
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ И НАУКИ ПЕРМСКОГО КРАЯ
государственное бюджетное профессиональное образовательное учреждение
«ПЕРМСКИЙ ХИМИКО-ТЕХНОЛОГИЧЕСКИЙ ТЕХНИКУМ»
МЕТОДИЧЕСКИЕ УКАЗАНИЯ
ДЛЯ ОБУЧАЮЩИХСЯ
ПО ВЫПОЛНЕНИЮ ПРАКТИЧЕСКИХ РАБОТ
ПО УЧЕБНОЙ ДИСЦИПЛИНЕ
ОП.06 Иностранный язык в профессиональной деятельности
по профессии
15.01.31 Мастер контрольно-измерительных приборов и автоматики
Пермь, 2019
СОДЕРЖАНИЕ
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
ПРАВИЛА ВЫПОЛНЕНИЯ ПРАКТИЧЕСКИХ РАБОТ
ОПИСАНИЕ РАБОЧЕГО МЕСТА ОБУЧАЮЩЕГОСЯ
ПРАКТИЧЕСКИЕ РАБОТЫ
Практическая работа №1
Практическая работа №2
Практическая работа №3
Практическая работа №4
Практическая работа №5
Практическая работа №6
Практическая работа №7
Практическая работа №8
Практическая работа №9
Практическая работа №10
Практическая работа №11
Практическая работа №12
Практическая работа №13
Практическая работа №14
Практическая работа №15
Практическая работа №16
Практическая работа №17
Практическая работа №18
Практическая работа №19
Практическая работа №20
Практическая работа №21
Практическая работа №22
Практическая работа №23
Практическая работа №24
Практическая работа №25
Практическая работа №26
Практическая работа №27
Практическая работа №28
Практическая работа №29
Практическая работа №30
Практическая работа №31
Практическая работа №32
Практическая работа №33
Практическая работа №34
Практическая работа №35
Практическая работа №36
Список рекомендуемой литературы
Рабочая программа учебной дисциплины ОП.06 Иностранный язык в профессиональной деятельности является частью основной образовательной программы ГБПОУ «ПХТТ» в соответствии с ФГОС по профессии СПО 15.01.31 Мастер контрольно-измерительных приборов и автоматики.
В результате изучения дисциплины обучающийся должен уметь:
- У1 понимать общий смысл четко произнесенных высказываний в пределах литературной нормы на известные темы (профессиональные и бытовые);
- У2 понимать тексты на базовые профессиональные темы;
- У3 участвовать в диалогах на знакомые общие и профессиональные темы;
- У4 строить простые высказывания о себе и о своей профессиональной деятельности;
- У5 кратко обосновывать и объяснить свои действия (текущие и планируемые);
- У6 писать простые связные сообщения на знакомые или интересующие профессиональные темы.
- У7 осуществлять поиск, отбор профессиональной документации с помощью справочно-правовых систем и др.;
- У8 переводить (со словарем) иностранную профессиональную документацию.
- У9 владеть навыками технического перевода текста;
- У10 понимать содержание инструкций и графической документации на иностранном языке в области профессиональной деятельности.
В результате освоения дисциплины обучающийся должен знать:
- З1 правила построения простых и сложных предложений на профессиональные темы;
- З2 основные общеупотребительные глаголы (бытовая и профессиональная лексика);
- З3 лексический минимум, относящийся к описанию предметов, средств и процессов профессиональной деятельности;
- З4 особенности произношения;
- З5 правила чтения текстов профессиональной направленности;
- З6 лексический и грамматический минимум, необходимый для чтения и перевода (со словарем) профессиональной документации.
Результатом освоения программы учебной дисциплины ОП.06 Иностранный язык в профессиональной деятельности является овладение обучающимися профессиональными (ПК) и общими (ОК) компетенциями:
ОК 01. Выбирать способы решения задач профессиональной деятельности, применительно к различным контекстам.
ОК 02. Осуществлять поиск, анализ и интерпретацию информации, необходимой для выполнения задач профессиональной деятельности.
ОК 03. Планировать и реализовывать собственное профессиональное и личностное развитие.
ОК 04. Работать в коллективе и команде, эффективно взаимодействовать с коллегами, руководством, клиентами.
ОК 05. Осуществлять устную и письменную коммуникацию на государственном языке с учетом особенностей социального и культурного контекста.
ОК 06. Проявлять гражданско-патриотическую позицию, демонстрировать осознанное поведение на основе традиционных общечеловеческих ценностей.
ОК 07. Содействовать сохранению окружающей среды, ресурсосбережению, эффективно действовать в чрезвычайных ситуациях.
ОК 08. Использовать средства физической культуры для сохранения и укрепления здоровья в процессе профессиональной деятельности и поддержания необходимого уровня физической подготовленности.
ОК 09. Использовать информационные технологии в профессиональной деятельности.
ОК 10. Пользоваться профессиональной документацией на государственном и иностранном языке.
ОК 11. Планировать предпринимательскую деятельность в профессиональной сфере.
ПК 1.2. Определять последовательность и оптимальные способы монтажа приборов и электрических схем различных систем автоматики в соответствии с заданием и требованиями технической документации.
ПК 2.1. Определять последовательность и оптимальные режимы пусконаладочных работ приборов и систем автоматики в соответствии с заданием и требованиями технической документации.
ПК 3.2. Определить последовательность и оптимальные режимы обслуживания приборов и систем автоматики в соответствии с заданием и требованиями технической документации.
Методические указания предназначены для проведения практических работ по учебной дисциплине ОП.06 Иностранный язык в профессиональной деятельности по профессии 15.01.31 Мастер контрольно-измерительных приборов и автоматики. Методические указания по учебной дисциплине имеют практическую направленность и значимость. Формируемые в процессе практических занятий умения могут быть использованы обучающимися в будущей профессиональной деятельности.
Методические указания разработаны в соответствии с рабочей программой учебной дисциплины ОП.06 Иностранный язык в профессиональной деятельности по профессии 15.01.31 Мастер контрольно-измерительных приборов и автоматики.
Содержание методических указаний по выполнению практических работ соответствует требованиям Федерального государственного стандарта среднего профессионального образования по профессии 15.01.31 Мастер контрольно-измерительных приборов и автоматики.
По учебному плану, и в соответствии с рабочей программой учебной дисциплины, на изучение ОП.06 Иностранный язык в профессиональной деятельности по профессии обучающимися предусмотрено 112 часов, из них практических – 104.
Каждая практическая работа содержит сведения о теме, цели ее проведения и формируемых компетенциях, включает пояснения к работе, содержание отчета, контрольные задания или вопросы, список литературы.
Основными этапами практического занятия являются:
− проверка знаний обучающихся – их теоретической подготовленности к занятию;
− инструктаж, проводимый преподавателем;
− выполнение заданий, работ, упражнений, решение ситуационных задач;
− последующий анализ и оценка выполненных работ и степени овладения обучающимися запланированными умениями.
Практические работы по учебной дисциплине ОП.06 Иностранный язык в профессиональной деятельности проводятся в аудитории, оснащенной компьютером, колонками, проектором, экраном, наглядными пособиями. Каждая практическая работа начинается с организационного момента, включающего проверку посещаемости, готовности обучающихся к занятию.
Перед началом преподаватель ставит перед обучающимися задачи, проводит общий инструктаж по выполнению заданий.
В ходе выполнения заданий преподаватель направляет, консультирует обучающихся, проводит проверку знаний и умений, делает анализ выполнения задания.
Занятие заканчивается оценкой работы обучающихся.
Раздел 1 Профессиональная деятельность специалиста.
Тема 1.1 Наука и техника.
Тема: Введение. Роль английского языка при освоении профессий СПО. Работа с текстом "Современные профессии".
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте и переведите текст «Современные профессии». Выполните лексические упражнения.
Read and translate the text.
Modern professions
The modern labor market is very variable. And according to the results of the research of a well-known European company in the near future we expect even more changes in the scale of demanded professions.
You can say for sure that very soon the demand of employers will be directed to
completely different specialties. Already at
the present time, graduates of the faculties of natural sciences, specialists
in the field of high technologies and IT specialists are much more
appreciated.
But let’s sort out the order and make the rating of the new professions of
the future.
Engineers. One of the leading positions in the ranking of demanded professions of the future is occupied by such a profession, forgotten by the young generation, as an engineer. Already, on a crowded economists and managers of the labor market, this profession is especially valued. There is a clear lack of technical specialists and professional engineers.
In this regard, their wages will grow, and the demand to rise. If you have several entities –for example, economic, technical and legal, then you will have a high career in the future.
IT professionals
Of course, few of us can imagine their lives without a computer. The same goes for almost any work area. Not surprisingly, IT specialists and programmers will become one of the most needed specialties of the future. The rapidly evolving progress of computer technology leads to the fact that the demand for such professions will only grow with time. Experts in the field of nanotechnology. Science all over the world is rapidly moving forward. Nanotechnology is the greatest field of research that will cover virtually all areas – mechanical engineering, space objects, medicine, food industry, and many others. Therefore, absolutely all specialties related to nanotechnology will be in demand. Nanotechnology is one of the newest professions of the future, which will only develop over time, and employers’ demand for it will grow.
Occupations related to the service
The incomes of the population grow every year. People often go to rest, make large purchases, visit beauty salons, use the services of home staff and so on. In this regard, professionals who can provide quality service, in the future will not remain without work.
Chemist. It is a well-known fact that oil reserves will last for another 10 years. Therefore, research on the search for and development of clean energy sources is already being actively conducted in our time. And, as a result, highly skilled specialists-chemists are required.
Logists. One of the modern and new professions that will also be in demand in the future is the logistician. This sphere of activity covers quite a wide range of responsibilities – such as the organization of the delivery of goods from the manufacturer or supplier to the final buyer, the formation of commodity stocks, the competent tracking of the entire supply chain. Therefore, in our century of trade and market relations, the logistics profession will be in demand for a long time and highly paid.
Ecologist. Probably, very few people can argue with the fact that the ecological situation in the world is steadily deteriorating every year. Abnormal phenomena and ozone holes, problems of environmental pollution and global warming will make ecologists one of the most indispensable people for saving the planet in the very near future.
Physician. The profession of doctors was always in demand. Now the growing demand for certain specialists in the field of medicine is associated with research in the field of life extension. They invest a lot of money, so the scientific specialists specializing in finding means for extending life will be very much in demand in the future.
Working professions with increasing demand in the labor market
Some new professions that do not require higher education will also be in demand in the future, but this does not become less payable.
Groomer. Groomer provides professional care for pets. The scope of services includes haircut, washing, trimming, painting, cosmetic procedures, complete preparation of the pet for the exhibition. Professional groomers are always in demand, as preparation for an exhibition is never without their services. And owners of non-exhibition breeds also constantly turn to animal care specialists, which makes this profession always necessary and highly paid.
Shopper. In fact, a shopper is a stylist. Higher education does not require such a profession. She is trained in image-maker courses for two to three months. Shoppers accompany the client to the shops and help him decide on the choice of clothing and style. In our time of constant business meetings and trips, many people need to look respectable and stylish at the same time, therefore such assistants in the fashion industry will be highly appreciated in the future.
Food stylist. Professional cameras now have many. And if you still have a creative vein and you have a rich imagination, then it is possible that such a new profession as a food stylist will suit you. The duties of a food stylist include such a task as photographing food nicely, brightly and deliciously. In connection with the development of information resources on the Internet, quality illustrations will always be required, so professional photographers in the future will have an increasing demand from employers.
PROFESSIONS
Exercise 1. Match the words and their translations:
Job библиотекарь
Nurse работа
Librarian зубной врач
Lawyer адвокат, юрист
Dentist медсестра
Engineer программист
Computer programmer инженер
Farmer водитель
Housewife писатель
Driver домохозяйка
Actor спортсмен
Writer фермер
Sportsman актер
Actress актриса
Artist художник
Doctor повар
Waiter доктор
Cooker продавец
Politician переводчик
Shop-assistant политик
Translator певец
Coach официант
Singer тренер
Exercise 2. Match the professions and their definitions:
1) an
architect a) works with the
computer
2) a teacher b) designs
buildings
3) a dentist c) plays
football
4) a vet d) teaches
children at school
5) a doctor e) looks after
peoples teeth
6) a photographer f) looks after sick
people
7) a secretary g) plays a musical
instrument
8) a lawyer h) takes
photos
i) looks
after sick animals
j) doеs
projects
k) knows
laws
l) works
with papers
Exercise 3. Try to choose an appropriate profession:
Possibilities: doctor, driver, artist, stewardess, director, singer
1. She speaks foreign languages. She works very long hours, but she doesn't work every day. She likes people and travel, and she travels а lot in her work. She is а ...
2. She doesn't work in an office. She is not а teacher. She works very lоng hours, and she often works at night – it's а hard job. She likes people and she help them. She loves her job. She is а ...
3. Не gets up at half past seven every day, has breakfast at eight o'clock, and starts work at half past nine. Не works in an office. Не has two secretaries and two telephones. Не does not work оn Sundays. Не likes people. Не is а ...
4. Не usually gets up at eleven o'clock, and has breakfast at 12. Не works at home. Sometimes he mау work outside. Не works in the afternoons, but not every day. Sometimes he works long hours, sometimes he does not work at аll. Не loves his job. Не is an ...
5. She lives in а big city. She gets up late and has а late breakfast. She works late in the еvеning. She goes to and from work bу taxi. People like to listеn to her аnd sometimes they send her flowers. She is а ...
6. Не gets up at five o'clock in the mоrning. Не has breakfast and lunch in motorway restaurants. Не works sitting dоwn аnd travels а lot in his work. Не likes his job. Не is а ...
Exercise 4. Name the profession:
1) I work outside and
I love flowers. I’m a …….. .
2) I look after sick people in a hospital, but I’m not a doctor. I’m a ………
.
3) I work in a small restaurant. I prepare food for out quests. I’m a …….
.
4) I love animals. Some people call me an animal doctor. I’m a ……… .
5) I’m an artist and my job is taking photographs. I’m a ……. .
6) I’m interested in fashion. I make clothes for women. I’m a …….. .
Тема: Работа с текстом "Инновационная техника в быту".
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Выучите новую лексику, прочитайте и переведите текст «Инновационная техника в быту». Выполните лексические упражнения.
Read and translate the text.
Text
Modern Technologies
It goes without saying
that life was much more difficult before technology had developed as much as it
has now. When it took two weeks for a letter to reach Australia, you couldn't
keep in touch with people easily. Or just travelling from your home to another
town a few kilometers away could take hours. And if you didn't live in a big
city, you didn't have much information because there was no television or the
Internet.
We have seen major technological advances over the
last twenty years and the next years or so are going to be equally exciting. I
believe that in the not-too-distant future, we won't have to carry our mobile
phones around but will implant them somewhere in the body - maybe in our teeth or
in our shoulders. I think that we won't have cash or credit cards any longer.
It will mainly be digital money. And supermarkets will probably have iris
recognition systems, so the money for our groceries will automatically be
transferred from your bank account into the supermarket's bank account as
you're standing at the checkout. Many people say it's science fiction but I
think it's our future. Soon we'll all have more time for our hobbies and
interests because robots will do all the work for us! I'm sure that new
technology will change our lives for the better.
However, we must admit, that our technological
progress has its drawbacks. For example, cars pollute our atmosphere. There is
a lot of radiation from TVs, computers, mobiles and other electronic devices.
Moreover, technology makes us lazy! Many teenagers would rather spend their
free time in front of their computer than meet their friends. As a result, they
don't have enough exercise and are getting fat. That's not healthy at all!
As for me, I'm a fan of modern technology. Now with
computers and e-mail we never have to lose contact with anyone. We can travel
from one place to another quickly and safely. What is more, because of
television, everyone has information about the world around them. I can't
imagine my life without technology. Of course, we've got things like a TV, a
video player, a computer and different kitchen appliances such as a microwave
oven and a dishwasher. But most of all I enjoy my new mobile because now I can
always stay in touch. I never go anywhere without it! I use it all the time and
send about twenty text messages every day! To sum up, I want to say that
technology has definitely made our lives easier and we couldn't live without
it!
Exercise 1. Answer
the questions:
1. Can you imagine your life without modern technology?
2. Does technology make our life easier?
3. Do you think we rely too much on technology?
4. Would you like to be an inventor? Why? What kind of things would you invent?
5. What technological advances can you see happening in your life?
6. How do you think the world will change over the next fifty years?
Exercise 2. Learn
Vocabulary
a dryer, a tumble dryer (BrE), a tumble drier (AmE) – сушилка;
an oven – духовка;
a blender – блендер;
a juicer – соковыжималка;
a coffee maker – кофеварка;
an espresso maker – аппарат для приготовления эспрессо;
an electronic kitchen scale – электронные кухонные весы;
an electric pressure cooker – скороварка;
a hotplate – небольшая электроплитка;
an ice cream maker – мороженица;
a hand mixer – ручной миксер;
a stand mixer – стационарный миксер;
a microwave oven – микроволновая печь;
a kettle – чайник;
a deep fryer – фритюрница;
a food steamer – пароварка;
a popcorn maker – аппарат для приготовления попкорна.
|
Слово |
Перевод |
|
to connect |
включить, подключить |
|
to disconnect |
отключить, отсоединить |
|
to insert |
поместить, вставить |
|
to increase the speed |
увеличить скорость |
|
to put a lid on smth |
накрывать крышкой |
|
to be plugged in |
быть включенным в розетку |
|
to press the start button |
нажать кнопку «Пуск» (кнопку «Старт») |
|
to be turned on/off |
быть включенным/выключенным |
|
to take out |
вынимать |
|
to turn the speed down |
уменьшить скорость |
|
to turn up/down |
увеличить/уменьшить |
|
to remove |
убрать, удалить |
|
to stop working/operating completely |
остановить работу (прибора) |
|
to unplug |
выдернуть вилку из розетки |
Exercise 3. Translate.
1.How is this dishwasher connected to the water line?
2.Ben suddenly remembered that he had forgotten to unplug the electric kettle.
3.It’s utterly important to slowly increase the speed of the blender when you blend the ingredients.
4.I forgot to put a lid on the blender while making a milkshake. Now my kitchen is a complete mess!
5.Wait! Make sure the coffee machine is plugged in.
6.If you don’t press the start button, the vacuum cleaner will not work.
7.Turn off the air conditioner! It’s freezing cold in the room!
8.Jessica opened the microwave oven, took out the glass of milk and went back to the kitchen table.
9.If you don’t want to get your hairdryer broken, turn the speed down and then turn it off.
10.Turn down the temperature in the oven otherwise you'll overcook or burn the meat.
11.Don’t try to open an electric pressure cooker until it stops working/operating completely.
12.When you leave home you should disconnect all the electric appliances.
Exercise 4. Test Household appliances
Выберите правильный вариант ответа.
· A reversible door
· A crisp zone
· A microwave oven
· A vacuum cleaner
· stack the dishes.
· turn on the vacuum cleaner.
· turn off the mixer.
· disconnect the radio.
· a coffee maker.
· a toaster.
· an ice dispenser.
· a deep fryer.
· sleep mode
· drain hose
· filter cover
· door
· white goods.
· gadgets.
· brown goods.
· black goods.
· put
· unplug
· disconnect
· remove
· take out
· connect
· turn down
· remove
· press the start button.
· remove it.
· stop completely.
· unplug.
· vacuum cleaner.
· juicer.
· air conditioner.
· dishwasher.
· food steamer.
· kettle.
· deep fryer.
· tumble drier.
Тема: Местоимения. Прилагательное. Наречие.
Цель: совершенствование грамматических навыков
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Повторите правила употребления местоимений, прилагательных, наречий в учебном пособии И.П. Агабекян «Английский язык для СПО». Обратите внимание на примеры. Выполните грамматические упражнения.
Exercise 1. Заполните пробелы личными местоимениями в объектном падеже:
1. My friend Tom lives in London. This is a parcel from (него) ____ . 2. I’m sorry, I can’t tell (тебе) ____ what happened. 3. The children are hungry. Give (им) ____ an apple. 4. We are thirsty. Can you give (нам) ____ some juice? 5. Jack is in the garden. Bring (ему) ____ his book. 6. Ann and Paul can’t do their homework. Can you help (им) ____ ? 7. I can’t help (вам) ____ tomorrow. I must visit my aunt. 8. These clothes are for poor children. Can you bring (их) ____ to the Red Cross? 9. This cake is for Carol and me. Please give (его) ____ to ____ (нам). 10. The roses are for mother. Please give ____ to (ей) ____ . 11. Where is father? Can you tell (мне) ____ where he is? 12. Where is the mouse? I can’t see (ее) ____ . 13. Where is the post office? Can you tell (мне) ____ where it is? 14. What’s your telephone number? I don’t know (его) ____ . 15. Our brother is very nice. He always helps (нам) ____ with the homework.
Exercise 2. Заполните пробелы возвратными местоимениями с -self (-selves) или местоименной конструкцией each other:
1. Tom cut ____ while he was shaving this morning.2. We really enjoyed ____ very much. 3. I repaired my bike ____ . 4. Why don’t you clean the windows ____ ?
