (1—6). There is one sentence that you do not need.
A The other 90% is a jungle Of junk — leftovers from half a century Of human activity in space.
B Fortunately, most of them landed in the sea.
C Because Of the extra CO, in our atmosphere now, Space junk is staying up longer.
D They were forced to get to their escape capsules and prepare for an emergency journey back to the Earth.
E These satellites then attach a device to the debris Which pushes it into the Earth's atmosphere, where it burns up.
AF And in the next ten years, the number Of satellites will grow by around 50%.
G On average. one object a day survives re-entry.
Ill IV
84 unit8
A piece of rubbish in outer space has threatened the lives Of six astronauts. prompting calls for something to be done about the mess we have created around our planet, The six astronauts - three Russians, two Americans and one Japanese - torm the crew of the International Space Station (ISS). The piece of debris came very near to station fortunately passed by Without causing any damage.
A Russian official said that only a tenth of all objects in space are working pieces of equipment. MD There are not only 22.000 large pieces Of rocket shuttle, satellite and sputnik, but also over 500,000 smaller bits, Which are only a few centimetres in size, Surrounding all of these are also millions of tiny particles, for example, flakes of paint that have come off space vehicles The problem is that all of this stuff travelling at several kil•netres per second. Even the tiniest almost nvislble speck could create a centimetre•deep hole in the side Of a rocket Or space station, potentially causing a leak. And a larger chunk could destroy it - and any human life on board.
Unfortunately, the situation can only get worse. The number Of satellites being sent into space is increasing rapidly. In the past ten years, an average of 76 satellites per year have been launched. C] The latest analysis of the situation suggests that 1,14S new satellites could be launched during that time, mostly for broactland and satellite phone systems. When satellites become defunct they stay Iow•Earth Orbit eventually falling and burning up when they re-enter the Earth's atmosphere, as meteorites do. New satellites will have to be built to new standards, so that when they reach the end of their useful life, they will have enough left to travel back immediately into our atmosphere to burn up. At the moment. of all space junk is around 1,200 miles above the Earth which is called low-earth orbit. Spacecraft have to orbit lower than this to avoid all the debris, and satellite companies have to navigate a way through the junk to place their equipment.
Unfortunately, not all space junk burns up while re•entering the Earths atmosphere. 4 C] An American woman in Oklahoma was knocked down in January 1997 When she was struck by a lump Of metal. Fortunately, she wasn't injured, The weight was comparable to an empty soda can.' the woman said. It was identified as debris from a rocket Other parts of the rocket including a steel tank and a titanium fortunately landed Without causing any harm.
4 Are the sentences true or false (F)?
The crew Of the ISS had to leave the space station and return to the Earth.
Flakes of rocket paint hitting working space equipment could damage it.
Space junk eventually burns up in the sun's atmosphere. Space junk caused a serious injury in Oklahoma in 1997. The Mir space station caused large pieces Of Space junk to fall to the Earth.
We can't use low-Earth orbit because Of a chain reaction Of fragmenting debris.
5 Complete these words that have a similar meaning to piece. They are all in the text. Can you explain any differences in meaning?
(paragraph 2) 5 c_ (paragraph 2)
2 p_ (paragraph 2) 6 L. (paragraph 4)
(paragraph 2) 7 f_ (paragraph 5) S— (paragraph 2)
D VOCABULARY BUILDER PAGE 141
However, in the world of space litter, the biggest piece Ot junk would have to be Mir. the Russian space station, Which is the heaviest object ever to orbit the Earth. apart from the Moon. The fifteenyear•old station began headine downwards on 23rd March 2001, and a month later. re-entered the Earth's atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean near Fiji. Though most Of the station, weighing 130,000 kilogrammes. burned up in the atmosphere, about 1.500 fragments reached the Earth's surface Holidaymakers on beaches in Fiji took photos Of little bits Of burning debris as they whizzed noisily through the sky above them.
Occasionally debris collides With Other debris, creating thousands more tiny pieces Of space junk. so tar. it is thought that there have been few such collisions, but what is feared is a kind of chain reaction, with debris fragmenting and going on to collide With Other debris. creating a cloud Ot rubbish that would make it impossible for us to use the IowEarth orbit around our planet at all.
6 Put these things in order of size, from the smallest to the largest (as you'd reasonably expect them to be). Find three Of them in the text (in paragraphs 1, 3 and 5).
asteroid constellation galaxy meteorite moon planet solar System Star universe
SMALLEST
» LARGEST
7 ![]() Work
in small groups. What extra-terrestrial events are we in potential danger from?
Look at the list below and put it in order from least dangerous to most
dangerous. Think about the probability of the event occurring and the likely
consequences.
Work
in small groups. What extra-terrestrial events are we in potential danger from?
Look at the list below and put it in order from least dangerous to most
dangerous. Think about the probability of the event occurring and the likely
consequences.
• space junk falling from the sky
• aliens visiting from outer space
• a meteorite hitting the Earth the sun dying
• the Earth colliding With the Moon or another planet
8 Present your ideas to the class, giving reasons for your decisions.
Some scientists think they might have up with a solution to the problem Of space junk. They want to big 'cleaning robots' into sky, in effect satellites which are able to "xate and manoeuvte alongside large pieces of space junk. The say that each robot could safely remove up to ten Objects a year. This would go some way to improving the situation, as long as collisions between debris do not increase in the meantime Whatever the solution to the problem, experts all agree that someth" needs to dcne to tidy up space sooner rather than later.
8
|
Defining relative clauses I A defining relative clause adds essential information. The sentence often doesn't make sense without it. This is the coal mine where my grandad worked. 2 We do not puta comma before the clause. Non-defining relative clauses 1 A non-defining relative clause adds extra information. The sentence still makes sense without it. Global worming is caused by greenhouse gases, which include carbon dioxide and methane. 2 We put a comma before the clause, and also after it if the sentence continues. Fossil fuels, which include coal and oil, are running out. Relative pronouns I In informal contexts. we can replace Who or which With that in defining relative clauses, but not in nondefining relative clauses. 2 In defining relative clauses which or Who can be omitted if it is the object of the clause. / welcome the measures the Government is taking to combat climate change. 3 We can replace who with whom ifit is the object ofthe clause, but it is formal. |
|
1
![]() Read the quotes. Which Of these causes would you support?
Which other charities do you know about?
Read the quotes. Which Of these causes would you support?
Which other charities do you know about?
2 Read the Learn this! box. Then 100k again at the quotes in exercise 1 and:
I decide Which are defining relative clauses and which are non-defining relative clauses.
2 identify the relative clause in which the relative pronoun can be replaced with that.
3
![]()
identify
the relative clause in Which the relative pronoun can be omitted.
![]() Unit 8
Unit 8
3 All these sentences contain mistakes in grammar, punctuation or style. Correct them.
1 The man. who's wearing a tie, is my uncle.
2 Space junk is a problem, Which is getting worse.
3 1've got a friend What lives in Japan.
4 Solar energy is an idea Which time has come. 5 Whom did you dance with at the night club?
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 8.2: PAGE 129 ![]()
4 Rewrite each pair Of sentences as one sentence. Use defining or non-defining relative clauses and appropriate punctuation.
I Here's the money. I owe itt0 you.
2 1 run three times a week. It keeps me healthy.
3 1 made loe a sandwich. He ate it at once.
4 1 live in a village called South Milton. It has a population of 600.
5 We 100k after Stray dogs. Their owners can't be traced.
5 Read the Learn this! box below. Find one participle clause in the quotes in exercise I.
|
Shortened relative clauses 1 Shortened relative clauses contain either a present participle, which replaces an active verb: The charity protects animals facing extinction. or they contain a past participle, which replaces a passive verb: Global warming is mostly caused by C02 emitted by power stations. 2 The verb they replace can be in any tense. The dodo was a bird hunted to extinction within a century of its discovery |
|
6 Rewrite the sentences using shortened relative clauses.
I People Who work for private companies usually get paid more than those in the public Sector.
2 Is that your dog that's making a mess on the lawn?
3 This self-portrait, Which was painted by Van Gogh in 1889, is one of his finest.
4 1 saw a young girl who was stealing a CD.
5 We visited a castle that was built in the sixteenth century. 6 1 only eat food which is made with fresh ingredients.
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 8.3: PAGE 129 ![]()
7
![]() Work in pairs. HOW many sentences can
you make in one minute by adding different relative clauses and Other words and
phrases?
Work in pairs. HOW many sentences can
you make in one minute by adding different relative clauses and Other words and
phrases?
|
1
Last week I met someone 2
is the place 3 What did you think of the |
4
1'vegota friend 5 I
was born in 19 6 A
good student is one |
|
listen to a student saying which poster she'd choose and why. TO what extent did the student follow the advice in the tip? Read the Learn this! box below. Then listen again |
Your school wants to encourage the students to recycle more. Which one of these posters would work best? Justify your choice and say why you rejected the Other posters.
EXAM TIP
When you are justifying your choice, try to give at least two reasons. When you are saying why you rejected the Other options, try again to give at least two reasons, and don't simply give the opposite reasons. Vary your arguments.
3 Use the words below to complete the phrases.
another believe main reason thing top
Justifying Vour opinion
The reason I _ that is because
![]()
The reason
is that![]()
![]() Why
do I think that? Well. for one
Why
do I think that? Well. for one ![]()
![]() thing
is that Another
thing
is that Another ![]() of that,
of that,![]()
4 Workin pairs. Do you agree with the student's opinions in exercise 2? Give reasons. Think about the design (colour and images), the message, the amount Of information and how appealing it is to teenagers. Use phrases from exercise 3 in your answer.
5 Listen to a student answering this question: What can be done to improve the environment where you live? Answer the questions below.
1 Which phrases from exercise 3 did the student use?
2 What specific examples did the student give to Support her arguments?
![]()
![]()
![]() and
identify two examples of do/did for emphasis.
and
identify two examples of do/did for emphasis.
|
do and did for emphasis We can use do and did to make statements stronger and to show a contrast. We stress do and did when they're used in this way. / do think we need to do something aboutglobal warming. / did enjoy the concert. The first poster is attractive but / do find it a bit depressing. |
7 Do you agree with the student's opinions? Give reasons. use phrases from exercise 3 in your answer.
8
![]() Make these statements more
Make these statements more
emphatic using do or did. Then listen and repeat.
I Weve got bins for recycling paper but we need to recycle glass tCH).
2 1'm all for cutting our carbon footprint butl think the
Government should come up With some better ideas.
3 We didn't install double glazing, but we insulate the loft. 4 It isn't easy to save energy, but we have to try.
5 The Government didn't cut carbon emissions, but it promised to invest in renewable energy.
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 8.4: PAGE 130 ![]()
9
![]() Work in pairs. Choose one question each
and take two minutes to prepare your answer. Then speak for one minute.
Work in pairs. Choose one question each
and take two minutes to prepare your answer. Then speak for one minute.
I Does your local council encourage you to recycle, and make it easy for you to do so?
2 DO you think that plastic bags should be banned?
![]() Work in pairs. Turn to page 144. DO the
exam task.
Work in pairs. Turn to page 144. DO the
exam task.
8 ![]()
![]() Read exam questions a—d. Then look
quickly at the essay below and say which question it is answering.
Read exam questions a—d. Then look
quickly at the essay below and say which question it is answering.
a Global warming is the most significant environmental problem facing us today. DO you agree?
b Who bears the greatest responsibility for pollution:
businesses, individual people Or the government?
c It is impossible to improve people's standard of living
and at the same time avoid damaging the environment. Do you agree?
d
![]()
![]()
technology to avoid the mistakes of
the past. ![]()
3
![]()
4
5
6
Look at these expressions. Which Ofthese expressions are in the essay in exercise I?
![]() additional points
additional points
Furthermore, Moreover.
What is mare,![]()
Similarly,
We should also remember that![]()
Introducing contrasting points
On the other hand. Having said that, ![]() And
yet, That said. . Even though _
And
yet, That said. . Even though _
Link these sentences together using an appropriate phrase from exercise 3 to start the second sentence.
![]() In the past, hunting elephants and
tigers was considered acceptable. Most people had no regard whatsoever for
In the past, hunting elephants and
tigers was considered acceptable. Most people had no regard whatsoever for
the welfare of wild animals.
![]() Today
we are much more aware Of environmental problems. Governments Often ignore
warnings given by environmental scientists.
Today
we are much more aware Of environmental problems. Governments Often ignore
warnings given by environmental scientists.
![]() There are lots Of ways individuals can
reduce their carbon footprint. TO make a really big difference we need
government action.
There are lots Of ways individuals can
reduce their carbon footprint. TO make a really big difference we need
government action.
![]() You
can't deny that global warming is taking place. Not everyone believes it is
caused by human activity.
You
can't deny that global warming is taking place. Not everyone believes it is
caused by human activity. ![]() We should use renewable sources Of
energy. We can use nuclear power, Which does not produce greenhouse
We should use renewable sources Of
energy. We can use nuclear power, Which does not produce greenhouse
gases.
Read the Exam tip below. Then read the final paragraph Ofthe essay and identify all the elements listed in the tip.
|
EXAM TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A good way to finish an Opinion essay is to: I Start With a concluding phrase and State your opinion 2 concede an opposing opinion, then repeat your Strongest argument in favour. |
||||||||
Rewrite the last paragraph Ofthe essay to express the opposite opinion. Use the same structure. Choose a different concluding phrase from the list below.
Concluding phrases
In
conclusion, All things considered, To sum up, .![]()
On balance. All in all, In
the final analysis, .![]()
(conttuding phrase}. (state opinion), While![]()
2 Look at the plan for the essay in exercise I. Then mark where (concede art apposing point). (repeat sttangest point in the paragraph divisions should be. Which words helped you favour).
|
decide? |
|
|
• Paragraph I |
Introduction: explaining the title and giving your initial opinion. |
|
|
1st argument in support of your opinion. |
|
• paragraph 3 |
2nd argument in Support of your opinion. |
|
|
Argument(s) in support of the opposite opinion, and counter-argument(s) |
|
• paragraph 5 |
Summary, re-stating opinion. |
88 Unit 8
Work in pairs. Choose one Of the other tasks from exercise Use some Of the phrases in exercise 3 on page 88 to
|
1 on page 88. Decide on the key question that needs to be answered. Then agree on your opinion. |
|
introduce the points you listed in exercise 2. |
|
|
6 |
Write paragraph I (the introduction) of your essay using your |
The question need to answer is: .
Our opinion is: answer to exercise 1. Begin by explaining the key question in your own words, then State your initial opinion.
EXAM TIP It's
worth acknowledging from the start that ![]()
Make sure that you provide good points
on both sides The question we need to answer is ![]() Of
the argument, even if you strongly agree with one My Own Opinion is
Of
the argument, even if you strongly agree with one My Own Opinion is![]()
side only. 7 Use your notes from exercise 3 to write paragraphs of
|
|
|
|
your essay. use the phrases in exercise 4 to help you and the |
|
2 |
Read the Exam tip. Then make notes for and against the opinion you expressed in exercise 2. Write down as many |
|
ones in exercise 3 on page 88. |
|
|
ideas as you can in the chart below. |
8 |
NOW write the final paragraph, summing up your own opinion. Use the plan in the Exam tip and the phrases in exercise 6 on |
|
Points supporting your opinion |
|
|
|
Points supporting the opposite opinion, and counter-argument |
|
|
page 88 to help you.
9 Count the total number Of words in all five paragraphs. If there are fewer than 200, do one or more Of these things:
I Add more arguments to paragraphs 2 and/or 3.
2 Give more examples to support the arguments in paragraphs 2 and 3.
3
![]()
![]()
![]() Expand the introduction or conclusion.
Expand the introduction or conclusion.
If you have written more than 250 words, do one or more Of
|
|
|
|
these things: |
|
3 |
Choose ideas from your chart in exercise 2 to complete the |
|
1 Look for unnecessary repetition. |
|
|
plan for paragraphs 2—4. Use the chart in exercise 2 on page |
|
2 Look for words or sentences that you can cut Without |
|
|
88. |
|
spoiling the 'flow' of the arguments. 3 Cut one or more examples that support arguments. |
|
4 |
Complete these useful phrases With an infinitive with to or |
10 |
Check your work using the following checklist. |
|
|
With an -ing form. Use the verbs in brackets. Which two are in the essay in exercise I on page 88? |
|
|
|
CHECK YOUR WORK Have you: followed the paragraph plan? used some Of the useful phrases from exercise 3 on page 88 and exercise 4 on page 88? included strong points on both sides of the argument? ecked your spelling and grammar? |
![]() It's
no use/good that (argue)
It's
no use/good that (argue)
2 It's fair that (say)
![]() It's
important that (recognise)
It's
important that (recognise)
4 It's worth (acknowledge)
![]() It's
hard that (deny)
It's
hard that (deny)
6 It's impossible whether (say) ![]() It's
easy
It's
easy
8 It's worth that (point out) 11 NOW write the final version of your essay.
8
7-8 Language Review
I Match the two halves Of the compound nouns.
|
breaking |
|
broadcasts |
|
2 live |
b |
journalism |
|
3 human•interest |
|
news |
|
4 citizen |
d |
accounts |
|
eye.witness |
|
stories |
Mark: _ 15
2 Read the quotations, then complete the reported speech.
|
"I'm not going on holiday this year.' |
'I'd better go home.' |
|
did you get so angry?' |
|
•put your clothes away!' |
•Why
|
•When will my car be ready?' |
|
|
|
|
My mum my clothes away. 2 Mary go home.
|
|
Dad asked the mechanic |
ready. |
|
4 |
My aunt has told me |
holiday this year. |
|
|
The policeman asked me |
so angry. |
Mark: _ 15
3 Complete the sentences with the verbs below. Use the past simple.
claim convince insist Offer warn
1 They that I tell the whole story again.
2 He me against talking to the police.
The check-out assistant to help me pack.
4
My
sister![]() me to apply for the job.
me to apply for the job.
5
![]()
![]() My brother
My brother![]() not
to know why my laptop was broken.
not
to know why my laptop was broken.![]()
Mark: ![]()
4 Complete the sentences with must,
might or can't. ![]() She like ILS. She's got all their
albums.
She like ILS. She's got all their
albums.
2 They have been swimming. The
pool is closed. 3 I'm not sure where Brandon is. He ![]() be
in town.
be
in town.
4
![]()
![]()
5 Elsie knew about my accident. Somebody have told her.
![]()
Mark: _ 15
5 Complete the missing words.
We should all try to reduce our C..footprints.
The Government is planning to build twenty new Wind off the coast of Devon.
3 In the past, we all relied on f fuels for Our energy.
4 They have s— panels on the roof to generate electricity.
They built a dam across the river in order to generate h_ power.
Mark: _ 15
6 Complete the text With the words below.
be able could couldn't managed to succeeded in
Jason noticed the crowd in the street, but he t What they were all looking at. He tried to push his way through, but only 7 annoying a large man in a leather jacket. Then he had an idea: if he returned to the café and went upstairs, he would s to look down onto the street. He raced through the door, up the stairs and find a table by the window. Finally, he 5 see what the crowd were looking at. He turned away.
Mark:
7 Complete these sentences with a relative clause. Your sentences must be true as well as correct.
I A vandal is a person
2 Barack Obama, , was born in 1961.
3 A device is called a satnav.
4 Mount Everest is in the Himalayas,
5 A stadium is a place
Mark: 15
8
Write
the missing words to complete the monologue.![]()
'The Government should ban plastic bags completely. Why?
![]() Well,
for One t , they cause litter because people
Well,
for One t , they cause litter because people ![]() drop
them. On of that, they harm the environment because they aren't biodegradable.
Cloth bags are much
drop
them. On of that, they harm the environment because they aren't biodegradable.
Cloth bags are much ![]() better. The main is, you can re-use them
lots Of times. thing is that theVre very Strong. Paper bags
better. The main is, you can re-use them
lots Of times. thing is that theVre very Strong. Paper bags ![]() aren't
as strong, but they s
aren't
as strong, but they s![]() biodegrade, at least.'
biodegrade, at least.'
Mark: _ 15

![]()
Language Review 7—8 ![]()
3.12 Listen. List all the different locations.
2 Read the text. Use it to improve your definition of 'hacktivise. Anonymous is the name of a group of computer hackers who take part in cyber attacks on companies, organisations and even governments. They are often referred to as 'hacktivists• (a mixture of the words 'hackers' and •activists') because, unlike many hackers, they use cyber•attacks as a form of protest. t C]GeneralIy speaking, they oppose any form of Internet censorship and support total freedom of expression online. They are considered by some to be courageous activists, and by others to be irresponsible cyber-criminals. As an Organisation. Anonymous does not have a clear Structure or leadership. It is thought that most of the people involved are aged between 18 and 24. A small. inner circle Of members is believed to make the final decisions about When and where the specific cyberattacks take place.
The group rose to prominence in 2008. when it
launched a campaign against the Church Of Scientology. The campaign targeted
the organisation•s website, bombarding it with web traffic from thousands Of
different PCs. a In 2010, Anonymous launched a campaign to support the
anti-secrecy site WikiLeaks. Any organisation which was believed to be hostile
to WikiLeaks was likely to be targeted for cyber-attacks. These included the
United States Department of Justice, who had begun an investigation into
possible criminal charges against the founder of WikiLeaks.![]()
Anonymous has also supported websites Which Offer free file-sharing services. When the Megaupload file-sharing site was shut down by authorities in the USA in 2012, Anonymous responded with What was described as 'the single largest Internet attack in its historV. The targets were the Justice
![]()
![]()
![]() Department,
the FBI, Universal Music Group and the Motion Picture Association of America.
But while Anonymous continues to campaign for a completely tree and open
Internet, other groups insist that laws are needed to prevent online piracy.
Defending the right to swap files online, th claim. risks fatally damaging the
music and film industries. That is a debate which will be held not Only in
cyberspace but in courts Of law around the world.
Department,
the FBI, Universal Music Group and the Motion Picture Association of America.
But while Anonymous continues to campaign for a completely tree and open
Internet, other groups insist that laws are needed to prevent online piracy.
Defending the right to swap files online, th claim. risks fatally damaging the
music and film industries. That is a debate which will be held not Only in
cyberspace but in courts Of law around the world.
![]() Stefan doesn't chat with Daisy because
a she isn't at home. c he doesn't know what to say. b Spikey won't allow it. d
Daisy is angry With him.
Stefan doesn't chat with Daisy because
a she isn't at home. c he doesn't know what to say. b Spikey won't allow it. d
Daisy is angry With him. ![]() Spikey blames Stefan for the failed
cyber-attack because a he's the only Other person who knew about
Spikey blames Stefan for the failed
cyber-attack because a he's the only Other person who knew about ![]() b he
knows about Internet security.
b he
knows about Internet security.
c
he
admits that he mentioned it to somebody. d he told a friend he was going to
Stop the attack. ![]() On the phone. What reason does Daisy
give Stefan for being at the charity event? a She wants to support the charity.
b She wants to discuss somethingwith him.
On the phone. What reason does Daisy
give Stefan for being at the charity event? a She wants to support the charity.
b She wants to discuss somethingwith him. ![]() c
She doesn't give a reason.
c
She doesn't give a reason.
d Spikey convinced herto go.
4 Why is Daisy meeting her father? a Spikey asked her to talk to him.
b She wants to find
Out more about Wesley's. c She wants to see him, but not at his house. d She
wants to discuss moving back to his house. ![]() When
Daisy talks about her group's next big protest. she a tells Stefan Which day it
will take place. b explains what kind Of protest it Will be. c says where the
protest will take place. d gives away none Of the information above.
When
Daisy talks about her group's next big protest. she a tells Stefan Which day it
will take place. b explains what kind Of protest it Will be. c says where the
protest will take place. d gives away none Of the information above.
6 Discuss the following statement. saying ifyou agree or disagree and giving reasons.
It should be possible and legal to exchange whatever files you want to online.
![]() 7
Write an opinion essay discussing the statement in exercise 6. Remember to
include some points supporting the opposite opinion from your own.
7
Write an opinion essay discussing the statement in exercise 6. Remember to
include some points supporting the opposite opinion from your own.
5 03.12 Listen again. Choose the correct answers.
Skills Round-up 1-8
8 Get Ready for your Exam
1 memory. Why has it stuck in your mind?
2 Do the exam task.
READING exam task
Read the text. For each question, select the correct option: A, B, C or D.
I am on the boat, looking out blindly. counting on my frozen fingers the people I love. Sandeep, my daughters, my mother, my brother. It is a pitifully short list. and does not cheer me up at all. My mother is dying — perhaps she is already dead. How much of my husband's fondness for me is simply daily habit? In how many ways will my daughters and I disappoint each other as they grow up? And my brother? Is he as anxious for me to go as I am to leave?
Don't Cry, I Order myself. Make yourself smile. You did your best. You're going home tomorrow.
'Look!' Tarun is pointing to something white on a nearby piece of floating ice. I hope my eyes haven't turned red. and try to show some interest. Will this miserable boat trip never end? •Look!' It's some sort Of large bird, With thin red legs. As the boat gets closer, it spreads its White wings and looks calmly at us. I've seen a bird like this somewhere before.
•Didi. doesn't it 100k like a sharash?'
Yes, indeed it does. aut am more surprised by the Bengali name for the bird, so unexpected in my brother's mouth. And the childhood name for me. Which he hasn't used for years. Didi. A small word Of love, like a magic jewel from one Of my mother's stories.
I remember when we last saw sharash. It is soon after my father's death. I am eight, my brother three. My mother has Sent us to stay at Third Uncle's house, Out in the country. We are homesick and miserable, and do not get on With Our cousins, who know how to milk cows and swim across the river. We hurt Ourselves trying to climb trees With them, and they laugh at us when we cry.
But One day, after a morning filled with rain, the sun Comes out, and Tarun and run across the fields. We get muddy from head to toe. but we don't care. Perhaps we can reach the railway, jump on a passing train. and make our wav back to our mother in Calcutta? Then suddenly We see them. fifteen or twenty sharash feeding in the flooded rice fields. My brother lifts his delighted hands, Look, Didi! as the birds fly up, a speeding cloud of silver light. For a moment the sky is full of wings. Whiteness and possibility. We stand with Our arms around each Other until they disappear.
Get Ready for your Exam 8
The ferry is closer now, and everyone is looking at the bird. Even the noisy young men are quiet. The bird's eyes sh'ne. It looks back at us. at me. I am Sure of this. It has flown all the way from Bengal, to bring me a message that Will Save us — if only I can hear rhe of wild things by Diva karuni
The narrator of this Story
A has her whole familv come and see her off.
