
Credit on the topic "non-Metals" - SUBSTANCES AND their PROPERTIES - LESSON PLANS for CHEMISTRY 11 class - lesson plans-lesson plans-author's lessons-plan-lesson summary - chemistry
Lesson objectives: test your knowledge and skills on the topic "non-Metals".
Equipment: task cards with two options.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment
Instructing students about the progress of the test tasks. Recommendation to the teacher
At the time of completing the test, the teacher checks the performance of homework in workbooks, setting grades.
II. Performing credit cards-tasks with two options
|
Option I |
Option II |
|
1. Features of the structure of the nonmetal |
|
|
chlorine |
sulfur atom |
|
Explain their possible C. O. s. in the ground and excited state. |
|
|
2. Compare the nonmetallicity of elements |
|
|
Cl, Br, I, F |
P, S, Cl, Si |
|
Arrange the elements in order: |
|
|
Increasing nemetallicheskie |
Of decreasing nemetallicheskie |
|
Give a reasonable answer. |
|
|
3. What is the chemical bond and what type of crystal lattice of non — metals-simple substances? |
|
|
Boron, hydrogen, IO. |
Diamond, bromine, oxygen |
|
4. Is it possible to have allotrope: |
|
|
a) chlorine. b) carbon; |
a) phosphorus; b) bromine. |
|
Give a reasonable answer. |
|
|
5. On the example of the corresponding reaction equations |
|
|
|
|
|
, Explain in which case |
|
|
phosphorus |
and sulfur |
|
manifest: |
|
|
a) oxidative properties; |
b) reducing properties |
|
6. Compare acidic properties: |
|
|
and) NSl and H2S. b) SO2and SO3. C) H2SO4and Hcl4. |
and) NSl and HF; b) SL2O and SL2O7; b) NSL2O4and Nvgo4. |
|
and explain the reason for their differences. |
|
|
7. Compare the basic properties |
|
|
of NH3and H2O |
PH3and NH3 |
|
and explain the reason for their differences. |
|
|
8. Draw up reaction equations according to the transformation scheme |
|
|
|
|
|
9. Solve the calculation problems for the derivation of the compound formula. |
|
|
1) when burning a hydrocarbon weighing 11.2 g, 35.2 g of carbon monoxide (IV) and 14.4 g of water were obtained. The relative density of the hydrocarbon in the air is equal to 1.93. Find the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon. 2) Output the formula of a gaseous compound, the mass fraction of nitrogen in which is 82.36%, and hydrogen-17.64%. The relative density of its hydrogen is 8.5. |
1) Find the molecular formula of a hydrocarbon, if burning 2 g of it formed 2.12 g of water and 6.48 g of carbon monoxide (IV). The relative vapor density of this substance in hydrogen is 34.2) Print the formula for a gaseous compound with a mass fraction of 87.5% silicon and 12.5 % hydrogen. Its relative oxygen density is 1. |
Answers to test questions
Option I
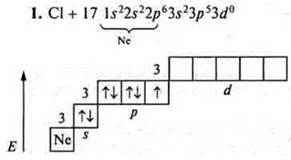
At the external energy level, there are seven electrons, three pairs of paired ones and one pair of unpaired ones. The level is close to completion, one electron is taken until stability; chlorine shows a C. o. -1, +1 in the ground state. At the chlorine atom, it is possible to open a 3d sublevel in the state of excitation. It is possible to steam 3Px, 3Py, 3s-electrons. Chlorine exhibits:
S. O. +3 (first excitement);
S. O. +5 (second excitement);
C. O. +7 (the third initiation).
2. In ascending order of nemetallicheskie I, Br, Cl, F. These are elements of group VII, the main subgroup. Nonmetallicity increases to the beginning of the group, the main subgroup, because the radius of the atom decreases the number of electrons at the external energy level does not change.
3. Boron, hydrogen, and iodine are covalent nonpolar bonds. Boron is an atomic crystal lattice. Hydrogen, iodine-a molecular crystal lattice.
4. Chlorine has an impossible allotrope, as the chlorine atom single unpaired electron.
A carbon atom has four unpaired electrons in its excited state. Allotropy is possible in the form of: diamond-SP3-hybridization, graphite-SP2-hybridization, carbine-sp-hybridization.

