
Oxides-SUBSTANCES AND their PROPERTIES - LESSON PLANS for CHEMISTRY 11 class - lesson plans-lesson plans-author's lessons-plan-lesson summary - chemistry
The purpose of the lesson: to consolidate knowledge of classification and nomenclature; chemical properties of oxides, to teach you to make reaction equations that confirm these properties; to consolidate the skills of solving calculation problems using chemical equations and formulas.
Basic concepts: salt-forming, non-salt-forming oxide, basic, acidic, and amphoteric oxide.
Equipment: CaO, CuO, ZnO, SASO3, S, a spoon for burning substances, a gas outlet tube, water, a set of reagents, test tubes, alcohol lamp, holder.
Lesson progress
I. Organizational moment
Setting goals and tasks for the lesson.
Analysis of the results of the test on the topic "non-Metals". Invite students to work on their mistakes.
Plan of presentation
1. Determination of the oxides. Classification, nomenclature, physical properties of oxides, chemical bond, type of crystal lattices.
2. Chemical properties: a) salt-forming oxides: basic oxides, acid oxides, amphoteric oxides; b) non-salt-forming oxides.
3. Production of oxides.
4. Solving calculation problems.
II. Front work
Remind students of the studied question about the classification of inorganic complex substances. Working with the scheme 6 p. 179 and the summary in the workbook, students remember the definition of oxides, their classification, nomenclature, features of physical properties and structure.
Write out the oxides from the given formulas: a) salt-forming: basic, acidic, amphoteric; b) non-salt-forming. Give them names.
Na2O, N2О5, NaOH, HNО3, CuO, SО2, CO, SCl2, Cl2O5, Mn2O7, FeS, Fe2O3, Cu2O, P2O5, N2O, ZnCl2, MgO, Cr2O3, CrO3, ZnO.
Answer: salt forming oxides:
a) main features:
Na2O — sodium oxide, Withu+2O-copper oxide (II), Fe2+3O3 — iron oxide (III), MgO — magnesium oxide, Cu2+1O — copper oxide (I).
b) acidic oxides: N2+5O5oxide of nitrogen (V), S+4O2— sulfur dioxide (IV), CL2+5O5oxide of chlorine (V), MP2+7O7 — oxide of manganese (VII), R+5O5- phosphorus oxide (V), SG+6O3oxide of chromium (VI).
C) amphoteric oxides: Cr2+3O3 — chromium (III) oxide, ZnO — zinc oxide.
Non-salt forming oxides: N2+1O-nitric oxide (I), C+2O — carbon monoxide (II).
Features of physical properties of oxides:
gaseous: SO2, CO, N2O;
liquid: MP2O7, CGO3;
solid: N2O5, Fe2O3, CaO, P2O5.
By structure, type of chemical bond: covalent polar bond SO2, CO, etc., ionic bond Na2O, CuO, etc.
Types of crystal lattice: ionic, atomic, and molecular.
Features of chemical properties of oxides:
a) basic oxides:

Experiment:

Experiment: CaO + H2O = Ca(HE)2+ Q-phenolphthalein-crimson color,
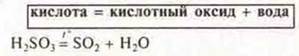
b) acid oxides:
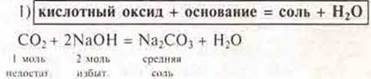
![]()
Experiment:
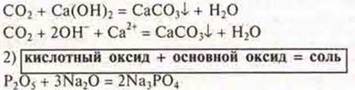
3) Most acid oxides react with water.
![]()
Experiment: SO2+ N2O = H2SO3-methyl orange-pink color.
SiO22+ N2O ≠
C) amphoteric oxides. Manifestation of the properties of basic oxides-interact with acids and acid oxides:
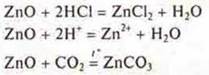
Manifestation of the properties of acid oxides — interaction with soluble bases and with basic oxides:
![]()
Experiment:
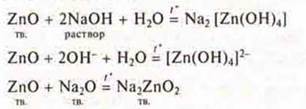
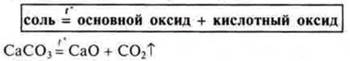
Getting oxides:

2) Decomposition of oxygen-containing acids.
3) Decomposition of insoluble bases.
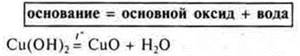
4) Decomposition of certain salts.
III. Do
I) which of the following substances will react with:
a) VAO; b) Al2O3; C) N2O5; SO3; P2O5; CaO, NaOH, HNO3Na2SO4.
Answer:
a) VAO is the main oxide:
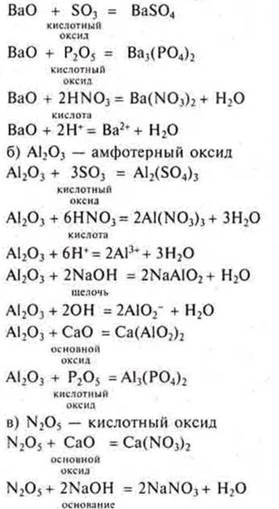
IV. Solving calculation problems
a) according to the formula; b) the chemical equation,
a) the Mass fraction of nitrogen will be the smallest in the oxide:
N2O, NO, NO2, N2O5.
Decision:
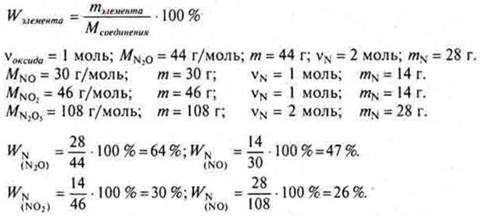
Answer: The lowest mass fraction of nitrogen in nitric oxide is (V) N2O526 %.
b) sodium Oxide weighing 12.4 g was dissolved in water. What is the volume of carbon dioxide (n.y.) will be required to neutralize the resulting solution of sodium hydroxide, if an acidic salt is formed?
Decision:
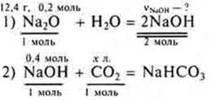
From equation (1):

From equation (2):

Answer: you will need 8,96 liters ofCO2.
V. Homework assignment
1) Summary in a notebook.
2) Draw up reaction equations confirming the properties of oxides: Li2O, VEO, P2O5.
3) Task 1. Calculate the mass fraction of the element that formed oxides: manganese (II) oxide, manganese (IV) oxide, and manganese (VII) oxide. Which oxide has the highest concentration W of the element?
4) Task 2. When passing carbon monoxide (IV) through a solution of calcium hydroxide, an acidic salt — calcium bicarbonate with a mass of 8.1 g was obtained. Determine the volume of carbon monoxide (IV) (n.y), which was passed through the solution.
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.