B is unsure of her spouse's affection.
C is disappointed With her family.
D has a brother who wants to go With her.
When they see the bird
A it looks scared by the boat.
B she learns that it has a name in Bengali.
C she recognises it as a bird from her mothers stories.
D her brother surprises her With his tenderness. 3 When the children were at Third Uncle's house A some Of their relatives were unkind to them.
B they ran away back to their mother.
C they found Out their father had died.
Dthey had to learn how to milk cows.
4 HOW do the children react to the flock Of sharash?
A They wave their arms in the air.
B They follow them across a flooded field.
C They lose them in the sun and clouds.
D They keep still and watch them fly away.
Seeing the sharash makes the narrator feel
A bitter. B hopeful. C irrititated. D nervous.
3 DO the exam task.
|
USE OF ENGLISH exam task |
Complete the text With a suitable word in each gap. A narrow rock that stands than the Empire State Building does not 100k like the welcoming place to set up home. But that did not Stop an insect which was 3 to be extinct for 80 years from building its last known colony on the 562-metre Ball's Pyramid in the South Pacific Ocean. Scientists have discovered 24 Of the creatures living around a plant on the rock. The 'tree lobster' insect, is as large as a human hand, had somehow made its camp the lack of food.
In 2001 Australian scientists decided to investigate claims by climbers who tackled Ball's that they had seen fresh droppings there. They too saw the droppings and upon returning dark with flashlights were stunned 8 discover the insect colony around the only plant on the rock. Mr Carlile said: 'It felt like stepping back into the Jurassic age, insects ruled the world.'
|
|
We usually form regular adverbs by adding -Ivto the adjective (loud -4 loudly). But remember:
erratic -s erratically
(exception: public publicly). if the adjective ends •y, we replace it with
•ily: happy happily, angry if the adjective ends we either use the same form for the adverb (early, daily, yearly) or we use an adverbial phrase instead of an adverb: friendly • in a friendly Some adverbs are the same as the adjective (fast, better, etc.) Some others (high. deep. late. etc.) have two forms with different meanings, One with •Iy and one without. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
We often use these structures to describe somebodrs behaviour: I It + be + adjective + of somebody to do something It was kind of vou to help. It
would be short-sighted Of Eva to leave school. 2 It/That+ be + adjective |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
![]() adjectives
below. Then choose one or two adjectives to describe the behaviour in each
photo.
adjectives
below. Then choose one or two adjectives to describe the behaviour in each
photo.
Describing behaviour altruistic careless clumsy considerate courageous cowardly cunning cynical deceitful disloyal eager foolish forgetful heroic hospitable hysterical over-sensitive pushy pretentious reckless romantic ruthless short-sighted spiteful thoughtless
3 Listen to six monologues. How would you describe the speakers' actions? Choose the best adjective from exercise 2 for each person.
![]()
Speaker
I: altruistic,
6 Read the Learn this! box. Then form adverbs or adverbial phrases from the adjectives in exercise 2.
7
4 Read the Learn this! box. Then listen again and make notes about the speakers' actions. Describe the actions using the structure in the Learn this! box.
I Ii altruistic Of him to give hit coatin his ticket,
Listen and complete the dialogue With the words
below. Is Archie right to be annoyed? Why?/Why not?
![]()
|
Libby But you know she's a close friend Of mine. I didn't want to take sides. I had to invite both Of you. Archie But you have told me she was coming! Libby She asked me not to. Maybe it was a mistake, but I promised her that I wouldn't tell you. Archie Well, you have given me a hint. If you'd warned me, I'd have stayed at home.
Archie True. aut still have warned me. |
|||
|
|
should/could/might/needn't have + past participle I We can use shouldn't have to express disapproval of past actions. She shouldn't have laughed at her brother. 2 We use should have, might have or could have to say what the right way to behave was, in our opinion. She should/could/might have been kinder! 3 We use needn't have to say an action was unnecessary. You needn't have shouted, / was right beside |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 Read the Learn this! box. Then join the sentences using should have, shouldn't have or needn 't have, and because.
I She told me Sam's address. I already knew it.
She needn't have told me Sam"
addrebs because ![]()
![]() it.
it.
2 You didn't go to the doctor's. You were feeling very ill.
3 She didn't give her dad a card. It was his birthday.
4 Mark took his camera to the match. He took no photos.
5 We took sun cream on holiday. It rained every day.
6 You spent all your money. You needed some for the bus.
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 9.1: PAGE 130 ![]()
|
Third conditional We use the third conditional to talk about how a situation in the past could have been avoided. Ifwe hadn 't stayed outso late, I wouldn 't have overslept. (But we did Stay out late so did oversleep.) The if clause can come before or after the main clause. We use the past perfect in the ifclause and would/ wouldn't have in the main clause. Be careful: had and would both have the same short form 'd. I'd have come ifvou'd invited me. (But you didn't invite me, so I didn't come.) |
|
3 Read the Learn this! box. Find an example Of the third conditional in the dialogue in exercise 1 and write an explanation like the ones in brackets in the box.
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 9.2: PAGE 130 ![]()
![]() Complete the second sentence so it
means the Same as the first. Include the word in brackets.
Complete the second sentence so it
means the Same as the first. Include the word in brackets. ![]() We
only arrived on time because we ran. (wouldn't) If we arrived on time.
We
only arrived on time because we ran. (wouldn't) If we arrived on time.
2 1 Wish you'd taken some photos! (might) photos!
3 was a bad idea to eat at the hotel. (shouldn't)
at the hotel.
4
He
panicked - that's the only reason he got lost. (if) He wouldn't have![]() panicked.
panicked.
![]() We'd never have won Without Vour help.
(helped)
We'd never have won Without Vour help.
(helped) ![]() we wouldn't have won.
we wouldn't have won.
6 You didn't have to buy me
a present. (needn't) You![]() a present.
a present.
5 Make notes about What you would have done if you had found yourself in these situations:
I a pet was sick on your school bag 2 you overslept by an hour
3 all your school clothes were dirty
4 you saw a house On fire
5 you couldn't find your keys/phone
6 
in pairs. Explain the meaning Of the
I Have you got an account on Facebook or any Other social networking site? If so, how often do you use it and What do you use it for?
2 Which family members, if any, are Facebook friends of yours? DO you like the idea of a parent being your Facebook friend? Why?/Why not?
2 ![]() Read
the text. In your Own words, say Why Dr Wright thinks parents should be
Facebook friends with their teenage children. DO you agree? Why? IWhy not?
Read
the text. In your Own words, say Why Dr Wright thinks parents should be
Facebook friends with their teenage children. DO you agree? Why? IWhy not?
Parents Of boys at a Sydney private school have been urged to monitor their sons' use of Facebook, With a warning that any mistakes made in teenage years could be permanently recorded on the Internet and catch up With them later in life.
The headmaster, Timothy Wright, wrote to parents on Thursday. explaining that younger boys were too to fully gauge the possible consequences of disclosing private information on social networking sites. •We now know that those parts Of the brain that deal With decisionmaking are still developing in a man in his 20s,' he said. •But mistakes made at fifteen may be still by an employer ten years later.
'Modern technology means that a word, a slanderous comment or an inappropriate photograph, are on permanent record and freely available to anyone Who has access. Stupidities that were once forgotten now last, spread and damage in ways unknown before this decade.'
Dr Wright said that harsh words spoken in the playground could be more easily forgotten, but those captured on the Internet or on mobile phone text messages could have far more lasting and more hurtful consequences. He said there was widespread use of Facebook by students, including those of primary school age. which was against the site's guidelines for use.
He urged parents to set ground rules for use Of mobile phones and the Internet and in particular to Set boundaries on taking and sending images that may be used to bully Others. •parents who are paying for the Internet service have an unquestionable right to insist they are a friend on Facebook. I would certainly insist on this until at least the end of year if not later,' he wrote. • Students are usually sixteen at the end ofyear 10.
3 Answer the questions about the text.
I Why does it matter if a fifteen-year-old makes a mistake On Facebook?
2 Why might it be difficult for fifteen-year-olds to think about the consequences of their online activity?
3 Why can online arguments Often be more damaging than playground arguments?
4 What kinds of rules does Dr Wright want parents to make?
5
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 6
6
7
8
highlighted adjectives in the text. Then list the words with a prefix and those with a suffix in the chart below. Which adjective has a suffix and a prefix?
suffixes
|
prefixes |
|
D VOCABULARY BUILDER
9.2: PAGE 142 ![]()
![]() Listen
to a radio journalist talking about
Listen
to a radio journalist talking about
Rebecca Black. Does he think it was a mistake for Rebecca to post the song on YouTube?
Why? / Why not? DO you agree?
Listen again. Are these sentences true m or false
![]() Ark Music Factory charge $4,000 for
recording a song and video, and extra for writing it.
Ark Music Factory charge $4,000 for
recording a song and video, and extra for writing it.
2 Rebecca Black's mother paid for Rebecca to record a Song with Ark Music Factory.
![]() Only 167 people watched Rebecca's video
the first month it was On YouTube.
Only 167 people watched Rebecca's video
the first month it was On YouTube.
4 Most of the people who watched the video on YouTube clicked 'dislike'.
![]() Rebecca was not particularly surprised
by the reaction.
Rebecca was not particularly surprised
by the reaction.
6 The song, Friday, was removed from YouTube but posted again later.
![]() Rebecca travelled to Australia to
publicise her new music video.
Rebecca travelled to Australia to
publicise her new music video.
Look at the online activities below. Do you think they might turn out to be mistakes? Why?/Why not?
You're fifteen years Old and you:
• post a love poem to a girl/boy you like on his/her Facebook page.
• post a funny clip of your friend falling over on YouTube.
• put an invitation to Vour birthday party on your public Facebook page.
• leave a negative comment about a photo on your friend's Facebook page, for a joke.
![]() In pairs, discuss your ideas from
exercise 7. DO you agree or disagree? Give reasons.
In pairs, discuss your ideas from
exercise 7. DO you agree or disagree? Give reasons.
1 95
I can understand a text about ethical problems.
If you had been brought up by a different family, What things about you might be the same or different? Discuss the ideas below in pairs.
appearance education food friends language money religion sport
2 Read the text below about two girls brought up by the wrong families. Which sentence (a—d) is true?
a The parents and children all get on well With each Other. b The children get on better than the parents. c The parents get on better than the children. d None of the people involved get on well.
EXAM TIP
When you read a complex text, it's Often helpful to make simple notes to remind you Of key details. These might even be in the form of a diagram — do whatever is most useful. For example, your notes could show: relationships between characters
• a basic sequence Of events
• the layout Of a place being described.
HOSPITAL MIN-UP
TWO RUSSIAN FAMILIES are united a terrible event that took mote than a decade ago Their newborn daughters were accidentally mixed up in the matM1ity hospital and grew up with the •wrong' parents.
Ina tiny rat in the Ural Mcwntains. Yulia Betyaeva and her twelve-year-old daughter Irina are through family photos.
One Of the pictures shows Irina as a newborn baby wrapped in a blanket. It was taken the day mother and daughter lett hospital But twelve )œars on. Yulia Belyaeva has discwered that the baby she'd taken home — the daughter she'd tMught she'd given birth to — is child
•I found this Out When ex-husband refused to pay maintenance: says Yulia. 'I took him to court to prove that he was IrinaS father We did all the DNA tests. the results were a total surprise Not only dœs ex-husband have no biological link to Irina — neithe I' police believe that 17 December tYEe was a terrible mix-up at the maternity FK)spitaI. Two were given wrong rwne tags — and the wrong gwents,
'At first I thought iiwasa joke,' recalls Yulia. Then I coudn't stop crying.
Whole world turned upside down I kept worrying what Irina would say. And kept thinking about real daughter. Maybe she'd been abancbned put in an orptmage. Or IHhaps she was begging on the streets.
Desperate to fnd her. Yulia to the police and they launched a search for her biological daughter Within weeks they ha' found her.
In a village half hour' five from Yulia BelyaevaS rat lives twelve-year-old Anya Iskandgrova. In a meadow opposite her house. she shows me her favourile cow. April. Anya is the girl Yulia had given birth ta She is spit'ing image Of biologicalyoth
3 Read the Exam tip. Then complete the diagram below With the correct names from the text.
up up
In the rouse is Naimat [Skanderov — the man Anya thought was her father. Nair-nat is frœn Tajikistan He married a Russian woman. but they had divorced. It was Nainat Who brcxght up Anya and his other children as devout Muslims When told him atmt mistake at the maternity hospital and that Arrya was not ms datÀ1ter. to with he refused to believe it.
'Then showed me a Of the other girl. Irina. one they said was my daughw.• Naimat tdE me, •When I saw face. it was like myself arms and legs gnking_ It was awful to think that my child had up with a-.other family and that I had brought up someone else •s daughter.'
The two families meet regularly now. parents admit is tension between them.
"It is difficult.' concedes Naimat 'One family is Christian. the other is Mushm. We have diffuent traditions What I fear mst is daughter I've raised will Start drinking in bars. tMt will praying and working. I'm worried will lose her religiom•
'There is tension tztween adults,' says Yulil 'Naimat doesn't on in Our family. don't like some things in their tune. Both Ofus are to lite as it has t8em Not as it Now it isa nightmare.'
More than anything Yulia tears that both children will desert her, She can see that the daughter she brought up is keen to smd time with her father. And the child she actually gave birth to is like a stranger.
•I try to show Anya mtherly Love.' Yulia says. •But she doesn't it She's bæn brought up differently. She's not used to terderness. We really understand each other. When ytM own daughter looks at like a stranger, thafs so painful.
Both families are suing the Maternity +kyspital mue than in damages. Its chief went on Russian TV to apologise for the mistake. bul argued the hospital could not afford to settle such a claim. prosecutors are considering criminal charges against the hospital staff respons& for the mix-up — alth01Oh that seems WIIikely, so many years have passed
For now the two girls say they do mt want parents They are just glad to have tmjnd each other.
To begin with we were a bit shy, • Irina tells 'but now we've the best Of friends.'
What I'd like.' says Anya. 'is all
Irina Anya born fifteen minutes apart. the truth atmt What happened rospital has brcnnht them togetwr_
Choose the best answers. How did your diagram from exercise 3 help you do this task?
1 Yulia only found out that Irina was not her biological daughter a when they looked at some family photos. b when they got home from hospital. c after twelve years. d after ten years.
2 Yulia's family had DNA tests in order to confirm a who Irina's father was. b Whether Yulia was Irina's mother.
c whether there had been a mix-up at the hospital. d whether a familv member had committed a crime.
3 When Yulia found out about the mistake, she a felt very upset and worried. b thought it was funny at first. c tried not to think about it too much. d was not very surprised.
4 Anya, Yulia's biological daughter. lives with a her biological mother's ex-husband. b her biological father. c Irina's biological father. d her biological parents.
5 Naimat is worried that a Anya Will reject her Muslim traditions. b Anya will want to live With her biological mother. c Irina Will want to come and live with him. d Irina won't want to become a Muslim.
6 Yulia is particularly worried that a Irina will convert to Islam. b Irina Will have terrible nightmares. c Naimat won't approve Of her family.
d neither Anya nor Irina Will want to live with her.
7 What Anya would like best is a to go and live With Irina and Naimat. b to get money from the hospital.
c to prove that the hospital is guilty of a crime. d to live with Yulia, Anya and Naimat.
![]()
meaning Of the underlined phrases below to your partner. TWO Russian families are united by a terrible event My ex•husband refusewtpvay maintenance.
I tank him tn rourt to prove that he was Irina's father.
She is rhe spitting image Of her biological mother.
But the parents admit there is tension between them.
Now it
She's not used to_tenderness.
30th families are suing the KopeyskMatemitYHospital formoretharvS300.ooo in damages. 10 The hospital could not afford to settle such a claim.
![]()
Then underline the noun formed from it.
dropout getaway hold up mixup sell out turn out
7 Form nouns from the other five phrasal verbs in exercise 6. Then write an example sentence for each one.
8 ![]() 3.18
Read and listen to the song. Choose the best adjectives to describe the
singer's feelings. Find evidence in the lyrics for your choices.
3.18
Read and listen to the song. Choose the best adjectives to describe the
singer's feelings. Find evidence in the lyrics for your choices.
conceited Courageous determined heroic optimistic pessimistic regretful ruthless
Miétake
Saw the world turninq in my sheets and again I cannot sleep.
Walk out the door and up the street; look at the stars beneath my feet.
Remember rights that I did wrong, so here I go.
I'm not calling for a second chance,
I'm screaming at the top of my voice.
Give me reason but don't give me choice.
'Cause I' I just make the same mistake again.
And maybe someday we will meet, and mavbe talk and not just speak
Don't buy the promises •cause, there are no promises I
keep.
And my reflection troubles me, so here I go.
I'm not calling for a second chance,
'm screaming at the top of my voice.
Give me reason but don't give me choice.
'Cause I'll just make the same mistake.
I'm not calling for a second chance,
I'm screaming at the top of my voice.
Give me reason but don't give me choice.
'Cause Ill just make the same mistake again.
Saw the world turning in my sheets and once again I cannot sleep.
Walk out the door and up the street; look at the stars.
Look at the stars fall down,
And wonder, where did I go wrong?
9 In pairs, discuss What the four underlined phrases in the song might mean. Then share your ideas with the class.
9
|
Look at a product that |
3 |
Read the Learn this! box. Underline all the examples Of mixed |
|
was invented by mistake. What |
|
conditionals in the text in exercise 2. Is each one type A Or |
|
do you think the inventor was |
|
type B? |
|
trying to make? |
4 |
Match halves the |
|
Choose from the |
|
the two Of mixed conditional sentences. |
|
ideas below. |
|
Then say if each one is type A or type B. |
|
a cleaning product |
|
I If you'd accepted that job at the bank, |
|
food for animals |
|
If she weren't so romantic, |
|
glue |
|
If we were Australian, |
|
a weapon |
|
If you hadn't forgotten the map, If it hadn't rained So much, |
|
, Complete the text with the words below. Then |
|
If your grandparents were alive, |
|
listen and check. |
|
she wouldn't have got married after three months. |
|
could didn't hadn't were would wouldn't |
|
we wouldn't be lost. |
|
'Mistakes are the portals for discovery,' wrote the Irish |
|
c they would have been proud Of your results. |
|
novelist lames Joyce, and it's true that certain mistakes |
|
d we'd have grown up speaking English. |
|
in history have turned Out to be lucky for the people |
|
e you'd be on a high salary by now. |
|
Who made them. Many
familiar |
|
|
|
-their inventors made lucky mistakes. In 1886, a pharmacist's assistant used fizzy water by mistake to mix a |
|
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 9.3:
PAGE 131
|
|
new medicine. The result? Coca-Cola. |
|
LOOK OUTI |
|
Around 1940, a scientist called Dr Percy Spencer |
|
We often use were instead of was in the if clause of a |
|
was doing military research with microwaves when he |
|
second or mixed conditional sentence. |
|
discovered that a chocolate bar in his pocket had melted. |
|
If she were older, they would have let her into the |
|
As a result, he realised
that microwave radiation |
|
nightclub. We use could to mean would be able to (would can). |
be used for cooking. If he hadn't had that candy bar, microwave ovens probably • exist today! If vou hadn't used all the milk, we could have coffee now.
|
Perhaps the most important accidental discovery was |
|
|
|
penicillin.
If today's doctors s |
5 |
Read the Look out! box. Then write mixed conditional |
|
other antibiotics. many of the students in your class |
|
sentences Which express the same information as each pair |
|
wouldn't have survived childhood. We have Alexander |
|
Of sentences below. |
|
Fleming to thank for its discovery. Back in 1928, he noticed |
|
|
|
the drug When it grew by accident in his messy laboratory. |
|
If it summer,
I wouldn't have gone out *ithout |
|
This proves another interesting fact; If scientists s |
|
coat |
|
always tidy and well organised, they wouldn't have made |
|
2 1 can't speak Portuguese. That's why I didn't visit Brazil. |
|
some of the most important discoveries in history! |
|
4 We got on the wrong train. That's why we aren't at |
|
Mixed conditionals A mixed conditional is a mixture of the 2nd and 3rd conditionals. It tells us about an imaginary situation which mixes past and present. There are two types. A When the ifclause is about the past, we use the past perfect. We use would + base form for the main clause. (past) If I hod worked harder at school, (present) I would be rich now. B When the ifclause is about the present, we use the past simple. We use would have ± past participle for the main clause. (present) If I were reallytall, (past) I would have joined the basketball team. |
|
Heathrow Airport now.
![]() I don't eat meat. That'S Why I didn't
go to the barbecue last weekend.
I don't eat meat. That'S Why I didn't
go to the barbecue last weekend.
6 It didn't snow again after the burglary. That's why the burglar's footprints are still visible.
6 ![]() Work
in pairs. Complete the sentences with your own ideas. Then discuss them With
another pair.
Work
in pairs. Complete the sentences with your own ideas. Then discuss them With
another pair.
I If mobile phones hadn't been invented,
people today would/wouldn't ![]()
2
If
my family were billionaires, I would/wouldn't have ![]()
3
If
I had studied harder since the age of six, I would/ wouldn't![]()
I can role-play a conversation about a mistake.
3 3.20 Read the Exam tip. Then listen again, and in pairs try to write the key words for each candidate.
|
candidate: |
|
|
|
||||
|
what the item is |
|
|
|
||||
|
the reason for the mistake |
|
|
|
||||
|
how you feel about it |
|
|
|
||||
|
what you'll do next |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Expressing regret We can use these phrases for expressing regret about the past: / (really) Wish / had/hadn't (seen it). If only I had/hadn't (spoken to her). I'd rather / had/hûdn't (been there). When the verb is can, we normally use could have or had been able to.' / wish could have helped/had been able to help. |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
Describe the photo in pairs. What do you think might happen next? Use the words below to help you.
accuse alarm item Of clothing security guard shoplift shoplifter thief
2 Work in pairs. Listen to three candidates doing the task below. Which candidate performs best, in your opinion? Discuss your reasons.
After you and a friend have been shopping in London, you realise that you have an item of clothing in your bag which you didn't pay for. You're discussing the situation. Address the following issues:
• what the item is.
• the reason for the mistake.
•
how you feel
about the situation. ![]() what you'll do next.
what you'll do next.
|
EXAM TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Make sure you clearly say something about all tour issues in the task. You Will lose marks if don't. Look carefully at the four issues before the conversation Starts and think Of One or two key words for each issue. Then tick them Off in your mind as you mention them during the conversation. |
|||||||
4 Read the Learn this! box. Then imagine you are one of the candidates from exercises 2 and 3. Use two different structures to express two regrets about the situation.
5 Rewrite sentences 1—5 using the words in brackets. Don't change the meaning.
I If only I'd put the T-shirt on the floor. (wish) 2 1 wish I hadn't answered the phone.
3 1 Wish the alarm had gone Off. (rather)
4 If only I'd looked in my bag earlier. (Wish)
5 1 Wish hadn't gone into that shop. (in
6
If Only I'd done
my shopping online. (rather) D GRAMMAR BUILDER 9.4: PAGE 131 ![]()
6 Look at the speaking task below. Then write down one key word for each Of the four issues.
During a day in town, you picked up somebody else's phone by mistake. You're discussing the situation with a friend.
Address the following issues;
• the reason for your mistake.
• the best to find the phone's Owner.
• how you feel about the situation.
• What you'll do next.
7 Think oftwo regrets you can include in your answer to the
task in exercise 6. Make a note of them using two different structures from the Learn this! box.
![]() DO the task in pairs, taking turns
to be the candidate and the examiner.
DO the task in pairs, taking turns
to be the candidate and the examiner.
Candidate: Use your notes from exercises 6 and 7. Examiner: Check that the candidate addresses all four issues in the task.
9
I can write a story on a given topic.
It Was a Saturday night in January and I was On my way to a sleepover at Nathan's house. I'd never been to his house before, but I'd been sent the address by text: 39 Western Avenue.
As I turned the corner into Western Avenue, a cloud went in front of the moon. Was this next house Nathan's? It was so dark now that I couldn't see the numbers clearly, but I walked up the driveway anyway, rang the bell and waited. Nobody came to open the door so I rang again. Then I saw I had gone to number 37 by mistake.
Read the task below and the Story above in pairs. Explain in your own words What mistake the main character makes and Why it turns out to be a good thing.
Write a Story in which the main character makes a mistake which turns out to be a good thing.
2 Put the events Of the story in the order they happened.
![]() •a
The narrator arrived in Western Avenue.
•a
The narrator arrived in Western Avenue.
![]() The narrator called the police.
The narrator called the police.
![]() The front door opened and two men ran
out.
The front door opened and two men ran
out.
![]() The narrator was Sent Nathan's address.
The narrator was Sent Nathan's address.
![]() Two detectives arrived at the scene of
the crime.
Two detectives arrived at the scene of
the crime.
![]() The narrator rang the bell of 37
Western Avenue. g The narrator picked up a brooch.
The narrator rang the bell of 37
Western Avenue. g The narrator picked up a brooch.
|
Talking about mistakes 1 We can use these phrases for talking about mistakes: to make a mistake (doing something) to do something by mistake/bv accident to get something wrong (e.g. / got her name wrong.) the wrong + noun (e.g. phoned the wrong person.) mistakenly (e.g. / mistakenly paid twice for the tickets.) 2 We add the prefix mis- to some verbs to show error: I misread/misheard/misspe/t/mistvped his address. They misjudged/misunderstood/misquoted me. |
|
3
![]() Read the Learn this! box. Then complete
the second sentence so it means the same as the first. Include a word or phrase
from the Learn this! box.
Read the Learn this! box. Then complete
the second sentence so it means the same as the first. Include a word or phrase
from the Learn this! box.
1 1
didn't put the correct address on the envelope. ![]() the
envelope.
the
envelope.
2 She didn't mean to mention her party on Facebook.
She![]() on Facebook.
on Facebook.
3 They didn't spell my name correctly on the poster.
They on the poster.
4 We didn't mean to get on that train.
5 He didn't understand the instructions properly. the instructions.
Then the door opened abruptly. There were no lights on in the house so I couldn't see much. There was a shout and a man pushed past me and ran towards the street. Another man followed. They were in such a hurry to leave that they dropped most of the things they were carrying. I picked one of them up so I could look at it more closely. It was a brooch. Suddenly, I understood what had been happening and phoned the police.
![]() After waiting for five Or ten minutes
on the doorstep, an unmarked police car arrived and two detectives got out. One
Of them went into the house so that he could 100k for clues while the other
asked me for a description Of the men. 'You did well,' he said. 'It really was
heroic Of you to those burglars and chase them away.'
