
|
Long-term plan unit: 10.1B Data representation |
School: |
||||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||||
|
Grade: |
Number present: |
absent: |
|||
|
The topic of the lesson:
|
Constructing truth tables |
||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
10.2.2.2 construct truth tables for the given logical expression |
||||
|
Assessment criteria |
● Consider the algorithm for constructing truth tables ● Teach how to construct a truth table ● Use logic gate diagrams for constructing truth tables and vice versa. |
||||
|
Success criteria |
All learners will be able to know: - know and be able to work out the truth tables for NOT, AND, OR logic gates; Most learners will be able to know: - be comfortable with the use of symbols to represent each gate; Some learners will be able to know: - be able to produce a truth table for a given Boolean logic formula; |
||||
|
Language objectives
|
Learners can: use the vocabulary and terminology to describe difference between NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR functions and convert English sentences into logic Subject-specific vocabulary and terminology: truth tables, logic gates, Boolean gates and statements, NOT, OR, AND, NAND, NOR, built, express, true, false Useful sets of phrases for dialogue and writing: We can build / express (this) in Boolean statements. How can we build / express (this) in Boolean statements. How can we express … as a Boolean statement? When … is not true / true / false, … is true / not true / false. In this statement, … means …
|
||||
|
Value links |
Soft skills Respect for each other when working in groups
|
||||
|
Cross curricular links |
English, math, physic |
||||
|
Previous learning |
Multiplication table (7-9 grade) |
||||
|
Plan |
|||||
|
Planned lesson stages |
Planned activities |
Resources |
|||
|
Beginning
0-3
3-10 |
Organizational moment: Question for students: - Can you remember what we discussed in our previous lesson?
Teacher: - I want (would like) to introduce today’s topic about …/ - What do you think today’s topic is? The presentation of the theme and lesson objectives. 10.2.2.2 construct truth tables for the given logical expression Teacher offers to answer questions: • What is meant by a logical expression? • What is a truth table? Learners answer questions. · Logical formula (logical expression) - a formula containing only logical variables and signs of logical operations. · A truth table is a breakdown of a logic function by listing all possible values the function can attain |
Presentation Slides #1-2
Slide#3
|
|||
|
Middle 10-13
15-25
25-28
28 - 35
|
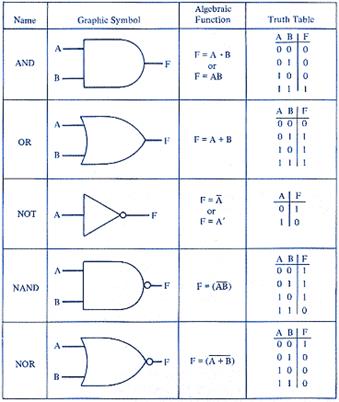
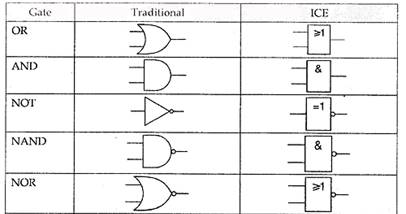
Theory Teacher offers to watch video using logic gate for constructing truth table. Teacher offers to answer the question: What is a logic gate? · A logic gate is an elementary building block of a digital circuit. Most logic gates have two inputs and one output. · A logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function; that is, it performs a logical operation on one or more binary inputs and produces a single binary output. · Logic gates perform basic logical functions and are the fundamental building blocks of digital integrated circuits. A logic gate is an assortment of electronically controlled switches that implement Boolean logic processes. Learners study the truth tables. Application 1.1-1.2 Teacher demonstrates an algorithm for solving tasks
Formative assessment Teacher offers to carry out tasks followed by self-assessment. For self-assessment teacher demonstrates correct answer(s) |
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N5VBSWRRdUw&
slides #5-9
Slide #11
|
|||
|
The end of the lesson 35 - 40 |
Teacher offers to carry out tasks followed by self-assessment using online source At the end of the lesson, learners reflect on their learning: ✓ What has been learned ✓ What remained unclear ✓ What needs more attention
|
https://logic.ly/demo/ |
|||
|
Differentiation – how do you plan to give more support? How do you plan to challenge the more able learners? |
Assessment – how are you planning to check learners’ learning? |
Health and
safety check |
|||
|
Differentiation can be expressed in the selection of tasks, in the expected result from a particular student, in providing individual support to the student, in selecting the educational material and resources, taking into account the individual abilities of the students (Theory of Multiple Intelligence by Gardner). Differentiation can be used at any stage of the lesson, taking into account the rational use of time. |
Use this section to record the methods that you will use to assess what the students have learned during the lesson.
|
Health and safety check links. Used active exercises. Items applied from the Safety Rules in this lesson. |
|||
|
Reflection
Were the lesson objectives/learning objectives realistic? Did all learners achieve the LO? If not, why? Did my planned differentiation work well? Did I stick to timings? What changes did I make from my plan and why?
|
Use the space below to reflect on your lesson. Answer the most relevant questions from the box on the left about your lesson. |
||||
|
|
|||||
|
Summary evaluation
What two things went really well (consider both teaching and learning)?
1:
2:
What two things would have improved the lesson (consider both teaching and learning)?
1:
2:
What have I learned from
this lesson about the class or individuals that will inform my next lesson?
|
|||||
Application 1.1
Application 1.2
Скачано с www.znanio.ru
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.