
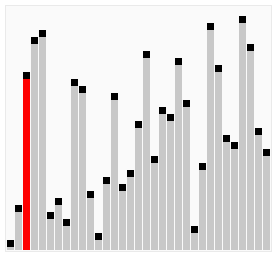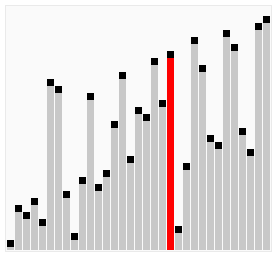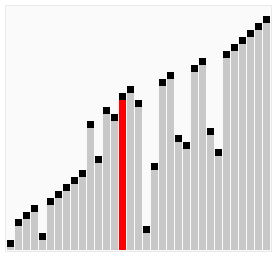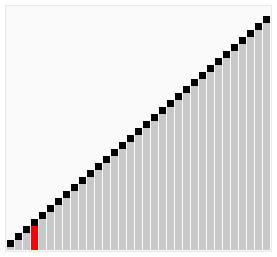
A bubble sort, a sorting algorithm that continuously steps through a list, swapping items until they appear in the correct order.
Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly stepping through the list to be sorted, comparing each pair and swapping them if they are in the wrong order. The pass through the list is repeated until no swaps are needed, which indicates that the list is sorted. The algorithm gets its name from the way larger elements "bubble" to the top of the list. It is a very slow way of sorting data and rarely used in industry. There are much faster sorting algorithms out there such as insertion sort and quick sort which you will meet in A2.
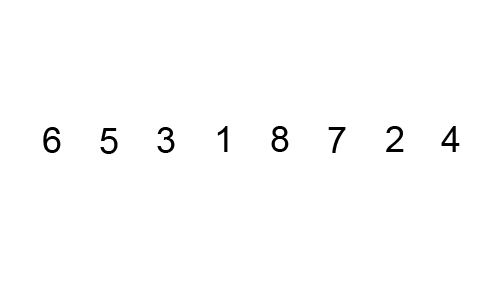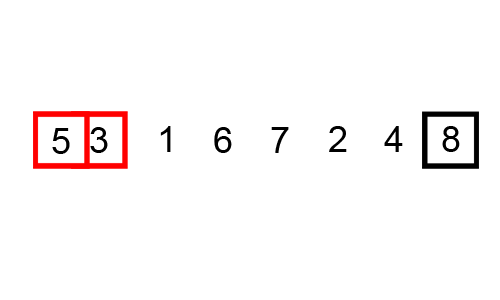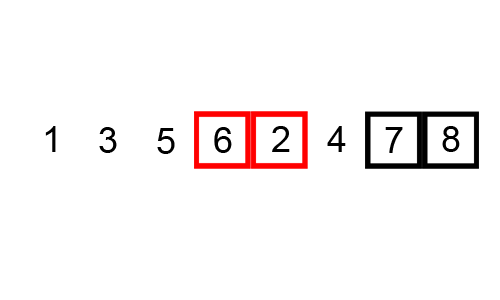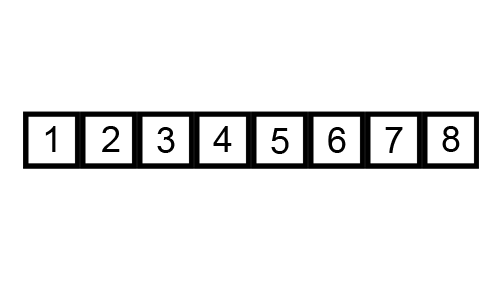
Let us take the array of numbers "5 1 4 2 8", and sort the array from lowest number to greatest number using bubble sort algorithm. In each step, elements written in bold are being compared.
First Pass:
( 5 1 4 2 8 ) ![]() ( 1 5 4
2 8 ), Here, algorithm compares the first two elements, and swaps them since 5
> 1
( 1 5 4
2 8 ), Here, algorithm compares the first two elements, and swaps them since 5
> 1
( 1 5 4 2 8 ) ![]() (
1 4 5 2 8 ), It then compares the second and third
items and swaps them since 5 > 4
(
1 4 5 2 8 ), It then compares the second and third
items and swaps them since 5 > 4
( 1 4 5 2 8 ) ![]() ( 1
4 2 5 8 ), Swap since 5 > 2
( 1
4 2 5 8 ), Swap since 5 > 2
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) ![]() ( 1 4
2 5 8 ), Now, since these elements are already in
order (8 > 5), algorithm does not swap them.
( 1 4
2 5 8 ), Now, since these elements are already in
order (8 > 5), algorithm does not swap them.
The algorithm has reached the end of the list of numbers and the largest
number, 8, has bubbled to the top. It now starts again.
Second Pass:
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) ![]() ( 1 4 2
5 8 ), no swap needed
( 1 4 2
5 8 ), no swap needed
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) ![]() (
1 2 4 5 8 ), Swap since 4 > 2
(
1 2 4 5 8 ), Swap since 4 > 2
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) ![]() ( 1
2 4 5 8 ), no swap needed
( 1
2 4 5 8 ), no swap needed
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) ![]() ( 1 2
4 5 8 ), no swap needed
( 1 2
4 5 8 ), no swap needed
Now, the array is already sorted, but our algorithm does not know if it is completed.
The algorithm needs one whole pass without any swap
to know it is sorted.
Third Pass:
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) ![]() ( 1 2 4
5 8 )
( 1 2 4
5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) ![]() (
1 2 4 5 8 )
(
1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) ![]() ( 1
2 4 5 8 )
( 1
2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) ![]() ( 1 2
4 5 8 )
( 1 2
4 5 8 )
Finally, the array is sorted, and the algorithm can terminate.
The algorithm can be expressed as:
procedure bubbleSort( A : list of sortable items )
do swapped = false for each i in 1 to length(A) - 1 inclusive do: if A[i-1] > A[i] then swap( A[i-1], A[i] ) swapped = true end if end forwhile swapped
end procedure|
Exercise: Bubble Sort We will now look at an example in Visual Basic using an array of people's heights. The following data set is being passed:
Sub bubbleSort(ByRef height() As integer) Dim swapped As Boolean Dim temp As integer 'sort the elements Do swapped = False For Count = 1 To MaxSize - 1 If height(Count + 1) < height(Count) Then temp = height(Count) height(Count) = height(Count + 1) height(Count + 1) = temp swapped = True End If Next Loop Until swapped = False 'Print out the elements For Count = 1 To MaxSize Console.WriteLine(Count & ": " & height(Count)) Next End Sub Construct a trace table for the above code:
Collapse Answer:
What does the above code output? Collapse Answer: 1: 12 Show the following lists after one pass of bubble sort: Sort into alphabetical order: Henry, Cat, George, MouseExpand Answer: Sort into alphabetical order: G, C, N, A, P, C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
From
https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/A-level_Computing/AQA/Paper_1/Fundamentals_of_algorithms/Sorting_algorithms
Скачано с www.znanio.ru
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.