After waiting for five Or ten minutes
on the doorstep, an unmarked police car arrived and two detectives got out. One
Of them went into the house so that he could 100k for clues while the other
asked me for a description Of the men. 'You did well,' he said. 'It really was
heroic Of you to those burglars and chase them away.'
|
EXAM TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
It's important to find a good ending for your Story. You could finish with: a surprise Or a revelation It turned out Our cleaner was really o spy! • something Which links back to the beginning Of the Story so finally, found the book I'd been searching for. • something Which links the Story to the present And
now, years later, I still think about her every day. |
|||||
4 Read the Exam tip. Then choose the best ending for the Story in exercise I from below. Think about why you prefer it. There is no correct answer.
![]() •Oh, I don't need a reward,' I replied,
putting my hand in my pocket to feel the diamond brooch.
•Oh, I don't need a reward,' I replied,
putting my hand in my pocket to feel the diamond brooch.
b The detectives put everything the burglars had dropped in a bag, got into their car and drove away. As they left, a police officer arrived on a motorbike. 'Did you call the police?' he asked me.
c I still think about that night Often and wonder if it was heroic Of me or just foolish!
d There was the noise of an engine starting, and I turned round just in time to see the burglars drive Off in the police car, laughing and waving out Of the Window.
5 ![]() Discuss
the ending in pairs. Do you agree which ending is best? Can you think Of a
better one?
Discuss
the ending in pairs. Do you agree which ending is best? Can you think Of a
better one?
|
|
Expressing purpose and result
went into town to buy/in order to buy a coat. The phrases with a view to and With the intention Of express purpose and are followed by an •ing form. went to the police station with the intention of complaining about my noisy neighbours. We can also express purpose With in orderthat, so that or so followed by a clause. He stood on a chair in order that / so / so that we could 011 see him. We can express a result with so (but not so that) The café was closed so I went home.
She was so tired that she fell asleep immediately. It was such a small bed that j fell out. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
You are going to do the writing task on page 100.
Read the Exam tip below, then work in pairs and think Of some more ideas for types Of mistakes. Make notes.
EXAM TIP
Brainstorming is the first Stage Of writing a Story. You need to think of several different ideas and write them down. You can then choose the best and use them in your story. Mistakes wrong bus / train / plane late for school / exam send text/email to wrong person fall over spelling mistake mistake With recipe when cooking
2 Discuss your ideas from exercise I and try to think how each Of the mistakes could end up being a good thing. Reject the idea if you can't think Of anything.
3 Match the two halves Of these Story ideas. Which do you
|
think is the best? Are any Of your ideas from exercise 2 better, |
|
|
|
in your opinion? |
5 |
Read the Learn this! box. How many purpose and result clauses can you find in the story in exercise I on page 100? |
![]()
![]() You
miss your train because you're late.
You
miss your train because you're late.
![]() You
mean to send a message to your friend about X, D GRAMMAR BUILDER 9.5; PAGE 132
You
mean to send a message to your friend about X, D GRAMMAR BUILDER 9.5; PAGE 132 ![]() a
girl/ bov you fancy, but you send it to Y by mistake.
a
girl/ bov you fancy, but you send it to Y by mistake.
6 Combine
3 At the theatre. you can't find your friends becauseeach pair of sentences into a single sentence that you're sitting in the wrong seat.brackets. or purpose clause. Include the word in
![]() includes a result
includes a result
![]() You
fall over While demonstrating your snowboarding skills to a friend. I It was a
cold night. I didn't want to go out. (such)
You
fall over While demonstrating your snowboarding skills to a friend. I It was a
cold night. I didn't want to go out. (such) ![]() It
gas such a
It
gas such a
5 While making a birthday cake for a friend, you getTia wanted to cold see night us. We that went I didn't into want London. to go (order)out.
2 the ingredients completely wrong. ![]() We
left the cinema. We weren't enjoying the film. (so)
We
left the cinema. We weren't enjoying the film. (so)
|
|
|
|
CHECK YOUR WORK
followed your writing plan? written 200-250 words? included an effective ending? included at least one of the expressions for talking about mistakes in the Learn this! box On page 100? included at least one purpose or result clause? ecked ygur spelling and grammar? |
|
notes using the headings below or a similar writing plan. Remember the advice in the Exam tip on page 100 about endings.
![]() Setting
the scene (where? when?):
Setting
the scene (where? when?):
![]() The
mistake (What? Why?):
The
mistake (What? Why?):
![]() The
result (why was it good?):
The
result (why was it good?): ![]() The ending:
The ending:
9
9 Get Ready for your Exam
could go wrong when going on holiday by plane.
2 DO the exam task.
|
LISTENING exam task |
Listen to an account Of a holiday full of problems. For each Sentence select the appropriate Option: A, B, C or D.
I The first problem with their trip was that A the tickets were very expensive.
B the family went to the wrong airport.
C they had to change airlines.
Dthe time Of their flight was changed.
2 In St Maarten
A the family had to phone all the airlines one by one.
B the airport officials were not very eager to help.
C they realised they had left some luggage on the plane.
D they were relieved to have the basic necessities.
3 Which sentence is true about the cruise?
A was delayed So the family had to wait a few days.
B Although everyone was a little upset, it was wonderful.
C They had to buy new equipment before joining it.
D They had to wear dirty clothes.
4 When the cruise was over.
A they felt the airlines should give them some money.
B the airport staff said some new baggage had arrived.
C all their luggage was waiting for them in the Storage
D the family had to sit in the airport for a long time again.
3 Do the exam task.
|
USE OF ENGLISH exam task |
Complete each gap in the text with a word formed from the word in brackets.
Technically, an outtake is any part Of a film or a programme that is removed in the final cut. However, outtakes have now come to represent the humorous mistakes made in the process Of filming. The (INCLUDE) Of outtakes in a film started with the actioncomedy film Hooper in 1978. The director wanted to show various angles Of the film's (IMPRESS) Stunts in the end credits. He also included funny
Get Ready for your Exam 9
mistakes by the actors, which proved so popular With audiences that subsequent films copied this. Now there are TV shows dedicated to these outtakes. Why are we so enamoured with these •bloopers'?
Actors are often not keen to be seen making mistakes. Obviously, it's embarrassing for them to seem silly and (PROFESSION), Which is probably why we, the audience, love seeing famous people getting it wrong. It makes them seem more human and a lot less • (GLAMOUR)! Everyone can identify With saying the wrong thing at the wrong time, or having to do something (REPEAT) because it just won't go right. And someone knocking into things Or falling over (INTENTION)? That has always made us laugh. Professional circus clowns have taken this one step further. Their Whole performance is comprised Of these classic 'bloopers'.
4 two groups: (1) making a complaint and (2) responding to a complaint.
a I'm afraid I'm not at all happy about b Leave it with me and I'll see what I can do. c I'm afraid there's nothing I can do about that. d I'll do what I can, but I can't make any promises. e I'm sorry, but this really isn't acceptable. f I'm afraid that just isn't good enough.
5 DO the exam task.
![]()
SPEAKING exam task
![]()
You and two relatives are staying at a hotel that has made several mistakes with your reservation. Speak to the manager about these problems:
Your two hotel rooms are too far apart. You have been given two double rcn)ms instead Of one double and One single.
• You asked for quiet rooms but they overlook the street.
• You booked for five nights but have been told the rooms are only available for three nights.
|
description, identify the venue and two pieces Of sports |
Sports equipment ball bat board cap club cue flag goal gloves goggles helmet hoop net pads puck racket shuttlecock skates strip stick wetsuit
2 ![]() In
pairs, underline the words in exercise I that you didn't use. In What sports
might you use these things? bat — baseball. table tennis.
In
pairs, underline the words in exercise I that you didn't use. In What sports
might you use these things? bat — baseball. table tennis.![]()
3 ![]() Complete
the list Of sports venues using the words below. Can you also add the person
Who does each sport?
Complete
the list Of sports venues using the words below. Can you also add the person
Who does each sport?
circuit course court pitch pool ring rink slope table track
equipment mentioned.
|
EXAM TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
When you answer a true / false question, don't mark the sentence as true just because you recognise some Of the details. Remember that the answer is only true if the Whole Of the sentence is true. Ifit contains any false details, the answer is false. |
|
|||||||
6 Read the Exam tip. Then listen again and mark the sentences true (T) or false (F). Which sentences contain One or two true details but are still false?
1 A dog ran on during the match and one of the linesmen caught it.
2 A golfer sneezed at the same time as playing a shot and ended up playing a bad one.
![]() The winner of the race was angry with
another competitor.
The winner of the race was angry with
another competitor.
4 A young boy played a few points because the professional was angry with himself.
5 When the fight started, the Other players didn't try to stop it.
7
![]() Work in pairs. Imagine you are setting
up a sports summer camp for teenagers. You can buy six different items Of
sports equipment. Which Will you choose?
Work in pairs. Imagine you are setting
up a sports summer camp for teenagers. You can buy six different items Of
sports equipment. Which Will you choose?
8
![]() Compare your ideas With Other pairs.
Give reasons
Compare your ideas With Other pairs.
Give reasons
for your choices. Explain Why you are rejecting Other items.
D VOCABULARY BUILDER 10.1: PAGE 143 ![]()
10 Gameon!
3 Rewrite the sentences you underlined in the message board without emphasis.
1 1'm looKing forward to watching Torah Bright.
LOOK OUT!
![]()
After
All or What (I) did was we use an infinitive with or
|
|
|
without to. What she did was (to) finish the course on one ski. However, after All that / What happened was we need a subject and a verb. We can put that before the subject: All that happened was (that) they deducted five points. |
|
message board |
4 |
Read the Look out! box. Then rewrite the sentences With |
|
The person I'm looking forward to watching is Torah Bright. |
|
or All (that) at the beginning. |
|
Its her technique that I really admire. Australians are lust |
|
1 They had to postpone the snowboarding final because of |
|
natural She'll Win gold. I'm sure. SHREDDER |
|
the weather. (What |
|
Not Sure I agree atl)ut Torah, Shredder. Aimee Fuller Who |
|
2
They just held the final the next morning. (All |
|
has shown the best form in the first half of the season. Al |
|
3 There was a snow storm. (What . J |
|
she needs is a bit Of luck. ROXY |
|
4 Nobody could see the snowboarders in action. (What m) |
|
I big Aimee fan too. Whats amazing is that she's from Northern Ireland, a country with no mountains! HOW she |
|
5
So they just turned the floodlights on. (All |
|
learned to snowboard in the first place I really don't knowl |
|
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 10.1:
PAGE 132 |
|
Its no mystery, Dreamer. What happened was that she went |
5 |
Rewrite the sentences below starting with the words in |
|
to live in the USA for a few years as a teenager. ThatS where |
|
brackets. use Structures from the Learn this! box in exercise |
|
She learnt to snowboard. ROW |
|
2 and the Look out! box. |
|
Aimee Full¾? No way will she win. The person with the best |
|
The spectators were most excited about seeing the young |
|
chance. in my opinion. Cilka Sadar. SheS from Slovenia. |
|
Czech snowboarder.
(The person |
|
What gives her a big advantage is that she used to be a |
|
2 The Czech girl had the best chance Of winning the event. |
|
gymnast, She has bts of strength and stamina. GOO" |
|
(It was 3 She just needed to finish the course without falling. (All
|
|
1 Read the snowboarding message board. What are the names |
|
4 She lost her board within ten seconds of starting the |
|
and nationalities of the different snowboarders it mentions? |
|
course.
(What |
|
Have you heard Of any Of them? |
|
5
A crowd has rarely looked so disappointed. (Rarely |
|
2 Read the Learn this! box. Underline all the examples of these |
6 |
|
|
Structures in the message board. |
|
answers with the words in brackets and use structures from |
the Learn this! and Look out! boxes.
|
|
Emphasis and inversion I We can make a Sentence more emphatic by adding an extra clause to highlight kev information. It The person feel sorry for is Eva. (I feel sorry for Eva.) All we need to do is (to) ask. (We just need to ask.) What happened was (that) it began to rain. (It began to rain.) 2 We can also make a sentence more emphatic by putting important words at the start. After a negative adverb or phrase, the subject•verb word order changes. Never had I seen such on exciting game. Under no circumstances was / going to leave early. |
|
|
|
|
|
I Which sports Star do you
most admire and why? (The sports star![]()
2 How can sports stars be good role models for young people?
(What they need m)
![]() What should sports Stars never do, in
your opinion? (Under no circumstances ...J
What should sports Stars never do, in
your opinion? (Under no circumstances ...J
![]() Can you describe the last time you
watched or played sport?
Can you describe the last time you
watched or played sport?
(What I did / What happened![]()
![]() Which sport is the easiest to start
playing/doing? Why? (I think is the easiest because all you need
Which sport is the easiest to start
playing/doing? Why? (I think is the easiest because all you need ![]()
104 Gameon!
List the following people in order Of income, from
the highest earning (1) to the lowest (4). Then list them in the order you think they should be. Are your lists different?
a P.E. teacher C] atop footballer:
a TV sports commentator:] a top triathletet::::]
![]() 2
2
3 appropriate words.
The top ten sports stars 1 ![]() the
world, from disciplines as diverse tennis. golf, racing and football, all earn
more than $30 million a year. Much this is from endorsements rather than prize
money or salary, with the result that the biggest names can continue earning
huge sums even after their retirement the Sport.
the
world, from disciplines as diverse tennis. golf, racing and football, all earn
more than $30 million a year. Much this is from endorsements rather than prize
money or salary, with the result that the biggest names can continue earning
huge sums even after their retirement the Sport.
![]() A
previous England football manager, Fabio Capello, believed that the players'
high earnings 5
A
previous England football manager, Fabio Capello, believed that the players'
high earnings 5![]() a negative effect on discipline. 'They
are young players, young boys, rich boys and this is the problem,' he said.
Basically, it was impossible for young players to have the right work ethic and
attitude when they were already rich beyond their childhood dreams. And one Of
the most famous footballers Of recent years, David Beckham, agrees 6
a negative effect on discipline. 'They
are young players, young boys, rich boys and this is the problem,' he said.
Basically, it was impossible for young players to have the right work ethic and
attitude when they were already rich beyond their childhood dreams. And one Of
the most famous footballers Of recent years, David Beckham, agrees 6 ![]() him.
In his view, young sportspeople need to be hungry for achievement — and too
money kills that hunger. 'You want that hunger there, you want the hunger to be
rewarded. Unfortunately, that's not the case these days. They can all afford to
buy Own cars.' Mind you, if it's taken you five minutes 9 read this article,
Beckham himself has earned more than $1,000 you began it!
him.
In his view, young sportspeople need to be hungry for achievement — and too
money kills that hunger. 'You want that hunger there, you want the hunger to be
rewarded. Unfortunately, that's not the case these days. They can all afford to
buy Own cars.' Mind you, if it's taken you five minutes 9 read this article,
Beckham himself has earned more than $1,000 you began it!
It isn't only the players Who are
affected by commercialism; the top few clubs in all the most popular sports are
now big businesses, With multi-million dollar sponsorship and n,' deals. Since
this allows them to buy and keep the best players, their position ![]() top
becomes unassailable. But long can a sport survive when there is no real
competition?
top
becomes unassailable. But long can a sport survive when there is no real
competition?
Look back at the Exam tip in Lesson A. Then decide if these sentences are true or false, according to the text.
1 Most top sportspeople earn over $30 million a year from endorsements.
2 Fabio Capello believes his players were too young to be well-disciplined.
3 David Beckham believes rich players have less desire to
4 David
Beckham earns more than $200 a minute. ![]() There
is less competition in Sport these days because there are fewer clubs.
There
is less competition in Sport these days because there are fewer clubs.
6
![]() 7
7
8
9
correct suffixes.
I achieve_ 3 earn— 5 commercial.
2 retire_ 4 child_ 6 sponsor![]()
D VOCABULARY BUILDER
10.2: PAGE 143 ![]()
03.24 Listen to five people giving their opinions ofthe role of money in sport. Which speakers think in general that some sportspeople are paid too much?
 3.24
Listen again. Match the sentences speakers (1—5). There are two extra
sentences.
3.24
Listen again. Match the sentences speakers (1—5). There are two extra
sentences.
A It's OK for sports stars to earn a lot of money provided they give to charity and help less fortunate people.
B
Sports
stars' massive earnings may not be deserved, but they're inevitable since Sport
generates so much money. ![]() People who complain that sports stars
are overpaid are basically just jealous of their wealth.
People who complain that sports stars
are overpaid are basically just jealous of their wealth.
D Other people earn even more than
sportspeople, who Often cannot work for more than a few years. ![]() There
are other jobs which deserve far greater financial rewards than playing
professional sport.
There
are other jobs which deserve far greater financial rewards than playing
professional sport.
F Today's sports stars have lost touch with the general public and are more interested in money than sport.
G It's unfair for some people to earn so much money when others in Our societies have nothing.
![]()
Complete the phrases used by the speakers to introduce statements and opinions.
ask doubt face fact line 100k see thinking
![]() Introducing
statements and opinions The
Introducing
statements and opinions The![]() TO
my way Of' _ so, basically
TO
my way Of' _ so, basically![]() There's no Personally, I think
There's no Personally, I think![]() The
way
The
way
If you![]() Let's
Let's
The wayl![]()
![]() In pairs, discuss all the ideas in
exercise 7. DO you agree or disagree? Give reasons. Use at least three phrases
In pairs, discuss all the ideas in
exercise 7. DO you agree or disagree? Give reasons. Use at least three phrases
from exercise 8 in your answers.
10
I can understand a text about ways to boost performance.
1 Ask and answer the questions in pairs. 1 Do you ever drink energy drinks or eat energy bars?
DO you think they work?
2 Do you wear anything (bracelets. crystals, etc.) which has been designed to improve your health?
3 Ifyou hurt your leg running or playing sport, which of the following would you be most likely to do? a rest it c take painkillers b put ice on it d nothing
2 Look quickly through the text opposite. Is each section (I —5) about something you (a) wear? (b) eat? or (c) lie in?
3 For each paragraph (1—5) choose the best summary (A—B. There is one extra Summary.
A This can definitely increase the speed Of recovery from minor injuries by increasing blood circulation.
B Tests have shown that this can increase an athlete's ability to use oxygen more efficiently. This product can improve performance partly by making you look more intimidating.
D Used immediately before exercise. this
has been shown to increase stamina and performance. ![]() Not
only will this aid the recovery of your muscles after exercise, but it will
also replace lost nutrients.
Not
only will this aid the recovery of your muscles after exercise, but it will
also replace lost nutrients. ![]() While this product is intended to boost
the amount Of oxygen taken in during exercise, there's little evidence that it
works.
While this product is intended to boost
the amount Of oxygen taken in during exercise, there's little evidence that it
works.
context to work out the meaning and match them with the correct definitions.
Anatomy circulation fibres ligament long-sightedness lungs passages short-sightedness sweat swelling
|
they to boost her powers of reccwery so she was fully primed for her race. A 50 g serving of cashews provides one-fifth of a womang daily iron requirements and arcn.Jnd one-tenth Of a mans nuts are a rich source of dietary protein — needed to enhance the recwery process of muscles after mtense activity,' says Jeanette Crosland. consultant dietician to the British Olympic Association. Nuts also provide carbohydrate and essential minerals. including Il)tassium in sneat, which makes them a Very Snack. 2 Ice baths Taking a dip a bath tub filled with icecold water is among the most fashionable therapies in sport at the moment. Believed to alleviate muscle soreness and tissue swelling that occur after hard exercise, it speeds up recovery. Some England players have taken the obsession to extremes by visiting a cryotherapy chamber (essentially a human deep freeze) at an Olympic training centre in Poland. They spend four minutes shivering at minus 120—160 degrees Celsius, Expert verdict: 'Ice obviously cools the area it is applied to. Once the body senses the drop in tempMature, it sends more blood to the area which boosts circulation and up healing.' says sports physiotherapist Jill Hendry. 'Sometimes tiny tears to muscle fibres and ligaments after a hard workout. and ice can help to heal them.' |
|
|
: an increase in size of part ofthe body, often caused by injury
: tiny. thin pieces of tissue in Vour body
: moisture which your skin produces when you are hot and/or exercise intensively
: a short piece of tissue in your body that connects two bones
: a condition in Which you cannot clearly see
Objects which are close to you
: the organs which transfer oxygen from the air to your blood
: the movement of blood around the body any tubes in your body for air, food etc. to move through
: a condition in which you cannot clearly see
Objects Which are far away
106
Professional will go to extraordinary lengths to gain an edge over their rivals. Increasingly, this means using a bizarre
Of tools to boost their speed, strength and stamina. But, for those who want to emulate the pros and boost their performance, what really works? GETTING
Kelly
Holmes. Britain's double-Olympic gold medalliSt, said cashew nuts were her weapon
in warding off fatigue at the Athens Olympics. Cashew nuts are my little
secret.' sne said. adding that
Developed wer eight years, the MaxSight contact Þns is designed specifically to imprcve the Sharpness of an athlete's visbn. lenses are currently being tested AC Milan players and use what the developers call 'Light Architecture' optics to filter specific wavelengths of light in order to •enhance key visual elements' - such as a ball — at the same time as reducing sun glare. A vision cmsultant developed amber lenses for tennis. football and rugtw, or grey for running. cricket and golf. which. according to tt"2 marketing literature. •makes the eye look competitive' (i.e. freaks out your opponents).
Expert veract: They have been approved by Americas and Drug Administration for daily wear to correct short- and long-sightedness.
•They could offer an advantage Over normal lenses for sport the glare Ot light and sun.' says Inuise Sutton. principal lecturer in
Health and Exercise Science at Leeds Metropolitan University.
|
|
5 |
Add the words from exercise 4 to the correct |
|
They look like sticking plasters and were developed |
|
part of the chart below. |
|
to help people with health |
|
A parts of the body |
|
problems like excessive snoring, but in recent years Breathe Right nasal strips |
|
muscles. bones. |
|
have gained in popularity among who |
|
normal functions of the body |
|
believe that they improve air-low through the nose and into the lungs. They can |
|
digestion. breathing. |
|
Often been seen worn by |
|
iniuries and problems with the body |
|
professional footballers and other athletes. Exe.t •Although we breathe mainly through our nose when resting. |
|
bruise, sprain |
|
during exercise when we begin breathing harder, the air coming in is predominantly supplied via the mouth.' says Sutton. 'It |
|
add to the chart in exercise 5 in three minutes? |
|
may improve airflow through the nasal passages, but there is no |
7 |
Choose one technique from the text that you would like to |
|
evidence that it reaches the lungs and boosts performance: |
|
try and one that you wouldn't. What are your reasons for |
|
Low oxygen tent |
|
choosing and rejecting those two methods? |
|
Exposure to thin, mountain air has long been known to benefit |
8 |
Discuss your ideas from exercise 7 With your |
|
competitors in endurance events like cycling, running and triathlons because it helps the body to adapt to using Oxygen |
|
partner. Use the phrases below to help you. |
|
more efficiently. A five-year study by the US Olympic Committee confirmed that people who live at high altitude and train for sport at low altitude perform better. Manufacturers have now |
|
would/wouldn't be keen On tryingX because |
|
developed hypoxic (IcwoxygenJ tents to simulate this effect. Expert veract: Stephen Day, an exercise physiologist at |
|
would/woutdn't interest me because |
|
Staffordshire University, carried out tests on elite runners to See how effective sleeping in a Iowoxygen tent can be. •We assessed numerous parameters and found that one elite |
|
I'd rather not try X because |
|
athletes aerobic capacity improved by a massive during several months Of sleeping in a low-oxygen tent; he says. |
|
sounds as ifitwould be |
I don't think I could be bothered
10
I can use the unreal past and 'had better'.
Read the dialogue. Who is less keen to go to the gym, Ava or Bella? DO you agree or disagree With her reasons? Why?
Bella There's a new leisure centre in Western Road. I'm thinking Of joining so can go to the gym and get fit. Ava Really? It's time I got fit. But I don't like gyms. Everyone's so image-conscious.
Bella What do you mean?
Ava They're all posing in front of the mirrors. They act as if they were contestants in a beauty contest.
Bella Well. I'd rather they didn't have all those mirrors. But it doesn't really bother me.
Ava I just don't feel relaxed. Bella Suppose we went together. You'd enjoy it more if you were With someone.
Ava Yes, maybe. But running on a treadmill is so boring!
Bella Stop making excuses. Imagine if we went to the gym every day after school. We'd both be so fit!
Ava Oh, OK. I'll give it a go. Is it expensive to join?
Bella No, it's really cheap if you're under eighteen. Shall we start tomorrow, then?
Ava I'd soonerwe left it until after our exams.
Bella But they're weeks away! I'd better join on my own. You can decide later.
2 Read the Learn this! box. Find and underline all the examples of the unreal past in the dialogue.
The unreal past
We use the past simple after certain expressions even though the meaning is present or future.
It's (high) time we went home.
I'd rather my brother weren't here.
I'd Sooner you paid for your own ticket.
Imagine (in you lived here!
Suppose vou gave me your phone number.
He acts as Was though / were his servant!
Note that we normally use were instead Of was in this kind Of sentence.
3 Rewrite the sentences below using the unreal past and the phrases in brackets.
I I'd prefer him to meet me at the arena. (I'd rather)
2 think we should go swimming again. (It's high time)
3 She'd prefer me to Stay at home this afternoon. (She'd sooner)
Please don't tell anyone about this conversation. (I'd rather)
5 1 don't want you to pay for my ticket. (I'd sooner)
6 Why don'tyou try sending her a text message? (Suppose)
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 10.2: PAGE 133
had better/ might as well
I We use had better (not) or might as well to give advice Or warnings and sav What the best course Of action is.
2 Had better implies that not following that course Of action will have bad consequences. We often use or + will to talk about those consequences.
She'd better apologise for missing the class or she'll have to see the head teacher.
You 'd better not forget my birthday!
3 Might as implies that the course of action is unappealing but there is no better option.
We'll never find it. We might as well give up.
4 Study the Learn this! box. Then give advice or warnings to these people using had better (not) Or mightas well.
•Some Of my brother's friends are planning a surprise birthday party for him.' better not tell him about
2 •I've had this cough for three months now, and I think it's getting worse.'
3 'I've had these jeans foryears. They're too small for me
4 'This prawn salad smells a bit funny.'
5 •I didn't realise we had an exam today until I got to school.'
6 •I borrowed a friend's white T-shirt and got tomato ketchup on it.'
•We're so late, we've missed three quarters ofthe film!'