5. Jack and I met ____ at the party five years ago. 6. At Christmas friends often give ____ presents. 7. They looked at ____ . 8. The film ____ wasn’t very good but I liked the music. 9. The old woman sat at the park bench talking to ____ . 10. Let’s paint the house ____ . 11. Did you write it ____ ? 12. She locked the door ____ . 13. The children cleaned their room ____ . 14. Ann baked the cake ____ . 15. The cat caught the mouse ____ .
Exercise 3. Заполните пробелы соответствующими притяжательными местоимениями:
1. John Anderson forgot (свою) ____ book. 2. Mary and Susan talk like (их) ____ mother. 3. Alex and I were late for (наш) ____ class. 4. Princess Caroline is wearing (свое)____ new Gucci gown. 5. Where are (мои) ____ keys? I can’t find them. 6. Where do you keep (свои) ____ money, in the bank? 7. Everyone should bring (свои) ____ signed receipt.
Exercise 4. Заполните пробелы возвратными местоимениями:
1. He built a boat all by ____ . 2. I hurt ____ quite badly falling down the stairs. 3. The children
did everything ____ without any help. 4. Maria and Alison, you really should look after ____ better. 5. Forget it! I’ll do it ____. 6. I burnt ____ on the oven yesterday. 7. She blames ____ for what happened. 8. Bob taught ____ to type last summer. 9. I talk to ____ all the time. It doesn’t mean I’m crazy. 10. We all enjoyed ____ very much on the picnic. 11. I was so stupid I could have kicked ____. 12. The protesters locked ____ into the church and refused to come out.
Exercise 5. Найдите и исправьте ошибки, если таковые имеются..
1.I`m busier than my little sister.
2.London is more old than New York.
3.It's the most sharp pencil I have.
4. Do you know the shortest way to the station?
5.This exercise is more difficult than that one.
6.Be activer at your lessons, please.
7.She is the most pretty girl I've ever known.
8.The boy is as taller as his father.
9.He makes more mistakes than you do.
10. Baseball is the popularest summer sport in America.
11.Yesterday he started to feel more bad.
12. Soon it began to get more darker and it was time 1 back home.
13. He said that money was the most important to him.
14.I've got a headache. Be quieter, please.
15. Mary's answer is correcter than yours.
16.Can you come more early next time?
17.You should be carefuler.
Тема: Глагол to be. Конструкции be going to, there be. Фразовые глаголы.
Цель: совершенствование грамматических навыков
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Повторите поравила употребления грамматических тем: «Глагол to be. Конструкции be going to, there be. Фразовые глаголы» в учебном пособии И.П. Агабекяна «Английский язык для СПО», Безкоровайной Г.Т. «Planet of English». Выполните грамматические упражнения.
Exercise 1. Заполните пропуски нужной формой глагола to be и переведите.
1. Не... born in 1985. 2. We... students now. 3. We... good friends at the college. 4. It... an interesting book. 5. Who... absent today? 6. He... a student. 7. What... he? 8. ... he a doctor? 9. These... my pencils. 10. Where... this book? It... on the table. 11. What... their names? 12. Mary... a girl. 13. Who... he? 14. What... you? 15. This man... in the room. 16. How... she? 17. How... you? I... fine. 18. How... your friend? 19. ... he your son? 20. Tomorrow we... at home. 21. ...you a sportsman?
Exercise 2. Напишите следующие предложения в прошедшем и будущем временах:
1. There is much snow in winter. 2. There are 5 theatres in our city. 3. There is no lift in our house. 4. There are many new books in our library. 5. There is little milk in the bottle. 6. There are 3 rooms in our flat. 7. There is a map on the wall.8.
Exercise 3. Поставьте в предложение подходящий фразовый глагол, используя глагол из первого столбца и необходимый предлог – из второго. Некоторые глаголы и предлоги используются не один раз. Поставьте глаголы в нужную форму.
1 2
take
put up
fill off
try forward
turn on
look for
give in
grow after
get out
go
Н-р: She … at 6 a.m. because her work starts early. (Она встает в 6 утра, потому что ее работа начинается рано.) – She gets up at 6 a.m. because her work starts early.
1. Can I … these sandals, please? (Можно примерить эти сандалии?)
2. It’s too cold outside. … a warm coat and a hat. (На улице слишком холодно. Надень теплое пальто и шапку.)
3. It’s too hot inside. Can I … my jacket? (В помещении слишком жарко. Могу я снять куртку?)
4. Mary is going to become a doctor when she … . (Мэри собирается стать врачом, когда вырастет.)
5. Don’t forget to … the light when you leave the bathroom. (Не забудь выключать свет, когда выходишь из ванной.)
6. Please … this registration form. (Пожалуйста, заполните этот регистрационный бланк.)
7. We’re … to meeting your wife. (Мы с нетерпением ждем встречи с твоей женой.)
8. Ann is so tolerant and kind. She likes … children and old people. (Аня так терпелива и добра. Ей нравится ухаживать за детьми и пожилыми людьми.)
9. …! The baby is going to fall! (Осторожно! Малыш может упасть!)
10. Sorry. I can’t … with you tonight. I am very busy. (Извини. Я не могу пойти прогуляться с вами вечером. Я очень занят.)
11. He is … a job as a lawyer. (Он ищет работу на должность юриста.)
12. Bob smoked for 20 years but he … six months ago. (Боб курил 20 лет, но бросил 6 месяцев назад.)
13. I’d like to watch the news. Could you … the TV, please? (Я бы хотел посмотреть новости. Не мог бы ты включить телевизор?)
14. This word is new for me. I have to … it … in my dictionary. (Это слово для меня новое. Мне нужно отыскать его в словаре.)
15. We must … our reports tomorrow morning. (Мы должны сдать наши отчеты завтра утром.)
16. Oh god! We have … at a wrong station. (О боже! Мы высадились не на той станции.)
Тема: Предлоги места, времени, направления. Фразовые глаголы.
Цель: совершенствование грамматических навыков, определение предлогов.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Пояснения к работе
Краткие теоретические положения:
Предлог Preposition
Предлог - это служебное слово, выражающее отношение существительного или местоимения к другим словам в предложении. Эти отношения бывают: пространственные, временные, причинные, целевые и др.
Формы предлогов:
По своей форме предлоги делятся на следующие группы:
1) Простые предлоги, например:
in - в, через; to - к, в; at -за, у, в; by- около; with- с.
2) Сложные предлоги, образованные путем словосложения, например:
Into- в; inside - внутри; before - перед; behind - за; upon - на; throughout - через.
3) Составные (или групповые) предлоги, которые представляют собой сочетание существительного, прилагательного, причастия или наречия с простым предлогом или союзом, объединенные единым значением.
Например: as far as до; as for что касается;because of из-за; in case of в случае; in front of перед
of (кого? чего?) родительный падеж
Предлог of, стоящий между двумя существительными, передает грамматические отношения, выраженные в русском языке родительным падежом (кого? чего?):
He showed us the plan of the port. Он показал нам план (чего?) порта.
The roof of the house is painted green. Крыша (чего?) дома выкрашена в зеленый цвет.
He is a teacher of the English language. Он - учитель (чего?) английского языка.
to (кому? чему?) дательный падеж
Предлог to перед существительным в функции дополнения передает отношения, выражаемые в русском языке дательным падежом (кому? чему?), обозначая лицо, к которому обращено действие:
He showed the plan to the workers. Он показал план (кому?) рабочим.
by (кем? чем?) творительный падеж
Предлог by после глагола в страдательном залоге и перед существительным, обозначающим действующий предмет или действ.лицо, передает отношения, выражаемые в русском языке творительным падежом (кем? чем?):
The letter was signed by the director. Письмо было подписано (кем?) директором.
with (кем? чем?) творительный падеж
Предлог with перед существительным, обозначающим орудие действия или предмет, используемый при совершении действия, передает отношения, выражаемые в русском языке творительным падежом (кем? чем?):
The letter was written with a pencil. Письмо было написано (чем?) карандашом.
Существует и обратное явление: в английском предложении предлог может отсутствовать, а при переводе на русский язык он обязателен, например:
We entered the room. Мы вошли в комнату.
Предлоги, обозначающие движение
to движение по направлению к предмету (лицу), протекающему процессу:
Come to me. — Подойдите ко мне.
from движение от предмета (лица), удаление от протекающего процесса:
Take this book from the table.— Убери книгу со стола. '
I come from Russia. — Я из России.
into движение внутрь ограниченного пространства:
Put the book into the bag. — Положи книгу в портфель.
out of движение из ограниченного пространства:
Take the book out of the table. — Достань книгу из стола.
on(to) /onto движение на поверхность:
Snow fell onto the ground. — Снег падал на землю.
through через, сквозь: Не went in through the door. — Он вошел через дверь.
Предлоги, обозначающие место
at местонахождение у предмета (лица), а также там, где протекает определенный процесс:
I am sitting at the table. — Я сижу у стола.
I study at school. — Я учусь в школе.
The pupils are at the lesson. —Ученики на уроке.
in местонахождение внутри ограниченного пространства:
Не is in the office. — Он в офисе.
The books are in the bag. — Книги в портфеле.
on местонахождение на поверхности:
The book is on the desk. — Книга на столе.
under местонахождение под другим предметом:
The book is under the table. — Книга под столом.
across через: My school is across the street. — Моя школа находится через дорогу.
above местонахождение над другим предметом:
There is a lamp above the table. — Над столом висит лампа.
between между: Between us. — Между нами.
in front of местонахождение предмета (лица) впереди другого предмета (лица:)
There is a telephone in front of him. — Перед ним стоит телефон.
behind местонахождение предмета (лица) позади другого предмета (лица):
There is a sport ground behind our school. — За нашей школой спортплощадка.
around местонахождение одного предмета вокруг другого предмета:
We are sitting around the table. — Мы сидим вокруг стола.
beyond по ту сторону: Beyond the limits of the city. — За пределами города.
over над, через, сверх: There is a bridge over the river. — Над рекой мост.
near вблизи, около, рядом с, возле, за:
She is sitting near the table. — Она сидит за столом.
up вверх: Up the river. — Вверх по реке.
down вниз: Down the river. — Вниз по реке.
Предлоги времени
in внутри временного отрезка: In April, in 1999. — В апреле, в 1999 году.
in через некоторое время: in an hour, in two days через час, через два дня
at в (точка во времени) at 5 o’clock, at midnight – в 5 часов, в полночь
on в (с названием дней недели, датами):
on Monday, on the 10th of February - в понедельник, 10 февраля
by к определенному моменту: by 8 o'clock tomorrow — к 8 часам завтра
from... till / from... to... от... до: from 5 till 6 o'clock/from 5 to 60' clock — с 5-ти до 6-ти
for в течение (отрезок времени): for an hour — в течение часа
during во время (чего-либо): during the lesson— во время урока
after после (чего-либо): after work — после работы
before перед (чем-либо): before the lesson- перед уроком
within внутри, в рамках: within a month — в течение месяца
Прочие предлоги
bу при, около, посредством: by the window, by plane — около окна, самолетом
with вместе с: with a friend – с другом
for для: I'll do it for you. - Я сделаю это для тебя.
Практическая часть.
Задание: выполните грамматические упражнения.
Exercise 1. Вставьте пропущенные предлоги в предложения (in, on, at, for):
1. I live … Washington.
2. His glasses are … the table.
3. She took an apple … her child.
4. The meeting begins … five.
5. Look … him!
6. … the contrary he wanted to come.
7. May I come …?
8. We’re going to visit a theatre … Saturday.
9. Kate was born … 1986.
10. He lives … the second floor.
11. We have done our task … that moment.
12. My birthday is … July.
13. She returns … time.
14. He is … love with her.
15. My children are … home.
16. John was busy… fact.
17. I shall come … an hour.
18. They don’t like the sour apples and … example, me.
19. A chair is … the door.
20. He made a surprise his hands for me.
Exercise 2. Вставьте пропущенные предлоги в предложения (to, by, over, into):
1. When we came the game was …
2. He went … school.
3. She came … my room, no resolution.
4. The book was brought … the girl.
5. The pencil belongs … me.
6. The document was signed … the director.
7. The ball fall … the water.
8. She is going … the sea.
9. Repeat the texts … again.
10. He quickly climbed … the fence.
11. I think … your propositions.
12. The sunny weather will be all … the country.
13. She went … the river.
14. They go … home.
15. The pupils came … the classroom.
16. The dog went … the lake.
17. Put money … the pocket.
18. He couldn’t sleep and turn side … side.
19. The lamp is… the bookcase.
20. My sister prefers travelling … car.
Контрольные вопросы:
1.Что такое предлоги?
2.Какие предлоги вы знаете (по группам)?
Тема: Работа с текстом "Промышленная электроника".
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте и переведите текст «Промышленная электроника». Выучите новую лексику. Выполните лексические упражнения.
Read and translate the text.
lndustгial electгonics
Hundreds of electronic equipments arc now used for scientific, industrial and everyday purposes. They help to do jobs better or more rationally than before and take over jobs that couldn't bе done otherwise.
So, industrial electronics undoubtedly plays а very important role today. You can easily find many electronic equipments at lюme: а tape recorder, а ТV set, an МРЗ player, а computer and many others.
The application and use of electronic equipments demands а good knowledge of their fundamentals.
In meters and lamps electricity flows in the wire. But inside any transistor or microchip (and previously, in radio tubes) electric current passes through the space (or semiconductor) separating certain parts in this detail. Such action is called electronic. It's not difficult to imagine it because the same happens in lightning. There you actually see how electricity jumps through space.
The first electronic equipments used radio lamps. They were: а radio set, а ТV set, computing machines (predecessors of modem calculators), computers (which occupied big rooms), tape recorders.
The next stage came when transistors were invented. The devices became more powerful and much smaller. The number of devices increased greatly, some multifunctional devices appeared (radio + tape recorder). Computers and calculators became smaller: cassette recorders and videocassette recorders appeared.
The next period was the period of microchips. They helped to reduce big parts of devices, computers and other devices.
Тhе latest period of industrial electronics development is the period of total digitization of all electronic devices, making them compatible with the computer. Photos are no longer made on film but on memory cards, cassettes and video cassettes are out of use. Television is also becoming digital.
Industrial electronics is а great part of our leisure time, it makes people's lives easier, and reduces their working time.
Exercise 1. Learn
Vocabulary
application - применение; приложение
calculator- калькулятор
cassette -кассета
certain - определенный
compatible -совместимый
computing - вычислительный
current -ток
demand - требовать
detail -деталь
digitization -переход на цифровой формат
electric -электрический
electricity - электричество
electronics -электроника
everyday -каждодневный
film -1. пленка 2. фильм
flow - v течь n поток
fundamental - n основа al(j основополагающий
imagine -представить
increase -увеличиваться
inside -внутри
jump -прыгать
lamp -лампа
leisure - отдых, развлечение
lightning - молния
осcuру - занимать
otherwise - иначе
pass -проходить
powerful - мощный
predecessor -предшественник
previously - прежде
purpose - цель
radio -радио
rational - рациональный
reduce - уменьшать
scientific -научный
semiconductor -полупроводник
space - пространство
tape -лента, tape recorder- магнитофон
television - телевидение
total -полный
transistor -транзистор
tube - трубка
undoubtedly - несомненно
video-cassette recorder -видеомагнитофон
wire-провод
Exercise 2. Answer the following questions to the text.
1. For what purposes are electronic equipments used now? What do they help us to do?
2. Industrial electronics plays an important role today, doesn't it?
3. What electronic equipments are usually found at home? What can you find at home?
4. What is the difference between electric and electronic devices?
5. Where do you actually see how electricity jumps thгough space?
6. What were the first electronic equipments based on?
7. Did the first computers look like modem ones?
8. Did the next stage соте when transistors or cassettes were invented?
9. Why did computers become smaller when microchips were introduced?
10. How is the 1atest period of industrial electronics development called?
11. What devices became compatible with computer?
12. What does electronics mean in our life?
13. Do you think that electronics does only good to people?
14. What will bе the next period of industrial electronics development, in your opinion?
Exercise 3. Study the Active vocabulary. lnsert the missing words.
1. In lighting electricity _through _.
2. What do you like more: watching _or listening to the _?
3. 1 can't _how people lived without _devices.
4. Do you have any _at home? No, 1 have only disks. I'm for _.
5. Does this camera have much _? No, this camera is not digital. It has а 5-millimetre _
6. Devices which have _, and not tubes are much smaller and much more powerful.
7. The number of digital devices _every year. We depend on _more and more.
8. Many electronic devices are used for ___, not for work.
9. Computers and digital cameras are _devices. It means that they can exchange information.
Exercise 4. Continue the following statements.
1. Electronic equipments are used for ...
2. You can find many electronic equipments at home: а ТУ set ...
3. Inside any transistor electric current passes ...
4. In lightning you actually see ...
5. The first electronic equipments used .. .
6. The devices with transistors become .. .
7. Microchips helped to reduce ...
8. The latest period of industria1 electronics development is ...
9. Photos are no longer made on 5-millimetre ftlm, but ...
10. Industrial electronics makes people's life ...
Exercise 5. Write an essay оп one of the following topics.
1. The role of industrial electronics in modern society. 2. Digitization and its influence on peop1e's leisure time.
Тема: Работа с текстом «Машины и механизмы»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте и переведите тексты по теме «Машины и механизмы». Выполните упражнения после текста.
Read and translate the text.
Machines and mechanisms
Technological Wonder
At all times, scientists have created a variety of tools and devices, which at some point became a breakthrough for science and elevated mankind to a new level of technological development. In the twentieth century, people invented airplanes, TV sets, mobile phones, computers, microphones, electric cars and lots of other useful things, without which we cannot imagine our lives.
I consider 3D printer one of the most interesting technical inventions of modern times. This device allows you to create 3D objects based on digital models. All 3D printers operate based on the accruals concept: they suggest a gradual, layer-by-layer construction of solid parts.
This technology was discovered and patented by an American scientist Chuck Hull back in the 1986, but the first equipment appeared only ten years later. First 3D printers were modernized ink-jet printers, but later models were created with the use of photo polymeric liquid plastic in their operation.
Before these devices were quite large, and now 3D printers can easily be located on a standard writing desk. I consider their broad sphere of application the main advantage of such inventions. As far as using a 3D printer you can create objects of various materials and produce ready-made parts, today these devices can be used in architecture, construction, medicine, automotive industry and even in the production of weapons. The possibility of the use of these devices in medicine, in my opinion, has the greatest importance to humans. Without 3D printers, it would not have been possible to create modern, high-tech prostheses, artificial internal organs, dental implants and more.
Thus, this technological wonder can make people's lives much easier and happier, as well as of give them new opportunities.
Задание: Найди соответствующий перевод в тексте
1. Сегодня эти устройства могут использоваться в архитектуре, строительстве, медицине, автомобилестроении и даже в производстве оружия.
2. Все 3D-принтеры предлагают постепенную, поэтапную конструкцию твердых деталей.
3. Без 3D-принтеров было бы невозможно создать современные, высокотехнологичные протезы, искусственные внутренние органы, зубные имплантаты и многое другое.
Industrial robot
An industrial robot is a robot system used for manufacturing. Industrial robots are automated, programmable and capable of movement on two or more axes.

Typical applications of robots include welding, painting, assembly, pick and place for printed circuit boards, packaging and labeling, palletizing, product inspection, and testing; all accomplished with high endurance, speed, and precision. They can assist in material handling.
In the year 2015, an estimated 1.64 million industrial robots were in operation worldwide according to International Federation of Robotics (IFR).
Some robots are programmed to faithfully carry out specific actions over and over again (repetitive actions) without variation and with a high degree of accuracy. These actions are determined by programmed routines that specify the direction, acceleration, velocity, deceleration, and distance of a series of coordinated motions.
Other robots are much more flexible as to the orientation of the object on which they are operating or even the task that has to be performed on the object itself, which the robot may even need to identify. For example, for more precise guidance, robots often contain machine vision sub-systems acting as their visual sensors, linked to powerful computers or controllers. Artificial intelligence, or what passes for it,[clarification needed] is becoming an increasingly important factor in the modern industrial robot.
Задание: Найдите соответствие.
|
Degrees of freedom – |
how closely a robot can reach a commanded position. |
|
Working envelope – |
how fast the robot can position the end of its arm. |
|
Carrying capacity or payload – |
this is usually the same as the number of axes. |
|
Speed – |
the region of space a robot can reach. |
|
Accuracy – |
how much weight a robot can lift. |
|
Repeatability – |
how well the robot will return to a programmed position. |
Тема: Множественное число существительных.
Цель: совершенствование грамматических навыков
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: повторите правила употребления множественного числа существительных, артиклей, притяжательного падежа существительных в учебном пособии И.П. Агабекян «Английский язык». Обратите внимание на примеры. Выполните грамматические упражнения.
Exercise 1. Напишите следующие существительные во множественном числе:
box, sheep, place, library, photo, mouse, lady, glasses, bush, dress, country, bus, party, wife, day, knife, knowledge, month, pen, hero, goose, company, life, deer, tomato, city, man, play, news, child, fruit, shelf, leaf, foot, fish, woman, money, information.
Exercise 2. Поставьте существительные в следующих предложениях во множественное число.
1.A new house is in our street. 2. This story is very interesting. 3. A woman, a man, a boy and a girl are the room. 4,. In the farm-yard we see an ox, a sheep, a cow and a goose. 5. Put this knife on that table. 6. Is this worker an Englishman or a German? — He is a Frenchman. 7. What is your name? 8. He keeps his toy in a box.9. This man works at our office.
