
Специальность:08.02.01. «Строительство и эксплуатация зданий и сооружений»
Учебная дисциплина: Иностранный язык (английский)
Тип учебного занятия: Комбинированное занятие
Тема: Развитие говорения. Монологическое высказывание о балках, основанное на полученной информации
" Types of Beams in Construction”
Формируемые компетенции:
1. ОК 1. Понимать сущность и социальную значимость своей будущей профессии, проявлять к ней устойчивый интерес;
2. ОК 5. Осуществлять поиск, анализ и оценку информации, необходимой для постановки и решения профессиональных задач, профессионального и личностного развития.
3. ОК 6. Работать в коллективе и команде, обеспечивать ее сплочение, эффективно общаться с коллегами, руководством, потребителями.
Цели учебного занятия:
· Образовательная цель - закрепление и систематизация знаний профессиональной лексики по теме урока, развитие речевых умений, навыков чтения и понимания профессионально ориентированных текстов, аудирования
· Развивающая цель – развитие логического мышления, умения обобщать и систематизировать знания; развитие у студентов умения объяснять, сравнивать, делать выводы
· Воспитательная цель – формирование коммуникативной культуры, навыков социального общения через активизацию понятий, связанных с профилем специальности.
По результатам занятия студент должен знать: профессиональную лексику по теме «Типы фундаментов», порядок слов в английском распространенном предложении.
По результатам занятия студент должен уметь: систематизировать профессиональную лексику, называть части зданий и типы фундаментов, читать и понимать тексты профессиональной направленности.
Организация деятельности студентов –индивидуальная
Межпредметные связи –. «Проектирование зданий и сооружений» (архитектура, строительные конструкции)
Методы обучения:
- Репродуктивный – ответ на поставленные вопросы
- Продуктивный – группировка профессиональной лексики, составление слов и предложений по теме урока
- Частично-поисковый – самостоятельная работа студентов с учебным материалом, презентациями, поиск оптимального решения поставленной проблемы.
Технические средства обучения: электронные образовательные ресурсы, презентация по теме
1. Речевая подготовка:
Different types of beams are used in construction of building and structures. These are horizontal structural element that withstand vertical loads, shear forces and bending moments. Beams transfer loads imposed along their length to their end points to walls, columns, foundations, etc.
In this article, different types of beams used in building construction will be discussed based on their manner of support, cross-section shape (profile), length, and their material.
2. Этап тренировки.
There are different types of beams which are classified based on the following conditions
Based on Support Conditions
3. Этап речевой практики
It is the one of the simplest structural elements that both ends are rest on supports but are free to rotate. It contains pinned support at one end and roller support at the other end. On the basis of assign load, it sustains shearing and bending.
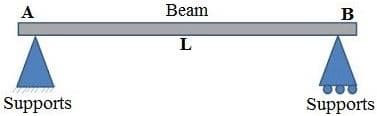
Fig. 1: Simply supported beam
It is supported at both ends and fixed to resist rotation. It is also called a built-in beam. The fixed ends produce fixing moments other than the reactions.
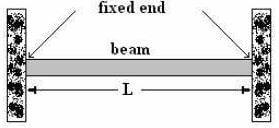
Fig. 2: Fixed beam
If a beam is fixed at one end and set to be free at the end, it is termed as cantilever beam. The beam distribute the load back to the support where it is forced against with a moment and shear stress. Cantilever beams allow the creation of a bay window, balconies, and some bridges.

Fig. 3: Cantilever beam
A continuous beam has more than two supports distributed along its entire length.
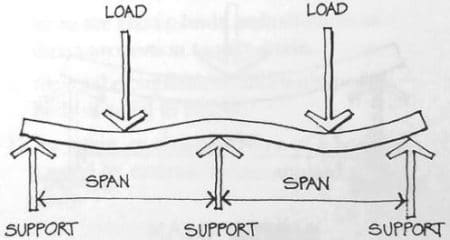
Fig. 4: Continuous beam
Based on Construction Materials
It is constructed from concrete and reinforcement as shown in Fig. 5.
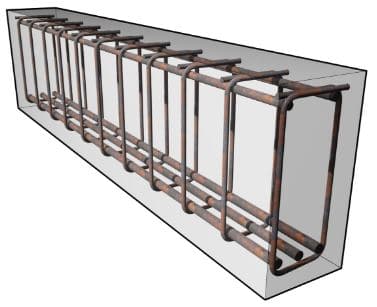
It is constructed from steels and used in several applications.

Fig. 6: Steel beam
This type of beam is constructed from timber and used in the past, but its application is significantly declined now.