D GRAMMAR BUILDER 10.3: PAGE 133
5 Complete the second sentence in each pair so that it means the same as the first. Include the word or words in brackets.
I I think we should travel by boat. by boat. (sooner)
Saying sorry for insulting her is the best thing to do. for insulting her. (better) He seems to think he Owns the school!
He acts the school! (as though) I'd prefer you to come with me to the gym. to the gym. (rather)
We should buy a new car — ours keeps breaking down. — Ours keeps breaking down. (time)
6 The party's over, so there's no point in staying.
The party's over, So we home. (might)
6 Work in pairs, taking turns to be A and B. Student A: Invent another problem or situation like the ones in exercise 4. Tell student B.
Student B: Listen to student A and give advice or a warning
using had better (not) or might as well.
3.28 Listen again. Which phrases do the two candidates
|
EXAM TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
It's easier to give a full description of a photo if you create a logical structure in your mind, rather than mentioning random details as they occur to you. For example: 1 overall scene and location 2 main focus of the photo 3 clothes and Other props 4 expressions and actions. |
|||||||||
2 3.26 Read the Exam tip. Then listen to candidates describing the photo in exercise I. Which description (I or 2) follows the advice better, in your opinion? Is the structure the same as in the Exam tip?
3 3.26 Listen again. Complete the useful expressions for referring to things in the photo you can't see clearly.
Describing unclear details
Their faces are of
focus![]()
The instructor is out Of 2![]()
I
can
just out a few more faces ![]()
![]() although it isn't
although it isn't ![]()
![]() although
her face is partly
although
her face is partly ![]()
![]() because his _ is blurred.
because his _ is blurred.
4 Read the examiner's three questions for the photo in exercise I. In pairs, discuss the first question and make notes of your ideas.
I Why do you think the people in the photo are using we'ghts in an exercise class?
2 Do you think it's important to be physically fit? Why do you think so?
3 Tell me about some physical exercise that you did recently.
5 3.27 Listen to the first candidate answering the first question. Does she mention your ideas from exercise 4?
LOOK OUT!
If an examiner's question has two parts. make sure you answer both. If you have to give an opinion, you Will get better marks if you justify your opinion.
6 Read the Look out! box. Then listen to both candidates answering question 2 from exercise 4. Which answer is better, in your opinion? Why? (There is no correct answer.)
![]() use
to Structure their answers? Write 1 or 2 next to the phrases.
use
to Structure their answers? Write 1 or 2 next to the phrases.
Phrases for structuring an answer
First and foremost,
For a start,
Secondly,
And thirdly,
Also. let's not forget
![]() And
most importantly'
And
most importantly'
8 3.29 Listen to candidate 2 answering the third question from exercise 4. In What order does he give the following
information? What would a better order be, in your opinion?
a where it happe ned d an interesting incident
b when it happened e your overall opinion Of it now
c how you felt then f who was there
9 Do the exam task below in pairs. First, describe the photo. Then answer the questions I —3.

I Why do you think they are wearing helmets?
2 What positive effects, mental and physical, could rafting have, in your opinion?
![]() Tell me about something you found
difficult but managed to do successfully in the end.
Tell me about something you found
difficult but managed to do successfully in the end.
10 1409
|
of an event I can write a description of an event. The Only time I've been to a professional basketball game was last winter in New York. I was on a bæak with my parents and my cousin Connor, who lives in Boston. Connor, who's a real sports fæl, was desperate to see the Knick-g play at Madison Square Garden, I wasn't so keen but I agreed to go along — and I'm glad I did because it was the best evening of the holiday! We arrived at Madison Square Carien about an hour before the start of the game and went straight to our seats, In the front rcw sat dozens of Knick-g fans all dressed in the team calourg_ My cousin explained that it was a crucial game, one that the Knick-s really needed to win. He was feeling nervous and go were thousands of other fans the match started, the crcwd went Wild. They were cheering e'æry point. Far most of the match the Knicks were neck and neck with their opponents, the New Jersey Nets Ten secondg from the end, the Knicks had a free throu to win the game. Vffien the ball went through the hoop, the arena erupted, The Knick-g had vnn! And then it was time to leave. Into the cold night air went, surrounded by ecstatic fans, The excitement and adrenaline rush meant |
Describe the photo. DO you think this is an amateur or a professional game? Why do you think so?
2 Read the task and the description below. HOW well does the description address the underlined parts of the task? Give examples to support your opinion.
Write a description Of a sporting event, amateur or professional, that you remember for its great atmosohere and excitement.
3 In pairs, decide where the paragraph breaks should come in the text. In this text, there should be four paragraphs.
|
EXAM TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A description Of an event needs a clear, chronological structure — for example: A Set the scene — where? when? who with? B The build-up to the event — atmosphere, feelings, etc. C The event itself— focus on key moments D After the event — how did it affect you? Make sure your description matches the task and includes any specific information requested. |
||||||||
4 Read the Exam tip. Then 100k again at your answer to exercise 3 and Check that the paragraphs match the plan.
5 ![]() Match
the two halves Of these compound nouns from the text. Then choose three Of them
and write your own example Sentences.
Match
the two halves Of these compound nouns from the text. Then choose three Of them
and write your own example Sentences.
|
I basketball |
|
|
2 sports |
|
|
3 front |
c throw |
|
4 team |
game |
|
5 free |
e rush |
|
6 adrenaline |
|
we hardly noticed the freezing All in all, it was an unforgettable experience and one love to æpeat some day
6 Read the information below. HOW many of these expressions can you find in the text in exercise 2? You can make descriptions more colourful by using extreme equivalents Of simple verbs and verb phrases.
Extreme
equivalents want to do it be dying/desperate to do it shout ![]()
get excited go wildictatv/berserk feel sad feel heartbroken
be neck and neck beat somebody thrash somebody give it everything
7 Rewrite these Sentences using more extreme equivalents Of the verbs.
1 When the substitute ran onto the pitch the crowd got excited.
2 1 wanted to play her at tennis because she'd beaten me the last time.
3 The two teams were level. and both managers were shouting at their players to try harder.
4 She felt sad When She lost the match because she had really tried.
8 ![]() In
pairs, discuss the advantages and disadvantages
In
pairs, discuss the advantages and disadvantages
Of watching a sports event live rather than on TV.
110
|
|
Adverbial phrases I When we Start a sentence with an adverbial phrase Of direction. position, etc.. the subject-verb word order which follows is usually inverted: In the middle Of the room stood a policeman. However. when the subject is a pronoun, we do not invert. Away dzoæ-theï. X Away they drove. 3 When the verb form is there is/are, we miss out there instead Of inverting. On the table were three envelopes. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 Plan your description using the structure below. Write notes.
a Set the scene — Where? when? who With? b The build-up to the event — atmosphere, feelings, etc. c The event — focus on key moments. d After the event - how did it affect you?
3 Read the phrases below. Use one of them to write an alternative beginning for the Story on page 110.
Phrases for starting@ description of an event
It all happened (last summer. a few months ago, etc.)
![]() When
I „
When
I „
![]()
![]()
![]() It
was (last winter. six months ago, etc.) when I first
It
was (last winter. six months ago, etc.) when I first
|
|
memories
that day (last spring, two months ago. etc.) when |
5 |
Read the Learn this! box. In the text in exercise 2 On page |
|
|
(Last autumn. about a year ago, etc,) I watched a thrilling |
|
110, find two examples of sentences which start with an |
|
|
(football)
match between |
|
adverbial phrase. Which one includes a pronoun as subject? |
|
|
One
of the best (hockey) games I've ever seen took place |
6 |
Rewrite these sentences starting With the adverbial phrase. |
|
4 |
Read the Exam tip below. Answer all the questions for the |
|
I There was a tennis racket on the chair. |
|
|
sport vou have chosen to write about. |
|
2 The striker sprinted towards the corner flag. 3 The umpire stood in the centre of the court. |
I have very clear Of
|
EXAM TIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Make sure you use the right vocabulary for the sport you are describing. For the sport youWe chosen: • Where is it played? (court, pitch, rink, etc.) • What players are involved? (defender, goalie, forward, etc.) • What officials are involved? (umpire, referee, line judge, etc.) • DO players score goals or points? do judges give them marks? • Do the players pass, kick, catch, throw or hit a ball? |
||||||
4 A small dog ran onto the pitch.
5 All six swimmers jumped into the pool.
6
![]() There were six defenders in front of the goal.
There were six defenders in front of the goal.
![]()
D
GRAMMAR BUILDER 10.4: PAGE 133
|
CHECK YOUR WORK e you:
included
at least one extreme equivalent (from exercise 6 on page 110) to add colour
and excitement? included vocabulary that is specific to the sport you
started
at least one sentence with an adverbial phrase ecke4 your spelling and grammar' |
7 Write your description. Follow the plan you made in exercise 2. Write 200—250 words in total.
10 •
I Match an adjective below with each statement.
considerate heroic Over•sensitive romantic ruthless
I •I'm going to become leader Of this
political party and I don't care how I do it.'![]()
2
'I'm
going to dive into the lake and save that dog!' ![]()
![]()
3
'A
dozen red roses for you, my darling. And here's a ![]() poem
I've written about your eyes.'
poem
I've written about your eyes.'![]()
4
•I
didn't tell you about the party because I didn't want you to feel bad that they
didn't invite you.'![]()
5
•Why
did that person look at me just then? Is my hair a mess? Does this top not suit
me?'![]()
Mark: _ 15
2 Complete the sentences with the words below.
could hadn't needn't shouldn't wouldn't
I Thanks for the food, but you![]() have brought so much. There are only
three of us.
have brought so much. There are only
three of us.
![]() If I'd known how difficult this job was
going to be, I
If I'd known how difficult this job was
going to be, I ![]() have started it!
have started it!
![]() These bags are heavy. You
These bags are heavy. You![]() have
offered to help me!
have
offered to help me!
4 I don't mind her winning, but she really have boasted about it.
5 1 wouldn't have known about it ifyou told me.
Mark: _ 15
3 Complete the second sentence so it means the same as the first. (They are all mixed conditionals.)
I We're lost because you forgot to bring the map.
We wouldn't map.
He doesn't like you because you teased him. He would
He screamed because he's afraid Of
spiders. If he![]() screamed.
screamed.
4 1'm tired because you woke me up at dawn. I wouldn't dawn.
5 1 bought two DVDs because they're on special Offer.
If
DVDs Mark: _
15 ![]()
5
6
![]()
![]()
![]()
7
8
Circle the correct preposition and complete the sports venues.
I in /
on a boxing r![]()
2
in
/ on a football p![]()
3 in / on a ski s_
4 in / on a swimming p—
5 in / on a golfc_
Mark: ![]()
Match the two parts Of the Sentences.
|
1 What happened |
|
|
was |
news channel. |
|
|
|
|
circumstances |
stadium. |
|
|
c feel Sorry for are the players. |
|
4 It was my cousin |
|
|
who |
continue. |
|
|
|
Mark: _ 15
Complete the second sentence in each pair so it means the same as the first.
1 We need to buy our tickets.
It's
high ![]()
![]() There's no reason notto take the bus.
There's no reason notto take the bus.
We might as![]()
3 It would be a bad idea to carryyour passport with you.
You'd better![]()
4 I don't think you should invite the neighbours.
I'd sooner
5 HOW about leaving the car at home?
Suppose
Mark: 15
Complete the monologue with the words below.
also first foremost importantly start
, exercise is good forvou. For a
, it makes the muscles in your body stronger.
![]()
Complete each wish or regret
With the appropriate word(s). ![]() ,
let's not forget that it has a positive effect on your
,
let's not forget that it has a positive effect on your
1 I wish lacted so foolishly. mind and emotions. aut most s , it makes your heart
![]()
2 If![]() I
had been able to speak Italian. more efficient.'
I
had been able to speak Italian. more efficient.' ![]() you
hadn't told anyone. Mark: 15
you
hadn't told anyone. Mark: 15
4
I
wish I![]() have taken a year off.
have taken a year off. ![]()
5
1
really![]() you had been there with me.
you had been there with me.
![]()
Language Review 9—10
Match the words below to make three famous sports events. Which event does the photo show?
Bowl de France Grand Monaco prix Super Tour

2 In pairs, take turns to do the speaking task below.
Imagine you can have free tickets to one Of the sporting events in exercise 1. Which will you attend? Give reasons for your choice and say why you are rejecting the other options.
3 Read the text. Match four Of the headings (A—E) to the four sections (1—4). There is one extra heading.
![]() A
The early years D A British Grand Slam
A
The early years D A British Grand Slam
B Wimbledon customs E Playing for money
C The future of the tournament
![]()
![]() 1
The Wimbledon Tennis Championship, held for two weeks every year at the end of
June and the beginning
1
The Wimbledon Tennis Championship, held for two weeks every year at the end of
June and the beginning ![]() Of July, is one Of the highlights Of the
British Summer for sports lovers. For many tennis players and fans. it is still
the most prestigious Of the four Grand Slam tournaments (the Other three being
the Australian Open, the French Open and the US Open). It is the only Grand
Slam tournament to be played on grass, and each year, around half a million
spectators Come to watch the world's top tennis players compete in singles and
doubles events.
Of July, is one Of the highlights Of the
British Summer for sports lovers. For many tennis players and fans. it is still
the most prestigious Of the four Grand Slam tournaments (the Other three being
the Australian Open, the French Open and the US Open). It is the only Grand
Slam tournament to be played on grass, and each year, around half a million
spectators Come to watch the world's top tennis players compete in singles and
doubles events.
2
The
Championship was first held in 1877, making it the oldest tennis tournament in
the world. The women wore long dresses and the men full-length trousers. ![]() Until
1922, the reigning champion played Only in the final, against whichever player
had won through the other rounds. For many decades, it a tournament for
Until
1922, the reigning champion played Only in the final, against whichever player
had won through the other rounds. For many decades, it a tournament for
![]()
amateur rather than
professional players. NO prize money was awarded, but even so, the event was
very popular with spectators and was televised as early as 1937. ![]()
3
The
professional era began in 1968. At first, prizes were ![]()
modest, with
£2,000 being awarded to the men's singles ![]() champion
and only £750 to the ladies' singles champion. Today, the prize money is
over £1 million and since 2007 has been equal for men and women. And as
With all modern sports stars. the champions can expect to earn
champion
and only £750 to the ladies' singles champion. Today, the prize money is
over £1 million and since 2007 has been equal for men and women. And as
With all modern sports stars. the champions can expect to earn ![]() far
more from advertising deals than they get in prizes.
far
more from advertising deals than they get in prizes.
4
![]()
![]()
Although
there have been recent improvements to the venue — like a retractable roof over
Centre Court — tradition is very important at Wimbledon. The players still have
to dress in white and the courts are not surrounded by advertising boards. The
ball boys and ball girls, Who collect the tennis balls during the matches, are
all from local schools. And since the very first tournament ![]() back
in 1877, spectators at Wimbledon have eaten
back
in 1877, spectators at Wimbledon have eaten ![]() strawberries
and cream. These days, about 28.000 kilos of strawberries and 7,000 litres Of
cream are served during the fortnight.
strawberries
and cream. These days, about 28.000 kilos of strawberries and 7,000 litres Of
cream are served during the fortnight.
4 Are these sentences true (T) or false (B?
I The Wimbledon Championship always ends in July.
![]() Players
regard it as less important than the Other Grand Slam tournaments.
Players
regard it as less important than the Other Grand Slam tournaments.
![]() Between
1878 and 1922, the champion from the previous year only played one match.
Between
1878 and 1922, the champion from the previous year only played one match.
![]() Cash prizes were awarded when the
tournament started being televised.
Cash prizes were awarded when the
tournament started being televised.
5 The men's champion gets a bigger prize than the women's champion.
![]() Children
apply from schools all over the country to be ball boys and girls at Wimbledon.
Children
apply from schools all over the country to be ball boys and girls at Wimbledon.
7 Strawberries and cream are one Of the Oldest traditions at Wimbledon.
5 3.30 Listen to parts 1—5. Why did the protest go wrong?
6 3.30 Listen again. Match one Of the sentences (A—F) to each part. There is one extra sentence.
A Daisy tells Stefan she is planning to record some video footage and post it Online.
B They're on their way to a famous place but Stefan does not know where.
C Daisy blames Stefan for the fact that the protest is not going well.
D They decide to go somewhere that Stefan has been before but Daisy hasn't.
E Daisy is confused because things do not seem to be going to plan.
![]() Daisy
finds out that one member Of her group is not what he appeared to be.
Daisy
finds out that one member Of her group is not what he appeared to be.
7
Imagine you are Stefan. Write a description of your day at Mrnbledon. Use your
own ideas and anything you remember ![]() from
the Listening section.
from
the Listening section.
D CHECK YOUR PROGRESS: PAGE 4 ![]()
Skills Round-up 1-10 013
|
Get Ready for your Exam |
1 associate With yoga? Give reasons.
relaxing hazardous soothing extreme religious modern boring demanding
2 DO the exam task.
READING exam task
Read the text. Mark the sentences (1—6) true false (F) or not stated (N)?
Doing yoga as exercise is incredibly popular in the western world. There are now classes in most leisure centres in Europe and America, but what exactly is it and where did it come from? Yoga originated in ancient India as a physical, mental and spiritual discipline. It evolved as part Of Hindu philosophy and religion. The original goal of yoga. or the person practising yoga, is the attainment of a state of perfect spiritual tranquility while meditating on the concept Of divinity. The Sanskrit word •yoga' has the literal meaning •to join, unite Or attach'. The idea is to unite the body, breath and mind into one quiet energy. It was used as a word to describe a system Of meditation as early as the 2nd century BC. Someone who practises yoga or follows the yoga philosophy with a high level Of commitment is called a •yogi' for a man or 'yogini' for a woman. Theyvow to follow a plain and simple life of self•discipline in order to achieve the perfect state of harmony and tranquility.
There are several types of yoga. The one that we associate most with in the West is Hatha Yoga. Which is sometimes referred to as •psychophysical yoga'.
'Ha' means 'sun' or •vital life force' and •tha' means •moon' or •mental force', while •yoga' signifies the union between the two. The Hatha Yoga school emphasised mastery of the body to focus the mind. It evolved in 15th century India. and instead Of just sitting while practising meditation, Hatha Yoga developed a series of poses for the body. Yoga came to the attention Of an educated western public in the mid-19th century alongwith Other forms Of Hindu philosophy. The first Hindu teacher to actively promote aspects of yoga to a western audience was Swami Vivekananda. Who toured Europe and the United States in the 1890s.
In 1947 the first Hatha Yoga school in the US opened in Hollywood. In the 'Flower power' hippie years Of the 1960S, interest in Hindu spirituality reached its peak. Pop stars. such as the Beatles and many Hollywood actors, followed Hindu meditation and philosophy for a While to inspire creativity and as an antidote to the materialism of western culture. However, for us in the
Get Ready for your Exam 10
west, yoga has now become almost completely detached from its religious context and is typically undertaken as a form Of exercise, With its powerful combination of controlled movement and deep breathing.
Yoga now more popular it-ithe We Stern world than in India, its country of origin.
Achieving a calm and peaceful state is an important element of yoga.
Hatha Yoga is physically more demanding than some other types.
Prior to Swami Vivekananda's tour, yoga was unknown to westerners.
The first Hatha Yoga school in the US was primarily attended by Hollywood stars.
Although most westerners do yoga to improve their body, they have not lost sight
below into two groups: (1) feelings associated with winning, and (2) feelings associated With losing. Can you add any more adjectives?
dejected despondent devastated dismayed ecstatic elated inconsolable Overjoyed relieved triumphant
Do the exam task.
SPEAKING exam task
Describe the picture. Then answer the questions.
Why is this man in such a Strange pose?
2 Would you like to be a professional athlete?
Why / Why not?
Tell me about an international sport event which you attended or watched on television.
|
1.1 |
present perfect simple We use the present perfect
• for recent events, particularly when giving news. Have iou heard? The presiåeni has ousi) resigned
• for an action that happened at some unspecified time in the past. (If we specify the time, we use the past simple.) Have you (ever) seen a koala?
I've been to New
• With State verbs, to say how long a situation has existed. (We use for, since or how long.) I've Known Eva for vars.
I've never baseball.
• for recent events that have a result in the present.
![]()
![]() I've
(alread•i) boughå the ticEetB_ We can go inside.
I've
(alread•i) boughå the ticEetB_ We can go inside. ![]() I
can't go out, I haven't done
I
can't go out, I haven't done
Present perfect continuous
We use the present perfect continuous
• for actions that have been happening recently and repeatedly.
![]() been plaNin9 a new computer game
recenth•.
been plaNin9 a new computer game
recenth•.![]()
I've been *Or¥ing
hard this term, ![]()
![]()
• ![]() with
dynamic verbs to how long an action has been in
with
dynamic verbs to how long an action has been in ![]() progress.
(We use for, since or how long.)
progress.
(We use for, since or how long.) ![]() Take
hat been watching TN for three hour*
Take
hat been watching TN for three hour* ![]()
![]()
• to
explain a current situation in terms of recent events.![]()
I'm tired because I've (just) been ![]()
Additional points Of contrast
• We
use the simple form to emphasise that an action is ![]() complete.
Compare:
complete.
Compare:
I've been reading The Hobbit (I'm half through)
![]()
I've read The Hobbit (li great!)
• Ifwe specify an exact number Of occasions, we cannot use the continuous form. We've been arguing a lot.
(NOT
• We can use the simple or continuous form with just and already. However, we do not use the continuous form With yet.
I've just spoken to Tack./l'vejust been speaking to I've alread•i worn it/t•ve been wearing it.
![]() 1
Complete the sentences with the present perfect simple and continuous Of the
verbs in brackets.
1
Complete the sentences with the present perfect simple and continuous Of the
verbs in brackets.
(search) for hours but I (not find) my phone yet.
(visit) the USA a few times but (n ever see) a baseball game.
(you I see) my watch? I (100k) for it since this morning.
(just / talk) to Abby on the phone. DO you want a quick word With her?
(eat) all morning. I'm so full!
(you / see) Martha? •yes. She (work) in the library. You can go along and see her.'
7 I'm tired because I've (play)
three tennis matches ![]() today.
today.![]()
![]() 8 We've (watch) Twilight. Do
you want to see the end With us?
8 We've (watch) Twilight. Do
you want to see the end With us?
9
Fantastic!
England have (win) the world ![]() championship!
championship! ![]()
10 Have you ever _ (take) part in a sports competition?
|
1.2 |
Dynamic verbs describe actions and can be used in simple or continuous tenses.
Compare:
Dad mazes dinner even Friday. regularly)
Dad can't come to the phone; he's making dinner now) Sake hat watched TV even night this *eeg. recently and repeatedly)
Thi* evening. he's been watching TN for three hours, action in progress With for)
State verbs describe States, not actions.
They are Often connected with abstract ideas: ![]()
• emotion care, envy, fear, hate, like. love, mind, prefer. want
• possession belong, own, possess
• thought agree, believe, disagree. doubt, know. mean, recognise, understand
• others contain, cost, depend, pt. matter, need. seem, weigh
State verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses.
I hate cheese. hate this song. (NOT Fm-hating I've known Eva for 'ears,
I've never understood baseball.
Has he packed Vt? (NOT Has-he-been-peekintye?) (NOT
Some verbs can be state or dynamic depending on the meaning. Only the dynamic sense can be used in continuous tenses.
|
|
Dynamic verb |
State verb |
1.3 Verb patterns |
|
|
I'm thinking about work. |
I
think she's at work. |
|
|
|
|
|
When we put two verbs together, the second verb is usually in |
|
|
I'm not feeling confident. |
He
feels I'm selfish.
|
the infinitive Or •ing form. Sometimes it is an infinitive With to |
|
|
He's having a shower/ |
She
has three cats.
|
or a past participle. Which pattern we use depends on the first |
![]()
![]() a
piano lesson/lunch.
a
piano lesson/lunch.
![]()
![]()
![]() look What
are you looking at? He looks very calm.
look What
are you looking at? He looks very calm. ![]() verb
to infinitive
verb
to infinitive ![]() see I'm seeing Dan later. I
See what you mean. agree. arrange, ask, beg, dare, decide, expect, foil,
happen,
see I'm seeing Dan later. I
See what you mean. agree. arrange, ask, beg, dare, decide, expect, foil,
happen, ![]() smell Why are you smelling Does
the sandwich smell
smell Why are you smelling Does
the sandwich smell ![]() hope, manage, mean, offer, prepare.
pretend, promise. refuse, that sandwich? all right?
hope, manage, mean, offer, prepare.
pretend, promise. refuse, that sandwich? all right? ![]() seem,
want, Wish, would like, would prefer, help (can also be
seem,
want, Wish, would like, would prefer, help (can also be
![]()
![]() infinitive
without to) She's tasting the soup. The soup tastes great!
infinitive
without to) She's tasting the soup. The soup tastes great!
![]()
![]() Choose
the Correct tense.
Choose
the Correct tense.
(mean).'
-O•why (VOU / laugh) at my T-shirt?'
'Because it (not fit) you!'
3
![]()
![]() 'This bag that I (carry I weigh) a ton!'
'This bag that I (carry I weigh) a ton!'
![]() (know).
It (contain) all my books.'
(know).
It (contain) all my books.'
4 (you / like) this play?'
|
|
I regret to inform that your application was unsuccessful. / t regret not telling him bow I feel, |
![]() 'Not
really, but it (not matter). I (not mind) staying until the
end.'
'Not
really, but it (not matter). I (not mind) staying until the
end.'
![]()
![]()
![]() on,
consider, delay, dislike, deny, enjoy, envisage, fancy, feel like, finish, give
up, have difficulty, like, imagine, intend, it's no good, it's not worth,
justify. keep (on), mind, miss, postpone, practise, propose, put Off,
recollect, recommend, risk, stop, spend (time), suggest
on,
consider, delay, dislike, deny, enjoy, envisage, fancy, feel like, finish, give
up, have difficulty, like, imagine, intend, it's no good, it's not worth,
justify. keep (on), mind, miss, postpone, practise, propose, put Off,
recollect, recommend, risk, stop, spend (time), suggest
• ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Some
verbs can be followed by an •ing form or an infinitive with little or no change
in meaning: begin, continue, hate, intend, like, love. prefer, Start.
Some
verbs can be followed by an •ing form or an infinitive with little or no change
in meaning: begin, continue, hate, intend, like, love. prefer, Start.
• ![]()
![]() I
won't forget meeting the President / forgot in
I
won't forget meeting the President / forgot in
![]()
![]() He on Singing. /
He went on to become a teacher
He on Singing. /
He went on to become a teacher
![]()
![]() I
remember locking the door. / Please remember to lock the
I
remember locking the door. / Please remember to lock the ![]() 2
Complete the Sentences with the correct form Of the verbs door.