6. a) HCl and H2S — hydrogen compounds of elements of the III period of hydrogen compounds, the acidic properties are enhanced by the end of the period
![]()
HCl as an acid is stronger than H2S.
b) S+4O2and S+6O3-salt-forming oxides. S. o. at sulfur in SO2+4, at sulfur in SO3+6; the higher the PH, the more pronounced the acidic properties of the oxide. Thus, the acidic properties of SO3are stronger than the acidic properties of SO2.
C) H2S+6About4and NSl+7About4oxygen-containing acids are formed by elements-nonmetals located in the III period. The strength of oxygen-containing acids increases towards the end of the period.
NSl+7O4is stronger than H2S+6O4. C. O. Sl+7is greater than C. O. S+6, the radius of the ion CL+7is less than the radius of the ion S+6.
7. the Main properties of NH3are more pronounced than H2O, since the dorsal joints are formed by elements N and Olocated in the II period. The main properties weaken by the end of the period, because the COC increases and the radius of the nonmetal ion decreases.
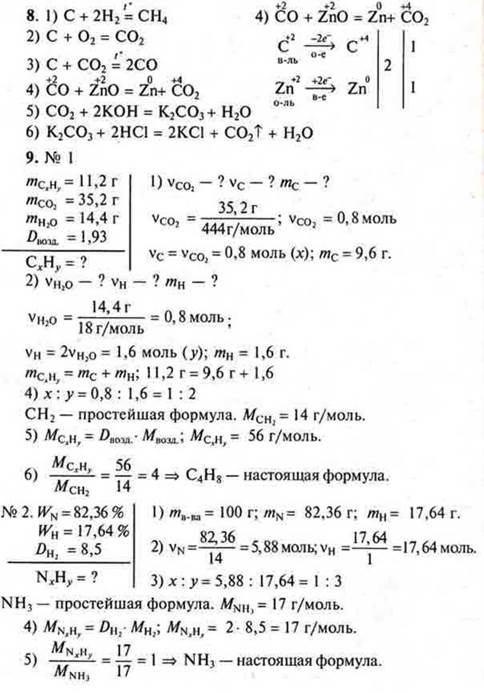
Option II
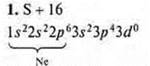
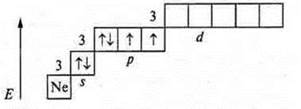
At the external energy level, there are six electrons, two pairs of paired and two pairs of unpaired ones. The level is close to completion, two electrons are taken before stability. Sulfur shows C. O. in the basic state -2; +2.
At the sulfur atom, it is possible to open a 3d sublevel, and in the state of excitation, it is possible to steam 3Px, 3s electrons. Sulfur manifests:
S. O. +4 (first excitement); S. O. +6 (second excitement).
2. In descending order of nemetallicheskie P, S, Cl, Si. These are elements of the third period. By the end of the period nemetallicheskie is enhanced, and the beginning of the period decreases, increasing atomic radius decreases as the nuclear charge of the atom decreases the number of electrons in the outer energy level.
![]()
the decrease of nemetallicheskie
3. Diamond, bromine, oxygen-covalent nonpolar bond.
Diamond is an atomic crystal lattice.
Bromine, oxygen-a molecular crystal lattice.
4. phosphorus can have allotropy, because in the ground state in the phosphorus atom there are three unpaired electrons: P-red, P4— white.
In the bromine atom there is one unpaired electron, allotropy is impossible.

6. a) HCl and HF are hydrogen compounds of elements of group VII, the main subgroup. Acidic properties of hydrogen compounds are enhanced by the end of the group, the main subgroup, because the radius of the ion increases, and the PH does not change. HCl as an acid is stronger than HF.
b) CL2+1O and CL2+7O7 are salt-forming oxides.2O +1, in CL2O7+7. The greater the PH of the element, the more pronounced the acidic properties are. The acidic properties of CL2O7are stronger than those of CL2O.
C) Hcl+7O4and HBr+7O4are oxygen-containing acids. They are formed by elements of group VII, the main subgroup. The strength of oxygen-containing acids weakens towards the end of the group, since the element's C. S. O. does not change, and the ion radius increases towards the end of the group.NSLO 4 acidis strongerthan Nvgo 4 acid ..
7. the Main properties of NH3are more pronounced than the main properties of PH3. Hydrogen compounds are formed by elements of one V group, the main subgroup. By the end of the group, the acidic properties of hydrogen compounds are enhanced, the main properties are weakened, because the ion radius increases, and the SR does not change.

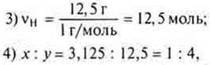
SiH4is the simplest formula. MSiH3= 32 g/mol;
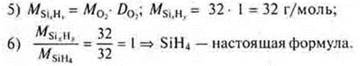
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.