Exercise 3. Употребите, где требуется, артикли а, an, the:
1. ... Volga is... longest river in... Europe. 2. What is... nearest way to... Drama Theatre? 3. ... butter and... cheese are made of... milk. 4. Usually I get up at... 7 o'clock in... morning. 5. ...Rostov is situated on... Don. б. Will you have... cup of... tea? 7. This... pencil is broken. Give me that... pencil, please. 8. I have ... ten programmes on my TV. 9. My friend has... car .... car is broken now. 11. I got... letter from my friend yesterday. ... letter was very long. 12. She has two... daughters and one... son. Her... son is... student. 13. My... brother's... friend has no... dog. 14. This is... house. ... house is white. 15. They have... party. ... party is... birthday party. 16. I read ... good
Exercise 4. Употребите притяжательный падеж существительных.
Образец: The poems of Lermontov. (Lermontov's poems.)
1. The toy of their children. 2. The questions of my son. 3. The wife of my brother. 4. The table of our teacher. 5. The life of animals. 6. The voice of this girl. 7. The new book of the pupils. 8. The letter of Peter. 9. The car of my parents. 10 The room of my friend. 11. The handbags of these women. 12. The flat of my sister is large. 13. The children of my brother are at home. 14. The room of the boys is large.
Тема: Артикль.
Цель: формирование грамматических навыков чтения и письма.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Пояснения к работе:
Краткие теоретические сведения.
Определение. Артикль - служебное слово в английском языке.
Употребляется перед существительным и поясняет его. Если перед существительным стоит
определяющее слова или слова, то артикль ставится перед всеми определениями.
В русском языке артиклей нет и они, как правило, не переводятся на русский язык.
Два типа артиклей:
· неопределенный (indefinite) - 'a' and 'an'
· определенный (definite) - 'the'
Неопределенный артикль a (an) происходит от числительного one (один), определенный — от указательного местоимения that (тот).
Артикль употребляется:
• перед каждым нарицательным существительным.
Если перед существительным артикль не употребляется, то нужно уметь объяснить, почему.
Артикль не употребляется если перед существительным стоит:
• указательное или притяжательное местоимение,
• другое существительное в притяжательном падеже,
• количественное числительное,
• отрицание no.
Например: This is my book. It's friend's book. I have one book.
Упоминая предмет впервые, мы употребляем перед ним неопределенный артикль а (ап). Упоминая этот же предмет вторично, мы ставим перед ним определенный артикль the.
Например: This is a book. The book is interesting.
Неопределенный артикль a (an)
употребляется перед единичным, отдельным предметом, который мы не выделяем из класса ему подобных. Неопределенный артикль an обычно стоит перед существительным, которое начинается с гласного звука: an apple, an egg.
Например: I bought a book yesterday. Я купил вчера книгу (одну из многих ей подобных). I have an apple. У меня есть яблоко (одно, какое-то).
Неопределенный артикль a (an) может употребляться только с исчисляемыми существительными, стоящими в единственном числе. Перед неисчисляемыми существительными или существительными во множественном числе неопределенный артикль опускается.
Неопределенный артикль не употребляется:
а) с неисчисляемыми и «абстрактными» существительными:
I like coffee and tea. Friendship is very important in our life.
б) с существительными во множественном числе:
They are students now.
в) с именами собственными:
I told Jane about that.
г) с существительными, перед которыми стоят притяжательные или указательные местоимения:
This car is better than that. My bike is old.
д) с существительными, за которыми следует количественное числительное, обозначающее номер:
I have read page eight of the magazine.
Неопределенный артикль а необходим в конструкциях:
I have a... This is a...
I am a... I see a...
There is a... He is a...
What a fine day!
Определенный артикль the
Определенный артикль the выделяет предмет или предметы из класса им подобных:
The book I bought yesterday was interesting — Книга, которую я купил вчера, была интересной (это — конкретная книга, которую говорящий выделяет из класса ей подобных).
Определенный артикль the употребляется как с исчисляемыми, так и с неисчисляемыми существительными, как с единственным, так и с множественным числом.
Например: This is a book. The book is interesting (исчисляемое в единственном числе).
This is meat. The meat is fresh. (неисчисляемое)
These are books. The books are good. (множественное число).
Определенный артикль употребляется:
а) когда известно (из контекста, из окружающей обстановки) о каком предмете (предметах, явлениях) идет речь: Open the door, please. I am going to the Academy.
б) когда речь идет о единственном в своем роде предмете или явлении: The moon is shining brightly.
в) когда существительное имеет ограничивающее определение, чаще всего с предлогом of.
I don't know the name of this pupil.
г) в словосочетаниях типа in the north, to the west, at the cinema, the same, in the country, the rest of the...
д) если перед существительным стоит прилагательное в превосходной степени
This is the most interesting book.
e) перед порядковыми числительными
He lives on the fifth floor.
Географические названия и артикль
С географическими названиями и с именами собственными, артикль, как правило, не употребляется, кроме следующих случаев:
а) с названиями морей, рек, океанов, горных хребтов, групп островов используется определенный артикль: the Pacific Ocean, the Black Sea, the Thames, the British Isles.
б) определенный артикль используется с несколькими названиями стран, областей и городов, (хотя обычно с этими типами названий артикль не используется):
the Ukraine, the Crimea, the Caucasus, the Netherlands, the Hague, the Riviera, the Congo, the West Indies
в) определенный артикль используется с названиями стран типа:
the Russian Federation, the United States of America, the United Kingdom.
г) перед собирательным именем семьи The Petrovs — Петровы
Практическая часть:
Exercise 1.. Translate into Russian. Explain the use (использование) of definite (определенных) and indefinite (неопределенных) articles:
1. Last week I met my friend. He was with a young girl. The girl was a student of our Academy.
2. This is a pencil. The pencil is red.
3. She is a teacher. She is our teacher of English.
4. It is a lake. The lake is deep. It's one of the deepest lakes in the world.
5. There are many flowers in your garden. The flowers are beautiful.
6. Did you write a plan? Give me your plan, please. Is this plan effective?
7. The Black Sea is in the South of Russia.
8. This is Mike. He works as an engineer. Mike is a highly qualified engineer.
9. There are some schools in our street. The schools are new.
10. Gagarin was the first cosmonaut of the world.
11. In summer the sky is blue and the sun shines brightly.
12. The Petrovs are very friendly.
13. This is Ann's book. I don't like such books.
14. Winter begins in December.
Exercise 2.Insert (вставьте) the article where necessary:
1. This... pencil is broken. Give me that... pencil, please.
2. I can see three... boys. ... boys are playing.
3.1 have... bicycle. ... bicycle is black. My... friend has no... bicycle.
4. Our... room is large. 5. We wrote... dictation yesterday. ... dictation was long.
6. She has two...daughters and one...son. Her...son is...pupil.
7. My...brother's... friend has no... dog.
8. This is... tree. ... tree is green. 9. She has...ball. ...ball is...big.
10. I got... letter from my... friend yesterday. ... letter was interesting.
Exercise3.. Use the articles a, an, the where it is necessary:
1. Yesterday I saw... new film, but... film wasn't very interesting.
2. London is situated on... Thames.
3. Yuri Gagarin was... first man to fly over... Earth in spaceship.
4. My daughter will go school... next year.
5. I decided to visit... Ivanovs, but they were not at... home.
6. In... summer we live in... country.
7. Lomonosov,... great Russian scientist, was born in... small village on... shore of... White Sea.
8. ... United States of America is one of... most powerful countries of the world.
9. Is your dress made of... silk or... cotton?
10...Peter's brother is... student and we are...pupils.
11. What would you like:... apple or... orange?
12. What... strange man he is!
Exercise 4.Use the articles a, an, the where it is necessary:
1. ... Volga is... longest river in... Europe.
2. ...History and... Literature were... my favourite subjects at... school.
3.What is... nearest way to... Drama Theatre?
4. ...butter and... cheese are made of... milk.
5. Usually I get up at... 7 o'clock in... morning.
6. ..Rostov is situated on... Don.
7. Will you have... cup of... tea?
8.What... good friend you are!
9. We shall go to...cinema... next week together with... Petrovs.
10. This is... book, ... book is very interesting.
11. Do you see... sun in... sky today?
12.He is... engineer by... profession.
Exercise5.. Insert (вставьте) the article where necessary:
Three men came to... New York for... holiday. They came to... very large hotel and took... room there. Their room was on... forty-fifth floor. In... evening... friends went to... theatre and came back to... hotel very late.
«I am very sorry,» said... clerk of... hotel, «but... lifts do not work tonight. If you don't want to walk up to your room, we shall make... beds for you in... hall.» «No, no,» said one of... friends, «no, thank you. We don't want to sleep in... hall. We shall walk up to our room.»
Then he turned to his friends and said: «It is not easy to walk up to... forty-fifth floor, but we shall make it easier. On... way to... room I shall tell you some jokes; then you, Andy, will sing us some songs; then you, Peter, will tell us some interesting stories.» So they began walking up to their room. Tom told them many jokes; Andy sang some songs.
At last they came to... thirty sixth floor. They were tired and decided to have... rest. «Well,» said Tom, «now it is your turn, Peter. After all... jokes, I would like to hear... sad story. Tell us... long and interesting story with...sad end.» «... story which I am going to tell you,» said Peter, «is sad enough. We left... key to our room in...hall.»
Вопросы для самоконтроля:
1. Что такое артикль?
2. С какой частью речи употребляется артикль?
3. Какие артикли существуют? В чем разница в употреблении?
4. Когда артикли не употребляются?
5. Назовите особые случаи употребления неопределенного и определенного артикля.
Тема: Экологические проблемы
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте и переведите текст «Экологические проблемы». Выполните лексические упражнения.
Read and translate the text.
Ecological problems
We are in an environmental crisis because human beings have broken out of the circle of life and are destroying the environment. To survive, we must learn how to restore the wealth we have borrowed from nature.
What does the environmental crisis mean? To understand this we must begin at the source of life itself: the earth’s thin skin of air, water and soil, bathed by the radiant solar fire. Life appeared here several billion years ago and was nourished by the earth’s matter. Living things formed a global network of various habitats, where everything is directly or indirectly dependent on everything. This is the ecosphere (biosphere), the home that life has built for itself on the planet.
In nature all processes are in constant balanced interaction. There is no waste in nature. Nothing is created, nothing is lost. Everything is recycled endlessly. The environmental crisis means that this perfect and delicate balance has begun to break down, and the relationship between life and its earthly surroundings have begun to collapse.
The environmental degradation continues to accelerate. The ozone layer, vital for survival, is thinning. Acrid rain is destroying huge areas of forest and tens of thousands of lakes. We pollute our rivers, lakes and oceans, and the sky, forgetting that we need water and air to live and breathe. We destroy rainforests, picturesque landscapes, and slaughter the world’s most beautiful animals.
As a result of our new technologies of land use we lose soil, which is the basis of civilization. And, worst of all, the earth is steadily warming with potentially dangerous effects.
That is why the environmentalists of the world call for fundamental changes NOW!
The planet strikes back
The US National Wildlife magazine pointed out 1988 as the year when “Planet Earth began to strike back through drought, heat waves, soil erosion and other human-induced natural hazards”.
The environmental awareness of human kind has become task number one for scientists.
Here are two headlines of different publications dealing with human-induced natural hazards which threaten our ecosphere.
Read the sentences below and find these two publications. Decide which sentences go with headline a) and b).
a) GREENHOUSE EFFECT b) ACID RAIN
1. The atmosphere is a blanket of gases around the Earth.
2. A lot of dangerous gases enter the atmosphere from tall chimneys of factories and power stations.
3. For thousands of years these gases have trapped some of the sun’s heat and kept the planet’s temperatures at a steady level.
4. The present climate zones and other natural habitats have been formed under those temperatures.
5. Then they mix with water in the air and form a cocktail of acidic chemicals.
6. But now because pollutant gases accumulate in the atmosphere, they trap the heat from the Earth like the glass of a greenhouse stops the sun’s heat from leaving.
7. After that the wind carries them for hundreds or even thousands of kilometers away.
8. So, the Earth gets hotter.
9. And finally, this killing mixture falls back on Earth as acid rain.
10. It causes damage or death of forests, lakes, wildlife, humans, buildings, works of art.
11. When the Earth’s temperature rises, the weather will change everywhere.
12. The soil in parts of Scandinavia is now ten times more acid than fifty years ago.
13. Leaves and roots of trees are damaged, and they are dying all over Europe.
14. The ice at the North and South Poles will start to melt and as a result, the level of the sea will rise.
15. When scientists in Britain tried to put new fish into one lake, all the fish died in less than two days.
16. There will be serious floods in many countries.
17. This liquid killer is also attacking many of Europe’s most famous sculptures and buildings: for example, Notre Dame in Paris and St. Paul’s in London.
18. Millions of people will lose their homes.
19. Millions of living organisms will perish.
20. When the climate changes, there will be less food in the world.
21. Vast territories of America and Central Russia will become too hot for farming.
22. Medical statistics show more lung and kidney illness in countries with high levels of acid pollution.
23. Other areas may become wetter, but the soil there isn’t as rich.
24. It won’t be possible to grow the same amount of food.
Тема: Роль технического прогресса.
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте и переведите текст «Роль технического прогресса». Выполните лексические упражнения.
Read and translate the text.
Тhе role of technical progress
The scientific and technical revolution has changed our life very much. The computers, the mobile phones and other digital devices have entered our everyday life.
The atomic, space and energy age was followed bу the age of computers. The tasks which had seemed eternal before have been solved one bу one bу computers. During the last decade many fundamental changes occurred because of electronic devices. It is even difficult to imagine the social and economic consequences of the microelectronic revolution.
The large use of computers has influenced our life in such а way that it was difficult to imagine 15 or 20 years ago. On the one hand, computers have simplified our life greatly. If you typed а text on the typewriter and made а mistake you had to type the whole page again. Making several copies of the same document used to bе а difficult job too. But now it's quite different. Correcting rnistakes is easy. Computer also helps us to buy goods, find information, book tickets, make presentations and annual reports, and make difficult calculations. Time is saved for leisure.
Leisure time is also influenced bу computer and other periphery devices. You no longer go to the music shops - many things are available on the internet. You needn't write letters to your relatives or friends – you can send an e-mail. And your photo albums are on computer too.
Computer games are probably also а part of your free time. They became more and more realistic and complicated, and for many people it becomes impossible to tear themselves away. This means that electronic devices, such as computer and ТV set are used mostly for entertainment and consume most of the time that could Ье spent on work, going for а walk and sleeping. Man becomes а slave of the devices which were designed to make him stronger.
Is there а way out? In fact, there is, but many people don't know it and are still slaves. The best decision is not to give these equipments place in your heart. They should do their work. And when you have а rest, prefer real communication to virtual one and living an active life to watching films about crime. Then electronics will bе not our lord or enemy but our friend!
Exercise 1. Learn
Vocabulary
age- век
annual -ежегодный
atomic -атомный
availbe -доступный
consequence -следствие
сору -копия
correct -исправлять
crime -преступление
decade - десятилетие
document -документ
e-mail (=electronic mail)-
электронная почта
enemy - враг
enter -вводить, входить
good -добро
impossbe -невозможный
influence -влияние и влиять
lord -господин
occur -возникать
periphery -периферия
photo album -фотоальбом
progress -прогресс
realistic -реалистичный
relative -родственник
report -отчет
simplify -облегчать
slave -раб
social -социальный
tear ( oneselt) away -оторвать( ся)
ticket -билет
type -печатать
typewriter –печатная машинка
virtual -виртуальный
Exercise 2. Answer the following questions to the text.
1. The technical revolution has changed our life very much, hasn't it?
2. What were the predecessors of computer age?
3. Do computers make our life easier and simpler? In what way?
4. Computers influence our free time too, don't they?
5. Can you get music and video on the Intemet? What other
infoпnation can you get there?
6. What devices became compatible with computer during the last years?
7. Can you communicate with your friends on the Intemet? Do you like such communication or you prefer real one?
8. In what way do computer games influence the people?
9. Do electronic devices take all our free time?
10. Is man а slave of the devices which were designed to make him stronger?
11. Does the author suggest а way out?
12. What is the way out in your opinion?
Exercise 3. Study the Active vocabulary. Iпsert the missing words.
1. ___helps you to send letters quickly.
2. If there is an interesting program on ТV, it's difficult for а person to
3. During the last two ___ scientific progress and digitization took place.
4. For some people а computer is an equivalent of а ___: а device for printing and editing documents.
5. Do you have many ___?- Yes, I have parents, grandparents, two sisters and three brothers.
6. 1 don't buy __ any more, all my photos are on my computer.
7. Computer is а multifunctional device. So the ___ is that it сап bе used both for work and for leisure.
8. ____age was followed bу а microelectronic one.
Exercise 4. Coпtinue the followiпg statemeпts.
1. The atomic, space and energy age was followed bу ...
2. It's difficult to imagine the social and economic consequences ...
3. Computers have simplified ...
4. Computer helps us to buy goods, find information ...
5. Leisure time is also influenced ...
6. You no longer go to the music shops ...
7. You needn't write letters to your relatives ...
8. Computer and ТV set are used mostly for entertainment ...
9. The best decision is not to give these equipments .. .
10. When you have а rest, prefer real communication .. .
Exercise 5. Make а рlап of the text апd retell the text lookiпg iп уоur рlап.
Тема: Работа с текстом «Международные отраслевые выставки»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте и переведите тексты по теме «Международные отраслевые выставки».
Industrial exhibitions
Expocentre
Expocentre is a world-known Russian organizer of major trade shows and congresses in Russia, the CIS and Eastern Europe with close to 60 years of experience.
All own trade shows of Expocentre are supported by Russian federal executive authorities and national industry associations. Most of these shows are also held under auspices of the Russian Chamber of Commerce and Industry.
Expocentre was the first Russian company to join UFI, the Global Association of the Exhibition Industry, in 1975. In 2005 we played host to the 72nd Annual Congress of UFI, the main international association of exhibition organizers.
Expocentre is a founding member of RUEF, the Russian Union of Exhibitions and Fairs (since 1991), and a member of the Guild of Exhibition and Fair Organizations of the Moscow Chamber of Commerce and Industry.
Due to the development of convention activity, Expocentre also joined AIPC, the International Association of Congress Centres; ICCA, the International Congress and Convention Association; IFES, the International Federation of Exhibition and Event Services; EMECA, the European Major Exhibition Centres Association; and IAEE, the International Association of Exhibitions and Events.
Annually, Expocentre Fairgrounds hosts more than 100 international trade shows with more than one million professional visitors attending and about 30 thousand companies from more than 100 countries participating. It also accommodates more than 900 conventions, conferences and similar events.
Today, Expocentre Fairgrounds comprises 9 fully equipped exhibition pavilions and 38 multifunctional halls for conventions, press conferences, meetings, seminars and symposia. The total exhibition space at Expocentre Fairgrounds is 165,000 sq m comprising 105,000 sq m of indoor space and 60,000 sq m of outdoor space.
Bureau international des expositions
The Bureau International des Expositions or the Bureau of International Expositions (BIE) is an intergovernmental organization created to supervise international exhibitions (also known as expos or world expos) falling under the jurisdiction of the Convention Relating to International Exhibitions.
The BIE was established by the Convention Relating to International Exhibitions, signed in Paris on 22 November 1928, with the following goals:
· to oversee the calendar, the bidding, the selection and the organization of World Expositions; and
· to establish a regulatory framework under which Expo organizers and participants may work together under the best conditions.
Today, 170 member countries have adhered to the BIE Convention.
The BIE regulates two types of expositions: Registered Exhibitions (commonly called World Expos) and Recognized Exhibitions (commonly called Specialized Expositions).
List of world expositions is an annotated list of every world exposition sanctioned by the Bureau International des Expositions (BIE), including those recognised retrospectively as they took place (long) before BIE came into existence.
The designation "World Exposition" or "Expo" refers to a class of the largest, general scope exhibitions of 3 to 6 months' duration.
Planned expositions
|
Date |
Country |
City |
Category |
Name of Exposition |
Theme or symbol |
|
2020 |
United Arab Emirates |
Dubai |
World Expo |
Expo 2020 |
Connecting Minds, Creating the Future |
|
2023 |
Argentina |
Buenos Aires |
Specialized Expo |
Expo 2023 |
Creative Industries in Digital Convergence |
Тема: Работа с текстом "Карьера в области электроники".
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте и переведите текст «Карьера в области электроники». Выучите новую лексику. Выполните лексические упражнения. Повторите правила образования Времен Действительного залога. Выполните грам. упражнения.
Read and translate the text.
Text
Career in electronics
Hi, there! Here is Ann Sokolova again. I am afraid this will be my last meeting with you because I need to pack my suitcase. I am leaving for Sochi tonight. I have passed all the exams successfully and I'm free till the 1st of September.
As I have already told you, I was always good in mathematics and physics. My parents bought me a computer when I was in the 10th form. Since then I knew that I would become a specialist in computer technologies — a computer engineer.