2
Complete the Sentences with the correct form Of the verbs door.
|
have
100k see think |
|
|
but no sound came Out. • The verbs see, hear, watch and feel can be followed by Object |
|
|
at our car. |
|
+ infinitive
Without to to talk about a completed action, or |
|
2
My great-grandfather |
Object
•ing form to talk about an action in progress. |
|
|
|
I Danni batketbali
in the garden |
|
|
I missed my stop because about dinner. |
verb + object to infinitive |
|
|
When we arrived, the teachers a meeting. |
allow, ask, command, dare.
enable, encourage, expect, forbid, |
|
|
It's raining, but I it will stop soon. |
force, get, inspire. invite. order, permit, persuade. remind. |
|
|
|
request. teach, tell, trust, urge, warn. want, Wish, would like, |
|
8 |
That game fun. Can I have a go? |
would
prefer |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() below.
Use each verb twice, once in a simple and once in a
below.
Use each verb twice, once in a simple and once in a ![]() She
stopped Singing, / She stopped to tie her shoes continuous form.
She
stopped Singing, / She stopped to tie her shoes continuous form.![]() tried
shouting for but nobody heard. / I tried to
tried
shouting for but nobody heard. / I tried to
![]() verb + Object + infinitive Without to
verb + Object + infinitive Without to ![]() have,
make, let, help (can also be infinitive with to)
have,
make, let, help (can also be infinitive with to)![]()
![]() verb
+ Object + past participle get, have, need, want
verb
+ Object + past participle get, have, need, want
116![]()
(NOF My dad would be a policeman.)
• never used to and would never are common negative forms.
![]()
![]() I
never used to *ear glasses would never return phone calls,
I
never used to *ear glasses would never return phone calls,
• If we stress the word would, it implies that we found the habit annoying.
I had to get rid Of our cat. Well it would leave dead mice at the bottom of my bed!
![]()
![]()
![]() Choose
the correct endings: a, b or both. 1 1 love carrots now, but when I was a
child, 1 a didn't use to like them. b wouldn't like them. When I was at primary
school a I would getup at seven o'clock every morning. b I used to get up at
seven O'clock every morning. I sometimes got angry with my brother because a he
would interrupt my phone calls. b he constantly interrupted my phone calls. For
five years in the 1990s, we a lived in France.
Choose
the correct endings: a, b or both. 1 1 love carrots now, but when I was a
child, 1 a didn't use to like them. b wouldn't like them. When I was at primary
school a I would getup at seven o'clock every morning. b I used to get up at
seven O'clock every morning. I sometimes got angry with my brother because a he
would interrupt my phone calls. b he constantly interrupted my phone calls. For
five years in the 1990s, we a lived in France.
b used to live in France.
![]()
![]()
![]() 5
When Joe was a small boy a he never used to wear glasses. b he didn't use to
wear glasses. When we lived in London
5
When Joe was a small boy a he never used to wear glasses. b he didn't use to
wear glasses. When we lived in London
a we didn't own a dog.
b we wouldn't own a dog.
7
![]()
![]()
![]() My elder brother a used to be interested in planes and
trains. b would be interested in planes and trains.
My elder brother a used to be interested in planes and
trains. b would be interested in planes and trains.
|
2.2 |
8
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() My uncle a would work all his life in a factory in
Manchester. b worked all his life in a factory in Manchester.
My uncle a would work all his life in a factory in
Manchester. b worked all his life in a factory in Manchester.
•
![]() We use the second conditional to talk about an imaginary
situation or event and its result. It can referto the present or the future.
We use the second conditional to talk about an imaginary
situation or event and its result. It can referto the present or the future.
If I were better at football, would be in the school team.
(present)
If I failed rn•i nest Near, I wouldn't get into university. (future)
•
![]() We use the past tense to describe the situation or event.
We use would or wouldn't* infinitive without to to describe the result.
We use the past tense to describe the situation or event.
We use would or wouldn't* infinitive without to to describe the result.
If I had a Of monei, I would travel round the world.
![]() I I
can't decide Whetherto persuade a friend
I I
can't decide Whetherto persuade a friend
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() (come)
camping With me or risk _ (go) on my own. We'd agreed (meet) outside the
cinema but Jake failed (turn up).
(come)
camping With me or risk _ (go) on my own. We'd agreed (meet) outside the
cinema but Jake failed (turn up).
3 1 haven't managed (contact) my cousins in Peru, but I'll keep (try).
4
![]() 1 suggest (stay) at my flat, ifyou don't mind (sleep) on
the floor.
1 suggest (stay) at my flat, ifyou don't mind (sleep) on
the floor.
She pretends (like) him, but in fact she can't stand (be) in the same room.
My brother admitted (take) my camera and promised (ask) next time.
7 1 really dislike (argue) and I can't envisage ever (have) a relationship with an argumentative person.
8
![]() He carried on _ (play) the guitar even though
everyone in the room wanted him (stop).
He carried on _ (play) the guitar even though
everyone in the room wanted him (stop).
2 Choose the best verb form in these sentences.
![]()
![]()
![]() I 'l
can't find my phone.' 'Have you tried your own number?' a call b calling c to
call
I 'l
can't find my phone.' 'Have you tried your own number?' a call b calling c to
call
![]() 2
Liverpool were two goals down at half time, but they went the match.
2
Liverpool were two goals down at half time, but they went the match.
a Win b winning c to win
3
![]() When I saw a manin our garden, I asked him what he
wanted.
When I saw a manin our garden, I asked him what he
wanted.
a stand b standing c to stand
4
![]()
![]()
![]() a to
catch b catching c caught
a to
catch b catching c caught
5
![]()
![]() This
a great track. It Will get everybody a dance b dancing c danced
This
a great track. It Will get everybody a dance b dancing c danced
|
2.1 |
6
![]() Please remembersome photos for me to look at. a take b
taking c to take used to and would
Please remembersome photos for me to look at. a take b
taking c to take used to and would
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() • We
use used to or would to describe habits and situations in the past that are now
finished.
• We
use used to or would to describe habits and situations in the past that are now
finished.
![]()
![]() I a
child, I used to sport at
I a
child, I used to sport at
![]() When
I lived in the citi, I'd go jogging in the par* every morning.
When
I lived in the citi, I'd go jogging in the par* every morning.
I didn't to lige ite cream, but do now.
Did there use to be a corner shop at the end of the road?
• We don't use used to or would when we say how long a (situation) (result) situation or habit in the past continued; we use the past simple.
He wore the same blue suit to work for ten Nears.
• The ifclause Can come before or after the main clause. If it comes after. we don't use a comma.
If he weren't homeless, he wouldn't be a Squatter.
He goulån•i be a Squatter if he weren't homeless
• In the if clause, we can use were instead of was as the past tense Of be, singular. It is considered to be a little formal. The meaning doesn't change.
If I was rich, I'd buy a house in the countrl,
If I were rich, I'd a house in the
I Complete the sentences. Use the second
conditional. 1 Ifyou![]() (work Out) your total income, you
(work Out) your total income, you ![]() (know)
how much you had to spend.
(know)
how much you had to spend.
![]()
![]() 2
Your children (manage) their money better if you (let) them take responsibility
for financial decisions.
2
Your children (manage) their money better if you (let) them take responsibility
for financial decisions.
3
You![]() (be
able) to afford a holiday if you
(be
able) to afford a holiday if you![]()
(not spend) all your money on music dcrwnloads.
4
If
you (give) me a bigger allowance, I ![]() (not
be) broke all the time.
(not
be) broke all the time.
5 My dad he (not have) a credit card if interest rates (not be) so IOW at the moment.
6
If
my dad (win) the lottery, he![]() (retire).
(retire).
2
Write second conditional sentences. ![]()
![]()
![]() I
can't afford a holiday because I'm hard up.
I
can't afford a holiday because I'm hard up.
If I weren't hard up, I could afford a holiåa•f
2 He won't lend you money because he's stingy.
![]() The painting isn't worth a fortune
because it's a copy.
The painting isn't worth a fortune
because it's a copy.
![]() 4
The restaurant is rather pricey, so we don't eat there often.
4
The restaurant is rather pricey, so we don't eat there often. ![]()
![]() He's
careless with his money, so he's always broke.
He's
careless with his money, so he's always broke.
He doesn't budget well, so he gets into debt
all the time. ![]()
![]()
![]() 7 1
don't borrow money because it's difficult to pay back. 8 You waste your money,
so you're always short.
7 1
don't borrow money because it's difficult to pay back. 8 You waste your money,
so you're always short. ![]()
![]()
|
2.3 |
Past perfect simple ![]()
• With action verbs and for or since to say how long an action had been in progress.
I'd been plating the lotteri for years before I won anything,
![]()
I He Was in debt because he (not be) careful with his money.
![]() She
was never short Of money because she (always keep) some back for a rainy day.
She
was never short Of money because she (always keep) some back for a rainy day.![]()
3 1 didn't know where she was because she (not
tell) me where she was going.
![]() 4 They
4 They![]() (be)
comfortably off before the stock market
(be)
comfortably off before the stock market ![]() crash.
crash.
![]()
![]() you
ever
you
ever![]() (visit) Germany before you Started to
learn German?
(visit) Germany before you Started to
learn German?
6 She was late for work because she![]() (get up) late.
(get up) late.
![]() (know) you were a vegetarian, I wouldn't
have
(know) you were a vegetarian, I wouldn't
have ![]() cooked meat!
cooked meat!
2 Complete the sentences. Use the past perfect continuous and a phrase below.
|
2.4 |
![]()
![]() sunbathe
all day cook dinner not sleep welt walk in the woods not pay travel for six
hours sit at my desk
sunbathe
all day cook dinner not sleep welt walk in the woods not pay travel for six
hours sit at my desk
![]() The path was slippery because
The path was slippery because
![]() Fran looked tired because she
Fran looked tired because she
![]() When I got home, there was a
When I got home, there was a
4 When we finally got to Devon, we
![]() Liam couldn't do the exercise because
Liam couldn't do the exercise because
6 I had backache because I
![]() 7 Their shoes were muddy
7 Their shoes were muddy
8 My face was very sunburnt
• We use the past simple:
a for an action or event at a definite point in the past.
• ![]() for
for ![]()
We past.use an the action past that perfect happened simplebefore a specific time in the b We for He Joined actions played the volleyball or team events at last the that Saturday.age happened Of
![]()
After I had washed up I watched TN. I passed the to him ard he scored.
![]()
• with
how state long an verbs action (know, had be, been like, in etc.) progress.and
for or since to say ![]() c With She got certain up. had verbs a
shower. that are got not dressed used in and continuous left the house.tenses:
c With She got certain up. had verbs a
shower. that are got not dressed used in and continuous left the house.tenses:
![]()
![]() been here at home for a fe8 minutes
when
been here at home for a fe8 minutes
when![]() for example, believe, hate, know, like,
love, need, prefer,
for example, believe, hate, know, like,
love, need, prefer,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() grandmother
phoned,
grandmother
phoned,![]() want.
want.
Past perfect continuous ![]() I
believed his (NOT We use the past perfect continuous • We use the past
continuous for a
I
believed his (NOT We use the past perfect continuous • We use the past
continuous for a
• to show the cause Of something in the past. the past.
His
hands uere dirty. He had been gardening.  raining.
Some children *Bre playing
raining.
Some children *Bre playing
• We often use the past continuous and the past simple in the same sentence. The past continuous describes a background action or event; the past simple describes a shorter action or event that interrupted it.
I having breakfast when the phone rang. MI friends were watching TV When arrived.
• We can use the past simple or the past continuous with When, as and While.
What were thinking at you aged down the street?
What were iou thinking as you were walking down the street?
• We often use as with the past simple for two short actions that happened at the same time.
I left the room tripped over the cat.
Complete the sentences. Use the past simple or past continuous of the verbs in brackets. Sometimes both tenses are possible.
The sun (shine) and the birds (sing) when (leave) the house.
2 The moment I (see) him I (realise) I'd met him before.
3
What you (do)
when Joe![]() (call) you?
(call) you?
4
While
we (wait) foryou. it![]() (start) to rain. 5 She (walk) into the
room,
(start) to rain. 5 She (walk) into the
room, ![]() (sit down) and
(sit down) and ![]() (start)
to read the paper.
(start)
to read the paper.
6
Atthe
time Of the earthquake,![]() (live) in Tokyo. I
(live) in Tokyo. I ![]() (move)
back to the UK shortly afterwards.
(move)
back to the UK shortly afterwards.
7
Harry
_ (play) a lot of football while he![]() (live)
in Oxford.
(live)
in Oxford.
8
As
I ![]() (leave) the house the sun
(leave) the house the sun![]() (come
out).
(come
out).
|
3.1 |
•We can use an indirect question When we feel that a direct
![]() question might sound rude or
aggressive. Indirect questions use the same word order and verb forms as
affirmative
question might sound rude or
aggressive. Indirect questions use the same word order and verb forms as
affirmative ![]() statements:
statements:
Where do live? (direct question)
Loulå iou me where iou live? (indirect question)
•We can use the following
phrases to introduce an indirect question. Note that the first two do not
require a question mark at the end. I like to Know![]()
Could •iou tell me ?/Can iou tell me
?Nould iou mind ![]() telling me ?/Can I ask you ?
telling me ?/Can I ask you ?
Have iou ani idea ?/DO gou Know ?
•The phrases above are followed by the Same question word
(Who, Which, where, etc.) as in the equivalent direct question. is he sad?
![]() Have
ani idea •ah•f he's sad?
Have
ani idea •ah•f he's sad?
•![]()
![]() If
the equivalent direct question is a yes/no question, we use ifor Whether. Are
they in love?
If
the equivalent direct question is a yes/no question, we use ifor Whether. Are
they in love?
I wonder if/whether In love.
1 Change the indirect questions into direct questions.
1 1'd like to know how much this shirt costs.
2 DO you know whether the help desk is open?
3 Could you tell me where the bank is?
4 Can you tell me if you need any help?
5 Have you any idea what time she'll beback? 6 1 wonder what the matter is.
2 Read the direct questions and completethe equivalent indirect questions.
Why are you laughing?
Would you mind
Are they married or just engaged?
I wonder
What does this word mean?
Can you
4 How old are you? can I
5 Is there a fast train to Liverpool from here?
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 6
6
Do you know
7
I'd
like _ ![]() 8
8
Could you
• The following question words can be the subject or object of a question: +1hO ?, Which (one/ones) ? and What ?
• When the question word is the subject, it is followed by a normal, affirmative verb form:
![]() in
that Office? *Orgs in that Office)
in
that Office? *Orgs in that Office)![]()
![]()
Which car won the race? (The red car the race)
• When
the question word is the object, it is followed by an ![]() interrogative
verb form:
interrogative
verb form:
![]() do you know at this Parti? (l know
everybodi.)
do you know at this Parti? (l know
everybodi.)
What did iou bui? (l bought a T-shirt)
• When the question includes a preposition, we use the Object form. We usually put the preposition at the end. What are you looking at? (I'm looking at the moon)
Vlho did iou talk to?
(l to ![]()
• ![]() In
formal English, we sometimes put the preposition at the Start, before the
question word. If the question word is Who, it becomes whom When we put a
preposition before it. TO *horn did iou give the monq? (formal)
In
formal English, we sometimes put the preposition at the Start, before the
question word. If the question word is Who, it becomes whom When we put a
preposition before it. TO *horn did iou give the monq? (formal)
Who did you give the money to? (less formal)
1 Read the statements. Then complete the questions for the answers that are given.
He gave his number to Grace.
? Grace.
2 They won a brand new car!
What _ ? A brand new car.
3 My dad drove them to the airport.
Who ? My dad.
4 A faulty IV caused the fire.
What ? A faulty TV.
5 The Fiat won the rally.
Which car ? The Fiat.
6 Sandy always sits nextto Noah. ? Noah.
|
3.3 |
• Comparative
and superlative adjectives are formed with -er ![]() and
•est or more and most, unless they are irregular:
and
•est or more and most, unless they are irregular:
(regular) difficult more difficult most difficult hot hotter hottest
(irregular) good better
far furth![]()
• Comparative
and superlative adverbs are usually formed with more and most, unless they are
irregular. (regular) more slowl.f most ![]()
![]() (irregular)
badli worse worst
(irregular)
badli worse worst ![]() better best
better best
• • A
few comparative and superlative adverbs are formed With ![]() -er
and .est, like adjectives: early, fast, hard. late, near. soon.
-er
and .est, like adjectives: early, fast, hard. late, near. soon. ![]() We'll
be there sooner than thought.
We'll
be there sooner than thought. ![]()
who gets up the earliest in your family?
• ![]()
![]() Some
determiners also have comparative and superlative forms. few fvaer feuest
little less least much/rnanN more most
Some
determiners also have comparative and superlative forms. few fvaer feuest
little less least much/rnanN more most
• ![]() We
can use (so) much or far to make the meaning of a comparative form more
extreme. It's far garmer than I npectBå
We
can use (so) much or far to make the meaning of a comparative form more
extreme. It's far garmer than I npectBå
She drives so much more safely than she used to
• We use even to express surprise. I'm tall bui you're even taller!
• We can use a little, o bit or no to modify a comparison.
It'* a bit harder than I realisedL
ThB•i played no better than last week,
• We can modify a comparison with as as by using just, almost, nearly, nowhere near Or nothing like. ihe•sjust as argumentative ae her brother.
Sgateboarding is nowhere near as difficult SÉiing.
• We can talk about a gradual change by repeating a comparative form.
![]() It's getting harder and harder to find
apartments.
It's getting harder and harder to find
apartments.
•
The more he spends. the poorer he gets
• Comparisons often have a clause after than.
Driving to London is than it used to be.
Complete the sentence so that it means the same as the first.
London is far bigger than Paris.
Paris is nowhere London.
2 I expected yoga to be difficult, but not this difficult!
Yoga is even I expected.
3 New York is almost as far south as Madrid.
Madrid is only a bit New York.
4 Greenland is much smaller than it looks On most maps.
Greenland isn't nearly on most maps.
The ice caps are shrinking due to climate change.
The ice caps are getting due to climate change.
6 If you drink more coffee, you won't sleep as well. The more coffee you'll sleep.
2 Rewrite the sentences to include a comparative form followed by a clause. Keep the same meaning.
I I didn't realise Mark was so rich.
Mark is much richer than real,iseå
![]() This restaurant didn't use to be so
popular.
This restaurant didn't use to be so
popular.
![]() This phone shouldn't be so hard to use.
This phone shouldn't be so hard to use.
4 I didn't plan to spend so much money.
![]() This hotel didn't 100k so comfortable
from the Outside.
This hotel didn't 100k so comfortable
from the Outside. ![]() I didn't imagine Chicago would be such
an exciting city.
I didn't imagine Chicago would be such
an exciting city.
|
3.4 |
• We
use question tags to turn a statement into a question. We usually add negative
tags to affirmative statements and affirmative tags to negative Statements. ![]() hot
isn't it?
hot
isn't it?
You don't need a lift to school. do •iou?
• With affirmative sentences Which have a negative meaning because they include a word like never, nobody or nothing, we add an affirmative tag.
I've had nothing for breakfast, have l?
![]() never
'thank does she?
never
'thank does she?
• If the sentence includes a modal verb (can, might, should, will, etc.) we use it in the tag. ôhe can't sing. tan she? Ii won't hurt. will it?
• If the sentence includes an auxiliary verb (is/ore, have, had, etc.) we use it in the tag. They're leaving. aren't they?
You haven't told have •iou?
• If the sentence includes a simple, finite verb form, we do (or did) in the tag.
This phone belongs to doesn't it? you went home lait night. didn't •iou?
|
|
Nobodi wants to give up, do ihe•f? E'.'tnthir.g doe.ån't it?
Nothing matters now, does ![]()
• We use a rising intonation on the question tag When we need or expect an answer.
It isn't my turn. is it? (l think it might be.)
• We use a falling intonation on the question tag when we do not need or expect an answer.
Of course help You're besi friend, aren't you? (We both know that.)
1 Add question tags.
![]() Nothing's
ever as simple as it seems,
Nothing's
ever as simple as it seems, ![]()
![]() t's rained a lot recently,
t's rained a lot recently,![]()
![]() Don't spend too much money.
Don't spend too much money. ![]() 4
Nobody knows what you're thinking,
4
Nobody knows what you're thinking,![]()
5 You haven't been listening to me,![]()
![]() Everything changed after he retired,
Everything changed after he retired,![]()
7 Let's start at the beginning,![]()
![]() Leave your bags by the door,
Leave your bags by the door,![]()
9 Your parents used to live there, ![]() 10
You're going to invite me,
10
You're going to invite me,![]()
|
4.1 |
will
• We
use will for making predictions about the future. We often use I think and /
don't think with Will. I don't ![]() tonight.
tonight.
• We
can use shall/shan't instead Of Will/won't With I and we, but Will is more
common. ![]() thing we shall visit Ital•/ summer
thing we shall visit Ital•/ summer
• We also use will to make assumptions about the present.
It's 4.40 F-ighi now Jim be on hie way home.
Helen will bt getting on the plane
• We also use will to express our assumptions about the present.
It's Mum will be preparing dinner.
rm sure the football match will have finished bf nos.
must and can't
• We use must for talking about things Which we can deduce
are definitely true.
He must be at work called me from his office.
• We use can't for talking about things which we can deduce are impossible.
She can't be abroad. hasn't got a passport.
• They often referto a future event.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Be careful Kith those
plates. You might them.
Be careful Kith those
plates. You might them. ![]()
• We can use the negative forms may not and might not. However, we cannot use the negative form couldn'tin this sense.
I've bent her a postcard, but it not/might not arrive. (NOT I've sent her a postcard. but it could-not arrive.)
• couldn't has a similar meaning to can't and expresses impossibility. It's often used with possibly.
I couldn't possibly accept the invitation to Tan's party. I'll be
![]()
• We use should to say that something is likely to happen, in
Our opinion.
I should be home sis o'clock
Tim might be a bit late for the meeting, but that shouldn't be a
• We can use other phrases to express
probability. ![]() be bound to it's certain)
be bound to it's certain)
The store is 4—0 With minutes to go. They're bound to win. chances are (that) it's probable (that))
Chances are I uon't hand in my homework on time. very
probable) be likely be probable)
Is it likely rain tomorrow?
![]() Complete
the sentences With the correct form Of must. can't, may, might, could and
should. Sometimes more than one answer is possible.
Complete
the sentences With the correct form Of must. can't, may, might, could and
should. Sometimes more than one answer is possible.
![]() I'm not Sure what we're doing tomorrow.
We go to the cinema.
I'm not Sure what we're doing tomorrow.
We go to the cinema.
![]() Fiona
Fiona![]() be at the leisure
centre. It's closed.
be at the leisure
centre. It's closed.
3 You shouldn't drive So fast. You have an accident one day.
4 1 can see people opening their umbrellas. It be starting to rain.
5
![]() Jake be wearing his coat. It's on the peg over
there.
Jake be wearing his coat. It's on the peg over
there.
![]() It's five o'clock now and the bus takes
twenty minutes, so
It's five o'clock now and the bus takes
twenty minutes, so ![]() get home just after five twenty.
get home just after five twenty. ![]()
7
1
went past the new noodle bar in town. It be very ![]() good
— there was nobody in it!
good
— there was nobody in it!
8
"Where's
Sid?' 'l don't know. He![]() be in town shopping.'
be in town shopping.'
![]() Barcelona are much better than
Manchester United at the moment, so they
Barcelona are much better than
Manchester United at the moment, so they![]()
|
2 Rewrite sentences 1, 3, 6, 7, 8and 9 from exercise I. Use one Of these phrases: be bound to, chances are, and be likely. You may need to make other changes too.
I I'm not sure what we're doing tomorrow.
Chances are ![]() go to the cinema,
go to the cinema,
|
4.2 |
Future continuous
We use the future continuous
• to talk about an action that Will be in progress at a specific paint in the future.
At sis O'clock tomorrow evening be watching The K Factor
• to talk about planned events, or events that we expect to happen. In this usage, it is similar to the present continuous for arrangements.
I'll be going to the shops later. Is there an•ithtng gou need?
• to make polite enquiries. Using the future continuous instead ofQhe future simple to ask about somebodVs plans makes questions sound politer and less direct.
Can you let me "hen be leaving?
Future perfect simple
We use the future perfect simple to talk about a completed action or event in the future.
![]() the
time get to the cinema, the film have alread•i
the
time get to the cinema, the film have alread•i
Marled.
Future perfect continuous
We normally use the future perfect continuous to say how long an action or event will have been in progress at a specific point in the future.
![]() the end of this •fear. he'll have been
learning f-ngli%h for nine
the end of this •fear. he'll have been
learning f-ngli%h for nine
![]() I
Write sentences about What George will be doing at the times
I
Write sentences about What George will be doing at the times  given.
Use the future continuous.
given.
Use the future continuous.
2 Complete the sentences With the future perfect simple or future perfect continuous.
1 By Christmas Mandy (know) Roger for five years.
![]() Next
Easter my mum (work) at the doctor's surgery for six months.
Next
Easter my mum (work) at the doctor's surgery for six months.
3
![]()
![]() If
Dave passes his physics exam, he
If
Dave passes his physics exam, he![]() (pass) all his schoo Heaving exams.
(pass) all his schoo Heaving exams.
4
I
hope you![]() (wash up) the dishes before you go
(wash up) the dishes before you go ![]() out.
out.
![]() By this time next year we
By this time next year we![]() (live)
in London for six years.
(live)
in London for six years.
6
When
William is sixteen he ![]() (play) basketball for three years.
(play) basketball for three years.
7
By
the time we getto the stadium the race![]() (start).
(start).
8 'Kate is going to try and pass her driving test again.'
|
4.3 |
• We use Will to make factual Statements about the future, and to make predictions.
The sun Will rise at 041 morning.
DO gou think finish your homeworE before midnight?
•
We
use Will for things we decide to do as we are speaking (instant decisions,
Offers, promises). ![]() the phone ringing. arts*er it.
the phone ringing. arts*er it.
This bag is heavi' carry it;
Ill ring you as soon as get io Lonåon.
•
We
use going to or the future continuous for things we have already decided to do
(intentions). I'm going to visit my grandparents at the![]()
I'll be visiting my grandparents ai the wee'end_
• We use going to to make a prediction based on present evidence.
Look at those clouds It's going to rain.
