
RECOMMENDATIONS
for teachers on lesson “Motion of Charged Particles in Electric Field”
There are some problems on this topic with solutions in slides #6-10. Teacher might replace problem #2 with the ones from Attchment 1.
According to the lesson plan there isnt a problem on a case when a charged particle enters a E field at right angles to the lines. However, if teacher decided that it is neccecary to solve with students problems on that here is some problems in Attachment 2. These problems might be given to those who are more able and interested in physics more that others.
If internet is available mare able students can investigate about CRT more and present their ideas as addition to the video material.
Teachers can find answers to the MCQ and structured questions below.
Marking scheme on problems in class:
1 B [1]
2 C [1]
3 D [1]
4 D [1]
5 B [1]
6 The two units are: V m–1 [1]
and N C–1. [1]
7 E = ![]() =
= ![]() [1]
[1]
E = 3.0 ´ 104 V m–1 [1]
8 F = EQ = 5.0 ´ 105 ´ 3.2 ´ 10–19 [1]
F = 1.6 ´ 10–13 N [1]
9 a E = ![]() =
= ![]() [1]
[1]
E = 2.0 ´ 104 V m–1 [1]
The field acts towards the
negative plate. [1]
b The electric field is uniform between
the plates (except at the ‘edges’). [1]
The electric field is at right angles to the plate. [1]
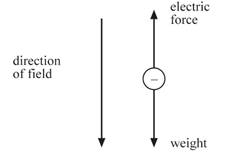 c i Since
the droplet is stationary,
c i Since
the droplet is stationary,
the electric force on the droplet
must be equal and opposite to its weight. [1]
The
electric force must act upwards,
so the charge on the droplet must
be negative. [1]
ii E = ![]()
Q = ![]() =
= ![]() [1]
[1]
Q = 3.2 ´ 10–19 C [1]
10 a F = QE
=1.60 ´ 10–19
´ 2.4 ´ 106 [1]
F =
3.84 ´ 10−13 N » 3.8 ´ 10−13 N [1]
b F = ma Þ a
= ![]() [1]
[1]
a =
![]() N
N
a = 2.30 ´ 1014 m s−2 [1]
c Zero; the force is at right angles to the field. [1]
11 E
= ![]() =
= ![]() ´ 10−2 = 4.0 ´ 103
N [1]
´ 10−2 = 4.0 ´ 103
N [1]
F = EQ Þ Q = ![]() =
= ![]() [1]
[1]
Q = 8.0 ´ 10−8 C [1]
Attachment 1 Additional problems on topic Motion of Charged Particles in Electric Field
1. An electron starting from rest is accelerated by a uniform electric field of 1000Volt/metre for a distance of 5 cm. Calculate:
(a) the acceleration of the electron
Electric force = resultant force
Eq = ma
a =
![]() =
= 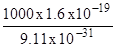
a = 1.76 x 1014 m s-2 towards the positive plate.
(b) the velocity of the electron after 5 cm of travel
v22 = v12 + 2a Ds
= 0 + 2 x 1.76 x 10 14 x .05
v2 = 4.2 x 10 6 m s -1 in the direction of 'a'
(c) the time it takes to travel the 5 cm
a = ![]()
Dt = ![]() =
=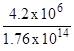
Dt = 2.38 x 10 -8 s
(d) the kinetic energy of the electron at the 5 cm position
E = ![]() m v 2 =
m v 2 = ![]() x 9.1 x 10 -31 x (4.2 x 10 6) 2
x 9.1 x 10 -31 x (4.2 x 10 6) 2
E = 8.03 x 10 -18 J
2. (a) A test charge of 1.6 x 10-19 C experiences a force of 3.2 x 10-19 N. What is the electric field strength?
E =![]() = 2 N C-1
= 2 N C-1
(b) A charged body shows an acceleration of 10 m s-2. What is the electric field strength, assuming that it alone is responsible for the acceleration, if the body has a mass of 1.0 x 10-15 kg and carries a charge of 1.6 x 10-19 C?
a = 10 m s-2
m = 1.0 x 10-15 kg
q = 1.6 x 10-19 C
F = ma
= 1.0 10-15 x 10
= 1.0 x 10-14 N
E
= ![]()
=![]()
E = 62.5 x 103 N C-1 parallel to force on + charge
(c) In the absence of an electric field a charged sphere falls freely under gravity. The weight of the sphere is 10-14 N. When the electric field is operational the sphere remains stationary. What is the electric field strength if the charge on the sphere is 1.6 x 10-19 C?
Fg = 1.0 x 10-14 N
q = 1.6 x 10-19 C
As there is no net force Fg = FE
Fg = Eq
E =![]() =
= 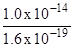
E = 6.25 x 104 N C-1
direction of field will depend on sign of charge.
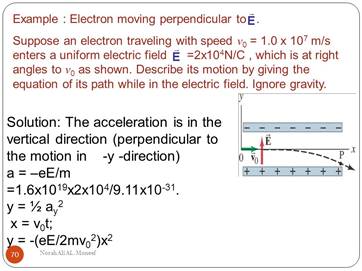
Attachment 2 Additional problems on topic Motion of the charged particle entering at a right angles to the E field

Useful recources for teachers:
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-physics/chapter/motion-of-a-charged-particle-in-a-magnetic-field/
https://www.physics.mun.ca/~ayethiraj/teaching/p1051ay/lectures/L21_MagneticFields.pdf
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/electric/elefie.html
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/physics/chapter/18-4-electric-field-concept-of-a-field-revisited/
Скачано с www.znanio.ru
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.