
Methodological Instructions
Theme: Principles of textual programming
Objective: 10.2.3.1 compare tables for character encoding such as Unicode and ASCII Assessment criteria
● study the coding table Unicode
● study the coding table ASCII
● compare tables for character encoding such as Unicode and ASCII
Basic Level:
Logical operations, binary code, initial skills in MS Excel (7-9 grade)
Key words and phrases:
ASCII, Unicode, binary, encode, hexadecimal, coding, decoding, symbol, truth table.
Dictionary of specific terms and terminology:
· In order to translate a number from decimal to binary system…
· Truth table is made for….
· Logical multiplication is also called …
· ASCII is …
· Encoding is
· Decoding is
A distinctive feature of Unicode is…
I. THEORY
Computers store text using character codes. The most prevalent computer character set is the American Standard Code for Information Interchange, more commonly known as ASCII (pronounced "ask-ee"). The ASCII character set represents each character with a 7-bit binary code (the decimal numbers 0 to 127). The first 32 codes in the ASCII character set are used for control functions such as line feed, tab, escape, and carriage return. The remaining 96 codes are used for alphanumeric English characters, as shown in the following table.
ASCII defines 128 characters, which map to the numbers 0–127. Unicode defines (less than) 221characters, which, similarly, map to numbers 0–221 (though not all numbers are currently assigned, and some are reserved).
Unicode is a superset of ASCII, and the numbers 0–128 have the same meaning in ASCII as they have in Unicode. For example, the number 65 means "Latin capital 'A'". Because Unicode characters don't generally fit into one 8-bit byte, there are numerous ways of storing Unicode characters in byte sequences, such as UTF-32 and UTF-8.
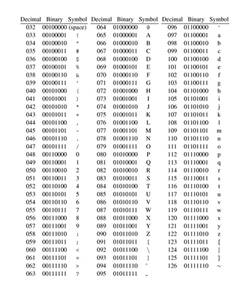
Picture 1
if
you look at a complete table of ASCII values you will see that the character
values increase from A to Z. and from a to z. This means it is possible to sort
these characters based on their numeric value. For example, A is less than B, B
is less than C, etc.
Note that a is larger in value than A and Z, so when you sort words 'Zebra'
comes before 'apple'.
ASCII was very useful for transmitting textual messages but it fails to deal
with the range of other characters we often need, such as those used in various
non-English languages and mathematical symbols.
As 8-bit computers became the norm the ASCII character set extended to use 8
bits rather than 7, this meant another 128 characters could be included. It
also conveniently uses just one byte to store each character.
Unicode
The Unicode system for encoding characters uses up to 32 bits (4bytes) providing more than 4 billion possibilities. Within the Unicode system the original 128 ACII characters still occupy the same values, so ASCII could now be considered a subset of the Unicode System for coding characters.
П. TESTS AND ASSIGNMENTS FOR SELF-ASSESSMENT
1.
Encode text using the ASCII code table.
Happy Birthday to you!
Write binary and hexadecimal representations of code
In hexadecimal
48 61 70 70 79 20 42 69
72 …
6F …
2.
In binary
1001000 1100001 1110000 1110000 1111001
0100000 1000010 1101001
1101111 …
Decode the text from ASCII international coding table
(given a decimal representation).
72 101 108 108 111 44 32 109 121 32 102 114 105 101 110 100 33
3. Using the ASCII code table, decrypt the text presented in the binary form
01010000 01100101 01110010 01101110 00100000 01010101 01101110 01101001 01110110 01100101 01110010 01110011 01101001 01110100 01111001
4. What is meant by the character set of a computer?
5. Explain how ASCII represents each character set of a computer.
6. What happens if you sort the list 'Apple', 'bear', 'Charlie', 'dog', 'elephant' in a program using ASCII or Unicode to represent the character set?
7. Explain the difference between using an ASCII character set and a Unicode character set?
VISUAL AIDS AND MATERIALS.
1. Slides
2. Computer text view: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3BDE0oxevUQ
3. https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Unicode
4. https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/A- evel_Computing/AQA/Paper_2/Fundamentals_of_data_representation/ASCII_and_unicode
5. http://school.dtv.su/kodirovanie-tekstovoy-informatsii/
6. Measuring textual information and rules for presenting information: http://school497.ru/download/u/02/les10/les.html
7. For differentiation: http://msk.edu.ua/ivk/Informatika/1_kurs/Z2/6_Kodirovanie_teksta.pdf
8. https://cacm.acm.org/blogs/blog-cacm/203554-five-principles-for-programming-languages-for-learners/fulltext
Скачано с www.znanio.ru
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.