• We use the present continuous for things we have already agreed to do. usually With somebody else (arrangements). I'm plaiing football on Saturåa•i afternoon.
•
We
can use the present simple for timetabled and scheduled ![]() events.
events.
What time does your train leave iomorrou? The concert starts at S pm. on Saturday.
Choose the best form. Where more than one
answer is possible, explain the difference in meaning. ![]()
1 Bye!
' ![]() you tomorrow.
you tomorrow.
![]()
![]() a
•Il see b 'm seeing c •m going to see
a
•Il see b 'm seeing c •m going to see
2 'Have you got any plans for this evening?' 'l Vicky.' a •llgo out b 'm going out c 'm goingtogoout
3 Myflight![]() at
five so we need to be at the airport a
at
five so we need to be at the airport a ![]() good
two hours before that.
good
two hours before that.
a Will leave b 's leaving c 's going to leave
![]()
4 •I'm going to spend my gap year in Africa.' 'Really? What
![]()
![]() a
will you do b are you doing c are you going to do
a
will you do b are you doing c are you going to do
5 Look!
That car's going too fast. It![]()
a 'Il crash b 's crashing c 's going to crash
6 1'm
sure you'll get into university, but what![]() if
you
if
you
a
![]() will you do b are you doing c are you going to do James
this evening?
will you do b are you doing c are you going to do James
this evening?
you see b Will you be seeing c Are you going
![]()
![]() 8 By this time tomorrow I
8 By this time tomorrow I ![]() my
exams.
my
exams.
a 'Il finish b 'Il have finished c 'm finishing
![]() to town later. Can I give you a lift?
to town later. Can I give you a lift?
![]() a 'Il drive b 'Il be driving c 'm
driving
a 'Il drive b 'Il be driving c 'm
driving ![]() 10 This time next week we
10 This time next week we![]() in
Spain.
in
Spain.
![]() a 're going to arrive b 'Il be arriving
c 'Il have arrived
a 're going to arrive b 'Il be arriving
c 'Il have arrived
|
5.1 |
Passive: all forms
•
We
form the passive with the correct form of the verb be and ![]() the
past participle. The tense Of a passive construction is
the
past participle. The tense Of a passive construction is ![]() determined
by the tense ofthe verb be. For example:
determined
by the tense ofthe verb be. For example: ![]() The
hotel i' used by 3,000 a var. (present simple) It budt in 1615, (past simple)
The
hotel i' used by 3,000 a var. (present simple) It budt in 1615, (past simple)
![]() It is
being renovated at the moment (present continuous) It will be reopened nest
•fear the Mawr. (future simple)
It is
being renovated at the moment (present continuous) It will be reopened nest
•fear the Mawr. (future simple) ![]() new
dining room *ill have been added. (future perfect)
new
dining room *ill have been added. (future perfect)
•
![]() We use by to say Who is responsible for the action. This
usually goes at the end of the sentence. The bus shelter destroyed vandals.
We use by to say Who is responsible for the action. This
usually goes at the end of the sentence. The bus shelter destroyed vandals.
• We can use the passive with present and past forms of modal verbs.
![]() The paintings can't be found,
The paintings can't be found,
![]() Thei must have been hidåen_
Thei must have been hidåen_
• Prepositions which belong with the verb go immediately after the past participle.
Burglars broKe into school.
The school into.
•
Most
adverbs go immediately before the past participle. ![]() However.
adverbs of frequency and the adverbs still, just, already and even go
immediately before be or been in compound tenses.
However.
adverbs of frequency and the adverbs still, just, already and even go
immediately before be or been in compound tenses.
![]() The school is being completeli rebuilt.
The school is being completeli rebuilt.
![]() The libram has alreadi been knocked
down.
The libram has alreadi been knocked
down.
The still be used for bas'eibal_
• We don't use the present, past or future perfect continuous form Of the passive:
The•í haveThad/Will have been chasing him for weeks,
(NOT chased for weeksJ
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 1
1
2
3
Complete the sentences with the passive of the verbs in brackets. Use the correct tense.
1
My
bike![]() (steal) three times since Christmas!
(steal) three times since Christmas!
2 Ifwe Win the quiz again next week, we _ (win) it ten weeks in a row.
![]() They couldn't use the phone because the
SIM card
They couldn't use the phone because the
SIM card ![]() (remove).
(remove).
4 When we arrived at the
zoo, the elephants ![]() so we watched.
so we watched.
![]() Scientists say their research
Scientists say their research![]() (not complete) for another five years at least.
(not complete) for another five years at least. ![]() I've
moved into my cousin's fiat because my flat
I've
moved into my cousin's fiat because my flat ![]() (decorate)
at the moment.
(decorate)
at the moment.
![]() The shop refused to exchange the dress
because it
The shop refused to exchange the dress
because it ![]() (wear) several times.
(wear) several times.
8 The Grand Hotel![]() (build) in 1905.
(build) in 1905.
Rewrite these active sentences in the passive. Use by to say Who is responsible for the action.
![]() The Chinese invented paper about 2,000
years ago.
The Chinese invented paper about 2,000
years ago.
![]() Ada
Lovelace wrote the first computer program.
Ada
Lovelace wrote the first computer program. ![]() Marie
Skiodowska•Curie discovered polonium and radium.
Marie
Skiodowska•Curie discovered polonium and radium.
![]() The Wright brothers built the world's
first aircraft.
The Wright brothers built the world's
first aircraft.
![]() Sony manufactured the first CD player.
Sony manufactured the first CD player.
![]() The computer giant IBM designed the
first successful home computer.
The computer giant IBM designed the
first successful home computer.
7 ![]() lack
Dorsey created Twitter in 2006.
lack
Dorsey created Twitter in 2006.
8 Google bought YouTube for $1.65 billion.
Complete these sentences in the passive. Use the modal verb and the verb in brackets.
I Helmets (must / wear) at all times on the building
![]()
![]() Our car isn't where we parked it. It
(must / steal). 3 Ifthe weather's bad tomorrow, the athletics tournament
Our car isn't where we parked it. It
(must / steal). 3 Ifthe weather's bad tomorrow, the athletics tournament ![]() (might
/ cancel).
(might
/ cancel).
![]() That
homework (should / hand in) days ago!
That
homework (should / hand in) days ago! ![]() These
vouchers (can / exchange) for cinema tickets anywhere in the
country.
These
vouchers (can / exchange) for cinema tickets anywhere in the
country.
![]() Are you sure your bag was stolen? it
(could / take) by mistake.
Are you sure your bag was stolen? it
(could / take) by mistake.
7 Don't throw that plastic bag away. It (can I use) again.
8 My phone has run out of power again. It (can't / recharge) properly.
|
|
5.2 |
Using
the passive ![]()
•
We
use the passive when we don't know or don't want to say who or what is
responsible for the action. ![]() phone made in China,
phone made in China,
We can also use the passive for stylistic reasons, especially to allow the main focus of the sentence to be the subject of the verb.
One of me/ favourite paintings is Van Gogh's
'Siarq Night'. It ![]() was painted in ISB6.
was painted in ISB6.
• With verbs that Often have two objects (ask, award, give, offer, owe, pay, send, show, teach, tell, etc.), either object can become the subject of a passive sentence. Tnt•i sent me a DVD in the post, a I was seni a DVD in the PO%i b DVD sent to me in the post.
It is much more common for the indirect Object (usually a person) to be the subject of the passive sentence (example a above).
![]() Rewrite the sentences in the passive.
Make the underlined words the main focus.
Rewrite the sentences in the passive.
Make the underlined words the main focus.
I Panasonic are going to release kind OfTV next year.
![]() Scientists
in Oxford are building a quantum computer. 3 Van Gogh painted
Scientists
in Oxford are building a quantum computer. 3 Van Gogh painted ![]() in
1890 and gave it to a friend.
in
1890 and gave it to a friend.
4 LK. Rowling wrote all the Harry potter novels between 1996 and 2007.
5 lim Carrey. the Hollywood actor. will host the_next awards ceremony.
6 Henry Ford designed the-Mode.LT, one of the earliest motor cars.
2 Rewrite the sentences in the passive. Remember, it's usually
![]()
the indirect object which becomes the subject.
![]() I My aunt gave me a games console for
my birthday.
I My aunt gave me a games console for
my birthday. ![]() was given a games console for mi birihda•f
bi aunt 2 The school awarded my brother first prize for art.
was given a games console for mi birihda•f
bi aunt 2 The school awarded my brother first prize for art.
![]() The hotel manager showed us Our room.
The hotel manager showed us Our room.
![]()
4 My grandfather has
told me that story many times. ![]()
![]() They paid my friend £20 to hand
out leaflets.
They paid my friend £20 to hand
out leaflets.
![]() 6 They Offered me my money back, but I
refused.
6 They Offered me my money back, but I
refused.
7 The police showed the suspect the CCTV footage. 8 Arthur Rubinstein taught my grandmother piano.
|
5.3 |
• We sometimes use would. especially when the future event was a long way off or lasted for a long time.
In IqG4. she met the
man who later be her husband, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() It
was a holiday she would never forget
It
was a holiday she would never forget![]()
• We use the past continuous when the future event was an arrangement.
I toog boots with me because were going for a after lunch.
![]() Rewrite these sentences in the past.
You may need to change some of the time expressions too.
Rewrite these sentences in the past.
You may need to change some of the time expressions too.
![]() Jack's on the diving board. He's going
to jump.
Jack's on the diving board. He's going
to jump.
![]() I'm excited because we're going on
holiday tomorrcrw.
I'm excited because we're going on
holiday tomorrcrw.
3 I don't know my exam result, but I'll find out soon.
4 I've borrowed my brother's laptop. Will he notice?
![]() We're at the station. The train leaves
in ten minutes. 6 It's going to be a long winter.
We're at the station. The train leaves
in ten minutes. 6 It's going to be a long winter.
|
6.1 |
Passive with believe, know, think, etc.
• Verbs like believe, consider, expect, know, report, say, and think are often used in passive constructions, especially in formal language.
• We
can use an impersonal construction with it 4 passive: it passive (present or
past)![]()
It was believed by many people until the Iqth centum that tomatoes uere poisonous
It is known that thn are not.
• Alternatively we use a passive construction with an infinitive: subject ± passive (present Or past) to dolto have done something.
Tomatoes believed to be poisonous. • We
can use an impersonal construction With there passive (present or past) + to
do/to have done![]()
There were thought to be 1.000 people at the demonstration.
He is Known to have been very![]()
• If the sentence refers to a present belief about a past event, we use the present simple passive followed by a perfect infinitive (to have done something).
Tea is Known io have originated in China,
Passive modals, gerunds and infinitives
• We
can use passive structures with modal verbs. ![]()
Homework should be handed in on time.
• Verbs
that are followed by an infinitive Or gerund can also be followed by a passive
infinitive or gerund: NO one to be criticised. ![]() can't
stand being kept waiting,
can't
stand being kept waiting,
• When we're talking about the past, we sometimes want to refer to things which were still in the future at that time. We use wcs going to when the future event was a plan or intention.
She bought eggs and flour because she was
going to mage ![]() a birihda•i cake,
a birihda•i cake, ![]()
I Rewrite the sentences in two ways using passive structures. Start With the Words given.
1 They think that the burglar climbed in through a window. a 'tis b The burglar is
2 They say that she owns five houses. a It is said b She is said
3 They once believed that the earth was flat. b The earth
4 They reported that the ship sankvery quickly. b The ship
5
They
expect that the Government will raise ![]()
![]() b The
Government
b The
Government![]()
6
They
now know that the car was stolen. ![]() a
lt.. b The car
a
lt.. b The car
2 Correct the mistakes in these sentences.
1 Coats can to be left in the cloakroom.
![]() They enjoyed to be taken to the cinema.
They enjoyed to be taken to the cinema.
3 The washing-up ought have been done last night.
![]() Put this cream on to avoid be bitten by
insects.
Put this cream on to avoid be bitten by
insects.
![]() My
mum expects to being promoted at work.
My
mum expects to being promoted at work. ![]()
6 Batteries must being disposed of with care.
![]() 7 Stand up for yourself. Don't let
yourself to be bullied.
7 Stand up for yourself. Don't let
yourself to be bullied. ![]()
![]() 8 Can
you imagine What it's like be followed everywhere by the paparazzi?
8 Can
you imagine What it's like be followed everywhere by the paparazzi? ![]()
6.2 Articles ![]()
a/an
We use the indefinite article alon
• when we say what something is or what itis like. What's that? It's a smartphont_ MY uncle lives in a small flat.
• When we say What somebody's job is.
![]() MY sister is a flight attendant.
MY sister is a flight attendant.
• : When we mention something for the first time.
I've got a new
• when we mean any example Of something.
It, there a bank near here?
• to mean per or for each, brother earns EDO a week.
The bus was travelling at 50 an hour.
We use the definite article the
• when it's clear what we are talking about. This can be a because we've already mentioned it got a cat and a å09. The eat is called b because there is only one of something time the Bun set this evening?
c because it's clear from the situation
Let's go to the beach. the beach that's near here.)
• With most nationality words.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The
Italians have a reputa'ion for being friendly.
• With the names of rivers, mountain ranges, deserts and Seas. the Nile. the Himala•fas. the Sahara Desert, the Baltic
• with a few countries and most groups Of islands. the united kingdom the the Netherlards the gepublic the Channel Islands
• in various set phrases. for example:
90 to the the atre/cinerna listen the raåio/the news play the violin, the piano
• with an adjective to refer to everybodywho has that characteristic. the poor/the rich
No article
We don't use an article
• when we are making generalisations.
Cats eat mice and birå%_
• With most countries, continents, towns, lakes and mountains.
I live in Krakow, in Poland
Toronto it situated on the Of Lake Ontario.
MY friend has just dimbed Mount ![]()
• With some nouns following a preposition. toga t .org/school at home at night bus
in bed/hospital/prison
• With meals.
have breakfast/lunth/dinrit.r
I Complete the Sentences With a/an, the or no
article![]()
I 'Shall we go for walkalong river? 'Nðt
now — I've got to go to work in half an hour,' The bananas are €1 kilogramme.
3 I love looking at Moon and
4 Turn on news is on in a moment.
5 •Shall go out for lunch?' 'NO, let's eat at
|
|
|
|
6 Alexej is from Budweis in |
Czech Republic. |
7 'Is there
Quantifiers
Have
Grammar Builder and Reference | 125
• We use anvwith uncountable and plural nouns in affirmative sentences where the meaning is negative.
I came out without any rnonn.
There is seldom ani snow in the south of Frantt_
• We can use any in affirmative sentences to mean it doesn't matter Which.
![]() friend
Of is a friend Of mine.
friend
Of is a friend Of mine.
• We use no (meaning not any) when we want to be emphatic.
There's no pint in complaining.
No shop* open after 10 0'clock
• We use (a) few With plural nouns and (a) little With uncountable nouns. I've onl•f got a little mone•f.
A feu Of the trees have alread•f lost their leaves.
• We use few/little instead of a few/a little to emphasise the smallness Of the number or quantity.
He has little money and few friends
• We normally use Whole with singular countable nouns. He ate the whole packet Of biscuits.
• We normally use al/ with uncountable nouns and plural nouns.
He ate all the biscuits in the patwt. Have we used up the butter?
• We use both, either and neither to talk about two things. both shopt are npenSive, Neither shop is cheap.
You tan bui cheese at either shop
• Most quantifiers can be followed by Of and a determiner (e.g. the, these, my, etc.): most Of the , a few of his several Of those , of us, each of them, many of, etc.
![]() Of the teachers are in the staff room,
Of the teachers are in the staff room,
However, no and every cannot be followed by Of. Instead, we say none of and every one of. None oftakes a singular verb in formal contexts.
![]() Ont
Of must take the esam.
Ont
Of must take the esam.
None of the leathers are under 30,
None Of the teachers is under (formal)
Choose the correct quantifier.
1 The teacher made all / the Whole class Stay in at break time.
![]() Any / Some questions? Is everything
clear?
Any / Some questions? Is everything
clear?
3 1've just made some / any tea. Would you like some / any?
4 I hardly got some / any sleep last night.
![]() There are a little / a few potatoes in
the fridge but
There are a little / a few potatoes in
the fridge but
a little / little cheese.
6 The police arrested both / either drivers after the accident.
7 There's no / any time to talk now.
8 Any NO student caught cheating will have ten marks deducted.
![]() Why are you walking about without some
/ any shoes?
Why are you walking about without some
/ any shoes?
![]()
10
In the exam you should answer either / both question 1 or question 2.
2 Complete the sentences with ofor leave them blank.
![]() Several the apples were bruised so I
took them back to the supermarket.
Several the apples were bruised so I
took them back to the supermarket.
2 Most pop stars are very well paid.
![]() None my
Old jeans fit me now.
None my
Old jeans fit me now.
4 Did you eat the whole pizza?
![]() Some people
can be really annoying.
Some people
can be really annoying.
6 Many my friends are into sport.
7 Read each question carefully before you write your answer.
8 None his family live in London.
|
7.1 |
Tense changes
•
When
we report somebody's words rather than quoting them directly, we usually change
the tense Of any verbs. ![]() hungry,' he said, He said that he was
hungry.
hungry,' he said, He said that he was
hungry.
The normal pattern Of tense changes in reported speech is:
|
direct
speech |
reported speech |
|
present simple |
past simple |
|
present continuous |
past continuous |
|
past simple |
past perfect simple |
|
present perfect simple |
past perfect simple |
|
present perfect continuous |
past
perfect continuous |
|
past continuous |
past perfect continuous |
would mav/migh t might
must/had to could
• We don't normally change the tense when:
1 the reporting verb is present or present perfect. 'l fatt cars.' ihe *a-dB she fast cars.
2 we are reporting a past perfect verb, would, could, should or hod better. •you go,'
He said that I should go.
• We Often omit the word thatfrom the beginning Of the reported speech clause:
He said it was hoi
![]()
• There
are often changes in words which refer to the people, time or place. These are
dictated more by logic than by rules. ![]() Tm
corning here tomorrow: she said.
Tm
corning here tomorrow: she said.
![]() says she's corning here tomorrow
(reported on the same day, in the same place)
says she's corning here tomorrow
(reported on the same day, in the same place)
She sat, the's going there tomorrow (reported on the same day. in a different place)
f.he said she going there the åa•f,
(reported later, in a ![]() different place)
different place)
However, these time expressions frequently change in the following way:
direct speech ![]() reported speech today that
day tonight that night tomorrow the next/following day next week the
next/following week ago before last week/month the previous
week/month the week/month before
reported speech today that
day tonight that night tomorrow the next/following day next week the
next/following week ago before last week/month the previous
week/month the week/month before
say and tell
• The Object Of the verb say is always what was said. It is Often a clause.
'It's late: said Torn. She said she thirsty.
• If we want to mention the person who is addressed, we must use the preposition to.
'I'm going now,' she said to her friend.
• The object of the verb tell is usually the person who is addressed. We do not use the preposition to.
Have you told Your mum? He told me he tired.
• We also use tell in set phrases like tell a lie, tell the truth, tell a story, etc.
Change the reported speech into direct speech.
![]() Caroline says she'll wear her new dress to the party.
Caroline says she'll wear her new dress to the party.
![]() Kate says she isn't coming dancing With us this evening. 3 Max told me
that he'd like to study law at college.
Kate says she isn't coming dancing With us this evening. 3 Max told me
that he'd like to study law at college.
4 Pam said that she had been to Italy the previous spring.
5 Jon complained that I'd kept him waiting fortwo hours.
6 Joseph told me his team hadn't won a single match before their victory last Sunday.
![]() Martha explained that she didn't want to go out because she hadn't been
feeling very well.
Martha explained that she didn't want to go out because she hadn't been
feeling very well.
|
7.2 |
• When we report questions, we use affirmative word order and verb forms after the question word.
'Where do you live?' she at*eå him.
She asked him where he lived.
• To report a yes/no question (one that has no question word) we use whether orif.
'15 it raining?' he He if it raining.
'DO iou like milk in your coffee?• she asked me.
She
asked me *hether liked milk in mi coffee. ![]()
![]() Report the questions. Begin with
Harry asked me.
Report the questions. Begin with
Harry asked me. ![]()
![]() 'Why haven't you tidied yourbedroom?
'Why haven't you tidied yourbedroom?
2 "When's Kate arriving?'
![]() 'Would you like a cheese sandwich?'
'Would you like a cheese sandwich?'
4 'Why were you laughing?'
![]() 'Could I use your rubber?'
'Could I use your rubber?'
6 •What do you think you're doing?'
• •What have you been doing?'
![]() 'Will you be needing a lift home this evening?'
'Will you be needing a lift home this evening?'
|
7.3 |
• We form indefinite pronouns with some•, any- and no..
|
People |
|
Places |
|
Things |
![]() anywhere nowhere something anything
nothing
anywhere nowhere something anything
nothing
• We use pronouns with some- in the same way as we use some: in affirmative sentences and in offers and requests.
Somebodi has drunk toffee.
Can you leave the shopping somewhere in the kitchen?
•
We use pronouns
With an" in the same Way as we use any: in negative sentences. in
questions, in affirmative sentences Where the meaning is negative. and in
sentences Where it means it doesn't matter Who/which/where. ![]() bored. I haven't got anything to do.
bored. I haven't got anything to do.
Have 90t anywhere io stay tonight?
He musi be fretting. He's hardh wearing anithing. That's An•fone knows that'
Complete the indefinite pronouns in these sentences.
Use some-, or no-. Sometimes more than one answer is possible. ![]()
I Does one know the answer to this question? 2 Would you like thing to eat?
![]() body wanted to go to the cinema With me, so I went by myself.
body wanted to go to the cinema With me, so I went by myself.
•
There was hardly![]() body I knew at the party.
body I knew at the party.
5
1 don't mind
where we go on holiday.![]() where as long it's warm sunny!
where as long it's warm sunny!
6
I heard a noise
outside.![]() one's outside.
one's outside. ![]()
|
7.4 |
We can use Other verbs instead of say and tell when we report statements, e.g. add, admit, agree, answer, argue, boast. claim, complain, confess, confirm, deny, explain, Observe, predict, promise, reply, reveal, Swear, warn. 'This pitta told.'
He complained that his pitta us ![]()
![]() certainly tonight:
certainly tonight:
He predicieå that it would snow that night.
We can use Other Structures when we report Offers, promises. requests, commands, suggestions, etc.
Reference
• verb + infinitive with to agree, offer, promise, refuse, threaten He refused to "ear a tie.
To make the infinitive negative we add not before to.
He promised not to be latE
•
verb + Object +
infinitive With to ![]() advise, ask, beg, command, dare, encourage. forbid,
advise, ask, beg, command, dare, encourage. forbid, ![]() instruct, invite, ordered, persuade,
remind, request, tell.
instruct, invite, ordered, persuade,
remind, request, tell. ![]() urge, warn
urge, warn
She
reminded me to post the letter, ![]()
•
verb + gerund
admit, deny, mention, propose, recommended, report, ![]() suggest
suggest ![]()
He admitted stealing the monel_
These verbs can also be used with a that clause.
He admitted that he'd stolen the monq.
• verb preposition + gerund apologise for, boast Of, confess to, insist on He apologiaed for keeping us •ailing.
• Nerb • Object preposition + gerund accuse 5b Of, congratulate sb on, warn sb against She congratulated me on passing mi driving test.
• verb + that + should-clause advise. demand, insist, propose, recommend, request, suggest,
He insisted ihai she should leave immediately
• In formal English we also occasionally use the subjunctive with these verbs.
He insisted that she leave immediately.
The minister that all illegal immigrants be Sent to their Of origin.
I Report the sentences. Use the reporting verb in brackets.
I 'I'll feed the cat,' said Andy. (Offer) offered to
2 'I'm sorry was so late,' said Susannah. (apologise)
3 'You broke my new smartphone!' Brenda said to Zoe.
(accuse)
4 'Stay away from the cliff edge.' said Denise to her Son.
(warn)
'Could vou all put your pens down?' said the teacher to us. (request 4 should clause)
6 The doctor says it would be better if Sam took more exercise. (recommend subjunctive)
7 'l think smoking should be banned in all public places,' said the minister. (propose + subjunctive)
2 3.02 Listen and report the direct speech. Use the verbs given followed by the appropriate Structure.
I She admitted brea<ing the glass.
1 admit 3 boast 5 suggest invite
2 beg 4 congratulate 6 refuse 8 insist
Grårómar
|
8.1 |
can and be able to
• We normally use can/can'tto talk about ability in the present.
We can also use be able to although it is less common.
Fran can speag Chinese. Fran is able to speak Chinese
• We normally use will be able to to talk about ability in the future.
I'm sure
people Wild be able to travel to Mar* before 2050. ![]()
However,
we often use can/can'tto talk about future ![]() arrangements.
arrangements.
• can't come to the cinema With Iou thiB evening.
• We use be able to When we need an
infinitive. (can has no ![]() infinitive form.)
infinitive form.) ![]() should be able to finish all homework ten.
should be able to finish all homework ten.
• We use being able to when we need an •ing form.
I hate not being able to watch satellite TV. There are 60 9008 programmes on those channels.
• We use be able to when we wantto use the present perfect tense. (can has no present perfect form.)
Sue hasn't been able to since her accident.
Talking about ability in the past
• We use could for general ability in the past.
I read when I four,
• When we're talking about one occasion, we use a different expression, such as managed to do or succeeded in doing. We can also use was/were able to. did manage io repair the DVD player?
They were able to win despite onl\ having ten players,
• However, we use the negative couldn't whether we are talking about general ability or one Occasion.
Carla couldn't BWim until she was fourteen. couldn't get to sleep last night,
• We use could with verbs of perception. like feel, hear, see, smell, taste, even if it's one occasion.
I could dinner cooking soon came in,
1 Complete the sentences with the correct form of can or be able to. Wherever possible, use can.
1 hate drive. I have to ask my dad for a lift all the time.
you play the piano?
Ifwe stop saving money, we afford to buy a house.
4 1 might help you ifyOu tell me What's the matter. you give me a lift to the station this evening?
6 Miriam should ski — she's had quite a few lessons, receive any emails since my computer went wrong.
8 I'm sorry I come to the cinema With you tonight.
|
|
whom (Object. |
whom (object, |
|
|
formal) |
formal) |
|
things |
|
which |
|
places |
where |
where |
|
dates |
when |
when |
|
possessives |
whose |
Whos e |
Relative clauses Combine the two sentences With a defining relative clause. Use Who, Which, where or whose.
|
Defin ing relative clauses
•![]() A
defining relative clause gives essential information about 2 the
noun in the main clause Which it refers to. Without the
A
defining relative clause gives essential information about 2 the
noun in the main clause Which it refers to. Without the ![]() information
the sentence would be incomplete.
information
the sentence would be incomplete.