Computer industry is developing so fast, that it comprises almost all spheres of professional life. No business now is possible without computers. This is especially true about automated manufacturing of products and robotics. Computer control of automated production opens new horizons for the cheap and quality production of goods. Information is now generated, transmitted, received, and stored electronically through computer networks on a scale unprecedented in history, and there is every indication that the explosive rate of growth in this field will continue.
Computer engineering is a general field. It deals with both electric and electronic industries.
Electronic engineering deals with the research, design, integration, and application of circuits and devices used in the transmission and processing of information.
Engineers in the field of electric and electronic engineering are concerned with all aspects of electrical communications, from fundamental questions such as «What is information?» to the highly practical, such as the design of telephone systems. In designing communication systems, engineers rely on various branches of advanced mathematics, such as Fourier analysis, linear systems theory, linear algebra, differential equations, and probability theory.
Engineers work on control systems which are used extensively in automated manufacturing and in robotics.
Major developments in the field of communications and control have been the replacement of analogue systems with digital systems; fibre optics are used now instead of copper cables. Digital systems offer far greater immunity to electrical noise. Fibre optics are likewise immune to interference; they also have great carrying capacity, and are extremely light and inexpensive to manufacture.
Computer engineering is now the most rapidly growing field. The electronics of computers is the design and manufacture of memory systems, of central processing units, and of peripheral devices. The most prospective industry now is the Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) and new computer architectures. The field of computer science is closely related to computer engineering; however, the task of making computers more «intelligent» (artificial intelligence), through creation of sophisticated programs or development of higher level machine languages or other means, is generally regarded as the dream of computer science.
One current trend in computer engineering is microminiaturization. Engineers continue to work to fit greater and greater numbers of circuit elements onto smaller and smaller chips.
Another trend is towards increasing the speed of computer operations through the use of parallel processors and superconducting materials.
So, as you see, there are a lot of employment opportunities in my field. I don't worry about finding a job. The most important thing for me now is to study well and to graduate from the Academy.
Exercise 1. Learn
Vocabulary
to comprise — включать в себя
automated manufacturing of products — автоматизированное производство товаров
robotics — робототехника
horizons — горизонты
cheap — дешевый
to generate — генерировать, производить
to transmit — передавать
to store — хранитьъ
scale — масштаб
unprecedented in history — не имеющий прецедентов в истории
indication — указание, свидетельство
explosive — взрывной
to deal with — иметь дело с, заниматься чем-либо
integration — интеграция
application — приложение, использование
circuits — электрические схемы, цепи
device — устройство
transmission — передача
processing — обработка
to rely — полагаться
Fourier analysis — анализ Фурье
linear systems theory — теория линейных систем
linear algebra — линейная алгебра
differential equations — дифференциальные уравнения
probability theory — теория вероятности
extensively — широко
replacement — замещение
fibre optics — оптоволоконные технологии
copper — медь
digital — цифровой
immunity — защищенность, невосприимчивость
carrying capacity — пропускная способность
light — легкий
rapidly growing — быстрорастущий
artificial intelligence — искусственный разум
sophisticated — сложный
superconducting — сверхпроводимость
Exercise 3. How do you see your future profession? Please answer the following questions:
1) What kind of work are you interested in?
a) well paid
b) interesting
c) in a large and famous company
d) quiet
e) in an industry which has a future
f) prestigious
g) not to sit the whole day in the office
h) to travel a lot
2) What position would you like to have?
a) to manage people — manager
b) to work for someone else — an employee
c) to be your own boss — self-employed, businessman
d) to be responsible for everything — top manager, director
e) to work for the state — state employee
Exercise 4. Please discuss with your group advantages and disadvantages of your future profession. Do you think that engineering profession is prestigious? Is it well-paid?
How difficult is it to find a good work in this field?
Exercise 5. Найдите и исправьте ошибки.
1. When I came, he was having breakfast. 2. When she worked there, she often made mistakes. 3. When he was phoning, she had a bath, 4. While I was ironing, he read a newspaper, 5.1 cooked supper when I heard this news. 6. He was working in this company in 1997. 7.I could not answer your call, I worked in the garden then. 8. They wished to stay because they enjoyed themselves.9. Were you quarreling all evening? 10. The train was approaching the city when it was raining heavily, 11. The secretary still typed when the boss came in and was putting some documents on the table. 12. When he came up to the square, he saw a lot of people: they sang, danced and shouted. They were celebrating New Year, 13. Just as I was coming into the room, the students discussed the first report. 14, All the time I was writing, he was annoying me with silly questions. 15, The children played while the mother put the room in order.
Раздел 2. Электричество
Тема 2.1 Электрическая цепь
Тема: Работа с текстом "Арифметические действия. Числительные.»
Закон Ома. Решение задач.
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Краткие теоретические положения:
Сегодня ситуация в мире такова, что людям любых профессий рано или поздно приходится иметь дело с английским языком. Для профессионального общения, для сдачи экзаменов при получении работы и многого другого. В данном разделе рассмотрим общую для многих специальностей науку — математику.
Начнем с самых простых действий, встречающихся в любой формуле:
· прибавить — plus/add
· отнять — minus/subtract
· умножить — multiply (умножить на 2 — multiply by two)
· разделить — divide (делить на 2 — divide by two)
· равно — is equal to
· больше — is greater than
· меньше — is smaller than
· пропорционально — is proportional to
Дробные числа. На письме целая и дробная части разделяются точкой, которая по английски называется point. Например, 4.62 — four point sixty two. Если же нужно назвать часть целого числа (например, 2/5 — две пятых), то в этом случае вспоминаем порядковые числительные и говорим two fifth.
Квадратный корень — √ — на английском называется square root или просто root. Корень из 25 будет звучать как square root of 25.
Степень. Два в квадрате — two squared, два в кубе — two cube. Два в любой другой степени, допустим, в степени х — two to the power x. Если же соединить корень и степени в одной формуле и написать, например, корень n-ой степени из x, то получим N-th root of x.
Логарифм и интеграл звучат как logarithm (log) и integral соответственно.
Антилогарифм — antilogarithm или antilog. Функция — function. Сумма — ∑
— sum/sumation. Разность — Δ — delta/difference.
Например,
· логарифм от b — log b — logarithm of b.
· функция от х — f (x) — function of x
· интеграл f от x поdх - ʃf(x)dx — integral of the f of x over dx
Верхний предел логарифма — upper limit, нижний предел — lower limit.
Тригонометрические функции:синус — sine, косинус — cosine, тангенс — tangent, котангенс — cotangent, арксинус — arc/inverse sine, гиперболический синус — hyperbolic sine.
С этими функциями тоже употребляется предлог of, если после них вы употребляете какое-либо число. Например, косину сх — cos x — cosine of x, арксинус х — arcsin x- inverse sine of x.
Математические действия (Numbers for Maths)
· Сложение (Addition)
1 + 2 = 3
One and two is seven. One plus two equals eight.
· Вычитание (Subtraction):
7 – 6 = 1
Seven minus six is one. Seven subtract six equals fourteen.
· Multiplication (Умножение):
5 x 6 = 30
Five times six equals twenty-one.Five multiplied by six is twelve.
· Division (Деление):
9 ÷ 3 = 3
Nine divided by three equals three. Three goes into nine three times.
· Другие символы и их чтение (Other symbols)
|
< |
less than |
меньше |
5<6 |
Five is less than 6 |
|
> |
greater than |
больше |
7>5 |
Seven is greater than 5 |
|
¼ |
fractions |
дробь |
¼ 1¼ |
one fourth one and one fourth |
|
% |
percent |
процент |
2% 2.5% |
two per cent two per cent point five |
|
° |
degrees |
градусы |
90° |
ninety degrees |
|
1.666 |
decimals |
десятичная дробь |
1.666 0.25 |
one point six six six nought point two five |
Задание: Прочитайте и переведите текст «Арифметические действия. Числительные», «Закон Ома. Решение задач». Выполните упражнения на арифметические действия.
Задание 1: выполните упражнения.
Упражнение № 1. Запишите примеры по-английски.
|
11 x 2 |
6 X 8 |
7 X 6 |
4 X 9 |
|
6 X 4 |
7 X 7 |
81 : 9 |
12 x3 |
Упражнение № 2. Дайте письменный вариант следующих числительных:
a) 30 ; 13 ; 200 ; 21st; 13th ; 3.67 ; 2/3 ;
b) 5/8 ; 1/4; 2 3/7 ; 1/3 tons ; 2 1/2pounds
; 1/2km
Упражнение 3. Запишите даты по образцу :
16.6.99. – June the sixteenth nineteen ninety-nine .
3.5.72. ; 12.7.89. ; 5.4.91. ; 17.11.97. ; 1.2.80. ; 5.12.00. ; 7.4.01. .
Задание 2: Read and translate the text.
Text 1
GEORGE SYMON OHM
GEORGE SYMON OHM (1784–1854) is a famous German physicist. In 1805 he entered the Erlangen University. Though he did not graduate from this University, he managed to write and defend a thesis in 1811. Later, he was a teacher at the gymnasiums of Gottstadt and Wamburg. Beginning from 1833 he became professor at the Polytechnical School in Nürenberg, and since 1849 – at the München University.
He is most famous for establishment of the general law of the electric circuit, stating the relation between resistance, electromotive force, and strength of the current in the electric circuit. The law was discovered experimentally and first formulated in 1826. Further investigations made use of this law. The unit of resistance was named after Ohm at the International Congress of Electricians in 1881.
Text 2
Ohm's Law
One of Ohm's major contributions was the establishment of a definite relationship between voltage, resistance and current in a closed circuit. A circuit consists of a voltage source and a complete path for current. Ohm stated this relationship as follows:
Current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance.
As a formula, it appeals like this:
Voltage (in volts)
Current (in amperes)= _______________
Resistance (in ohms)
This formula is commonly known as Ohm's Law.
About 1817 Ohm discovered that a simple correlation exists between resistance, current and voltage. That is: the current that flows in the circuit is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance. A current is measured in amperes, a voltage, or potential difference is measured in volts. A resistance is measured in ohms.
Exercise 1. Complete the puzzle. Write these numbers in words.
|
1 10 11 12 2 20 3 13 90 4 40 5 50 16 7 8 |
|
F |
|
|
|
S |
|
|
T |
|
|
N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F |
|
Y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T |
|
E |
|
T |
Y |
|
E |
|
Y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T |
|
|
R |
|
|
|
N |
|
|
|
Exercise 2. Match the sums with the numbers.
|
1) 45: 5 2) 9∙6 3) 29-12 4) 73+12 |
a) eighty-five b) fifty-four c) nine d) seventeen |
1 __ 2 __ 3 __ 4 __
Exercise 3. Read out these problems. Solve them:
Example: (a) 98.4 · 5= 492 492:12= 41
(a) Multiply 98.4 by 5 and divide the answer by 12. ________________________________
(b) Add 33.5 to 26.35 and subtract 45.8 from the answer._____________________________
(c) Divide 40.5 by 5, and multiply the answer by 8. _________________________________
(d) Add 235.08 to 51.73, and subtract the answer from 326.2. _________________________
(e) Subtract 54.93 from 85.01. Add 2.27. Subtract the answer from 61.9. ________________
Exercise4.
Task: Resistance equals 80 ohm, voltage equals 55 volt.
How much is the current in the circuit?
Exercise 5. Translate
· This is a series circuit.
· It includes a voltage source and two resistors.
· The elements are connected in series.
· The value of current is the same in all the elements of this circuit, while the value of voltage is different.
Тема: Работа с текстом "Электрическая цепь"
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Изучите и запишите новые слова и выражения. Прочитайте и переведите текст «Электрическая цепь». Выполните упражнения.
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
|
circuit |
[ˈsəːkɪt] |
цепь, контур |
|
conductor |
[kənˈdʌktə] |
проводник |
|
function |
[ˈfʌŋkʃn] |
назначение |
|
difference |
[ˈdɪfrəns] |
разница |
|
open |
|
обрыв |
|
short |
|
короткое замыкание |
|
trouble |
[ˈtrʌbl] |
повреждение |
|
no |
[nou] |
никакой, нисколько |
|
to reduce |
[rɪˈdjuːs] |
сокращать |
|
to supply |
[səˈplaɪ] |
снабжать |
|
to connect |
[kəˈnekt] |
связывать |
|
to compare (with) |
[kəmˈpɛə] |
сравнивать (с) |
|
to pass through |
[ˈpɑːs ˈθruː] |
проходить через |
|
to result in |
|
приводить к, иметь результатом |
|
to result from |
|
следовать, проистекать из |
2. Translate into Russian:
1. An open and a short are troubles in a circuit.
2. A trouble in a circuit results in no current in it.
3. What does an open in a circuit result in?
4. What does a short in a circuit result in?
5. What does a trouble in a circuit result from?
![]() Electric Circuit
Electric Circuit
This is a circuit. Its elements are a voltage source, a resistor and a conductor. The circuit consists of a voltage source, a resistor and a conductor. A voltage source supplies current. A resistor reduces current. A conductor connects the elements of the circuit.
![]() Compare
circuit a with circuit b. What is the difference between them? Current
passes through circuit a while no current passes through circuit b.
Circuit b has an open. No current through circuit b results from
an open. An open and a short are troubles in a circuit. A trouble in a circuit
may result in no current in it.
Compare
circuit a with circuit b. What is the difference between them? Current
passes through circuit a while no current passes through circuit b.
Circuit b has an open. No current through circuit b results from
an open. An open and a short are troubles in a circuit. A trouble in a circuit
may result in no current in it.
3. Complete these sentences, using the correct variant:
|
1. Circuit a consists of |
a) resistors and conductors. b) a voltage source and resistors. c) a voltage source, a resistor and a conductor.
|
|
2. A voltage source |
a) conducts current. b) reduces current. c) supplies current.
|
|
3. A conductor |
a) connects the elements. b) supplies voltage. c) conducts current.
|
|
4. A resistor |
a) connects the elements. b) supplies current. c) reduces current. |
|
5. No current results from |
a) an open. b) a short. |
4. Answer the following questions:
1. What elements does a circuit consist of?
2. What is the function of a voltage source?
3. What is the function of a conductor?
4. What is the function of a resistor?
5. When is there no current in a circuit?
6. What does an open or a short result in?
7. What does no current in a circuit result from?
5. Solve these problems:
1. How much is the current in the circuit if a 60-volt source is connected to a resistance of 1,600 ohms?
2. How much is the voltage in a circuit having a current equal to 25 amp, if a 25-ohm resistance is connected to it?
3. A 70.35-ohm resistance is connected to the circuit. How much is the voltage if the current equals 4.5 amp?
6. Pair work. Ask your groupmate to compare circuits a and b (see Fig. 1).
1. What do they have in common?
2. Which of the circuits has a trouble?
3. What does the trouble result from?
4. What does it result in?
Тема: Работа с текстом «Параллельная и последовательная цепь»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Изучите и запишите новые слова и выражения. Прочитайте и переведите текст "Параллельная и последовательная цепь". Выполните упражнения.
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
|
branch |
[brɑːntʃ] |
отвод |
|
line |
|
линия |
|
value |
[ˈvæljuː] |
величина |
|
voltage drop |
|
падение напряжения |
|
series |
[ˈsɪəriːz] |
последовательное |
|
parallel |
[ˈpærələl] |
параллельное |
|
main |
[meɪn] |
главный, основной |
|
to use |
[juːz] |
использовать |
|
in order (to) |
|
для того чтобы |
Series Circuit and Parallel Circuit
Compare circuits a and b. Circuit a consists of a voltage source and two resistors. The resistors are connected in series. Circuit a is a series circuit.
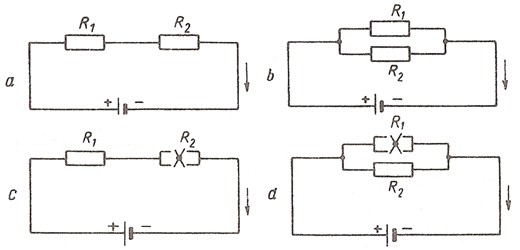
Fig. 2
Circuit b consists of a voltage source and two resistors. The resistors are connected in parallel. Circuit b is a parallel circuit.
A parallel circuit has the main line and parallel branches.
In circuit b the value of voltage in R1 equals the value of voltage in R2. The value of voltage is the same in all the elements of a parallel circuit while the value of current is different. A parallel circuit is used in order to have the same value of voltage.
In circuit a the value of current in R1 equals the value of current in R2. The value of current is the same in all the elements of a series circuit while the value of voltage is different. A series circuit is used in order to have the same value of current. In R1, V1 = I × R1 is the voltage drop in R1. In R2 the voltage equals I × R2; I × R2 is the voltage drop in R2. In circuit c a trouble in one element results in no current in the whole circuit. In circuit d a trouble in one branch results in no current in that branch only, a trouble in the main line results in no current in the whole circuit.
2. Complete these sentences using the correct variant:
|
1. A parallel circuit has |
a) parallel branches only. b) the main line and parallel branches. |
|
2. A parallel circuit is used in order
|
a) to have the same value of current in all the elements. b) to have the same value of voltage in all the elements. |
|
3. In a parallel circuit a trouble in one branch |
a) results in no current in that branch only. b) results in no trouble in the whole circuit. |
|
4. No current in a parallel circuit |
a) results from a trouble in one branch. b) results from a trouble in the main line. |
|
5. The sum of IR voltage drops |
a) equals the value of voltage in the circuit. b) is less than the smallest voltage drop. c) is more than the value of voltage in the circuit. |
3. Complete the sentences using while. Follow the model:
Model: Resistors connected in series have the same value of current ... .
Resistors connected in series have the same value of current while resistors connected in parallel have the same value of voltage.
1. Resistors connected in series have different values of voltage while ... .
2. A trouble in one element of a series circuit results in no current in the whole circuit while ... .
3. In order to have the same value of current in all the elements, a series circuit is used while ... .
4. No current in a parallel circuit results from a trouble in the main line while ... .
4. Answer the following questions:
1. What type of circuit has the main line and parallel branches?
2. What type of circuit is used in order to have the same value of current in all the elements?
3. What type of circuit is used in order to have the same value of voltage in all the elements?
4. What does a trouble in the main line result in?
5. What does a trouble in a branch result in?
6. What does no current in a series circuit result from?
7. How much does the sum of IR voltage drops equal?
8. What is the difference between series and parallel circuits?
5. Pair work. Ask your groupmate to draw and describe a series-parallel circuit.
Тема: Работа с текстом «Резистор»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Изучите и запишите новые слова и выражения. Прочитайте и переведите текст "Резистор". Выполните лексические упражнения.
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
|
capacity |
[kəˈpæsɪtɪ] |
емкость |
|
power |
[ˈpauə] |
мощность |
|
heat |
|
теплота, нагрев |
|
rate |
|
скорость, степень |
|
to produce |
[prəˈdjuːs] |
производить |
|
to change |
[tʃeɪndʒ] |
менять(ся) |
|
to vary |
[ˈvɛərɪ] |
варьировать(ся) |
|
low |
[lou] |
низкий |
|
high |
[haɪ] |
высокий |
|
fixed |
[fɪkst] |
постоянный |
|
any |
|
(зд.) любой |
|
variable |
[ˈvɛərɪəbl] |
переменный |
|
the (more) … the (more) |
|
чем (больше) ... тем (больше) |
2. Read the words and put down their Russian equivalents:
|
[ˈtemprətʃə] |
temperature |
___________________________ |
|
[ˈenədʒi] |
energy |
___________________________ |
|
[wɔt] |
watt |
___________________________ |
|
[ˈkɔnstənt] |
constant |
___________________________ |
|
[pouˈtenʃəl] |
potential |
___________________________ |
3. Translate into Russian using чем ... тем.
1. The more one studies nature, the better one knows its laws.
2. The longer one learns, the more one knows.
3. The higher the atmosphere, the less is its pressure.
4. The heavier the object, the more work one has to do in order to lift it.
5. The greater the number of free electrons in any metal, the higher is its conductivity.
2. Translate into Russian. Mind no.
1. There is no energy in this machine.
2. No charges move through an open circuit.
3. No material is a perfect conductor of electricity.
4. No electric machinery is used without protection.
5. No special material is needed in this case.
Resistors
A resistor is one of the most common elements of any circuit. Resistors are used:
1. to reduce the value of current in the circuit;
2. to produce IR voltage drop and in this way to change the value of the voltage.
When current is passing through a resistor its temperature rises high. The higher the value of current the higher is the temperature of a resistor. Each resistor has a maximum temperature to which it may be heated without a trouble. If the temperature rises higher the resistor gets open and opens the circuit.
Resistors are rated in watts. The watt is the
rate at which electric energy is supplied when a current of one ampere is
passing at a potential difference of one volt. A resistor is rated as a 1-W
resistor if its resistance equals 1,000,000 ohms and its current-carrying
capacity equals 1/1,000,000 amp, since
P = E × I = IR × I = I2R where P - power is given in watts, R - resistance is given in ohms and I - current is given in amperes.
If a resistor has a resistance of only 2 ohms but its current-carrying capacity equals 2,000 amp, it is rated as a 8,000,000-W resistor.
Some resistors have a constant value - these are fixed resistors, the value of other resistors may be varied - these are variable resistors.
5. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
|
1. A resistor is used
|
a) to measure the resistance. b) to reduce the current. c) to change the resistance. d) to produce IR voltage drop. |
|
2. When current passes through a resistor |
a) its temperature drops. b) its temperature rises.
|
|
3. Resistors are rated |
a) in ohms. b) in volts. c) in watts. |
|
4. Power is given |
a) in amperes. b) in watts. |
|
5. Fixed resistors have
|
a) a constant value. b) a variable value. |
|
6. The value of a variable resistor |
a) is fixed. b) is varied. |
|
7. A two-ohm resistor rated as a 8,000,000-W resistor
|
a) has a current-carrying capacity equal to 2,000 amp. b) has a current-carrying capacity equal to 200 amp. |
|
8. The higher the value of current,
|
a) the lower is the temperature of a resistor. b) the higher is the temperature of a resistor. |
6. Complete the sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
1. The value of a fixed resistor is constant … .
2. Current-carrying capacity is given in amperes … .
3. The lower the value of current, the lower is the temperature of a resistor … .
4. An electric source produces energy … .
7. Pair work. Put these questions to your groupmate and let him/her answer them.
1. What is a resistor used for?
2. When does the temperature of a resistor rise?
3. What element is used to change the value of voltage?
4. How are resistors rated?
5. What types of resistors do you know?
6. When does a resistor get open?
7. What does an open resistor result in?
8. What is the difference between a fixed resistor and a variable resistor?
9. How much is the current-carrying capacity of a two-ohm resistor?
10. What resistors have a variable value?
8. Solve the problem:
What is the maximum current for a resistor having a 5-watt capacity and a resistance of 20,000 ohms?
Тема: Работа с текстом «Электрические батареи»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Изучите и запишите новые слова и выражения. Прочитайте и переведите текст «Электрические батареи». Выполните упражнения.
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
|
cell |
[sel] |
элемент |
|
output |
[ˈautput] |
емкость, мощность |
|
bulb |
[bʌlb] |
электрическая лампа |
|
to light |
[laɪt] |
зажигать, освещать |
|
to increase |
[ɪnˈkriːs] |
увеличивать(ся), возрастать |
|
to substitute |
|
заменять |
|
... and so on |
|
и так далее |
2. Read the words and put down their Russian equivalents:
|
[ɪˈlektroud] |
electrode |
___________________________ |
|
[ɪˈlektrəlaɪt] |
electrolyte |
___________________________ |
|
[stɑːt] |
start |
___________________________ |
|
[ˈɔpəreɪt] |
to operate |
___________________________ |
|
[ˈaɪsəleɪt] |
to isolate |
___________________________ |
3. Translate into Russian and put down the Russian equivalents. Then translate the Russian equivalents back into English (orally).
|
a. current capacity |
______________________________ |
|
resistor temperature |
______________________________ |
|
voltage output |
______________________________ |
|
current value |
______________________________ |
|
b. to start supplying energy |
______________________________ |
|
to stop operating |
______________________________ |
|
to start lightening |
______________________________ |
|
to stop lightening the bulbs |
______________________________ |
|
|
|
|
c. to operate well |
______________________________ |
|
to operate badly |
______________________________ |
|
to increase the voltage output |
______________________________ |
|
to substitute the resistor |
______________________________ |
4. Read and translate into Russian. Mind one:
1. The element has a trouble. It operates badly. It should be substituted by a new one.
2. The element with a trouble was substituted with a new one and the cell started operating.
![]()
![]() Electric Cells
Electric Cells
An electric cell is used to produce and supply electric energy. It consists of an electrolyte and two electrodes. Electrodes are used as terminals, they connect the cell to the circuit - current passes through the terminals and the bulb lights.
Cells can be connected in series, in parallel and in series-parallel. In order to increase the current capacity cells should be connected in parallel. In order to increase the voltage output cells should be connected in series. In case a battery has a large current capacity and a large voltage output, its cells are connected in series-parallel.
When cells are connected in series the positive terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the second cell, the positive terminal of the second cell - to the negative terminal of the third ... and so on.
When cells are connected in parallel their negative terminals are connected together and their positive terminals are also connected.
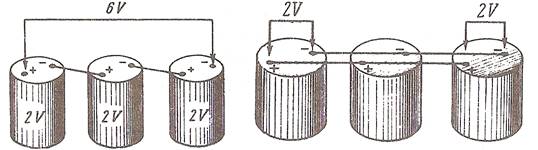
Fig. 6 Fig. 7
In case a cell has a trouble it stops operating or operates badly. This cell should be substituted by another one.
5. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
|
1. A cell is used
|
a) to increase the voltage output. b) to reduce the current capacity. c) to supply electric energy. |
|
2. The terminals of a cell are used |
a) to conduct current. b) to increase voltage. c) to connect the battery to a circuit. |
|
3. When cells are connected in series
|
a) all the positive terminals are connected together. b) all the negative terminals are connected together. c) the positive terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the second. |
|
4. Cells are connected in series in order |
a) to increase the current capacity. b) to increase the voltage output. |
|
5. In order to increase the current capacity |
a) cells are connected in series, b) cells are connected in parallel. |
6. Answer the following questions:
1. What is a cell used for?
2. What does a cell consist of?
3. What is the function of the terminals?
4. In what way are cells connected in order to increase the voltage output?
5. In what way are cells connected in order to increase the current capacity?
6. In what way are the terminals of series cells connected?
7. In what case does a cell stop operating?
8. What should be done in case it stops operating?
7. Solve these problems:
1. Suppose that you have four electric cells. The current capacity of each cell equals l.5 amp, the voltage output equals 2 V.
a) Connect the cells in series. In what way should it be done?
b) Connect the battery to a circuit whose resistance value equals 15 ohms. What is the value of current in the circuit?
2. Suppose that you have three cells of the same value.
a) Connect them in parallel. In what way should it be done?
b) Connect the second battery to the same circuit: what will it result in?
Suppose that one of the cells stops operating. What should be done in this case?
Тема: Работа с текстом «Конденсатор»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Изучите и запишите новые слова и выражения. Прочитайте и переведите текст "Конденсатор". Выполните упражнения.
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
|
capacitor |
[kəˈpæsɪtə] |
конденсатор |
|
insulator |
[ˈɪnsjuleɪtə] |
изолятор |
|
frequency |
[ˈfriːkwənsi] |
частота |
|
distance |
[ˈdɪstəns] |
расстояние |
|
advantage |
[ədˈvɑːntɪdʒ] |
преимущество |
|
disadvantage |
|
недостаток |
|
plate |
|
анод (лампы) |
|
part |
[pɑːt] |
часть |
|
to apply |
[əˈplaɪ] |
прилагать, применять |
|
to move |
[muːv] |
двигать(ся) |
|
to prevent |
|
предотвращать |
|
reason |
|
причина |
|
for this reason |
|
по этой причине |
|
besides |
|
кроме того |
|
provided that |
|
при условии что |
2. Translate into Russian and write down the Russian equivalents. Then translate the Russian variants back into English (orally).
|
a. paper insulators |
_____________________________ |
|
air insulators |
_____________________________ |
|
electrolyte capacitors |
_____________________________ |
|
advantages of electrolyte capacitors |
_____________________________ |
|
disadvantages of air insulators |
_____________________________ |
|
|
|
|
b. cells under test |
_____________________________ |
|
capacitors in common use nowadays |
_____________________________ |
|
radio sets under test |
_____________________________ |
|
PC in common use nowadays |
_____________________________ |
|
|
|
|
c. a radioman |
_____________________________ |
|
radio work |
_____________________________ |
|
radio parts |
_____________________________ |
|
telephone and radio work |
_____________________________ |
3. Translate into Russian. Mind provided that.
1. A circuit operates well provided that it does not have any trouble.
2. The bulb lights provided that the circuit is connected to the cell.
3. A cell supplies energy provided that its electrodes are of different materials.
Capacitors
A capacitor is one of the main elements of a circuit. It is used to store electric energy. A capacitor stores electric energy provided that a voltage source is applied to it.
The main parts of a capacitor are metal plates and insulators. The function of insulators is to isolate the metal plates and in this way to prevent a short.
In the diagram one can see two common types of capacitors in use nowadays: a fixed capacitor and a variable one. The plates of a fixed capacitor cannot be moved; for this reason its capacity does not change. The plates of a variable capacitor move; its capacity changes. The greater the distance between the plates, the less is the capacity of a capacitor. Variable capacitors are commonly used by radiomen; their function is to vary the frequency in the circuit. Fixed capacitors are used in telephone and radio work.
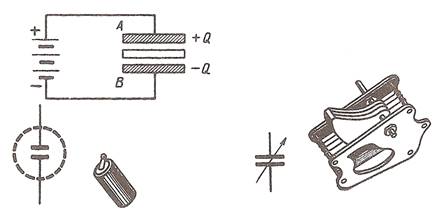
Fig. 8 Fig. 9
Fixed capacitors have insulators produced of paper, ceramics and other materials; variable capacitors have air insulators. Paper capacitors are commonly used in radio and electronics; their advantage is their high capacity: it may be higher than 1,000 picofarad.
Besides, electrolyte capacitors are highly in use. They also have a very high capacity: it varies from 0.5 to 2,000 microfarad. Their disadvantage is that they change their capacity when the temperature changes. They can operate without a change only at temperatures not lower than -40° C.
Common troubles in capacitors are an open and a short. A capacitor stops operating and does not store energy in case it has a trouble. A capacitor with a trouble should be substituted by a new one.
4. Complete these sentences using the correct variant:
|
1. A capacitor is used
|
a) to supply voltage. b) to increase the voltage output. c) to store energy. |
|
2. The main parts of a capacitor are
|
a) insulators only. b) metal plates only. c) metal plates and insulators between them. |
|
3. The function of insulators is
|
a) to store energy. b) to isolate the metal plates. c) to prevent a short between the metal plates. |
|
4. The capacity of a capacitor depends on
|
a) the size of the plates. b) the distance between the plates. c) the material of the insulators. |
|
5. The capacity of a fixed capacitor
|
a) is constant. b) is varied.
|
|
6. The plates of a variable capacitor
|
a) can be moved. b) cannot be moved. |
|
7. In order to charge a capacitor a voltage source is applied |
a) to the metal plates. b) to the insulators. |
|
8. The greater the distance between the plates, |
a) the greater is the capacity of a capacitor. b) the less is the capacity. |
|
10. Electrolyte capacitors have
|
a) a very low capacity. b) a very high capacity. |
|
11. In case a capacitor has a trouble
|
a) it operates. b) it stops operating. |
5. Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13:
1. The plates of a fixed capacitor cannot be moved to vary the capacity ... .
2. The capacity of a variable capacitor is varied … .
3. Electrolyte capacitors change their capacity when the temperature changes … .
4. The less the distance between the plates, the greater is the capacity … .
5. When a capacitor has no trouble it stores energy … .
6. Pair work. Put these questions to your groupmate and ask him/her to answer them.
1. What is a capacitor used for?
2. What are the main parts of a capacitor?
3. What is the function of insulators?
4. What does the capacity of a capacitor depend on?
5. What is the difference between a fixed capacitor and a variable one?
6. What should be done in order to change a capacitor?
7. What is the relation between the value of capacity and the distance of plates?
8. What type of insulators have variable capacitors?
9. What should be done in case a capacitor has a trouble?
7. Solve these problems:
Draw a diagram of a circuit consisting of two resistors and two capacitors connected in parallel. A battery of four cells is applied to the circuit. Two ammeters are used: one is connected to the main line, the other - to a parallel branch. What is the function of each element? In what way can one increase the value of resistance in the circuit?
Suppose one of the branches stops operating. What does it result from?
Тема: Работа с текстом «Проводники и изоляторы»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Изучите и запишите новые слова и выражения. Прочитайте и переведите текст «Проводники и изоляторы». Выполните упражнения.
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
|
cheap |
|
дешевый |
|
ˈcopper |
|
медь |
|
decrease |
[ˈdɪkriːs] |
уменьшение |
|
load |
|
нагрузка |
|
make smb (smth) do smth |
|
заставить кого-л. (что-л.) делать что-л. |
|
thus |
|
таким образом, так |
|
difficulty |
|
трудность |
|
ˈrubber |
|
резина |
|
since |
|
так как |
|
to decrease |
[dɪˈkriːs] |
уменьшать |
|
increase |
[ˈɪnkriːs] |
увеличение |
2. Read the words and put down their Russian equivalents:
|
[ˈdaɪəɡræm] |
diagram |
___________________________ |
|
[ˌkouɪˈfɪʃənt] |
coefficient |
___________________________ |
|
[ˈfʌŋkʃən] |
function |
___________________________ |
|
[trænsˈfɔːmə] |
transformer |
___________________________ |
|
[trænsˈfəː] |
to transfer |
___________________________ |
3. Form adverbs. Follow the model.
Model: wide - widely
|
cheap - |
_____________________ |
positive - |
____________________ |
|
high - |
_____________________ |
negative - |
____________________ |
4. Put down the Russian for:
|
load resistance |
______________________________________ |
|
wire conductors |
______________________________________ |
|
silver wire conductors |
______________________________________ |
|
temperature ˈdecrease |
______________________________________ |
|
temperature ˈincrease |
______________________________________ |
5. Translate into Russian. Mind since.
1. Copper conductors are widely used since they are much cheaper than silver ones.
2. A minimum voltage drop is produced in copper wire conductors since they have a low resistance.
3. A bulb connected to an open circuit does not light since an open circuit has no current.
Conductors and Insulators
Conductors are materials having a low resistance so that current easily passes through them. The lower the resistance of the material, the more current can pass through it.
The most common conductors are metals. Silver and copper are the best of them. The advantage of copper is that it is much cheaper than silver. Thus copper is widely used to produce wire conductors. One of the common functions of wire conductors is to connect a voltage source to a load resistance. Since copper wire conductors have a very low resistance a minimum voltage drop is produced in them. Thus, all of the applied voltage can produce current in the load resistance.
It should be taken into consideration that most materials change the value of resistance when their temperature changes.
Metals increase their resistance when the temperature increases while carbon decreases its resistance when the temperature increases. Thus metals have a positive temperature coefficient of resistance while carbon has a negative temperature coefficient. The smaller is the temperature coefficient or the less the change of resistance with the change of temperature, the more perfect is the resistance material.
Materials having a very high resistance are called insulators. Current passes through insulators with great difficulty.
The most common insulators are air, paper, rubber, plastics.
Any insulator can conduct current when a high enough voltage is applied to it. Currents of great value must be applied to insulators in order to make them conduct. The higher the resistance of an insulator, the greater the applied voltage must be.
When an insulator is connected to a voltage source, it stores electric charge and a potential is produced on the insulator. Thus, insulators have the two main functions:
1. to isolate conducting wires and thus to prevent a short between them and
2. to store electric charge when a voltage source is applied.
6. Find answers to these questions in the text above:
1. What materials are called conductors?
2. What is the advantage of copper compared with silver?
3. What is the most common function of wire conductors?
4. Why is a minimum voltage drop produced in copper conductors?
5. What is the relation between the value of resistance and the temperature in carbon?
6. What materials are called insulators?
7. What are the most common insulators?
8. What are the two main functions of insulators?
7. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
|
1. Insulators are materials having
|
a) low resistance. b) high resistance. |
|
2. Current passes through conductors |
a) easily. b) with great difficulty. |
|
3. Copper and silver are |
a) common conductors. b) common insulators. |
|
4. Air, paper and plastics are
|
a) common insulators. b) common conductors. |
|
5. In case a high voltage is applied to an insulator |
a) it does not conduct current. b) it conducts current. |
|
6. Insulators are used |
a) to store electric charge. b) to reduce voltage. c) to prevent a short between conducting wires. |
|
7. Metals increase their resistance |
a) when the temperature decreases. b) when the temperature increases. |
|
8. Carbon decreases its resistance
|
a) when the temperature increases. b) when the temperature decreases. |
|
9. Metals have |
a) a positive temperature coefficient of resistance. b) a negative temperature coefficient of resistance. |
8. Complete the sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
1. Conductors have a low resistance … .
2. Current passes through insulators with great difficulty … .
3. Metals are common conductors … .
4. To make insulators conduct, currents of great value must be applied … .
3. Carbon decreases its resistance when the temperature increases … .
6. Metals have a positive temperature coefficient of resistance … .
9. Pair work. Put these questions to your groupmate, and ask him/her to answer them:
1. What is the difference between conductors and insulators?
2. How does current pass through insulators?
3. What materials are commonly used to produce insulators?
4. What materials are commonly used to produce conductors?
5. In what case do insulators conduct current?
6. How does resistance change when the temperature decreases?
Тема: Работа с текстом «Трансформатор»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Изучите и запишите новые слова и выражения. Прочитайте и переведите текст «Трансформатор». Выполните упражнения.
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
|
core |
|
сердечник |
|
winding |
[ˈwaɪndɪŋ] |
обмотка |
|
turn |
|
виток |
|
to step up |
|
повышать |
|
to step down |
|
понижать |
|
frequency |
[ˈfriːkwənsɪ] |
частота |
|
due to |
[ˈdjuː tə] |
благодаря, из-за |
2. Put down the Russian for:
|
iron core |
_____________ |
primary winding |
_____________ |
|
closed core |
_____________ |
secondary winding |
_____________ |
|
input voltage |
_____________ |
step-up transformer |
_____________ |
|
output voltage |
_____________ |
step-down transformer |
_____________ |
Transformers
A transformer is used to transfer energy. Due to the transformer electric power may be transferred at a high voltage and reduced at the point where it must be used to any value. Besides, a transformer is used to change the voltage and current value in a circuit.
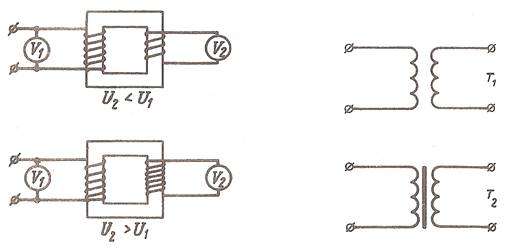
Fig. 10 Fig. 11
A two-winding transformer consists of a closed core and two coils (windings). The primary winding is connected to the voltage source. It receives energy. The secondary winding is connected to the load resistance and supplies energy to the load.
The value of voltage across the secondary terminal depends on the number of turns in it. In case it is equal to the number of turns in the primary winding the voltage in the secondary winding is the same as in the primary.
In case the secondary has more turns than the primary the output voltage is greater than the input voltage. The voltage in the secondary is greater than the voltage in the primary by as many times as the number of turns in the secondary is greater than the number of turns in the primary. A transformer of this type increases or steps up the voltage and is called a step-up transformer. In case the secondary has fewer turns than the primary the output voltage is lower than the input. Such a transformer decreases or steps down the voltage, it is called a step-down transformer.
Compare T1 and T2 in the diagram. T1 has an iron core. For this reason it is used for low-frequency currents. T2 has an air core and is used for high frequencies.
Common troubles in transformers are an open in the winding, a short between the primary and the secondary, and a short between turns. In case a transformer has a trouble it stops operating or operates badly. A transformer with a trouble should be substituted.
3. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
|
1. A transformer is used
|
a) to store charge. b) to prevent the change of energy. c) to transfer energy. d) to change the voltage and current value in a circuit. |
|
2. Electric power is transferred at a high voltage and reduced to any value
|
a) due to resistors. b) due to capacitors. c) due to transformers. |
|
3. A transformer consists of
|
a) cores only. b) the primary and the secondary windings. c) a core and the primary and the secondary windings. |
|
4. The function of the primary is
|
a) to prevent the change of voltage. b) to supply energy. c) to receive energy. |
|
5. The function of the secondary is
|
a) to receive energy. b) to supply energy. c) to transfer energy. d) to decrease the value of charge. |
|
7. A step-down transformer is used
|
a) to step down the secondary voltage. b) to step down the primary voltage. |
|
8. A transformer with an iron core
|
a) is used for high-frequency currents. b) is used for low-frequency currents. |
|
9. A transformer with an air core is used
|
a) for high-frequency currents and for low-frequency currents. b) for high-frequency currents only. |
|
10. In a step-up transformer
|
a) the number of turns of the secondary winding is greater than the number of turns of the primary. b) the number of turns of the primary winding is greater than the number of turns of the secondary. |
|
11. A transformer should be substituted
|
a) in case it has an open in the winding. b) in case it has a short between the primary and the secondary. c) in case it has a short between turns. |
4. Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
1. The secondary winding of a transformer is connected to the load resistance … .
2. The primary winding receives energy … .
3. A step-down transformer decreases the primary voltage … .
4. An air core transformer is used for high-frequency currents … .
5. In a step-up transformer the number of turns of the secondary winding … .
is greater than the number of turns of the primary winding … .
5. Pair work. Put these questions to your groupmate and ask him/her to answer them.
1. What is a transformer used for?
2. What does a transformer consist of?
3. What is the function of the primary winding?
4. What is the function of the secondary winding?
5. What type of transformer is called a step-up transformer?
6. What type of transformer is used for high-frequency currents?
7. What type of transformer is called a step-down transformer?
8. What type of transformer is used for low-frequency currents?
9. What is the relation between the number of turns in the windings and the value of current?
10. What are common troubles in a transformer?
11. What should be done in case a transformer has a trouble?
6. Read about current transformers. Answer the questions that follow.
Current Transformers
Current transformers are used for operating ammeters, wattmeters, and other measuring devices. They produce in the meters a current lower than the measured current but proportional to it.