Fig. 7: Timber Beam
Composite beams are constructed from two or more different types of materials such as steel and concrete, and various valid cross sections have been utilized as shown in fig.8.
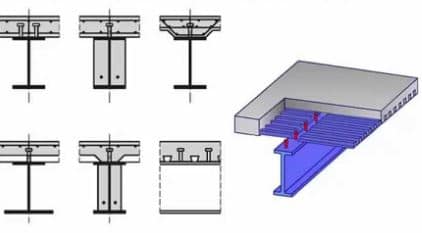
Fig. 8: Composite beam
Based on Cross-Section Shapes
Several cross sectional shapes of beams are available and used in different parts of of structures. These beams can be constructed from reinforced concrete, steel, or composite materials:
Reinforced concrete cross sectional shapes include:
This type of beam is widely used in the construction of reinforced concrete buildings and other structures.
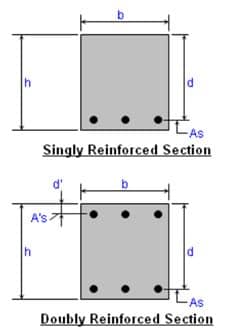
Fig. 9: Rectangular Reinforced concrete beam
This type of beam is mostly constructed monolithically with reinforced concrete slab. Sometimes, Isolated T-beam are constructed to increase the compression strength of concrete.
Added to that, inverted T-beam can also be constructed according to the requirements of loading imposed.
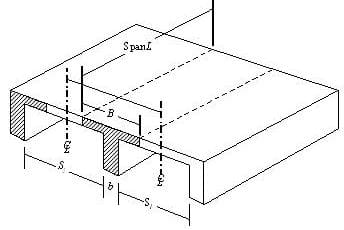
Fig. 10: T-beam
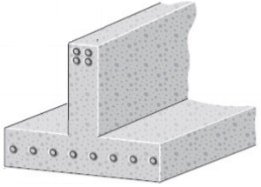
Fig. 11: Inverted T-beam
This type of beam is constructed monolithically with reinforced concrete slab at the perimeter of the structure, as illustrated in Fig. 10.
Steel cross sectional shapes include:
There are various steel beam cross sectional shapes. Each cross sectional shape offer superior advantages in a given conditions compare with other shapes.
Square, rectangular, circular, I-shaped, T-shaped, H-shaped,C-shaped, and tubular are examples of beam cross sectional shapes constructed from steel.

Fig. 12: Steel beam cross sectional shapes
Different types of beams based on cross sectional shapes constructed from composite materials are shown in Fig. 8.
Based on Geometry
Beam with straight profile and majority of beams in structures are straight beams.
Fig. 13: straight beam
Beam with curved profile, such as in the case of circular buildings.
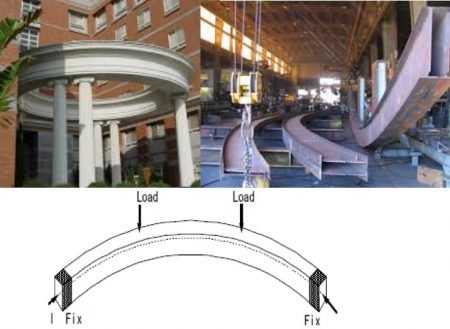
Fig. 14: Curved beam
Beam with tapered cross section.

Fig. 15: Tapered beam
5. Based on Equilibrium Condition
For a statically determinate beam, equilibrium conditions alone can be used to solve reactions, i.e the number of unknown reactions are equal to the the number of equations.
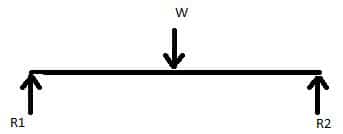
Fig. 16: Statically determinate beam
For a statically indeterminate beam, equilibrium conditions are not enough to solve reactions. So, the analysis of this type of beam is more complicated than that of statically determinate beams.
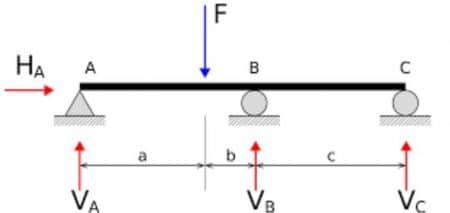
Fig. 17: statically indeterminate beam
Based on Method of Construction
This type of beam is constructed on project site. so, forms are initially fixed then fresh concrete is poured and allowed to be hardened. Then, loads will be imposed.

Fig. 18: Cast in situ beam
This type of beam is manufactured in factories. So, the construction condition is more controllable compare with on-site construction. Consequently, the quality of concrete of the beam will be greater. Various cross sectional shapes can be manufactures such as T- beam, Double T-beam, Inverted T-beam and many more.
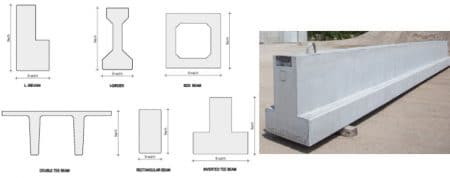
Fig. 19: Precast concrete beam
This type of beam constructed by stressing strands prior to applying loads on the beam. Pre-tensioned Concrete beam and post-tensioned Concrete Beam are variations of pre-stressed concrete beam.

Fig. 20: Prestressed concrete beam
Others
beams that have large depths, and its clear span to depth ratio is less than 4 according to ACI Code. Significant amount of the load is carried to the supports by a compression force combining the load and the reaction. Consequently, the strain distribution is no longer considered linear as in the case of conventional beams.

Fig. 21: Deep beam
Beams that take heavy loads, generally steel sections are used.
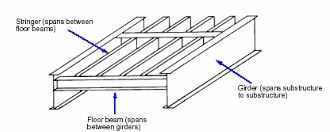
Fig. 22: Girder
4.Заключительный этап. Подведение итогов..Рефлексия.
I can read and understand the information about …
I can listen and understand the information about…
I can write….
I can speak about…
I can ask and answer the questions about
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.