She's the woman who telling
iou about ![]() 3
3
Shelter is a charity organisation whose aim
i} to help homeless ![]() people
people
•It can go at the end or in the middle Of a Sentence. We use commas around the defining relative clause.
![]()
The doctor treated
me![]()
![]() I met
the Fung woman Who" just started teaching at primary
I met
the Fung woman Who" just started teaching at primary![]()
• The relative pronoun Which or who can be omitted if Object of the clause (but not if it is the subject).
![]() That" the man who lives round the
cornefl (Who subject)
That" the man who lives round the
cornefl (Who subject)
That's the man who I (who object)
![]()
• That's the man I (who Object — omitted)
• We can replace which with that. In informal contexts, we can replace Who With that.
![]() Coal is formed from trees that have been
buried underground
Coal is formed from trees that have been
buried underground
4 I met Some eco•protesters. The police were trying to evict them.
5 1 support a charity. It's campaigning against the use of fossil fuels in energy generation.
6 I found a piece of space junk. It hadn't burnt up in the Earth's atmosphere.
7
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
In which sentences in exercise I can we (a) omit the relative pronoun? (b) replace Who or which with that?
Combine
the two sentences With a non-defining relative ![]() clause,
either in the middle or at the end Of the sentence. Add the correct
punctuation.
clause,
either in the middle or at the end Of the sentence. Add the correct
punctuation.
Fossil fuels are not a renewable source Of energy. They
![]()
![]() are
found deep underground.
are
found deep underground.
Fossil fuels. which arc found
Shale gas is becoming an increasingly
important source Of natural gas. It is gas trapped in shale formations. ![]()
3
There
are many types of renewable energy. Governments are investing in them. ![]()
4 People in industrialised countries should be the first to reduce carbon emissions. They have already benefitted from years of economic growth.
5 Farm animals release a lot Of methane. Methane is a very
![]()
potent greenhouse gas.
6 Nuclear power stations produce a lot Of radioactive
![]()
for milliont of![]()
She's the girl that's going out Bith kim's brother.
Non-defining relative clauses
•A non-defining relative clause gives extra information about the noun in the main clause which it refers to. The sentence makes Sense without it.
•The verb they replace can be
in any tense.![]()
![]()
![]() cloud of smoke. rising from the factori.
blocked the sun.
cloud of smoke. rising from the factori.
blocked the sun. ![]() which was rising)
which was rising) ![]() drove
past a factori maging cars, which makes)
drove
past a factori maging cars, which makes) ![]()
![]()
I Combine the two sentences. Use a shortened relative clause.
![]()
![]() Was that your brother? He was talking to
Sue.
Was that your brother? He was talking to
Sue. ![]()
![]() that
your brother talking to
that
your brother talking to![]()
![]() 2
The police have arrested the woman. She was seen shoplifting on CCTV.
2
The police have arrested the woman. She was seen shoplifting on CCTV.
![]() 3
I've got a photo of my grandad. He's driving an old
3
I've got a photo of my grandad. He's driving an old ![]()
![]() Mercedes.
Mercedes.
4 The man was a climate change scientist. He lived next door.
5 1 live in a farmhouse. It was built in 1855.
6
I
can't find the address book. It contains all my friends' ![]() contact
details.
contact
details.
|
8.4 |
![]() The
insurance company have replaced the vase. It was broken by the removal men. do
and did for emphasis
The
insurance company have replaced the vase. It was broken by the removal men. do
and did for emphasis
• We can use do and did to make statements stronger and to show a contrast. We stress do and did when therre used in this way.
You do liÉe
arguing, don't We did the ballet ![]()
• We
can use do in imperatives to make them more emphatic. DO be careful with that vase! ![]()
• We can use do and did to show a contrast. He's sometimes bit rude but I do him.
I Use door did to make the sentences more emphatic orto show a contrast.
I You didn'tget much sleep last night. GO to
bed early ![]() tonight.
tonight.
![]() 2
It's a very important meeting. Be on time!
2
It's a very important meeting. Be on time! ![]()
![]() 3 1 don't much like him, but I like his
brother.
3 1 don't much like him, but I like his
brother.![]()
4 We enjoyed the play.
5 1 like your new top!
![]()
6 Be quiet, will you!
|
9.1 |
7
I
didn't cook the meal but I did the washing up. ![]() should/could/might/needn't
have
should/could/might/needn't
have
![]() •
We can use shouldn't have to express disapproval of past actions.
•
We can use shouldn't have to express disapproval of past actions.
![]() You
shouldn't have sia•fed up all night.
You
shouldn't have sia•fed up all night.
![]()
![]() • We
use should have, might have or could have to saywhat
• We
use should have, might have or could have to saywhat ![]() the
right way to behave was, in our Opinion. you should have gone to bed before
midnight.
the
right way to behave was, in our Opinion. you should have gone to bed before
midnight.![]()
![]() We
sometimes use might have or could have to tell somebody what they should have
done. It is usually an
We
sometimes use might have or could have to tell somebody what they should have
done. It is usually an ![]() excla mation.
excla mation. ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() you could have saved some pitu for me!
you could have saved some pitu for me! ![]()
![]() We
use needn't have to say an action that took place was
We
use needn't have to say an action that took place was![]()
unnecessary:
you needn't have
worried. I ai m! friend's house. ![]()
![]() If
we talking about an action that was unnecessary and didn't take place, we use a
different structure. Compare: Thet didn9 have to pal for their tickets, Chidren
under eighteen get in free.
If
we talking about an action that was unnecessary and didn't take place, we use a
different structure. Compare: Thet didn9 have to pal for their tickets, Chidren
under eighteen get in free.
They needn't have paid for their tickets. MN uncle the cinemi (But they did pay for them.)
1 Choose the word which makes the most sense in these
![]()
I I don't mind you borrowing my phone, butyou might / needn't have asked me first!
![]() We shouldn't I needn't have eaten those
burgers; they
We shouldn't I needn't have eaten those
burgers; they ![]() were a week past their •use by' date.
were a week past their •use by' date.
3 1 forgot our homework was due in today —you could / needn't have reminded me!
4 I was only two minutes late. You might / shouldn't have waited for me!
5 We needn't / shouldn't have gone to Greece in March; the weather was terrible.
6 My mobile was switched Off — you needn't / should have tried my landline.
2 Rewrite the sentences so they include should, shouldn't, could, might or needn't have. Don't change the meaning.
I It was a bad idea for you to give chocolate to your dog.
![]() 2 She wore formal clothes. but it
wasn't necessary.
2 She wore formal clothes. but it
wasn't necessary.
3 Inviting your cousins to your party would have been a good idea.
4 I Wish you'd saved some chips for me!
![]() Leaving the front door unlocked was a
bad thingto do.
Leaving the front door unlocked was a
bad thingto do.
6 It was unnecessary for you to buy me a present.
![]() It would have been better if you'd
stayed at home.
It would have been better if you'd
stayed at home.
8 I Wish therd given us a lift to the station!
|
9.2 |
• We use the third conditional to talk about how a situation in the past could have been avoided:
If she hadn't lost her temper. Tack wouldn't have left.
(But she did lose her temper and Jack did leave.)
• The if clause can come before Or after the main clause. We use the past perfect in the if clause and would/wouldn't have in the main clause. Be careful: had and would both have the same short form: 'd.
She'd have been amazed if •fou'd asked her out.
(She would have been amated if you had asked her Out)
• We use could have in the main clause when we're talking about ability. It means have been able to:
|
Grammar |
If I hadn't had a bean suitcase with me. I have run for the
• We can use could have or might have in the main clause if the result is less certain.
If dad had gone to universiti. he might have become a teacher.
Complete these third conditional Sentences with the past perfect and would(n't) have form Of the verbs in brackets. 1 Ifvou (not leave) the door open. the burglars (not get) in!
(Win) the match ifwe (play) better in thesecond half.
3 It (be) better if you (not mention) our plan.
4 If my dad (not come) home, the party on) all night.
5 They _ (go) On holiday in the summer if they (not go) skiing already that year.
6 You (not guess) my secret if your sister (not give) you a clue.
(not write) a letter Of complaint if I be) so angry.
8 If you (ask) to borrow my football boots, I (say) yes.
|
9.3 |
• Mixed conditionals are a mixture of type 2 and type 3 conditionals and refer to hypothetical situations. Remember that type 2 conditionals refer to the present or future, and type 3 conditionals refer to the past. Mixed conditionals occur when the time reference in the ifclause is different from the main clause.
If had eaten your lunch. you wouldn't be hungry noW
past (type 3) present (type 2) If we hadn't fallen out with each other. we'd on holi4aN together again this f,urnmer,
past (type 3) future (type 2)
If I lived in London I would have gone to the match.
present (type 2) past (type 3)
• The choice ofverb forms in mixed conditionals depends on the time reference. If we're referring to the past in the if clause, we use the past perfect (simple or continuous) as we would in a type 3 conditional; we're referring to the present in the if clause, we use the past simple as we would in a type 2 conditional. Similarly, if we're referring to the past in the main clause, we use would have, as for type 3; if we're referring to the present or future in the main clause. we use would, as for type 2.
I Match the two halves of the sentences. Complete the second half With the correct form Ofthe verb in brackets.
If you weren't my best friend,
2 If they hadn't closed the bowling alley,
3 She might have become a model
4 You'd never have stood in a queue for three hours If there was a good restaurant in town,
6 He wouldn't have become a teacher
we (go) there tonight. b if she (be) a few centimetres taller. c if you (not be) British.
(not tell) you what I really think.
e if he (not like) children.
(not buy) fish and chips.
2 Rewrite each pair of sentences as a mixed conditional
1 They're very argumentative. That's why they fell out.
If thet weren't argumentative. the! wouldn't have fallen
2 He isn't fit. That's Why he didn't finish the race.
3 My grandfather owned a factory. That's whwWe live in a big house.
4 She worked hard last term. That's why she's disappointed with her exam results.
5 1 don't speak Spanish. That's why I didn't apply for a job in South America.
6 It rained all night. That's whywecan't use the tennis
7 You were rude to Ellie. That's Why she doesn't like
8 We're on holiday. That's why we didn't go to the barbecue.
|
9.4 |
• We use the follcM'ing structure to express regrets about the past:
I (really) wish + past perfect
I'd (much) rather past perfect
I wish I hadn't spent all ml money
I'd much rather sent me a message.
I Write a Sentence using the word in brackets to express these regrets about the past.
1 1 didn't revise for the exam. (wish)
I with reviÐBd for the
2 you told Jacqui my secret. (rather)
3 you didn't wear smart clothes. (rather)
4 I didn't ask for her phone number. (Wish) my favourite team didn't win. (wish)
6 we stayed in a hotel. (rather) you didn't give me money for my birthday. (rather)
-8 I promised to help Louis with his homework. (wish)
Refererice i
|
Normal |
Emphatic |
|
9.5 |
|
• We can express purpose with a simple infinitive or the phrase in Order (not) to or so as (not to). She Stood up in order to ask/90 as to ask a question, • We can also use the phrase With a view to or With the intention of followed by an -ing form. They renovated the hotel vith a view io charging mort for the • We can also express purpose With in order that, so that orsO followed by a clause. Sht sat in order that/so that/so the people behind her see. • We can express a result with so (but NOT so-that) t tired I went to bed • We can also express a result using so adjective or adverb or such (tadiective) ± noun followed by that and a clause. so tired that I went to bed at 1 p.m. They badly that they lost 8-0. It "as such a boring film that I fell The* such difficult questions that I couldn't answer an-I Of them. Choose the correct words to complete the sentences. I The supermarket was closed she went to the corner shop. a so that b in order that c so 2 We spent so long at the museum we didn't have time for the art gallery. a so b So that c that 3 She went to lots of parties in the first week Of term making friends. a in order to b SO that c with a view to 4 He logged onto his email account check his messages. a so that b in order that c to 5 They got a passport for their baby they could travel abroad. a so b in orderto c that 6 The film finished early they went to a café. a in orderthat b so that c so 7 She took Off her shoes not to get them wet. a so b so as c in orderto 8 They spent little time in France that they didn't learn any French. a such b so c that Emphasis and inversion • We can make a sentence more emphatic by adding an extra |
to go was beach. to go to the beach. I'd like to meet Lady Gaga. The person I'd like to meet is Lady Gaga. He really wants to visit China. One country he really wants to visit is China. I'll never understand One thing I'll never baseball. understand is baseball. She just walked the second All she did was (to) walk the half of the race. second half Of the race. The fire alarm went Off. What happened was (that) the fire alarm went off. • After All (I) did was or What (l) did we use an infinitive With or Without to: What they did (to) make a shelter in the woods. However, after All that happened was or What happened we need a subject and a verb. We can put that before the subject: All that happened was (that) they made a shelter in the woods, • We can also make a sentence more emphatic by putting a negative or limiting adverb (or adverbial phrase) at the front. These include: never, not since, not only, no sooner than, hardly, rarely/ seldom, under no circumstances, no way. After the adverb or phrase. the word order is inverted. Not Since his childhood had enjo•ted a holiåa•i BO much. Barely has there been a popular event, • For verbs in the present/past simple we use do/did. way does he deserve a priZ_e for that' Not did he 'Sin. but he won b-N pints. Rewrite the sentences With an extra clause at the start for emphasis. Begin with the words in brackets. I You always forgetyour keys. (It's you ) It's who always forgets lour KENS. 2 I really hate tomato Soup. (One thing ) 3 My parents met in Japan. (It was ) 4 The referee awarded a penalty. (What happened ) Lisa spent a year abroad after school. (What Lisa ) 6 I asked my dad for some money, that's all. (All I 7 1 enjoy talking to my grandfather. (One person 8 My uncle took me to my first sports event. (It was ) 9 We just need one more basketball player. (All we ) 10 You can't go to Antarctica on holiday. (One place Complete the second sentence in each pair so that it means the same as the first. 1've never seen such an impressive firework display. Never an impressive firework display. |
You wanted to the It you that/who wanted
clause to highlight key information. 2 You mustn't, under any circumstances, unlock the door. Under unlock the door.
Grammar
3 We haven't been to Scotland since our wedding.
Not since ![]() to Scotland.
to Scotland.
4 He certainly can't speak six languages!
![]() No
way
No
way![]() six languages!
six languages!
5 She broke her arm and also damaged her knee.
Not only![]() damaged her knee.
damaged her knee.
6
The
party ended as soon as we'd arrived. NO sooner![]() ended.
ended.
|
10.2 |
• We use the past simple after certain expressions even though the meaning is present or future. It's (high) time had a shower,
I'd rather didn't tell anyone
I'd sooner travelled by plane.
Imagine worked in New York!
• We can use the past or present simple after these expressions, without a significant difference in meaning: iuppose we hadThave dinner out tonight.
They as if/at thœJgh are/were married!
• When we use the unreal past, we normally use were instead of was.
I'å rather I weren't in the athletics team. Complete the second sentence so it means the same as the
1 1 don't wantyoutoread mydiary.
I'd rather ![]()
2 Why
don't we invite the Whole class? Suppose![]()
3 Wouldn't it be great to have a Ferrari?
Imagine![]()
4 We should return these books to the library.
It's time ![]()
5 1 don't want my parents to be friends with me on Facebook.
I'd sooner![]()
![]() The
Government should allow online voting. It's high time
The
Government should allow online voting. It's high time ![]() had
better/mightas well
had
better/mightas well
• We use had better followed by an infinitive Without to to give advice or a warning. Even though had is the past simple form Of have, we use had better to give advice about the present or future.
You'd better the teacher before iou leave.
He'd better start behaving himstlf!
The negative form Of had better is had better not (NOT hadn't-better) you'd better not do that again
TO describe the consequence of not following the advice, had better (not) is often followed by or will future.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
He'd
better not argue uith the captain or he'll his place in the team.
• We
use might as wellto say what course of action should be followed. does not
imply a strong recommendation for that course Of action, but rather that there
is nothing to lose by following it, or that the alternative is no better. Thai
plani is dead. 50 might as throw it ![]()
Rewrite these sentences With had better
(not). Include or * ![]() Will future if appropriate.
Will future if appropriate.
I I'll be furious if you borrow my laptop without asking.
![]() They should hurry up to avoid being
late.
They should hurry up to avoid being
late.
![]() If she doesn't apologise, I won't
invite her to my house again.
If she doesn't apologise, I won't
invite her to my house again.
4 It would be a bad idea to wake my dad up.
5 You won't geta good mark unless you answer all Of the questions.
6 1 should go home now. If I don't, my mum Will be worried.
2 Complete the sentences with might as well and an appropriate verb or phrase.
![]() The weather is terrible. We..
The weather is terrible. We..
![]() That torch doesn't work. You„.
That torch doesn't work. You„.
3
Tickets
for the lottery are Only El each.![]()
4
These
crisps won't stay fresh now the packet is open. ![]()
5
You'll
find out the truth sooner or later, so ![]() 6
There's nothing good On TV.
6
There's nothing good On TV.![]()
|
10 |
• When we start a sentence with an adverbial phrase of direction, position, etc., the subject-verb word order which follows is usually inverted. We usually do this with verbs of place Or movement (climb, come, fly, go, hang, lie, run, sit, stand, etc.) but not other verbs:
Near the door stood a man in a white coat.
the two men were Chatting (no inversion)
• However,
when the subject is a pronoun, we do not invert. ![]()
(NOT
• When the verb form is there is/are, we miss out there instead of inverting.
Dn the floor were three large bags,
1 Rewrite these sentences starting with the adverbial phrase. Invert the word order which follows only if appropriate.
![]() His aunt sat at one end of the sofa.
His aunt sat at one end of the sofa.
![]() My sister is asleep in the top floor
bedroom.
My sister is asleep in the top floor
bedroom.
3 An empty wine bottle lav on the grass.
4 There are three cinemas in the town centre.
![]() She ran out of the room, screaming.
She ran out of the room, screaming.
6 There's a tennis court behind the football pitch.
Reference
1
|
|
|
|
|
Synonyms and antonyms A synonym is a word which means the same as another word: unhappy and sad are synonyms. An antonym is word which means the opposite of another word: tall and short are antonyms. Some dictionaries include synonyms and antonyms. |
|
Compound adjectives Compound adjectives are adjectives formed from two words. The two most common types are: 1 adjective 4 noun with •ed ending kind-hearted, long-legged, big-headed 2 noun •ing form space-saving. meat-eating, time-wasting 3 adverb • past participle well•worn, thinly, veiled |
I Read the Learn this! box. Then match the adjectives in group 1 with their synonyms in group 2. Decide if each pair is positive or negative and Write them in the chart.
|
I cagey conceited condescending daring energetic friendly humorous intelligent irritable logical loyal |
Complete the adjectives from Learn this! box. |
|
relaxed timid unassuming |
I He gets so much praise from his parents that he's |
|
2 active adventurous amiable calm clever faithful |
become quite |
|
grumpy modest patronising rational secretivë shy |
Keeping the ball in the corner Of the pitch is a Common |
|
vain Witty |
tactic in football. plants get their nutrition from trapping insects. |
the sentences with six of the
|
positive |
negative |
|
|
cagey - secretive |
|
|
|
2 |
Make compound adjectives with a word from each group. |
|
2 Choose the best antonym for each word. |
|
|
Match them with the correct definitions. |
|
I approximately (adverb) |
|
|
able absent cold densely dimtý level mouth |
|
a very b nearly c exactly 2 calm (adiective) |
d correctly |
|
sure |
|
a exciting b excited -boring |
silent |
|
blooded bodied footed headed minded |
|
3 neat (adjective) |
|
|
populated watering |
|
a messy b c lazy |
reliable |
|
1 dark; without many lights |
|
4 truthful (adiective) a incorrect b false C different |
d dishonest |
|
: having a lot of people living iri small area |
|
5 adore (verb) |
|
|
forgetful |
|
a prefer b hate c love |
enjoy |
|
: delicious |
|
6 despair (noun) |
|
|
: cruel |
|
a optimism b fun c excitement |
d joy |
|
: unlikely to fall : calm |
|
3 Complete the sentences With the words you selected in exercise 2. |
|
: fit and healthy |
|
|
1 1'm embarrassed about my handwriting. |
3 |
Complete these sentences with compound adjectives. Then |
|
|
2 Can you imagine how you'd feel ifyou won the |
|
invent two similar sentences Of your own. |
|
|
lottery? |
|
1 People who wave flags are people. |
|
|
3 A marathon is 42.195 kilometres. |
|
Cats With short hair are |
|
|
4 It's a crime to give a answer to a question in |
|
People with strong minds are people. |
|
|
court. |
|
4 Bread that has been baked freshly is bread. |
|
|
5 1 simply __ all forms of motor-racing. |
|
A gadget which Saves time is a |
|
|
6 He always looks forward with |
|
6 A man with one arm is a |
|
4 She sometimes comes across as grumpy, but she's actually very
Most high•jumpers are extremelytall and
This French film is actually a attack on Hollywood.
8
|
2
Match the idioms With the definitions.
I get ripped Off cost an arm and a leg
3 come into some money 4 dip into your savings live from hand to mouth
6 make ends meet 12
7 tighten your belt 8 make a killing
a make a big profit spend all your money on basic needs like food Without being able to buy anything else c be given some money, usually after a relative has died d be charged too much money e spend some money that you had put aside to use later spend less money than usual g be very expensive h have just enough money to buy what you need
2 Complete the sentences With idioms from exercise 1. Use the correct form.
I •Was your new bike expensive?' "Yes, very. It
2 We had to to pay for a holiday last year. But we've still got a few hundred pounds left in the account.
3 Jim When his grandmother died. He was able to buy a new car.
4 Many people on State benefits , with barely enough money for basics like food and heating.
5 1 don't earn a great deal, but we manage to
6 You could have bought that computer for half the price on the Internet. You
My uncle when he sold his business. But then he lost it all When he invested in the stock market.
8 Prices are going up and wages aren't increasing. So we'll have to
|
|
Time and money We use the same verbs with time and money: be short Of, have time/money to spore, lose, make, run Out Of, save, waste. Hurry up and stop wasting time! Don 't waste your money on sweets/ |
Complete the adverts with the words be
amenities balcony for sale fully-fitted top-floor walking distance
3-bedroom 1 flat with . Separate kitchen. Within easy Of local bus routes and : £200,000.
available central heating double glazing furnished rent spacious apartment, Offered or part-furnished.
Benefits from and gas
1 May. £500 per month.
Match the adjectives in group A With the extreme adjectives in group B.
A angry beautiful crowded clean dirty funny hungry silly surprising tired ugly
B astonishing exhausted filthy furious gorgeous hideous hilarious packed ridiculous spotless starving
2 Complete the extreme adjectives that mean:
2 very good: f 3 very bad:
Can you add any more? Use a dictionary or thesaurus to help you.
|
Hungry? I'm starving! |
|
|
|
|
Then listen and reply to the sentences in the same way, using an extreme adjective. Copy the intonation in the example. I Are you hungry?
Choose the correct comment adverbs. Sometimes there is more than one correct answer.
Personally, / Apparently, / To my surprise, I don't believe in ghosts.
2 To be honest. I Foolishly. / Frankly. I'm notvery keen on Italian food.
3 1'm broke. so ideally obviously/ unfortunately I can't come Out tonight.
4 Hopefully / Ideally / Luckily I'll pass my driving test before my eighteenth birthday.
5 He fell off his bike, but fortunately I notsurprisingly / hopefully he didn't hurt himself badly.
|
3
I Number the stages of life below in the order that we reach them.
childhood
old age
adolescence
adulthood
middle age
infancy
2 Match the words below with the stages of life. Draw a spidergram. Some words can go With two stages.
career elderly forties grey hair kid marriage nappies OAP retirement seventies teenager toddler twenties walking stick White hair wrinkles
3 Can you add any more words to the spider-grams? Use a dictionary to help you if necessary.
Complete the sentences With up or down. Then listen and check your answers.
1 You're welcome to visit us on Saturday but I'm afraid we can't put you
2 He doesn't play as well as he can because he doesn't want to show the rest of the team
They often have terrible rows because they both refuse to back
4 When you talk to my grandfather about his health problems, he always plays them
At the time, his marriage was a huge scandal that took years to die
6 It's a comfortable hotel, but they need to do it 7 As the teacher started to wind the lesson, the students put their bCH3ks away.
8 He only took skiing after he'd retired.
9 There was an accident on the motorway Which held us for two hours.
10 He turned a job in a bank because he wanted to be a dancer.
|
Phrasal verbs (1) Phrasal verbs Can be transitive (they have an object) or intransitive (they don't have an object). He sat down. (intransitive) He putdown his bag. (transitive) 2 Transitive phrasal verbs are usually separable. This means the object can go before the adverb. / cut down the tree. We cutthe tree down. If the phrasal verb is separable and the object is a pronoun, the pronoun MUST come before the adverb. X / cut it |
2 Read the Learn this! box. Then match the phrasal verbs (1—10) With the meanings (a—D. Use the sentences in exercise I to help you. Is each verb transitive or intransitive?
|
back down |
renovate |
|
die down |
provide accommodation for |
|
3 do up |
c delay |
|
4 hold up |
refuse to accept |
|
play down |
e change your position or ideas |
|
6 put up |
minimise the importance Of |
|
7 show up |
bring to an end |
|
8 take up |
h start doing (as a hobby) |
|
9 turn down |
become weaker or quieter |
|
10 Wind up |
make look inferior |
3 Write another example sentence for each ofthe phrasal verbs in exercise 2.
4
I Complete the text With the correct form Of the words below. Use a dictionary to help you.
candidate coalition constituency general election hung parliament majority member Of parliament prime minister proportional representation vote (n)
The British Electoral System in Britain take place at least every five years. The country is divided up into (areas) in which the various , Who are usually members Of political parties, put themselves up for election. Each candidate hopes to become the for that constituency. The electoral system is not s , where the total number of for each party across the country is taken into account, but 'first past the post', where the winner in each constituency is elected and all the Other votes count for nothing. If a party Wins a 7 of seats in parliament, they form a government, and their leader becomes
. If no party has a majority, then it is and the opposing parties may agree to form a
I Match the logos with the international organisations.
a European Central Bank
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organisation) c WWF (Worldwide Fund for Nature) the ELI (European Union) e the LIN (United Nations)
Amnesty International g the Red Cross
World Trade Organisation
2 Describe the activities of the organisations. Use the words below to help you.
Verbs campaign for protect regulate support Nouns economic affairs environmental issues freedom of speech human rights military alliance political prisoner refugees trade
Complete the chart. Use a dictionary to help you. Be careful, not all the words end in •ist.
|
Noun / person |
Noun / person |
|
I feminism |
6 capitalism / |
|
2 vandalism / |
7 socialism / |
|
3 atheism / |
8 patriotism / |
|
4 extremism / |
9 nationalism / |
|
S pessimism / |
|
2 Match words from exercise I With these definitions.
I the belief that God does not exist a person who loves his or her country very much a person With extremely Strong political or religious opinions, sometimes prepared to use violence
4 the belief or feeling that bad things Will happen
5 the belief that women should have the same rights and opportunities as men
6 a person Who deliberately damages public property a person who wants their country to become independent an economic system in which businesses are mostly owned privately, not by the state an economic system in which businesses are mostly owned and controlled by the State
1 Listen and repeat the words below. Is the word a verb or a noun? Then say the word again changing the syllable that is stressed.
conflict 4 increase 7 record
2 import 5 produce 8 suspect
3 permit 6 protest
2 Complete the sentences With the correct form Ofwords from exercise 1. Then read the sentences aloud stressing the gapped word correctly.