Current transformers also insulate the instrument from the circuit which is being measured. This is necessary for high voltage circuits.
1. What is a current transformer used for?
2. What type of current does it produce?
Тема: Работа с текстом "Типы тока"
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Изучите и запишите новые слова и выражения. Прочитайте и переведите текст «Типы тока». Выполните упражнения.
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
|
alternating |
[ˌɔːltəˈneɪtɪŋ] |
переменный |
|
diˈrect |
|
прямой |
|
diˈrection |
|
направление |
|
flow |
[flou] |
течение |
|
necessary |
[ˈnesɪsərɪ] |
необходимый |
|
to con'sider |
|
рассматривать |
|
use |
[juːs] |
использование |
2. Read the words and write down their Russian equivalents:
|
[ˈsaɪkl] |
cycle |
___________________________ |
|
[taɪp] |
type |
___________________________ |
|
[pə ˈsekənd] |
per second |
___________________________ |
3. Put down the Russian for:
|
one time |
____________ |
direct voltage source |
____________ |
|
five times |
____________ |
alternating voltage source |
____________ |
|
sixty times |
____________ |
direction of flow |
____________ |
Types of Current
Current is a flow of electricity through a circuit. Let us consider two main types of current: direct and alternating. A direct current (d.c.) flows through a conducting circuit in one direction only. It flows provided a direct voltage source is applied to the circuit.
An alternating current (a.c.) is a current that changes its direction of flow through a circuit. It flows provided an alternating voltage source is applied to the circuit. Alternating current flows in cycles. The number of cycles per second is called the frequency of the current. In a 60-cycle alternating current circuit the current flows in one direction 60 times and in the other direction 60 times per second.
It is easy to transform a.c. power from one voltage to another by a transformer. Transformers are also used to step down the voltage at the receiving point of the line to the low values that are necessary for use.
When necessary a.c. can be changed into d.c. but this is seldom necessary.
4. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
|
1. D.c. is a current that
|
a) changes its direction of flow. b) flows in one direction. |
|
2. A.c. flows provided
|
a) a direct voltage source is applied. b) an alternating voltage source is applied. |
|
3. In an alternating current circuit |
a) current flows in one direction 60 times per second. b) current flows in one direction 60 times and in the other direction 60 times per second. |
|
4. A.c. |
a) can be changed into d.c. b) cannot be changed into d.c. |
5. Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
1. An alternating current changes its direction of flow … .
2. A direct current flows provided a direct voltage source is applied … .
6. Answer the following questions:
1. What is current?
2. What types of current do you know?
3. When does a direct current flow?
4. What type of current is called an alternating current?
5. What type of current is called a direct current?
6. What is called the frequency of current?
7. What device is used to transform a.c. power from one voltage to another?
8. Is it often necessary to change a.c. into d.c.?
7. Read about frequency, answer the question that follows.
Frequency
The number of cycles per second is the frequency of an alternating current. There are two frequencies: the standard for Europe is 50 cycles per second while the standard for the USA is 60 cycles per second. A standard frequency has a great advantage since different systems can be interconnected.
What is the advantage of a standard frequency?
Тема: Работа с текстом «Индуктивность»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Изучите и запишите новые слова. Прочитайте и переведите текст «Индуктивность». Выполните упражнения.
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
|
inˈductance |
|
индуктивность |
|
coil |
[kɔɪl] |
катушка |
|
size |
[saɪz] |
размер |
|
unit |
[ˈjuːnɪt] |
единица |
|
fast |
[fɑːst] |
быстрый |
|
mutual |
[ˈmjuːtʃuəl] |
взаимный |
|
to induce |
[ɪnˈdjuːs] |
индуктировать |
|
to provide |
[prəˈvaɪd] |
обеспечить |
|
to touch |
[tʌtʃ] |
касаться |
|
to bring |
|
приносить, подносить |
|
that is |
|
то есть |
|
definite |
[ˈdefɪnɪt] |
определенный |
2. Translate into Russian and put down the Russian equivalents. Then translate them back into English (orally).
|
a. definite value |
______________________________________ |
|
primary coil |
______________________________________ |
|
wire coil |
______________________________________ |
|
mutual inductance |
______________________________________ |
|
varying current |
______________________________________ |
|
one ampere per second |
______________________________________ |
|
b. 1. Coils of wire are called inductors. |
|
|
____________________________________________________________ |
|
|
2. Two coils are brought close together. |
|
|
____________________________________________________________ |
|
|
3. A source of current is applied to one of the coils. |
|
|
____________________________________________________________ |
|
|
4. Mutual inductance is measured in henries. |
|
|
____________________________________________________________ |
|
3. Which of the words are nouns and which are verbs?
resistor, resist, resistance; induce, induction, inductor, inductance;
conductor, conduct, conductance; compute, computer
Inductance and Mutual Inductance
Any conductor has some definite value of inductance. The inductance of a conductor shows how well it can provide induced voltage.
![]()
![]() Elements of a circuit with a definite
value of inductance are coils of wire called inductors. The inductance
of a coil depends upon its size and material. The greater the number of turns
of a coil, the higher is its inductance. An iron core also increases the value
of inductance. Coils of this type are used for low-frequency currents while coils
with an air core are used for high-frequency currents.
Elements of a circuit with a definite
value of inductance are coils of wire called inductors. The inductance
of a coil depends upon its size and material. The greater the number of turns
of a coil, the higher is its inductance. An iron core also increases the value
of inductance. Coils of this type are used for low-frequency currents while coils
with an air core are used for high-frequency currents.
Two coils A and В are brought close together and a source of varying current is applied to coil A. If a measuring device is connected across the terminals of coil В it will be found that a voltage is induced in this coil though the two coils do not touch. The secondary voltage, that is the voltage in coil B, is called induced voltage and energy from one coil to the other transfers by induction. The coil across which the current is applied is called the primary; that in which voltage is induced is called the secondary. The primary and the secondary coils have mutual inductance. Mutual inductance is measured in the same units as inductance, that is in henries.
Thus, when a rate of change of one ampere per second in the primary coil will produce one volt in the secondary coil, the two coils have one henry of mutual inductance.
It should be taken into consideration that induction by a varying current results from the change in current not in the current value. The faster the current changes, the higher the induced voltage.
4. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
|
1. Any conductor has |
a) some definite value of resistance. b) some definite value of inductance. |
|
2. Any conductor can provide |
a) electric power. b) induced voltage |
|
3. Elements with a definite value of inductance |
a) are called inductors. b) are called coils. c) are called sources. |
|
4. The inductance of a coil depends upon |
a) its size. b) its core. c) its material. d) its number of turns. |
|
5. An iron core |
a) increases the value of inductance. b) decreases the value of inductance. |
|
6. The value of mutual inductance is measured |
a) in watts. b) in henries. |
|
7. Induction by a varying current |
a) results from the change in current. b) results from the change in the current value. |
|
8. The faster the current changes, |
a) the lower is the induced voltage. b) the higher is the induced voltage. |
5. Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
1. An air core decreases the value of inductance … .
2. An iron core is used for low-frequency currents … .
3. The coil in which voltage is induced is called the secondary … .
6. Answer the following questions:
1. What value of inductance do conductors have?
2. What is the function of inductors?
3. What are elements with a definite value of inductance called?
4. What does the inductance of a coil depend upon?
5. How does the inductance of a coil depend upon the material of its core?
6. In what units is the value of mutual inductance measured?
7. What does induction by a varying current result from?
8. What is the relation between the current changes and the value of induced voltage?
9. What is the unit of resistance?
10. What is the unit of potential difference?
11. For what type of current is an air core used?
12. What is the relation between the number of turns of a coil and its inductance value?
7. Pair work. Tell your groupmate about mutual inductance. Let him/her put the questions of Exercise 6 to you and answer them.
Тема: Работа с текстом «Фильтры»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Изучите и запишите новые слова и выражения. Прочитайте и переведите текст «Фильтры». Выполните упражнения.
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
|
filter |
[ˈfɪltə] |
фильтр |
|
bypass |
[ˈbaɪpɑːs] |
шунт |
|
choke |
[tʃouk] |
дроссель |
|
high-pass |
[ˈhaɪpɑːs] |
высокопроходной |
|
low-pass |
[louˈpɑːs] |
низкопроходной |
|
to oppose |
[əˈpouz] |
оказывать сопротивление |
|
on the other hand |
|
с другой стороны |
|
choke coil |
|
дроссельная катушка |
|
bypass coil |
|
шунтовая катушка |
|
bypass condenser |
|
шунтирующий конденсатор |
|
high-pass filter |
|
фильтр верхних частот |
|
low-pass filter |
|
фильтр низких частот |
|
opposing coils |
|
противодействующие витки |
|
opposed current |
|
противоток |
![]() Filters
Filters
![]() This filter is used
to separate direct current from alternating current. It consists of a capacitor
and a choke coil. Direct current cannot flow through the capacitor since its
insulators oppose the flow of direct current. Therefore, it flows through the
choke coil. Its windings easily pass direct current through them. Alternating
current, on the other hand, passes through the capacitor, since it cannot
easily pass through the choke coil. In this way the direct and the alternating
currents are separated.
This filter is used
to separate direct current from alternating current. It consists of a capacitor
and a choke coil. Direct current cannot flow through the capacitor since its
insulators oppose the flow of direct current. Therefore, it flows through the
choke coil. Its windings easily pass direct current through them. Alternating
current, on the other hand, passes through the capacitor, since it cannot
easily pass through the choke coil. In this way the direct and the alternating
currents are separated.
I. A high-pass filter is used to pass high frequencies and to prevent the flow of low frequencies. It consists of a condenser and an inductance coil. The condenser passes currents of high frequencies and opposes the flow of low frequency currents. Low frequencies must be returned to the source and the inductance coil is used for a bypass.
II. A low-pass filter is used to pass low frequencies and to prevent the flow of high frequencies. It consists of an inductance coil and a condenser. The inductance coil passes low frequencies and opposes the flow of high frequencies. To return the high frequencies back to the source, a condenser is used for a bypass. Its capacity opposes the flow of low frequencies through it.
2. Complete the sentences using the correct variant
|
1. A filter is used in order |
a) to separate d.c. from a.c. b) to transfer energy from the primary to the secondary. c) to separate low frequencies from high frequencies. |
|
2. A filter consists of
|
a) a resistor and a transformer. b) a choke coil and a capacitor. c) an inductance coil and a capacitor. |
|
3. Direct current easily passes
|
a) through a choke coil. b) through a capacitor. |
|
4. Alternating current easily passes
|
a) through a capacitor. b) through a choke coil. |
|
5. A low-pass filter is used
|
a) to pass high frequencies and to prevent the flow of low frequencies. b) to pass low frequencies and to prevent the flow of high frequencies. |
|
6. In a low-pass filter
|
a) a capacitor is used as a bypass. b) an inductance coil is used as a bypass. |
|
7. In a high-pass filter
|
a) an inductance coil is used as a bypass. b) a capacitor is used as a bypass.
|
3. Complete these sentences using on the other hand. Follow the model.
Model: Direct current passes through the choke coil of a filter; alternating current, on the other hand, passes through the capacitor.
1. A low-pass filter is used to pass low frequencies … .
2. In a high-pass filter an inductance coil is used as a bypass … .
3. A high-pass filter is used to prevent the flow of low frequencies … .
4. Alternating current passes through a capacitor … .
4. Answer the following questions:
1. What is a filter used for?
2. What does a filter consist of?
3. What is the function of a low-pass filter?
4. What is the function of a high-pass filter?
5. What is the difference between a low-pass filter and a high-pass filter?
6. What elements are used as a bypass?
7. What is the function of a choke coil?
8. What is the function of an inductance coil?
5. Draw schemes of a choke input filter and a capacity input filter. Describe the schemes and the function of the filters.
Тема: Работа с текстом «Электронная лампа»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Изучите и запишите новые слова и выражения. Прочитайте и переведите текст «Электронная лампа» . Выполните упражнения.
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
|
tube |
[tjuːb] |
электронная лампа |
|
bulb |
[bʌlb] |
баллон |
|
grid |
|
сетка |
|
screen |
|
экран |
|
to contain |
[kənˈteɪn] |
вмещать |
|
to collect |
[kəˈlekt] |
собирать |
|
to emit |
[ɪˈmɪt] |
излучать |
|
to suppress |
[səˈpres] |
глушить, подавлять |
|
control circuit |
|
контрольная цепь |
|
control grid |
|
управляющая сетка |
|
screen grid |
|
экранирующая сетка |
|
screen grid tube |
|
экранированная лампа |
|
suppressor grid |
|
защитная сетка |
|
counter flow |
|
противоток |
|
oscillatory circuit |
|
колебательный контур |
2. Form nouns adding -er and translate them.
Model: to heat - heater
|
to emit - |
_______________________________________ |
|
to control - |
_______________________________________ |
|
to suppress - |
_______________________________________ |
3. Distribute the words below into the three columns.
|
Model: |
action |
process |
doer |
|
|
emit |
emission |
emitter |
collector, heat, collection, suppress, collect, suppressor, suppression, contain, reaction, container, react, heater, reactor, computer, compute, oscillate, oscillating, oscillator
4. Read the words and put down their Russian equivalents. Then translate them back into English.
|
diode |
[daɪəd] |
___________ |
cathode |
[ˈkæθoud] |
___________ |
|
triode |
[traɪəd] |
___________ |
metal |
[ˈmetl] |
___________ |
|
tetrode |
[tetˈroud] |
___________ |
glass |
[ɡlɑːs] |
___________ |
|
pentode |
[penˈtoud] |
___________ |
oscillator |
[ˈɔsɪleɪtə] |
___________ |
Electron Tubes
Let us consider electron tubes. Among the electron tubes in use nowadays there are a diode, a triode, a tetrode and a pentode. The main parts of electron tubes are electrodes. Electrodes are placed into a glass or metal bulb.
Fig. 14
A diode contains the cathode and the plate. When a diode operates the cathode emits electrons, the plate collects them.
A triode contains the cathode, the plate and the control grid. When the tube operates the cathode emits electrons, the plate collects them and the grid controls the flow of electrons. Therefore, the grid is called a control grid.
A tetrode contains the cathode, the plate, the control grid and the screen grid.
When a tube operates it may oscillate. The function of the screen grid is to eliminate oscillations. Therefore it is called a screen grid.
A pentode contains two electrodes and three grids: the control grid, the screen grid and the suppressor grid. When a pentode operates the suppressor grid eliminates the secondary emission.
Common troubles in tubes are an open heater and low emission. These troubles result from constant use or from some other reason. In case a tube has a trouble it stops operating or operates badly. A tube with a trouble should be replaced by another one.
5. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
|
1. A pentode contains |
a) the cathode, the plate, two screen grids and the suppressor grid. b) the cathode, the plate, the control grids, the screen grid and the suppressor grid. |
|
2. A tetrode contains |
a) the cathode, the plate, the suppressor grid and the screen grid. b) the cathode, the plate, the screen grid and the control grid. |
|
3. A triode contains |
a) the cathode, the plate and the screen grid. b) the cathode, the plate and the control grid. |
|
4. The function of the cathode is |
a) to collect electrons. b) to eliminate the secondary emission. c) to emit electrons. |
|
5. The function of the plate is |
a) to eliminate oscillations. b) to emit electrons. c) to collect electrons. |
|
6. The function of the control grid is |
a) to emit electrons. b) to control the electron flow. c) to eliminate secondary emission. |
|
7. The function of the screen grid is |
a) to collect electrons. b) to reduce the capacity. c) to eliminate oscillations. |
|
8. The function of the suppressor grid is |
a) to control the electron flow. b) to eliminate secondary emission. c) to eliminate oscillations. |
|
9. Constant use of a tube results in |
a) high emission. b) low emission. c) an open heater. |
6. Answer the following questions:
1. What types of electron tubes are used nowadays?
2. How many electrodes does a diode (a triode, a tetrode, a pentode) contain?
3. What is the function of the cathode (the plate, the control grid, the screen grid, the suppressor grid)?
4. What does the constant use of a tube result in?
5. What does low emission result from?
6. When must a tube be replaced?
7. Pair work. Think of five questions covering the article given below. Put these questions to your groupmate and ask him/her to answer them.
Pentode
When in an operating tube the screen-grid voltage is high, secondary emission does not return to the plate and passes to the screen grid. This results in a counter flow of electrons. To eliminate this counter flow, a third grid was placed between the plate and the screen grid and connected to the cathode. This grid is called a suppressor grid. Since the suppressor grid has a negative potential it returns the secondary emission back to the plate and thus eliminates it in the tube. The tube containing electrodes - the cathode, the plate, the control grid, the screen grid and the suppressor grid - is called a pentode. The cathode emits electrons, the plate collects them, the control grid controls the flow of electrons, the screen grid helps the plate to collect electrons and reduces the capacity between the control grid and the plate, the suppressor grid eliminates the secondary emission.
Раздел 3. Электроника и микроэлектроника.
Тема 3.1. Развитие электроники.
Тема: Работа с текстом "Развитие электроники"
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте и переведите текст «Развитие электроники». Выучите новую лексику. Выполните лексические упражнения.
Read and translate the text.
Development of electronics
Electronics is the science dealing with devices operated by control of the movement oа electric charges in a vacuum, in gases, or semiconductors: or with the processing of information or the control of energy by such devices. This definition covers the wholу complex family of vacuum and gaseous electron tubes and their applications. It also includes metallic contact or semiconductor rectifiers and the transistors which utilize the control of electrons or positive charges (holes) to process information or to convert energy.
Electrononics was born in the 19-th century. Like hydrolysis or chemistry it has come into its own only recently. Electronics first established itself, however, in wireless telegraphy. Industrial applications of electronics include
control gauging, counting, heating, speed regulation, etc. But in a larger field, electronocs leads to automatic control of large-scale industrial operations.
Today, electronics has started у new era. Electronocs devices are doing simple, but human-like thinking. Some industries are controlled by electronic robots. Automation is the industrial keynote of the day. Planes and rockets are electronically controlled. Some radiotelescopes work like radar to receive radio waves from outer space. Shortly speaking, electronics is not so much a new subject as a new way of looking at electricity.
Exercise 1. Learn
Vocabulary
charge – заряд
semiconductor – полупроводник
tube – труба, трубка
rectifier – ректификатор, выпрямитель тока
utilize – использовать
hole – отверстие, шпур
convert – переводить, превращать
has come into its own – заняла подобающее место
keynote – основа
Exercise 2. Answer the questions
1. What is electronics?
2. When was electronics born?
3. Where did electronics first establish itself?
4. What does electronics lead to in a larger field?
5. What thinking is electronics doing?
6. In what branches of science and technology is electronics used?
Exercise 3. Tranlate into English
1.Электроника заключает в себе производство и обработку пучков электронов. 2.Электрические сигналы производятся приборами, которые превращают первоначальный источник информации в слабые электрические токи. 3.Существуют два вида электрического сигнала: аналоговый и цифровой. 4.В современной электронике электрические сигналы могут обрабатываться двумя основными способами – посредством происхождения их через полупроводниковые приборы или посредством превращения их в пучок электронов. 5.Полупроводники обладают промежуточным сопротивлением потому, что у них есть некоторое количество свободных электронов, которые могут превращаться от атома к атому – в отличие от проводников, у которых есть много свободных электронов, и в отличие от изоляторов, у которых их нет.
Exercise 4. Make а plan of the text and retell the text looking in your plan.
Тема: Работа с текстом «Электроника»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте текст «Электроника». Выполните лексико-грамматические упражнения.
Electronics
I. Find out the words in the dictionary. Write them down and learn.
|
processing, to convey, device, to manipulate, to reduce, to amplify, to vary, to be subjected, intermediate, lattice, to free, boron, excess, junction |
II. Read the text. Use a dictionary, if necessary.
Text: “Electronics”
Electronics is a general term for the production and processing of electric signals (consisting of moving electrons, hence the name electronics) that convey information – for example, the sound reproduction by a radio or record player and the data output of a computer. Electronics also includes the production and processing of beams of electrons, used in such devices as cathode-ray oscilloscopes, television sets, and electron microscopes.
Electric signals. Electric signals are produced by devices that convert the primary information source (which is in the form of another type of energy – sound or light, for instance) into small electric currents. For example, a microphone converts sound into an electric current, and in input unit of a computer converts data. These currents, which constitute a signal, are then transmitted along wires or, after conversion to radio waves, via radio links. On reaching a suitable receiver, they may be electronically manipulated – to reduce distortion in the signal, for instance – and are than amplified so that they can drive an output device, such as a loudspeaker, television set, or computer printer.
There are two types of electric signal: analog and digital. Analog signals vary continuously in voltage or current, corresponding to variations in the primary information source; thus the electric signals produced by a microphone are electrical “copies” of the original sound waves. Digital signals are not continuous but consist of numerous bursts of electric current between two voltage levels (one of which may be zero).
A computer uses digital signals. They consist of binary codes that represent the numbers, letters, and symbols in the input data and in the various program instructions. In the computer’s central processor, the data codes are subjected to processes of binary arithmetic or are compared with each other to obtain the results required by the program.
