
Didactic material #1
1.https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cMoxpJBcivs
Answer the questions below on the video
What is the trajectory of the attraction?
What do you know of the body similar to the movement of the attraction?
What quantites can describe its movement
During its movement, what quantities can remain constant?
Didactic material #2
2.Using a textbook complete suggestions below (https://bilimland.kz/en/courses/physics-en/mechanics/kinematics/lesson/curvilinear-motion)
1.The motion is curvilinear, because its trajectory
.....................................................................
2.Body movement along a curved is even because.....................................................................
3.Speed vector direction...............................................................
4.direction of accelerated vector
.......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................(show on the chart)
3. (https://bilimland.kz/kk/courses/physics-kk/mexanika/kinematika/lesson/buryshtyq-zhyldamdyq-zhane-buryshtyq-udeu)
Introduction with the quantities describing curvilinear quantities
Radian and degrees
Angular velocity
Angular velocity and linear velocity
Angular acceleration
Translational and rotational motion
Angular acceleration and linear acceleration
Didactic material #3
Data needed to answer questions can be found in the Data, formulae and relationships sheet.
1 Convert the following angles into radians.
a 30° [1]
b 210° [1]
c 0.05° [1]
2 Convert the following angles from radians into degrees.
a 1.0 rad [1]
b 4.0 rad [1]
c 0.15 rad [1]
3 The planet Mercury takes 88 days to orbit
once round the Sun.
Calculate its angular displacement in radians during a time interval of:
a 44 days [1]
b 1 day. [1]
4 In each case below, state what provides the centripetal force on the object.
a A car travels at a high speed round a sharp corner. [1]
b A planet orbits the Sun. [1]
c An electron orbits the positive nucleus of an atom. [1]
d Clothes spin round in the drum of a washing machine. [1]
5 The diagram shows a stone tied to the end
of a length of string.
It is whirled round in a horizontal circle of radius 80 cm.
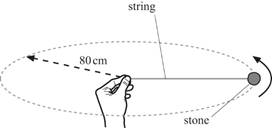
The stone has a mass of 90 g and it completes 10 revolutions in a time of 8.2 s.
a Calculate:
i the time taken for one revolution [1]
ii the distance travelled by the stone during one revolution (this distance is equal to the circumference of the circle) [1]
iii the speed of the stone as it travels in the circle [2]
iv the centripetal acceleration of the stone [3]
v the centripetal force on the stone. [2]
b What provides the centripetal force on the stone? [1]
c What is the angle between the acceleration of the stone and its velocity? [1]
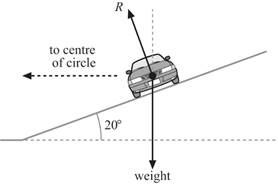 6 A car of mass 820 kg travels at a constant speed
6 A car of mass 820 kg travels at a constant speed
of 32 m s−1 along a banked track.
The track is banked at an angle of 20°
to the horizontal.
a The net vertical force on the car is zero.
Use this to show that the contact force R on the car is 8.56 kN. [2]
b Use the answer from a to calculate the radius of the circle described by the car. [4]
7. A stone of mass 120 g is fixed to one end of a light rigid rod.
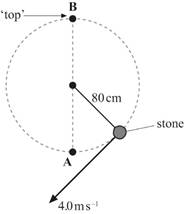
The stone is whirled at aconstant speed of 4.0 m s−1in a vertical circle of radius 80 cm.
Calculate
the ratio: ![]() [6]
[6]
Didactic material #4

Скачано с www.znanio.ru
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.