The Government refuses to teachers' salaries.
2 Usain Bolt first broke the 100 m world in 2008. The demonstrators were against the big rise in the price of petrol.
4 The police have arrested a man Whom they Of murdering his wife.
5 Britain a lot Of food from Other countries. China over 50% of the world's manufactured goods.
|
5
Match eight Ofthe words below With the pictures (I
aerial antenna axle battery blade brake bulb circuit board cog dial fan lead lens microphone microprocessor motor plug pulley SIM card speaker spring strap switch thermostat touchscreen
2 Divide all the words from exercise I into two groups. Write the ones you would find in a smartphone in box A; write the Others in box B with one example Of where you might find them.
|
A (smartphone components) |
B (other components) |
|
|
|
3 In pairs, decide which components from exercise I the following Objects probably contain.
|
I electric razor |
4 lawnmower |
|
2 hairdryer |
5 moped |
|
3 HD video camera |
6 microwave oven |
Workin pairs. Complete the chart With the missing words. Use a dictionary to help you.
|
Crime |
Criminal |
Verb |
|
arson |
|
set fire to (a building. etc.) |
|
blackmail |
blackmailer |
|
|
burglary |
|
burgle (a house, office, etc.) |
|
drug dealing |
|
deal drugs |
|
forgery |
forger |
|
|
|
fraudster |
defraud (somebody) |
|
hacking |
|
hack (into something) |
|
hijacking |
hijacker |
|
|
kidnapping |
|
kidnap |
|
joyriding |
|
go joyriding |
|
|
mugger |
mug (somebody) |
|
murder |
murderer |
(somebody) |
|
|
rapist |
rape |
|
robbery |
robber |
|
|
shoplifting |
|
shoplift |
|
|
thief |
steal (something) |
|
trafficking |
|
traffic |
|
|
vandal |
vandalise (something) |
2 Complete the crime reports with the words below.
convicted jury pleaded sentenced verdict lustin Jones was t of kidnapping and to nine years in jail. Although Mr Jones had — not guilty, the evidence against him was described by the police as
•overwhelming' and the took less than an hour to reach their 5 acquitted alibi evidence found trial witnesses
At the High Court today, Karl Macintosh, who was standing for the murder of two teenagers, was 7 after the jury him not guilty. Although prosecutors had argued that forensic linked Macintosh to the crime scene, several confirmed his accused arrest issued Offences question
Police would like to a man about a series of in the Liverpool area. He is of defrauding more than ten elderly couples out Of their life savings.
Police have a description of the man and are Offering a reward for information Which leads to and conviction.
|
6 6.1 Informal food idioms 6.2 Food and nutrition |
Match the informal idioms (1—10) With the meanings (a—I). Use a dictionary to help you.
|
I a couch potato |
6 go pear-shaped |
|
be paid peanuts |
7 be full Of beans |
|
3 in a nutshell |
8 butter somebody up |
|
4 be out to lunch |
9 pie in the sky |
|
spill the beans |
10 have a lot on one's plate |
a (Of a plan) to go badly wrong be full of energy and enthusiasm c to receive very little money d be very busy. with a lot of things to do and think about e something Which someone talks about that is very unlikely to happen behaving strangely g expressed clearly and in few words say nice things so that someone Will help you or give you something give away a secret person Who spends a lot Of time sitting and watching TV
2 Complete the sentences with idioms from exercise I. Use the correct form.
I 'Can I watch tellv, Mum?' 'NO, you've watched enough television today. You'll turn into a
2 He keeps On saying the weirdest things. I think he's a bit
3 The kids are . They've just played tennis and now they want to play football.
4 If you want to borrow his car, you'll have to first!
5 He's sympathetic, supportive, generous. a good listener. , he's a really good friend.
3 Replace the underlined words with idioms from exercise 1.
He talks about getting a new job, but it'll never happen. 2 lake and Sue are getting divorced, but rinn'r anvone.
3 I'd like to help you, I'm very busy at work and at home.
4 Her plan to sell her house and move to France has
He has a very responsible job but he gets paid verv little Complete the sentences with the words below.
additives calories cholesterol fair-trade fibre
GM foods tow-carb organic use-by date Wholemeal
are used to improve the flavour of food or change its colour.
2 contain plants that have been changed (genetically modified) in order to protect them from disease or to make them more productive.
3 food has been produced without the use Of artificial chemicals or fertilisers.
4 bread is made from the whole grain of wheat. It contains lots Of
5 If you follow a diet, you eat less bread, pasta, rice, etc. and more foods containing protein or fat.
6 goods help farmers in developing countries because the farmers receive a fair price for their produce. The recommended daily intake of in the UK is about 2,500 for men and 2,000 for women. 8 You shouldn't eat food that has passed its
9 Too much , can cause heart disease.
|
|
Verbs and nouns from adjectives We can add •en or -ise (US •ize) to some adjectives to form verbs. short - shorten make shorter) tight — tighten fictional — fictiona/ise general — generalise We can add •ness or •itvto some adjectives to make nouns. Sometimes the spelling changes. b itter — bitterness ready — rea diness real — reality possible — possibility |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Add some flour to the Soup. (thick) 2 was down to 50 m in the fog. (visible) 3 I don't think it's a good idea to cannabis. (legal) 4 The accident was the result of the driver's (careless) Wait till the plums before picking them. (ripe) 6 Shall your pencil for you? (sharp) Thanks for letting me know what you think. appreciate your . (frank) 8 is very important in business. (punctual) 9 The Government is planning to the steel industry. (national) 10 Joe bears a striking to his sister. (similar) |
Read the Learn this! box. Complete the sentences by making a noun or a verb from the adjective in brackets.
7
Match the words in A with words in B.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
breaking |
broadcast |
satellite |
page |
|
|
citizen |
journalism |
front |
blog |
|
|
|
flash |
eyewitness |
correspondent |
|
|
online |
news |
rolling news |
phone |
|
|
news |
edition |
news |
account |
|
|
news |
programme |
news |
channel |
|
2 Explain the meaning of these Words. You can find them all in a newspaper.
1 article 4 column
2 headline S editorial
3 human-interest story
Read the newspaper headlines (1—6). Explain them using the information below to help you.
|
Headline language |
|
|
riddle mystery |
gems jewels |
|
bid = attempt |
ban make illegal |
|
plea — request |
vow = promlse |
|
quit = resign |
pledge promise |
|
curb control; limit |
axe = cut |
1 Riddle of missing gems solved
2 Doctors in bid to ban smoking
3 Royal couple in privacy plea
4 Manager vows to quit at end of season
5 Minister pledges to curb inflation
6 Government to axe 5,000 jobs
2 Which headlines are 'hard' news? Which are •soft' news? Give reasons.
7.3 Phrasal verbs with on, off, out and in.
|
|
Particles and meanings Some particles Can give a phrasal verb a certain general meaning. For example, offtan convey the idea Of: 1 going away, e.g. takeoff, liftoff, clearoff 2 starting, e.g. kickoff, setoff, sparkoff 3 becoming less, e.g. wear off, die Off, cool off 4 resisting. e.g. fight Off, fend Off, hold Off |
Match the meanings below With the groups Of phrasal verbs (A—D). Then translate the verbs into your language.
arriving continuing discovering/solving ending
|
|
Translation |
|
|
|
|
carry on |
|
|
go on (about) |
|
|
Stay on |
|
|
|
|
|
log off |
|
|
ring Off |
|
|
call off |
|
|
|
|
|
work out |
|
|
find out |
|
|
sort out |
|
|
|
|
|
pull in |
|
|
get in |
|
|
check in |
|
2 Use the verbs in exercise 1 to complete the sentences. Use the correct form.
If you bank online, always remember to when you leave the website.
along this road until you reach the church. Then turn right.
Can you if Danny has got an email address Or not?
4 The football match has been owing to the bad weather.
5 1'm going to in this job untill've earned enough money for a new car.
6 we at the hotel and took our cases to our room. Before you take out a loan you should exactly how much vou earn and spend each month. Then you'll know if you can afford it.
8 What time did you last night? I didn't hear you so it must have been after I went to bed.
9 He's always about how much money he earns. He's such a bore!
10 The bus to the bus station and stopped.
Il I'll make the food for the party if you the music.
|
don't know Who was calling. |
12 As soon as I answered the phone, the caller
8
Complete the text with the words below.
breeding captivity conservation extinction habitat poaching reserves threats the wild
The population of gorillas living in is in decline.
to their survival include the destruction Of their natural (the forests in
Which they live are Cut down for fuel), and (they are hunted for their meat). In an effort to aid gorilla
number Of s have been created where the animals are protected. There are also programmes in zoos around the world, although there is a much debate On whether it is cruel to keep such intelligent animals in . They are an endangered species, but for the time being they do not face
|
anti- — against |
anti-clockwise |
|
ex- former |
my ex-wife |
|
mis- badly or wrongly |
misprono unce |
|
multi- many |
multi-storey car park |
|
over• = too much |
|
|
post- — after |
postgraduate |
|
re- again |
rewrite |
|
semi- = half |
semi-detached |
|
under- not enough |
un riced |
I Read the information above. Rewrite the sentences replacing the underlined words with a word or phrase that includes one of the prefixes.
1 Please arrange the desks in a ?leaee arrange the dB*" in semi-circle I failed to understand what you said.
3 Last weekend we took part in a demonstration
4 He used to be a policeman.
5 You shouldn't
This meat enough.
My dad was born in the era after the war.
The National Health Service
If you didn't understand it the first time, read-itagain.
10 The children are
Complete the dictionary entries with the verbs below.
damage harm hurt hurt injure wound
1 to cause physical harm to sth, it less useful valuable The fire bad/y damaged the house. 2 to have a bad on sb's life, health, happiness emotionally damaged children
to have a bad on Wsth; hurt sb/sth Pollution
Can harm marine life.
(rather informal) to have a bad effect on sbS life, health, happiness Hard work never hurt anyone.
Damage, hurt or harm? Hurt is slightly less formal. especially when Ys used in negative Statements. It *on't hurt him to have to wart a bit.
...bit-Harm is also otten used to talk about ways in which wildlife and the environment are damaged by human activity.
to harm yourself or sb else physically, in an accident He injured himself playing • people were injured in the accident.
(rather formal; Often pass,Ve) to injure part of the body, especially by making a hole in the skin. He was wounded jn the arm. • 50 people were senous/y wounded in the attack. •W6und is often used to talk about people being hutt in war or other attacks.
to cause physical pain to sb'yourself; to njure sb/ yourself. He hun his back p¼yjng tennis. • Did you hurt yourself? • Stop it. You hurting me! • My shoes hurt. tight
Hurt injure? Can hurt or injure a part Of the in an accident. Hurt the physical caused; injure that the pan Of body has in
2 Read the dictionary entries and then choose the correct verbs in the sentences.
I CO, emissions from factories are harming / injuring the environment.
2 The bus was badly harmed / damaged in the crash. Come on, Salty. eat your vegetables. They Wq:jn't hurt / damage you!
|
| |
4 He was injured I wounded in the arm in the knife attack. 5 My back is really hurting / injuring me today.
9
|
|
1 Some adjectives ending -'y keep the same form for the adverb: early, daily, weekly, monthly, yearly, etc. took the early train. She gets up early. It's a monthly newspaper. I get paid monthly. 2 Other adjectives ending -IV do not have an adverbial form: cowardly. disorderly, friendly, jolly, leisurely, lively, timely, etc. Instead, we put the adjective in an adverbial phrase: He always behaves in a friendly wav/fashion/manner. 3 Some adverbs have two forms: one With -IV and one without: close closely just justly deep deeply late lately hard hardly near nearly high highly wrong wrongly The meanings are sometimes close and sometimes unrelated: They sailed close to the shore.At's a closelyguarded Secret. She dived deep into the pool./The insult hurt her deeply. She works hard./You've hardly touched your dinner. The balloon flew high over the house./CrOCOdiIes are highly dangerous. I've just told you.(Were they treatedjustly by the courts? He arrived late./He's been doing that a lot lately. Don 't walk near the edge ofthe cliff./You nearly fell. You 've typed my number wrong./He was wrongly accused of burglary. |
Read the Learn this! box. Then complete the sentences using an adverb or adverbial phrase formed from these adjectives.
close cowardly deep friendly high late leisurely weekly wrong
I When he called the dog's name, it wagged its tail
2 His boss was angry because he arrived for work on his first day.
These Wild animals are dangerous.
4 They walked into the jungle.
5 Our plan worked perfectly at first but then everything went
6 The mugger Chose to target children and elderly people.
7 The Ferrari won the race. followed by the Mercedes.
8 Sunday is the only day we have time to relax and eat lunch
9 The sitcom is broadcast on MTV.
[
|
|
We can add suffixes to some nouns and verbs to make them into adjectives. (Sometimes the spelling changes.) Common suffixes are: •able: affordable, comfortable, dependable. washable •al: accidental, exceptional, national, occasional -ful: beautiful, fanciful, hopeful, useful •ive: attractive, creative, expressive, responsive •less: hopeless, iobless, penniless, pointless, useless -OuS; adventurous, dangerous, famous, mischievous •y: bree4', squeaky, thirsty, woo//v Some adjectives end in -ible (pronounced the same as •able). However, ifyou remove •ible from the adjective, you are not usually left with a complete word: audible, legible, tangible |
Read the Learn this! box. Complete the sentences With an adjective formed from the noun or verb in brackets. Use a dictionary to help you if necessary.
1 If he said something (offense), I'm sure it wasn't (intention).
Storing fireworks next to petrol and Other
(hazard) substances could be (disaster).
3 They went hiking in a (mountain) part of India.
4 The climate is usually (rely) in June, but this year; it was very (rain).
5 She'S the chief executive Of a (globe) electronics company.
6 She has an (envy) relationship with her parents, Who are always (support).
7 Many of these diseases are _ (prevent) ifyou follow a healthy lifestyle.
8 The meat was cold, (taste) and _ (chew). 9 His poetry is very (access) and extremely (meaning) too.
2 Choose the correct Spelling.
I They find each Other attractive, butthev're at all compatable / compatible.
The story he told the judge wasn't really credabte / credible.
3 These boots aren't suitable / suitible for climbing.
4 This cycle helmet is virtually indestructable / indestructible.
5 His qualification is notcomparable / compatible With a university degree.
6 Carbon monoxide is particularly dangerous because it's invisable / invisible.
7 Most infectious diseases are now curable / curible. Don't drop this box. the contents are breakable / breakible.
I Work in pairs. HOW many sports can you Write Which fit these patterns?
ball: handball,
_ing: bowling, surfing,
3 racing; horse racing,
2 Write the sports in the correct category.
aerobics cricket hockey ice hockey judo karate rock-climbing snooker squash tae kwon do water polo yoga
|
participants compete in teams |
|
|
|
participants Compete as individuals |
|
|
|
usually non-competitive |
|
|
3 Match the two halves Of the winter sports. Then write them under the correct photos.
bob boarding figure jump half pipe skating snow skating sleigh
3
4 6
|
|
We can add suffixes to some verbs and adjectives to make them into nouns. (Sometimes the spelling changes.) Suffixes include: •ism: capitalism, organism, patriotism, professionalism, racism, sexism, tourism, vandalism •ment• employment, encouragement, engagement, management, movement -ation: consideration, examination, expectation, interpretation, presentation, transformation •ing: dwelling, ending, failing, meaning, offering, recording -ings; bearings, belongings, earnings, proceedings, surroundings -ship; citizenship, championship, dictatorship, friendship. hardship, leadership, ownership, partnership, relationship -hood: adulthood. childhood, falsehood. motherhood |
Read the Learn this! box. Which Of the noun suffixes are usually added to (a) verbs? (b) adjectives? (c) nouns?
2 Complete the sentences With a noun formed from the word in brackets. Use a dictionary to help you if necessary.
I In 1932, my great-grandfather spent all his car. (save)
2 What is the of winning the lottery the firsttinié you enter it? (likely)
3 1 asked the hotel receptionist if she had any for restaurants nearby. (recommend)
4 His brother left the army and joined the . (priest) As people become more cynical about politics, of political parties has dropped. (member)
6 Some groups have called for more Ofwebsites like YouTube. (censor)
7 There was a minor between two members Of the
Same team. (disagree)
8 The main for the job is a degree in engineering.
(require)
9 He impressed the crowd With his dignity and despite losing the match. (sportsman)
10 Owing to a , the hotel didn't have a room for us when we arrived. (misunderstand)
11 The scientists published their in the journal
Nature. (find)
12 Many people think there is too much (commercial) in sport.
Workin pairs. Take turns to do the exam task below. Spend Work in pairs. Take turns to do the exam task below. Spend about a minute preparing your answer. about a minute preparing your answer.
![]()
![]() A
large number of relatives are visiting you this weekend, The Government is
asking everyone to reduce their carbon and you need to buy a lot Of food. Where
and how Will you
A
large number of relatives are visiting you this weekend, The Government is
asking everyone to reduce their carbon and you need to buy a lot Of food. Where
and how Will you ![]() footprint. What is the best way Of
doing this? Choose one Of buy the food? Choose one of the options in the
photos. the options in the photos. Justify your choice and Say why Justify your
choice and say why you rejected the other suggestions.
footprint. What is the best way Of
doing this? Choose one Of buy the food? Choose one of the options in the
photos. the options in the photos. Justify your choice and Say why Justify your
choice and say why you rejected the other suggestions.
![]()
![]() 2 Work in pairs. Take turns to answer the examiner's
questions.
2 Work in pairs. Take turns to answer the examiner's
questions.
Questions for Student A:
I Some people think that we should ban cars from all city,
town and village centres. TO what extent do you agree With this opinion?
2 What can we as individuals do to help limit
global ![]() warming?
warming?
Questions for Student B: ![]()
I Should petrol cost much more to discourage
motorists ![]() from driving?
from driving?
2 What campaigns are there in your country to
protect and ![]() improve the environment?
improve the environment?
Communicative activities
ox 2
Oxford University press is a department of the University
It s obj&tne of in scholarship. by p ubLIShing [s a trade
OfOXfOrd University in UK in ætries
C' Oxford 2013 moral rights o f the author have asserted
First published in '3
10 9 8 7 6 5 4
All rights reserved , NO part Of this in a system. or transmitted. in any or by wior in writing of University as by law. by or with the appropriate reprographies right S outside the Of e Rnt to ELT Rights University press. at the
You must not Citv-uJate this in Other and you must same condition on any acquirer
Links to third by Oxford in good faith and for only.
|
|
71 73 (sky/ 87 87 |
|||
|
The grants for rhe photocopying Of those pages marked |
102 (hotel check.in,'Mark 109 (Weight |
|||
|
to Individual purchasers |
Kobal p78 Ralph |
|||
|
for own by they teach. |
p74 artist in |
|||
|
for by staff studA1ts. but this |
OUV PPI 1 14 |
|||
|
permission does to additional or |
14 14 15 (Mobile |
|||
|
of this be for |
phone'Mark Bassett), 28 Kino 51 57 - 65 Pics). 89 |
|||
|
Printed in Dubai |
94 107 109 (White |
|||
|
This is and |
| 137 nag'. 1 SS (Light 143 143 144 144 144 Press Association Images pp38 |
|||
|
like to the their to |
'Student Gautammemotixl. 39 'Northern Island 50 |
|||
|
pp 14 class/ZtJMA 14 (drama |
'Magic mirror for Rex pp5 s |
|||
|
Wire 52 S 31m with |
Chim), S (High wire Chimn 11 |
|||
|
66 Segre). 66 |
Dallel. 20 IJX 47 4 63 |
|||
|
Greenbergþ. 73 RM 80 137 (NATO |
Cola u'vert). 74 Mail post sortingphilippe Hays'. 93 (BMX stunt/NealeA• |
|||
|
nag,'pererprobst). (UN nag/PeterProbstL 137 IEurosyrnEoI,jBH011imd1. |
93 'balancing earKbirky China 95 |
|||
|
37 'WTO 37 (WWT; Mere Spm Extra). t 37 |
106 sitting in 107 |
|||
|
IA. ty logoœetu |
a pp84 Space |
|||
|
Baker); Corbis ppb |
SS Butler): Shutter-stock pp |
|||
|
Mt. european pressphLRO 7 (TO Kill a Mockingbird by |
Kate t (Camera lensöandra (Sim c•wdl |
|||
|
12 posing-Atsuko Tanaka'. Images). |
IIS 143 skating[D19741; PPI 9 |
|||
|
14 Frink'Science 14 IS |
HeinllAll 21 (BOY O'*ning Christmas pt*-sents/ |
|||
|
15 N" hko). 16 |
Imago. 55 painting construction vehicle/CorbisÞ. 81 |
|||
|
W'gel). 17 Wiedel 18 |
SS S. NolaNage |
|||
|
Benedict,Transtock1. 21 (Opening Santa giftK:hris Roan. 22 Torn |
Cultura Limited). |
|||
|
bank de 23 fçw |
Getty (Spain. Vizcaya, Guggenheim Museum exteriot |
|||
|
Sayles). 31 with 36 Pi.). 35 on Menta 37 |
night,JOlu1 W Ban |
|
||
|
MandeW]aequFS M, Chenet). 37 37 (Aung San Suu Kyi,'Richard Wainwright). 40 (Speakers Corner. Hyde park/ Martyn Vickery). 45 IRetail ShcR 47 Wriedel |
|
by E studio |
pl 39; Andy Parker pp56.100; Anthony |
|
|
p' 7 (robot), |
|
|||
|
54 'Steve Kulish). 55 S (Mobile |
|
this |
in |
any |
|
57 Ni"tO/Art & 57 |
|
of copyright |
the publisher wul |
|
|
DSlHugtl 57 (Samsung Galaxy Tabler,-'Hugtl (DVD pir•a.cymeng Yub. 59 59 LSticky (Eating 61 (Eating 62 (Worker looking at CLAIgerl. 63 with jute sack'Renee Corner Photographyfthe Cola Drink and Diet/Mark Sykes'. 64 ßrape fiesta'Richard SS deliverylJanis Ctwistie), 69 70 & 7 S 79 (Cinema popot•n and drink,'Mona1yn 81 statiotk' Radius Images'. in Leeuwent*rgThe Stœyl. 83 Lyell), 85 (Rcwket debris*eng 97 98 103 (HtXkey player.'Roy McMahon). 103 player'Tim Torah Jane Morrisl. 105 (Lionel Messi/Matthew AshtotVAMA), I I I matchJulian towel 114 141 (Mountain |
or |
at the |
|
|
in any third party this
JH EditoriaVMinden 143 (Four skaters/
Randy LinCkS). 143 World sledding'
Alexander Hubrich), 144 144 'Fitting
Getty pp3 in
8 12 (Girt listening Graf'. 'ROW 15 (Teddy Kempþ. 15 (Framed 18
(Moss IS Wilsonl. 20 (Ralph
H. Walkm 27 urge Studio). 33 (reception/ Vis itBritaiAfBritain 33 (Hotel Fife'AFP). 34
37 GM'gela Gallup'. 37 WalesAI
FilmMagiCl. 37 (Hanna via
Getty tx»k/Phil Ashley), (Strikesyoan 47
(NHS staff via Getty 55 (Guitar via Getty SS
ROSSI. SS pit-a OYVAS[EKAJSPI.V. 59 Of "lad,'
Bret 60 i F_ating ice 63 'Friends having
65 Dog Image
67 Þting ' 1
93 (Man .99
104 competitionJCanúlla 105 (Roger
Finney). t 10 'Basketball via Getty Images'. 113 (Fl 144 Haro p29 (ageing - pp9 (Pointing at Oliver 26 'Ccwple in 49
Tuomas Kuja_nsuuy. 49 h omelMge/mbbitdy). 49 (Facvtx»k homepage/
49 I—page/KingWu).
63
|
2nd edition Solutions Activating all your learners A new, refreshed edition of the five-level English course for teenagers, enhancing the features that you love: Clear structure — Supported approach to speaking — Built-in practice — Exam preparation • Solutions gives every student, Whatever their level, the tools and opportunities to produce language actively and confidently and to take control Of their learning. • new content. more varied listening, vocabulary, speaking tasks plus extension and revision activities, are all at your fingertips to motivate students to learn for themselves, both in and out Of the classroom. Oxfords making• diaital sense Solutions gives teachers a flexible pick-and-choose package for use in the classroom, at home and on the move. |
For students
• Prihtworkbook with Audio CD Pack including solutions for mixed ability classes
• Online Workbook on Learn Online with Oxford: everything students need from a Workbook. PLUS learner-centred instant support, such as automatic marking and feedback on answers — a virtual teacher close at hand
• Words app for vocabulary reference and practice on the move
|
OXFORD |
|
•
![]()
![]() Even
more language practice freely available online at wmv.oup.com/elt/solutions
Even
more language practice freely available online at wmv.oup.com/elt/solutions
UNIVERSITY PRESS
www.oup.com/elt
For teachers
• Teacher's Book With Teacher's Resource CD-ROM Pack, With new extra resources for mixed abilities
• Learn Online with Oxford. our tailored learning managementsystem: track students' progress, analyse results and plan personalised learning
• iTOOIs: the Student Book and Workbook pages available on screen with pop-up answer keys, audio. video and extra interactive exercises and worksheets for every lesson
• Test CD-ROM with revision and extension material for mixed ability classrooms
• DVD-ROM With documentary episodes, interviews and functional dialogues
• Class Audio COs
• Further teaching support and material available Online at www.oup.com/elt/teacher/solutions
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.