
|
Long-term plan unit: 10.1B Presentation of Data |
School: |
||||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||||
|
Grade: 10 |
Number present: |
Grade: |
|||
|
The topic of the lesson:
|
Logical Basics of the Computer |
||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
10.2.2.4 convert logical expressions into logic circuits and the other way round; • 10.1.1.1 describe the functions of the control device (CD), arithmetic logical unit (ALU) and memory registers as individual processor components |
||||
|
Assessment criteria |
● Know the features a Control unit and ALU of the CPU ● Know the main components of the CPU ● Know the purpose of registers |
||||
|
Success criteria |
All learners will be able to know: CU, ALU, Registers, main memory
Most learners will be able to know: Main components of the CPU, purpose a main memory
Some learners will be able to know: Main components of the CPU, purpose a main memory, how to connect with peripheral devices |
||||
|
Language objectives
|
Useful phrases for dialogue / writing The types of operating systems are divided into ____ CU, ALU, Registers, main memory Main components of the CPU___________ Purpose a main memory is ___________ • СPU • ALU • CU • Address bus • Data bus • Control bus |
||||
|
Value links |
Group work , co-operation, time management |
||||
|
Cross curricular links |
English, math, physics |
||||
|
Previous learning |
Types of memory: main memory and secondary memory (7-9 grades) |
||||
|
Course of the lesson |
|||||
|
Planned stages of the lesson |
Planned activities at the lesson |
Resources |
|||
|
Beginning 0-2 2-7
|
Organizational moment: teacher prepares students for learning knowledge Activity Expand the lesson theme through the game “Find a mistake.” Groups create their own Von Neumann scheme intentionally allowing various kinds of errors. Groups must find a bug.
Acquaintance of students with the topic of the lesson and its objectives
|
Presentation
|
|||
|
Middle
7-10
10 – 15
15 - 30
30 - 35 |
Watch a video “Von Neumann architecture”, after watching a video discuss with students.
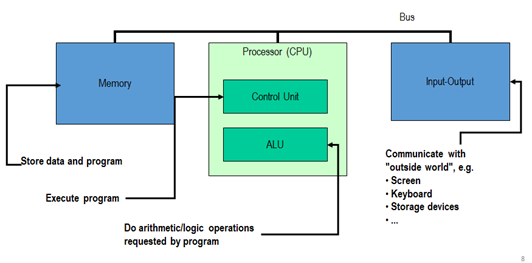
The teacher explains and discuss with students about the structure of the Von Neumann architecture and the functions they perform and the relationship between them. Application 1.1.
Activity - Draw the Von Neumann Architecture in the form of a diagram (draw on a poster), write the interaction between the main aspects
Differentiation is organized as follows: It is necessary to understand how this scheme works.
Pupils rate themselves-according to the principle of self-assessment according to the principle of academic integrity by descriptor. Assessment – application 1.2 Questions to control learned material: • What does the concept of computer architecture include? • Identify the principles of the computer, formulated by John von Neumann. • What does the architecture of computers of the first generations include? • What are the basic principles of a computer trunk device? • What are the new elements of architecture characteristic of modern PC? Homework: Answer to the questions in worksheet file.
|
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SbqXqQ-2ixs
|
|||
|
End 5 min |
Reflection - What has been learned - What remained unclear - What is necessary to work on - What competencies have you acquired? Answer the questions that were formulated at the beginning of the lesson. |
slide #9 |
|||
|
Differentiation – how do you plan to give more support? How do you plan to challenge the more able learners? |
Assessment – how are you planning to check students’ learning? |
Health and safety regulations |
|||
|
Additional support. Work in pairs / groups - support for classmates. Help the teacher, if required. More capable learners can demonstrate aspects of their decisions that seem interesting / more complex to the other learners. |
Answers questions and a session of answers. Use questions when completing a task. Use survey questions to understand the results / success of learners at each stage of the lesson. |
Remind of some safety rules when working with computer equipment, for example, that you must be careful when installing the screen, keyboard and mouse; beware of wires, as they pose a threat to movement. |
|||
|
Reflection Were the lesson objectives/learning objectives realistic? Did all learners achieve the LO? If not, why? Did my planned differentiation work well? Did I stick to timings? What changes did I make from my plan and why? |
Use the space below to reflect on your lesson. Answer the most relevant questions from the box on the left about your lesson. |
||||
|
|
|||||
|
Summary evaluation
What two things went really well (consider both teaching and learning)?
1:
2:
What two things would have improved the lesson (consider both teaching and learning)?
1:
2:
What have I learned from this lesson about the class or individuals that will inform my next lesson?
|
|||||
Application 1.1
Application 1.2
|
Criteria |
Descriptors |
Conclusion |
||
|
+ |
_
|
|||
|
Knowledge and understanding |
Draw a diagram |
|
|
|
|
All interaction is written correctly. |
|
|
||
|
||||
|
Analysis and application |
If finishes the project before his classmates, begins to "improve" the table |
|
|
|
Скачано с www.znanio.ru
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.