
Worksheet
Intermediate level
1 A cell has an electromotive force (e.m.f.) of 1.5 V. Calculate the chemical energy transferred when the following charges flow through the cell:
|
a |
1 C; |
[2] |
|
b |
600 C. |
[1] |
2 The potential difference across a filament lamp is 6.0 V. Explain what this means in
|
terms of energy transfer and charge. |
[1] |
3 Calculate the potential difference across a component that transfers 15 J
|
of energy when a charge of 4.2 C flows through it. |
[2] |
4 A 12 V, 36 W lamp is operated for 1 hour (3600 s). Calculate:
|
a |
the energy dissipated by the lamp; |
[2] |
|
b |
the current in the lamp. |
[2] |
|
5 Show that 1 kW h is equal to 3.6 MJ. |
[2] |
|
6 An electric heater of rating 900 W is operated for a total time of 2.0 hours.
|
a |
How much energy is transferred in joules and in kilowatt-hours? |
[3] |
|
b |
What is the cost of operating the heater if the cost per kilowatt-hour is 7.5p? |
[2] |
Higher level
7 A 100 Ω resistor can safely dissipate 0.25 W. Calculate the maximum current in
|
the resistor. |
[3] |
8 A filament lamp in a small torch is labelled as ‘1.5 V, 400 mA’. The filament lamp transfers 5.0% of the electrical energy into light and the remainder is dissipated as heat. Calculate:
|
a |
the power rating of the lamp; |
[2] |
|
b |
the power radiated as light; |
[2] |
|
c |
the resistance of the filament lamp. |
[2] |
9 A 60 W table lamp is operated for a total time of 6.0 hours.
|
a How much energy is transferred in kW h? |
[2] |
b For how long can a dishwasher of rating 800 W be operated for the same
|
cost as operating the 60 W lamp for 6.0 hours? |
[2] |
10 The diagram shows an electrical circuit.
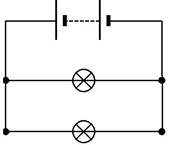 6.0 V
6.0 V
|
|
X |
12 W |
|
|
Y |
36 W |
|
a |
Calculate the current in lamp X. |
[2] |
|
b |
Calculate the ratio: |
|
|
|
resistance of lamp X |
|
|
|
resistance of lamp Y |
[3] |
Extension
11 The coiled filaments in a mains lamp and a car headlamp are made of the same material and have the same length. Use the information below to calculate the ratio:
|
cross-sectional area of mains lampfilament |
= |
|
|
|
cross-sectional area of headlamp filament |
[4] |
||
|
|
|
||
|
Mains lamp: 230 V, 100W |
Car headlamp: 12 V, 36 W
|
|
|
12 The diagram shows two resistance wires connected in series to a power supply.
+ –
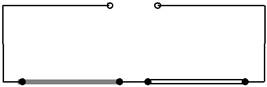
iron nickel
The resistance wires have the same length and diameter. The resistivity of nickel is six times that of iron.
|
a Which of these two wires will be hotter? Explain your reasoning. |
[3] |
b The two wires are now connected in parallel to the same power supply.
Explain which of these two wires will be hotter. [3]
Total: ––– Score:%
45
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.