
FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT
Name ___________________________________ Class _________________________________
1. Write parts of this system
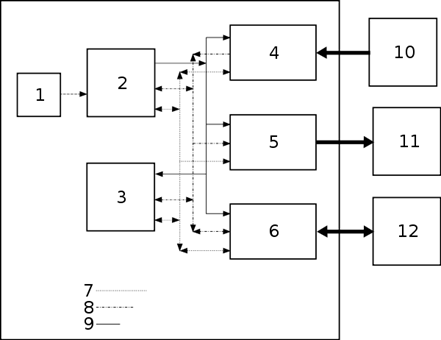
Pic.1
Do not worry about the size of this problem; we are going to tackle it bit by bit. The first step is to remember the differences between each of the components:
¾ Processor - connected to other devices using buses
¾ Data bus - bi-directional connection between devices
¾ Main memory - internal to the computer and linked through the buses
¾ Keyboard - external to the computer, an input device
¾ Secondary storage - external device, an input and output device
¾ Address bus - uni-directional connection between devices
¾ Clock - regulates the processor
¾ Monitor - external output device
¾ VDU controller - connects system to external monitor
¾ Disk controller - connects system to external secondary storage
¾ Keyboard controller - connects system to external keyboard device
¾ Control Bus - A bi-directional bus used to control signals between the components
2. Identify translator (compiler or interpreter) according to description.
A. Translates the program into machine code line by line ______________
B. When using this translator, the program runs faster ______________
C. Сan not fix errors ______________
D. Еasier to find error ______________
3. Write down the letters in the cells that correspond to the descriptions of the processors:
|
RISC |
CISC |
|
|
|
A. Has more complex hardware
B. More compact software code
C. More complicated software code
D. Takes more cycles per instruction
E. Can use more RAM to handle intermediate results
F. Has simpler hardware
G. Can use less RAM as no need to store intermediate results
H. Take one cycle per instruction
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.