
|
Long-term plan unit: 10.1B Presentation of Data |
School: |
||||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||||
|
Grade: |
Number present: |
absent: |
|||
|
The topic of the lesson:
|
Logical Basics of the Computer |
||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
10.2.2.4 convert logical expressions into logic circuits and the other way round; • 10.1.1.1 describe the functions of the control device (CD), arithmetic logical unit (ALU) and memory registers as individual processor components |
||||
|
Assessment criteria |
● Know the features a Control unit and ALU of the CPU ● Know the main components of the CPU ● Know the purpose of registers |
||||
|
Success criteria |
All learners will be able to know: CU, ALU, Registers, main memory
Most learners will be able to know: Main components of the CPU, purpose a main memory
Some learners will be able to know: Main components of the CPU, purpose a main memory, how to connect with peripheral devices |
||||
|
Language objectives
|
Useful phrases for dialogue / writing The types of operating systems are divided into ____ CU, ALU, Registers, main memory Main components of the CPU___________ Purpose a main memory is ___________
|
||||
|
Value links |
Group work , co-operation, time management |
||||
|
Cross curricular links |
English |
||||
|
Previous learning |
Types of memory: main memory and secondary memory (7-9 grades) |
||||
|
Plan |
|||||
|
Planned lesson stages |
Planned activities |
Resources |
|||
|
Beginning
0-1
2-3 |
Question for students: - Can you remember what we discussed in our previous lesson?
Teacher: - I want (would like) to introduce today’s topic about …/ What do you think today’s topic is?
The presentation of the theme and lesson objectives. Describe the features of a control unit (CU), arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and a memory register as separate parts of the processor |
presentation |
|||
|
Middle 3-5
5-8
8-25
25 - 35
|
Teacher ask a Question: Who can tell me what a CPU is? Listen answers students and discuss
Watch video (in the 3rd slide, 2:30 minutes) discuss about this video
Theory The CPU – Central Processing Unit Question: What does a CPU consist of? (Application 1.1 – 1.6)
Can anyone tell me how many OS there are? (Multitasking OS, Multi-user OS)
Teacher: Now, as we discussed what a processor is, it's time to see what the CPU consists of: • Control Unit (CU) • Immediate Access Store (IAS) or “Cache” • Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) Please write down this scheme in your copybook.
Teacher ask questions 1. Name three internal components of a processor. Control Unit ALU Registers 2. What is an I/O controller? I/O controller is an electronic circuit than one side connects to the system bus and on the other side connects to an I/O device.
|
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5BpgAHBZgec
|
|||
|
The end of the lesson 35 - 40 |
At the end of the lesson, learners reflect on their learning: ✓ What has been learned ✓ What remained unclear ✓ What needs more attention
|
|
|||
|
Differentiation – how do you plan to give more support? How do you plan to challenge the more able learners? |
Assessment – how are you planning to check learners’ learning? |
Health and safety check |
|||
|
Differentiation can be expressed in the selection of tasks, in the expected result from a particular student, in providing individual support to the student, in selecting the educational material and resources, taking into account the individual abilities of the students (Theory of Multiple Intelligence by Gardner). Differentiation can be used at any stage of the lesson, taking into account the rational use of time. |
Use this section to record the methods that you will use to assess what the students have learned during the lesson.
|
Health and safety check links. Used active exercises. Items applied from the Safety Rules in this lesson. |
|||
|
Reflection
Were the lesson objectives/learning objectives realistic? Did all learners achieve the LO? If not, why? Did my planned differentiation work well? Did I stick to timings? What changes did I make from my plan and why?
|
Use the space below to reflect on your lesson. Answer the most relevant questions from the box on the left about your lesson. |
||||
|
|
|||||
|
Summary evaluation
What two things went really well (consider both teaching and learning)?
1:
2:
What two things would have improved the lesson (consider both teaching and learning)?
1:
2:
What have I learned from this lesson about the class or individuals that will inform my next lesson?
|
|||||
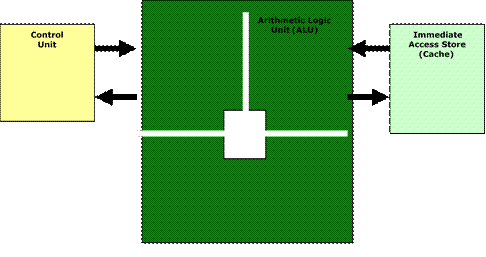
Application 1.1
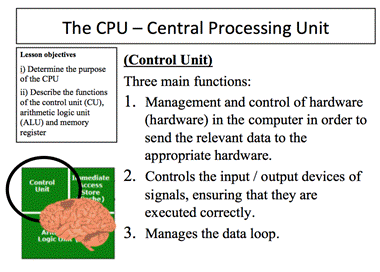
Application 1.2
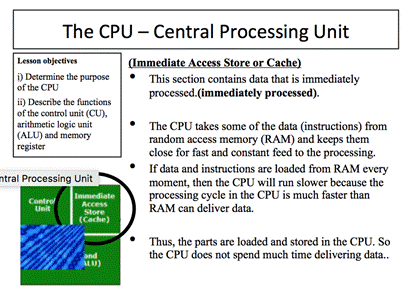
Application 1.3
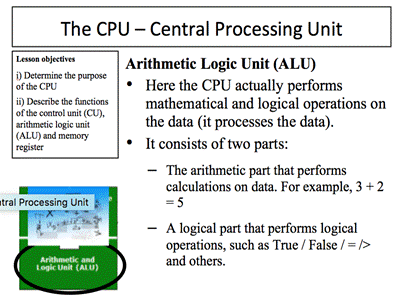
Application 1.4
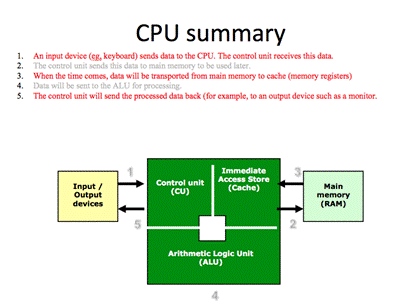
Application 1.5
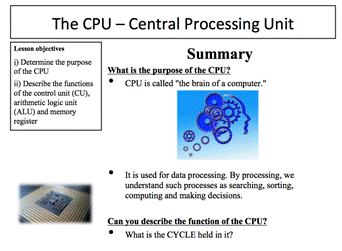
Application 1.6
Скачано с www.znanio.ru
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.