
Worksheet
1. Charged particles, each of mass m and charge Q, travel at a constant speed in a circle of radius r in a uniform magnetic field of flux density B.
Which expression gives the frequency of rotation of a particle in the beam?
|
A |
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
D |
|
|
2. The path followed by an electron of momentum p, carrying charge –e, which enters a magnetic field at right angles, is a circular arc of radius r.
What would be the radius of the circular arc followed by an α particle of momentum 2p, carrying charge +2e, which entered the same field at right angles?
A ![]()
B r
C 2r
D 4r
3. Which one of the following statements is correct?
An electron follows a circular path when it is moving at right angles to
A a uniform magnetic field.
B a uniform electric field.
C uniform electric and magnetic fields which are perpendicular.
D uniform electric and magnetic fields which are in opposite directions.
4. Two electrons, X and Y, travel at right angles to a uniform magnetic field.
X experiences a magnetic force, FX, and Y experiences a magnetic force, FY.
What
is the ratio ![]() if the
kinetic energy of X is half that of Y?
if the
kinetic energy of X is half that of Y?
A ![]()
B ![]()
C ![]()
D 1
5. A negatively charged particle moves at right angles to a uniform magnetic field. The magnetic force on the particle acts
A in the direction of the field.
B in the opposite direction to that of the field.
C at an angle between 0° and 90° to the field.
D at right angles to the field.
6. Two charged particles, P and Q, move in circular orbits in a magnetic field of uniform flux density. The particles have the same charge but the mass of P is less than the mass of Q. TP is the time taken for particle P to complete one orbit and TQ the time for particle Q to complete one orbit. Which one of the following is correct?
A TP = TQ
B TP> TQ
C TP< TQ
D TP – TQ= 1
7. Charged particles, each of mass m and charge Q, travel at a constant speed in a circle of radius r in a uniform magnetic field of flux density B. Which expression gives the frequency of rotation of a particle in the beam?
A ![]()
B ![]()
C ![]()
D ![]()
8. When a β particle moves at right angles through a uniform magnetic field it experiences a force F. An α particle moves at right angles through a magnetic field of twice the magnetic flux density with velocity one tenth the velocity of the β particle. What is the magnitude of the force on the α particle?
A 0.2 F
B 0.4 F
C 0.8 F
D 4.0 F
9. A jet of air carrying positively charged particles is directed horizontally between the poles of a strong magnet, as shown in the diagram.
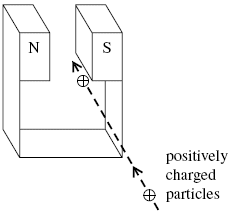
In which direction are the charged particles deflected?
A upwards
B downwards
C towards the N pole of the magnet
D towards the S pole of the magnet
10. An electron moving with a constant speed enters a uniform magnetic field in a direction perpendicular to the magnetic field. What is the shape of the path that the electron would follow?
A parabolic
B circular
C elliptical
D a line parallel to the magnetic field
11. An electron moving with a constant speed enters a uniform magnetic field in a direction at right angles to the field. What is the subsequent path of the electron?
A A straight line in the direction of the field.
B A straight line in a direction opposite to that of the field.
C A circular arc in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the field.
D An elliptical arc in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the field.
12.
The
path followed by an electron of momentum p, carrying charge −e,
which enters a magnetic field at right angles, is a circular arc of radius r.
What would be the radius of the circular arc followed by an α
particle of momentum 2p, carrying charge +2e, which entered the
same field at right angles?
A ![]()
B r
C 2r
D 4r
13. Particles of mass m carrying a charge Q travel in a circular path of radius r in a magnetic field of flux density B with a speed v. How many of the following quantities, if changed one at a time, would change the radius of the path?
• m
• Q
• B
• v
A one
B two
C three
D four
14. Protons, each of mass m and charge e, follow a circular path when travelling perpendicular to a magnetic field of uniform flux density B. What is the time taken for one complete orbit?
A
![]()
B
![]()
C
![]()
D
![]()
15. Particles of mass m, each carrying charge Q and travelling with speed v, enter a magnetic field of flux density B at right angles. Which one of the following changes would produce an increase in the radius of the path of the particles?
A an increase in Q
B an increase in m
C a decrease in v
D an increase in B
16. An electron moves due North in a horizontal plane with uniform speed. It enters a uniform magnetic field directed due South in the same plane. Which one of the following statements concerning the motion of the electron in the magnetic field is correct?
A It continues to move North with its original speed.
B It slows down to zero speed and then accelerates due South.
C It is accelerated due West.
D It is accelerated due North.
17. An α particle and a β– particle both enter the same uniform magnetic field, which is perpendicular to their direction of motion. If the β– particle has a speed 15 times that of the α particle, what is the value of the ratio
![]() ?
?
A 3.7
B 7.5
C 60
D 112.5
18. Which line, A to D, correctly describes the trajectory of charged particles which enter, at right angles, (a) a uniform electric field, and (b) a uniform magnetic field?
|
|
(a) uniform electric field |
(b) uniform magnetic field |
|
A |
circular |
circular |
19. An alpha particle moves at one-tenth the velocity of a beta particle. They both move through the same uniform magnetic field at right angles to their motion.
The
magnitude of the ratio ![]() is
is
A ![]()
B ![]()
C ![]()
D ![]()
20. An electron moves into a region of uniform magnetic flux density between the poles of a magnet as shown in the diagram.
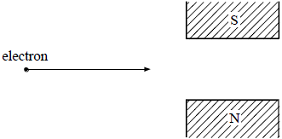
The deflection of the electron will be
A towards the pole marked S
B towards the pole marked N
C perpendicular to the plane of the paper towards you
D perpendicular to the plane of the paper away from you
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.