In modern electronics, electric signals may be processed in two main ways – by passing them trough semiconductor devices (such as transistors) or by converting them into a beam of electrons, as in the formation of a picture by a television set (which also uses semiconductors).
Semiconductors. Semiconductors are substances (such as silicon and germanium) whose electrical resistance lies between that of conductors and insulators. They have this intermediate resistance because they have a few free electrons that can drift from atom to atom – unlike conductors, which have many free electrons, and unlike insulators, which have none.
The semiconductors used in electronic devices are “doped” to change their electrical properties. Doping involves introducing minute traces of other elements into the semiconductor’s crystal lattice. Silicon and germanium each have four outer electrons per atom; doping them with an element with five outer electrons, such as phosphorus, frees the fifth electron so that the semiconductor has an electron excess. It is then known as an n-type (negative-type), because electrons have a negative charge.
Doping with an element that has only three outer electrons, such as boron, produces a crystal lattice with spaces, known as holes, which free electrons readily fill. This type of semiconductor has a lack of free electrons, which is equivalent to an excess of positive charges, and it is therefore known as p-type.
If a piece of n-type semiconductor is joined to a piece of p-type, the resulting device is called a p/n junction diode. If the diode is then connected to a battery so that the negative terminal is joined to the n-type semiconductor and the positive terminal to the p-type, current flows through the junction.
Transistors. Transistors are arrangements of semiconductor diodes that act as amplifiers. There are two main types: junction and field-effect transistors.
III. Find the sentences that can’t be found in the text.
1. The subject of electronics should, in its broadest sense, embrace all phenomena that are associated with the electron, the fundamental unit of negative electricity.
2. Electronics also includes the production and processing of beams of electrons, used in such devices as cathode-ray oscilloscopes, television sets, and electron microscopes.
3. There are two types of electric signal: analog and digital.
4. Semiconductors are substances (such as silicon and germanium) whose electrical resistance lies between that of conductors and insulators.
5. Semiconductors are materials which lie between conductors and insulators.
6. If a piece of n-type semiconductor is joined to a piece of p-type, the resulting device is called a p/n junction diode.
7. Transistors are arrangements of semiconductor diodes that act as amplifiers.
IV. Find English equivalents in the text.
1. движущиеся электроны ______________________________________
2. электронный (катодный) осциллограф ________________________
3. например __________________________________________________
4. уменьшать искажение ______________________________________
5. цифровой __________________________________________________
6. требуемые результаты ______________________________________
7. двумя основными способами ________________________________
8. полупроводниковые приборы ________________________________
9. промежуточное сопротивление _______________________________
10. кристаллическая решетка ___________________________________
11. внешний электрон __________________________________________
12. избыток электронов _________________________________________
13. недостаток свободных электронов _____________________________
14. соединение __________________________________________________
15. усилитель ___________________________________________________
V. Find Russian equivalents to the following expression in the text.
1. the production and processing of electric signals ______________________
2. convey information _____________________________________________
3. beams of electrons ______________________________________________
4. the primary information source ____________________________________
5. small electric currents ___________________________________________
6. are transmitted along wires _______________________________________
7. via radio links _________________________________________________
8. a suitable receiver ______________________________________________
9. may be electronically manipulated __________________________________
10. numerous bursts of electric current _________________________________
11. binary codes ___________________________________________________
12. minute traces __________________________________________________
13. act as amplifiers ________________________________________________
VI. Fill in the missing words.
1. Electronics is a general term for the _____ and _____ of electric signals that convey information.
2. Electric signals are produced by devices that the primary information _____ into small electric _____.
3. Digital signals consist of _____ codes that represent the numbers, letters, and symbols in the input data and in the various program instructions.
4. In modern electronics, electric signals may be processed in two main ways: by passing them through _____ _____ or by converting them into a _____ of _____.
5. Semiconductors are substances whose electrical resistance lies between that of _____ and _____.
6. Doping involves introducing minute traces of other elements into the semiconductor’s _____ _____.
7. Transistors are arrangements of semiconductor diodes that act as _____.
VII. Fill in the preposition, if necessary.
1. Electronics also includes ___ the production and processing ___ beams ___ electrons.
2. Analog signals vary continuously ___ voltage or current, corresponding ___ variations ___ the primary information source.
3. Digital signals are not continuous but consist ___ numerous bursts ___ electric current between two voltage levels.
4. ___ the computer’s central processor, the data codes are subjected ___ process ___ binary arithmetic or are compared ___ each other to obtain the results required ___ the program.
5. If the diode is then connected ___ a battery so that the negative terminal is joined ___ the n-type semiconductor and the positive terminal ___ the p-type, current flows ___ the junction.
VIII. Define whether the sentences are true or false.
1. Electric signals are produced by devices that convert the primary information source into small electric currents.
2. Digital signals vary continuously in voltage or currant, corresponding to variations in the primary information source.
3. Analog signals are not continuous but consist of numerous bursts of electric current between two voltage levels.
4. In the computer’s central processor the data codes are subjected to process of binary arithmetic or are compared with each other to obtain the results required by the program.
5. Semiconductors are substances whose electrical resistance lies between that of conductors and insulators.
6. Doping with an element that has only three outer electrons produces a crystal lattice without any spaces.
IX. Practice with someone asking and answering.
1. What is electronics?
2. What are electric signals produced by?
3. How many types of electric signal are there?
4. What signals does a computer use?
5. What do digital signals consist of?
6. In what ways may electric signals be processed in modern electronics?
7. What is semiconductor?
8. What does doping involved?
9. What is a transistor?
10. How many types of transistors do you know?
X. Put questions to the following sentences.
1. Electronics includes the production and processing of beams of electrons. (General)
2. Electric signals are produced by devices that convert the primary information source into small electric currents. (Disjunctive)
3. There are two types of electric signal. (Alternative)
4. The electrical resistance of semiconductors lies between that of conductors and insulators. (Special)
5. The semiconductors used in electronic devises are “doped” to change their electrical properties. (What …?)
6. Doping with an element that has only three outer electrons produces a crystal lattice with spaces, known as holes. (Disjunctive)
Тема 3.2. Техническое чтение.
Тема: Работа с текстом «Элементы питания»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте и переведите текст «Элементы питания». Выучите новую лексику. Выполните лексические упражнения.
Read and translate the text.
Batteries
Batteries as continuous sources of electrical energy are the result of a longseries of experiments which started with the discoveries of Alessandro Volta more than one hundred years ago. Today battery cells are manufactured in two common forms, dry cells being used in flash lights, portable radios, etc., wet cells being used in automobiles, airplanes, boats, etc.
We know each cell of every battery to have two terminals: one negative, the other positive. The difference of potential between the terminals of every dry cell, regardless of size, is approximately 1.5 volts, whereas the difference of potential between the terminals of a lead storage cell is approximately 2 volts. The larger the cell, the greater the amount of energy stored within in. The available energy in dry cells becoming exhausted, they are thrown away and new ones are secured, but when storage batteries become exhausted, they are recharged.
The difference of potential between the terminals of any dry or wet cell depends in principle upon the particular chemicals used in its construction, whereas the total charge capacity depends upon the quantity of chemicals present.
The negative terminal of a dry cell is the zinc metal container in which all chemical ingredients are sealed, whereas the positive terminal is a round carbon rod, the end of which protrudes through the surface at one end. The positive electrode of a storage cell is known to be set of lead grills filled with porous lead dioxide and fastened together with a single terminal. The negative electrode consists of a set of parallel grills filled with spongy lead. When these two sets of plates are put together with glass or wood separators and the entire ensemble immersed in dilute sulphuric acid, chemical activity between the lead and acid gives rise to electric charges.
Exercise 1. Learn
Vocabulary
dry cell – сухой элемент
flash light – импульсное освещение
wet cell – элемент с жидким электролитом
terminal – клемма, полюс
whereas – тогда как
lead storage cell – свинцовый элемент
storage battery – аккумуляторная батарея
protrude – выступать
grill – решетка
spongy lead – губчатый свинец
plate – пластина
sulphuric acid – серная кислота
dilute – разбавленный, разведенный
Exercise 2 . Answer the questions
1.What are the two common forms battery cells are manufactured?
2. What could these battery cells be used for?
3. How the difference of potential between the terminals of any dry or wet cell is explained?
4. What is the main distinction of dry and wet cells?
Exercise 3. Find equivalents in English in the text:
Alessandro Volta
discovery
difference
regardless
approximately
exhausted
particular
chemicals
charge capacity
zinc carbon
negative electrode
protrude
ensemble
Exercise 4. Iпsert the missing words.
To provide, to refer, strong, to invent, to be, to run, to transfer, to charge,to use, liquid, to coat.
1. The first battery … in 1800 by Alessandro Volta.
2. Near the end of the 19th century, the invention of dry cell batteries, which replaced … electrolyte with a paste, made portable electrical devices practical.
3. In the modern sense of the term, a battery is a device that … a current by means of an electrochemical reaction, wherein electrons … from one chemical to another.
4. However, the original usage of the term not to an electrochemical cell but to a set of linked Leyden jars, which, in the 18th century were used by scientists as a means of storing charge.
5. Leyden jars … the first capacitors, and basically consisted of a glass jar whose inner and outer surfaces with metal foil, and had an … electrode through its center.
6. They could … with a static generator, and … by touching a conductor to its electrode.
7. Scientists could obtain … discharges by linking the electrodes of multiple jars together.
8. It was Benjamin Franklin who, in 1748, first … the word "battery" to describe a similar assembly of glass plates with lead sheets pasted on either surface.
Exercise 5. Make а plan of the text and retell the text looking in your plan.
Раздел 4. Автоматизация технологических процессов. Тема 4.1. Автоматизация производства.
Тема: Работа с текстом "Автоматизированные системы управления"
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте и переведите текст «Автоматизированные системы управления». Выучите новую лексику. Выполните лексические упражнения.
Read and translate the text.
Automation
Automation is the system of manufacture performing certain tasks, previously done by people, by machines only. The sequences of operations are controlled automatically. The most familiar example of a highly automated system is an assembly plant for automobiles or other complex products.
The term automation is also used to describe non-manufacturing systems in which automatic devices can operate independently of human control. Such devices as automatic pilots, automatic telephone equipment and automated control systems are used to perform various operations much faster and better than could be done by people.
Automated manufacturing had several steps in its development. Mechanization was the first step necessary in the development of automation. The simplification of work made it possible to design and build machines that resembled the motions of the worker. These specialized machines were motorized and they had better production efficiency.
Industrial robots, originally designed only to perform simple tasks in environments dangerous to human workers, are now widely used to transfer, manipulate, and position both light and heavy workpieces performing all the functions of a transfer machine.
In the 1920s the automobile industry for the first time used an integrated system of production. This method of production was adopted by most car manufacturers and became known as Detroit automation.
The feedback principle is used in all automatic-control mechanisms when machines have ability to correct themselves. The feedback principle has been used for centuries. An outstanding early example is the flyball governor, invented in 1788 by James Watt to control the speed of the steam engine. The common household thermostat is another example of a feedback device.
Using feedback devices, machines can start, stop, speed up, slow down, count, inspect, test, compare, and measure. These operations are commonly applied to a wide variety of production operations.
Computers have greatly facilitated the use of feedback in manufacturing processes. Computers gave rise to the development of numerically controlled machines. The motions of these machines are controlled by punched paper or magnetic tapes. In numerically controlled machining centres machine tools can perform several different machining operations.
More recently, the introduction of microprocessors and computers have made possible the development of computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacture (CAD and CAM) technologies. When using these systems a designer draws a part and indicates its dimensions with the help of a mouse, light pen, or other input device. After the drawing has been completed the computer automatically gives the instructions that direct a machining centre to machine the part.
Another development using automation are the flexible manufacturing systems (FMS). A computer in FMS can be used to monitor and control the operation of the whole factory.
Automation has also had an influence on the areas of the economy other than manufacturing. Small computers are used in systems called word processors, which are rapidly becoming a standard part of the modern office. They are used to edit texts, to type letters and so on.
Exercise 1. Learn
Vocabulary
automation — автоматизация
previously — ранее
sequence — последовательность
assembly plant — сборочный завод
non-manufacturing — непроизводственный
device — устройство, прибор
resemble — походить
efficiency — эффективность
flyball governor — центробежный регулятор
steam engine — паровоз
household thermostat — бытовой термостат
facilitate — способствовать
punched — перфорированный
aid — помощь
dimension — измерение, размеры
Exercise 2. Answer the questions
1. How is the term automation defined in the text?
2. What is the most «familiar example» of automation given in the text?
3. What was the first step in the development of automaton?
4. What were the first robots originally designed for?
5. What was the first industry to adopt the new integrated system of production?
6. What is feedback principle?
7. What do the abbreviations CAM and CAD stand for?
8. What is FMS?
9. What industries use automation technologies?
Exercise 3. Find the following words and word combinations in the text:
1. автоматические устройства
2. автоматизированное производство
3. выполнять простые задачи
4. как легкие, так и тяжелые детали
5. интегрированная система производства
6. принцип обратной связи
7. механизм может разгоняться и тормозить
8. компьютер автоматически посылает команды
9. высокоавтоматизированная система
10. непроизводственная система
Exercise 4. Find equivalents in English in the text:
1. сфера применения
2. фиксированная последовательность операций
3. автоматические сборочные машины
4. определенные химические процессы
5. programmable automation
6. computer terminal
7. numerical-control machine-tool
Тема: Работа с текстом "Применение средств автоматизации в различных отраслях промышленности»
Цель: совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте и переведите текст «Modern technologies in industry and production».
Выполните задания к тексту.
Modern technologies in industry and production
We live in the era of high technologies, and we use modern inventions in our everyday life because they have brought us much comfort. New technologies have spread on every field over the past 15 years. Moreover, they are rapidly changing. For example, video-recorders, DVD-players or compact disks have already become obsolete and have been replaced by more up-to-date devices. Today we can hardly imagine our life without such modern mobile devices as cell phones or laptops. Our offices are fully equipped with computers, printers, scanners, air-conditioners, interactive whiteboards and wi-fi modems. Household appliances (vacuum-cleaners, coffee-machines, dish-washers, food processors and others) help us to save our time and energy.
However, we should realize that digital and electronic inventions have both negative and positive impact on our daily life.
I am absolutely positive that new technologies or gadgets are making things faster, easier, more comfortable and interesting. For instance, if you install a GPS (Global Positioning System) in your car you’ll never get lost again. And could we imagine just 15 years ago all the things we can do on the wireless Internet nowadays: connecting with friends from all over the world, online shopping and banking, distance online learning, finding virtual relationships and even working from home? Isn’t that awesome?! Our parents used to go to post-offices to send letters or pay bills, they went to libraries to find a good book and they used telephone-booths for phone-calls.
On the other hand, I know some people who are strongly against some modern inventions because they really miss those days when they talked to each other face to face in reality, and not virtually. I partially agree with that as I really believe that people are becoming anti-social and too dependent on their gadgets. Some of my friends also spend half of the time occupying their shiny gadgets (smart-phones or i-pads) even when we go out together. Besides, people who use various social networks a lot (such as Facebook or Instagram) should worry more about their privacy.
Summing up, I could say that there are serious arguments both for and against the use of new technologies but anyway it’s really difficult to imagine our life without them today.
Complete the sentences:
Intelligent Connected Systems
Connect systems, people and data to streamline multiple disciplines, drive innovation and generate more business.
Machines designed to think.
Industrial Equipment companies need increased functionality and information from their machines so they can respond quickly and accurately to market demands. Digital connectivity is empowering manufacturers with greater data and market knowledge with machines that are not only connected, but communicate with each other.
![]()
An intelligent connected environment is one where manufacturers can streamline the process of using multiple disciplines and focus on making better use of machine data. It increases the capacity to create and deliver innovative products because all internal and external resources have real-time access to the same unique information.
Intelligent Connected Systems connect people and technologies in a way that exponentially expands innovative capacity to create cutting-edge products that may not have been imagined yet. Real-time access to the same unique data provides tighter collaboration between groups supporting the same customers.
The 3DEXPERIENCE® platform is a single integrated environment that enables manufacturers to streamline the process of multiple disciplines by linking machine design, engineering, manufacturing and maintenance data. Providing a comprehensive view of product and process information for all of these disciplines inherently connects them together.
Вставьте пропущенные слова в предложения: collaboration / process / resources / capacity:
Тема 4.2. Техническое чтение
Тема: Системы автоматизации производства и проектирования: САМ и CAD. Причастия.
Цель: совершенствование навыков перевода, работы со словарем; совершенствование лексико-грамматических навыков.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте текст и выполните задания после него.
COMPUTER SCIENCE IN ENGINEERING
1. Computer science is a part of an applied mathematics. Specialists in computer science say that this field of knowledge is very interesting because it deals with computer-aided-design (CAD) and computer-aided-manufacturing (CAM).
2. Computers are intended to improve the productivity of labour of scientists, designers, engineers, managers, and other specialists, because computers offer quick and optimal solutions. One of the main goals of using CAD/CAM is to shorten the time between designing and manufacturing.
• Computer aided design (CAD) is the process of creating a design, known as drafting, using computer technology. Computer aided manufacturing (CAM) is the use of computers and computer software to guide machines to manufacture something, usually a part that is mass-produced. The relation between CAD and CAM is one of form to function and they are often used together.
• CAD creates the design and CAM builds it. CAM is usually dependent on CAD. The use of CAD created designs offers an easy way of inputting information into a CAM software system. CAM and CAD are both referred to as part of an overall process known collectively as computer aided engineering (CAE). They can render things in either two dimensions (2D) or three dimensions (3D).
• Many CAM machines have CAD software built-in, although not all designs require the use of a CAD created design. A CAD user will typically be an engineer with training in CAD software, whereas a CAM user will usually be a specially trained machinist. These types of machinists are highly skilled.
• Переведите на русский язык в письменной форме абзацы 2, 3, и 5.
• Заполните пропуски в предложениях.
• The use of CAD created … offers an easy way of … information into a CAM software system.
• CAM is the use of computers and computer software to … machines to manufacture something, usually a … that is mass-produced.
• A lot of CAM ... have CAD software ..., although not all designs ... the use of a CAD created design
• Computers are … to improve the productivity of labour of scientists, designers, engineers, managers, and other specialists, because computers … quick and
optimal ….
• Посмотрите на таблицу и выполните упражнения ниже.
Active Passive
Participle I drilling being drilled
Participle II - drilled
Perfect Participle having drilled having been drilled
The man sitting at the table is our teacher. — Человек, сидящий за столом — наш учитель.
The houses being built in our town are not very high. — Дома, строящиеся в нашем городе, невысоки.
Going home I met an old friend. — Идя домой, я встретил старого друга.
Having finished work I went home. — Закончив работу, я пошел домой.
The book translated from English is interesting. — Книга, переведенная с английского языка, интересная.
Given the task he began to work. — Когда ему дали задание он начал работать.
Having solved the problem correctly they changed the answer.- Решив пример правильно, они поменяли ответ.
• Переведите словосочетания с причастиями.
Participle I: Computers using superconducting material; the machine calculating mathematical problems; students coding the information.
Participle II: The given information; the name given to the machine; the coded data; the device used in World War II; the engine designed by engineers; dictation written the day before was corrected.
Тема: Страдательный залог
Цель: совершенствование грамматических навыков.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Пояснения к работе
Краткие теоретические сведения
Сегодня мы изучим правила образования пассивного залога в английском языке, а также на примерах разберемся в каких случаях он используется.
Далеко не всегда мы можем уточнить, кто выполняет действие, а порой нам это и вовсе не нужно. В таких случаях уместно употреблять пассивный или страдательный залог, который в английском языке называют passive voice. Давайте разберем, что такое passive voice и правила его образования, а затем рассмотрим случаи его употребления.
Образование passive voice
В английском языке существует два залога — активный (active voice) и пассивный или страдательный (passive voice). В активном залоге действие выполняет подлежащее. В пассивном залоге действие происходит над подлежащим.
Давайте сравним:
Mary cleans the office every morning. — Мэри убирает офис каждое утро. (активный залог)
Подлежащее (Мэри) выполняет действие (убирает).
The office is cleaned every morning. — Офис убирают каждое утро. (пассивный залог)
Неизвестно, кто выполняет действие. Подлежащее (офис) подвергается действию (его убирают).
She asked her students to come earlier. — Она попросила студентов прийти раньше. (активный залог)
The students were asked to come earlier. — Студентов попросили прийти раньше. (пассивный залог)
Страдательный залог в английском языке образуется с помощью вспомогательного глагола to be и смыслового глагола в третьей форме (Past participle). На месте подлежащего в утвердительных предложениях будет стоять человек или предмет, над которым будет производиться действие. Посмотрите на схеме ниже, как активный залог можно преобразовать в пассивный.
Рассмотрите все временные формы образования страдательного залога в сравнении с действительным залогом.
|
|
Active voice |
Passive voice |
|
Present Simple |
They repair cars. |
Cars are repaired. |
|
Present Continuous |
They are repairing cars. |
The car is being repaired. |
|
Past Simple |
They repaired the car. |
The car was repaired. |
|
Past Continuous |
They were repairing the car. |
The car was being repaired. |
|
Future Simple |
They will repair the car. |
The car will be repaired. |
|
Present Perfect |
They have repaired the car. |
The car has been repaired. |
|
Past Perfect |
They had repaired the car. |
The car had been repaired. |
|
Future Perfect |
They will have repaired the car. |
The car will have been repaired. |
Образование пассивного залога в разных временах представлено в таблице ниже.
Времена группы Perfect Continuous, а также Future Continuous в пассивном залоге не используются.
|
Время |
Когда используем |
Формула |
Пример |
|
Present Simple |
–регулярное действие –констатация факта |
is/am/are + V3 |
Thousands of dollars are spent on coffee in America every day. — Тысячи долларов тратятся на кофе в Америке каждый день. |
|
Past Simple |
–завершенное действие в прошлом |
was/were + V3 |
The radio was invented 150 years ago. — Радио изобрели 150 лет назад. |
|
Future Simple |
–действие произойдет в будущем |
will be + V3 |
The letter will be sent tomorrow. — Письмо отправят завтра. |
|
Present Continuous |
– действие происходит в момент речи, прямо сейчас |
am/is/are + being + V3 |
The car is being refueled now. — Машину заправляют сейчас.
|
|
Past Continuous |
– действие происходило в определенный момент в прошлом, акцент на продолжительности действия |
was/were + being + V3 |
The exam was being taken yesterday morning. — Экзамен сдавали вчера утром. |
|
Present Perfect |
– действие уже завершилось, акцент на результат |
has/have + been + V3 |
The flowers have already been watered. — Цветы уже полили. |
|
Past Perfect |
– действие завершилось до определенного момента или другого события в прошлом |
had + been + V3 |
The police had been called before the burglars ran away. — Полицию вызвали до того, как воры убежали.
|
|
Future Perfect |
– действие будет завершено до определенного момента в будущем |
will + have + been + V3 |
The article will have been rewritten by tomorrow morning. — Статью перепишут к завтрашнему утру. |
Для образования отрицательной формы пассивного залога необходима частица not. Ставим ее после вспомогательного глагола. Если вспомогательных глаголов несколько, ставим not после первого.
I left my camera on the bench and it was not stolen! — Я забыл камеру на лавочке, и ее не украли!
The car has not been transported yet. — Машину еще не перевезли.
Чтобы задать вопрос в пассивном залоге, необходимо поставить вспомогательный глагол на первое место.
Will the meeting be held next week? — Встречу проведут на следующей неделе?
Was the match canceled because of the weather? — Матч отменили из-за погоды?
Если есть необходимость указать, кем выполняется действие, в конце предложения ставим предлог by + того, кто выполняет действие.
The book was written by an unknown author. — Книга была написана неизвестным автором.
You will never be disappointed by your loyal employees. — Ты никогда не будешь разочарован своими верными сотрудниками.
Случаи использования passive voice
1. Когда тот, кто выполняет действие, неизвестен, неважен или очевиден. Действие важнее того, кто его совершает.
My project for English literature is ruined! Who did it? — Мой проект по английской литературе испорчен! Кто это сделал?
Your delegation will be met at the airport. You will see a card with your name. — Вашу делегацию встретят в аэропорту. Вы увидите карточку с вашим именем.
You may go to your room. Your suitcase will be taken there in a minute. — Вы можете проходить в свою комнату. Ваш чемодан принесут туда через минуту.
2.Когда описываем действие в новостях, заголовках, рекламных объявлениях.
The local shop was robbed this morning. — Местный магазин ограбили этим утром.
A big discount will be provided for the first ten customers. — Большая скидка будет предоставлена первым десяти покупателям.
3.Когда описываем общие факты, идеи, мнения.
Quentin Tarantino is known all around the world. — Квентина Тарантино знают по всему миру.
His picture was described as the best artwork of the past year. — Его картина была описана, как лучшая работа прошедшего года.
4.Когда хотим сделать высказывание более вежливым или формальным.
Have you cancelled the meeting? — Ты отменил встречу? (прямой вопрос)
Has the meeting been cancelled? — Встречу отменили? (более вежливый вопрос).
You haven’t paid for electricity since January! — Вы не платите за электричество с января!
The electricity hasn’t been paid for since January. — За электричество не платят с января.
Практическая часть
1. Употребите правильную форму глагола в пассивном залоге.
1. The roads (cover) with the snow. – Дороги покрыты снегом.
2. Chocolate (make) from cocoa. – Шоколад изготавливается из какао.
3. The Pyramids (build) in Egypt. – Пирамиды были построены в Египте.
4. This coat (buy) four years ago. – Это пальто было куплено 4 года назад.
5. The stadium (open) next month. – Стадион будет открыт в следующем месяце.
6. Your parents (invite) to a meeting. – Твои родители будут приглашены на собрание.
7. Where is your car? – It (mend) at the moment. – Где твоя машина? – В данный момент она ремонтируется.
8. The books already (pack). – Книги уже упакованы.
9. The castle can (see) from a long distance. – Замок можно увидеть издалека.
10. The guests must (meet) at noon. - Гости должны быть встречены в полдень.
2. Измените предложения по образцу:
Н-р: Shakespeare wrote “Romeo and Juliet”. (Шекспир написал «Ромео и Джульетту».) – “Romeo and Juliet” was written by Shakespeare. («Ромео и Джульетта» была написана Шекспиром)
1. Popov invented radio in Russia.
2. Every four years people elect a new president in the USA.
3. The police caught a bank robber last night.
4. Sorry, we don’t allow dogs in our safari park.
5. The postman will leave my letter by the door.
6. My mum has made a delicious cherry pie for dinner.
7. George didn’t repair my clock.
8. Wait a little, my neighbor is telling an interesting story.
9. My son can write some more articles about football.
10. You must clean your bedroom tonight.
3. Образуйте отрицательную форму предложения и переведите.
1. Ann was bitten by a homeless dog.
2. The zoo is being reconstructed at the moment.
3. The luggage must be checked at the customs.
4. Souvenirs are sold everywhere.
5. The job will be finished at 3 o’clock.
4. Дайте полные ответы на следующие вопросы.
1. Are the Olympic Games held every 10 years?
2. Is bread made from flour or potatoes?
3. Was the Eifel Tower built in Moscow?
4. Will the final exams be taken in summer or in winter?
5. When is Christmas celebrated in Europe?
Тема: Инструкции. Трудности перевода: Сложное подлежащее.
Цель: закрепление и систематизация теоретических знаний по лексической и грамматическим темам; совершенствование и развитие навыков устной и письменной речи, навыков чтения и перевода текста профессиональной направленности на английском языке.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте инструкции. Выполните задания после текста.
PENDANT KEYBOARD
The keyboard is broken up into eight sections: Function Keys, Jog Keys, Override Keys, Display Keys, Cursor Keys, Alpha Keys, Mode Keys and Number Keys. In addition there are miscellaneous keys and features located on the pendant and keyboard.
Power On- Turns the machine on.
Power Off- Turns the machine off.
Spindle Load Meter - Displays the spindle load, in percent.
Emergency Stop - This stops all axes motion, stops the spindle, turret, and turns off the coolant pump.
Jog Handle - This is used to jog all axes. It can also be used to scroll through program code or menu items while editing.
Cycle Start - Starts a program. This button is also used to start a program in Graphics mode.
Feed Hold - Will stop all axis motion. Note: Spindle will continue to turn during cutting.
Reset - Will stop the machine (axes, spindle, coolant pump, and turret are stopped). This is not a recommended method to stop the machine, as it may be difficult to continue from that point.
Power Up/Restart - When this key is pressed, the axes will return to the machine zero position and a tool change may occur. See Setting 81 in the Settings chapter for more information. This will not work for toolroom lathes, subspindle lathes, or automatic parts loader (APL).
Auto Off - Automatically positions axes to machine zero and prepares the machine for power down.
Memory Lock Key Switch - This switch prevent the operator from editing programs and from altering settings when turned to the locked position.
Work Light Switch - This switch will turn on the work light inside of the machine.
Keyboard Beeper - Located at the top of the parts tray. The volume can be adjusted by turning the cover.
• Ответьте на вопросы, используя инструкцию выше.
• How many sections does the keyboard have? What are they?
• What key turns the machine on?
• What is the function of the key «Power Off»?
• What key displays the spindle load?
• What is «Jog Handle» for?
• What button stops all axis motion?
• When will the axes return to the machine zero position?
• What key automatically positions axes to machine zero and prepares the machine for power down?
• What does the switch «Memory Lock Key Switch» prevent the operator from?
• What switch will turn on the light inside of the machine?
• How can the volume be adjusted?
Сложное подлежащее
В состав Сложного подлежащего входит имя существительное (в общем падеже) или местоимение (в именительном падеже) и инфинитив. Все предложение имеет следующую структуру:
The value is said to change. – Говорят, что это значение меняется.
Не is expected to come. - Ожидают, что он придет.
т. е. между существительным и инфинитивом стоит сказуемое предложения, выражающее мнение, суждение или предположение.
Мнение, суждение, предположение в таком предложении может быть выражено следующими глаголами:
1) в страдательном залоге:
|
This value
|
is expected is assumed is reported is considered is proved is found etc.
|
to change (to be changing) (to have changed)
|
Известно, … Предполагают, Ожидают, … Допускают,… Сообщают,… Считают, … Доказано, … Найдено, … и т. д. |
2) в действительном залоге:
|
This value
|
seems appears turns out proves is likely is unlikely is sure is certain |
to change (to be changing) (to have changed)
|
По-видимому … Оказывается… ““ “” Вероятно … Маловероятно … Безусловно … Непременно… |
Перевод английского предложения следует начинать со сказуемого предложения и переводить его неопределенно-личным предложением «Известно …», «Находят …», «Считают …» и т. д., за которым следует придаточное предложение с союзом что.
This device appears to be of some interest. - По-видимому, этот прибор представляет интерес.
It is supposed to be used in our experiment. - Предполагается, что он будет использован в нашем эксперименте.
• Переведите предложения, обращая внимание на перевод «Сложного дополнения» (См. таблицу выше).
• Light is proved to travel in straight lines.
• Popov is known to be the inventor of radio in Russia.
• Faraday is believed to be a great English physicist.
• He is believed to be a very talented person.
• Forging processes are expected to be performed at various temperatures.
• This device is sure to have changed the world.
Тема: Особенности перевода технических текстов.
Цель: совершенствование навыков чтения и понимания текстов профессиональной направленности; совершенствование перевода текстов профессиональной направленности
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте текст и выполните задания после текста.
TYPES OF AUTOMATION
Applications of Automation and Robotics in Industry
Manufacturing is one of the most important application area for automation technology. There are several types of automation in manufacturing. The examples of automated systems used in manufacturing are described below.
1. Fixed automation, sometimes called «hard automation» refers to automated machines in which the equipment configuration allows fixed sequence of processing operations. These machines are programmed by their design to make only certain processing operations. They are not easily changed over from one product style to another. This form of automation needs high initial investments and high production rates. That is why it is suitable for products that are made in large volumes. Examples of fixed automation are machining transfer lines found in the automobile industry, automatic assembly machines and certain chemical processes.
2. Programmable automation is a form of automation for producing products in large quantities, ranging from several dozen to several thousand units at a time. For each new product the production equipment must be reprogrammed and changed over. This reprogramming and changeover take a period of non-productive time.
3. Production rates in programmable automation are generally lower than in fixed automation, because the equipment is designed to facilitate product changeover rather than for product specialization. A numerical-control machine-tool is a good example of programmable automation. The program is coded in computer memory for each different product style and the machine-tool is controlled by the computer program.
4. Flexible automation is a kind of programmable automation. Programmable automation requires time to reprogram and change over the production equipment for each series of new product. This is lost production time, which is expensive. In flexible automation the number of products is limited so that the changeover of the equipment can be done very quickly and automatically. The reprogramming of the equipment in flexible automation is done at a computer terminal without using the production equipment itself. Flexible automation allows a mixture of
different products to be produced one right after another.
Vocabulary
equipment — оборудование
sequence — последовательность
initial — первоначальный, начальный
investment — инвестиция, вклад
to facilitate — способствовать
rate — скорость, темп
assembly machines — сборочные машины
quantity — количество
non-productive — непроизводительный
changeover — переход, переналадка
• Ответьте на вопросы
• What is the most important application of automation?
• What are the types of automation used in manufacturing?
• What is fixed automation?
• What are the limitations of hard automation?
• What is the best example of programmable automation?
• What are the limitations of programmable automation?
• What are the advantages of flexible automation?
• Is it possible to produce different products one after another using automation technology?
• Найдите в тексте перевод следующих словосочетаний
• сфера применения
• фиксированная последовательность операций
• автоматические сборочные машины
• определенные химические процессы
• станок с числовым программным управлением
• потерянное производственное время
• разнообразная продукция
Тема: Применение автоматизации и робототехники в промышленности
Цель: закрепление и систематизация теоретических знаний по лексической теме; совершенствование навыков чтения и понимания текстов профессиональной направленности.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте текст и выполните задания после него.
Robots in manufacturing
1. Read and translate the text.
Part I
Today most robots are used in manufacturing operations. The applications of robots can be divided into three categories:
1. material handling
2. processing operations
3. assembly and inspection.
Material-handling is the transfer of material and loading and unloading of machines. Material-transfer applications require the robot to move materials or work parts from one to another. Many of these tasks are relatively simple: robots pick up parts from one conveyor and place them on another. Other transfer operations are more complex, such as placing parts in an arrangement that can be calculated by the robot. Machine loading and unloading operations utilize a robot to load and unload parts. This requires the robot to be equipped with a grip-per that can grasp parts. Usually the gripper must be designed specifically for the particular part geometry.
In robotic processing operations, the robot manipulates a tool to perform a process on the work part. Examples of such applications include spot welding, continuous arc welding and spray painting. Spot welding of automobile bodies is one of the most common applications of industrial robots. The robot positions a spot welder against the automobile panels and frames to join them. Arc welding is a continuous process in which robot moves the welding rod along the welding seam. Spray painting is the manipulation of a spray-painting gun over the surface of the object to be coated. Other operations in this category include grinding and polishing in which a rotating spindle serves as the robot's tool.
Part II
The third application area of industrial robots is assembly and inspection. The use of robots in assembly is expected to increase because of the high cost of manual labour. But the design of the product is an important aspect of robotic assembly. Assembly methods that are satisfactory for humans are not always suitable for robots. Screws and nuts are widely used for fastening in manual assembly, but the same operations are extremely difficult for an one-armed robot.
Inspection is another area of factory operations in which the utilization of robots is growing. In a typical inspection job, the robot positions a sensor with respect to the work part and determines whether the part answers the quality specifications. In nearly all industrial robotic applications, the robot provides a substitute for human labour. There are certain characteristics of industrial jobs performed by humans that can be done by robots:
1. the operation is repetitive, involving the same basic work motions every cycle,
2. the operation is hazardous or uncomfortable for the human worker (for example: spray painting, spot welding, arc welding, and certain machine loading and unloading tasks),
3. the workpiece or tool is too heavy and difficult to handle,
4. the operation allows the robot to be used on two or three shifts.
Vocabulary:
handling — обращение
transfer — передача, перенос
location — местонахождение
pick up — брать, подбирать
arrangement — расположение
to utilize — утилизировать, находить применение
gripper — захват
to grasp — схватывать
spot welding — точечная сварка
continuous — непрерывный
arc welding — электродуговая сварка
spray painting — окраска распылением
frame — рама
spray-painting gun — распылитель краски
grinding — шлифование
polishing — полирование
spindle — шпиндель
manual — ручной
labour — труд
hazardous — опасный
shift — смена
2. Translate into English:
1. Существует несколько различных сфер использования автоматизации в производстве.
2. Для использования жесткой автоматизации необходимы большие инвестиции.
3. Жесткая автоматизация широко используется в химической промышленности.
4. Станки с числовым программным управлением — хороший пример программируемой автоматизации.
5. Гибкая автоматизация делает возможным перепрограммирование оборудования.
6. Время простоя оборудования оборачивается большими убытками.
7. Использование гибкой автоматизации делает возможным производство разнообразной продукции.
3. Answer the questions:
1. How are robots used in manufacturing?
2. What is «material handling»?
3. What does a robot need to be equipped with to do loading and unloading operations?
4. What does robot manipulate in robotic processing operation?
5. What is the most common application of robots in automobile manufacturing?
6. What operations could be done by robot in car manufacturing industry?
7. What are the main reasons to use robots in production?
8. How can robots inspect the quality of production?
9. What operations could be done by robots in hazardous or uncomfortable for the human workers conditions?
Тема: Техника безопасности
Цель: закрепление и систематизация теоретических знаний по лексической теме; совершенствование навыков чтения и понимания текстов профессиональной направленности.
Формируемые компетенции: ПК 1.2, ПК 2.1, ПК 3.2, ОК01-ОК11.
Оборудование: тетрадь, письменные принадлежности, словарь.
Содержание работы
Задание: Прочитайте текст и выполните задания после него.
SAFETY ENGINEERING
Accidents to people in industrial enterprises are called industrial traumatism (injury). They occur when workers have not acquired the requisite for skill and lack the necessary experience in handling tools and equipment. Accidents are also caused through neglect of safety rules and regulations in the factories and training workshops.
The purpose of safety engineering is to prevent accidents and to create such conditions of work in industry which will ensure maximum productivity of labour.
When taking up new duties or when first going to work at any industrial enterprise each worker is obliged to acquaint him thoroughly with, and to master the safety instructions.
Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
• How are the accidents to people in industrial enterprises called?
• When do the accidents to people occur?
• What must one do to prevent accidents?
• What is the purpose of safety engineering?
• What is a worker obliged to do when taking up new duties?
Найдите соответствия английских и русских предложений
a)
1. Wear safety boots!
2. Don’t enter!
3. Don’t use a mobile phone here.
4. Emergency exit this way!
5. Be careful. Dangerous liquid!
6. Don’t touch!
7. Wear safety goggles in the area!
8. Don’t park here!
9. Be careful! Explosive material! 10. Don’t switch on!
11. Danger of an electric shock!
12. Don’t smoke here!
13. Wear a hard hat!
14. Watch out! Danger! b)
a) Руками не трогать!
b) Парковка запрещена!
c) Осторожно! Взрывоопасные вещества.
d) Не курить!
e) Не включать!
f) Осторожно! Высокое напряжение!
g) Надеть обувь!
h) Запасной выход!
i) Осторожно! Опасно!
j) Отключить мобильные телефоны!
k) Не входить!
l) Для безопасности оденьте очки!
m) Осторожно! Опасные растворы! n) Надеть каску!
• Заполните пропуски словами, данными справа
1) These ear protectors must be carried everywhere in the 1_______ hangar.
2) These 2_______ must be lubricated every day.
3) Drivers are required to check the 3_______, lights, tyres, and water before a long car journey.
4) Apprentices must always wear 4_______ in the workshop. a) overalls
b) gears
c) brakes
d) aircrafts
Основные источники:
1. Соколова Н.И. Planet of English. Английский язык. Практикум: учебное пособие для студентов СПО/ Н.И. Соколова. - Москва: Издательский центр "Академия", 2020г.
2. Голубев А.П. Английский язык: учебник для студентов средних профессиональных учебных заведений /А.П. Голубев, Н.В. Балюк, И.Б. Смирнова. – М.: Издательский центр «Академия», 2017г.
3. Голубев А.П. Английский язык для всех специальностей: учебник / Голубев А.П., Балюк Н.В., Смирнова И.Б. — Москва: КноРус, 2020. — 385 с. — (СПО). — ISBN 978-5-406-07353-7. — URL: https://book.ru/book/933691 — Текст: электронный.
4. Карпова Т.А. English for Colleges = Английский язык для колледжей. Практикум + еПриложение: тесты: учебно-практическое пособие / Карпова Т.А., Восковская А.С., Мельничук М.В. — Москва: КноРус, 2020. — 286 с. — (СПО). — ISBN 978-5-406-07527-2. — URL: https://book.ru/book/932751 — Текст: электронный.
Дополнительные источники:
1. Агабекян И.П. Английский для инженеров: уч. пос. для технических вузов. - Ростов н/Д: Феникс, 2011 г.
2. Агабекян И.П. Английский язык: сервис и туризм. - М.: "Дашков и К", 2012 г.
3. Агабекян И.П. Английский язык: учебное пособие для студентов средних профессиональных учебных заведений. - Ростов н/Д: Феникс, 2014 г.
4. Байков В.Д. Новый немецко-русский, русско-немецкий словарь. 40000 слов и словосочетаний. - М.: Эксмо, 2011 г.
5. Карпова Т.А. Английский для колледжей. - М.: КНОРУС, 2013 г.
6. Кузьменкова Ю.Б. Английский язык: учебник и практикум для СПО. - М.: Издательство "Юрайт", 2015 г.
7. Михайлов Н.Н. Английский язык для направлений "Сервис" и "Туризм": учебник для студентов высших учебных заведений. - М.: Издательский центр "Академия", 2011 г.
8. Planet of English: учебник английского языка для студентов СПО. - М.: Издательский центр "Академия", 2015 г.
9. Радовель В.А. Английский язык для технических вузов: учебное пособие. - М.: Издательско-торговая корпорация "Дашков и К", 2010 г.
10. Real Life: учебник английского языка+рабочая тетрадь+CD. – 2013 г.
Скачано с www.znanio.ru
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.