
Methodological Instructions
Theme: Processor Specifications
Objective: 10.1.1.3 explain the main characteristics of a processor: capacity and clock speed
Assessment criteria
• understands the role of the processor in managing
• knows the characteristics of the processor
• knows the purpose of the processor memory registers
Knows and can determine the clock speed Basic Level:
Von Neumann architecture, CPU (7-9 grades)
Key words and phrases:
Control Unit,
Cache, Main Memory (RAM), Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU)
System bus, Control bus ,Address bus , Data bus
I. Theory
Processor
The processor is the main chip of the computer, its “brain”. It allows you to execute program code that is in memory and manages the work of all devices on your computer. The speed of his work determines the speed of the computer. Structurally, the processor is a silicon crystal of very small sizes. The processor has special cells called registers. It is in the registers that the commands that are executed by the processor are placed, as well as the data with which the commands operate. The processor is to select from memory in a specific sequence of commands and data and their execution. The execution of programs is based on this.
The main options of the processors are:
• clock speed
• bit depth operating voltage internal clock multiplication factor cache size.
Clock speed
The clock frequency determines the number of elementary operations (clock cycles) performed by the processor per unit of time. The clock frequency of modern processors is measured in MHz (1 Hz corresponds to the performance of one operation per second, 1 MHz = 106 Hz). The greater the clock frequency, the more commands the processor can execute, and the greater its performance. The first processors that were used in PCs operated at 4.77 MHz; today, the operating frequencies of modern processors reach 2 GHz (1 GHz = 103 MHz)
• The capacity of the processor shows how many bits of data it can receive and process in its registers in one clock cycle. The processor capacity is determined by the bit depth of the command bus, that is, the number of conductors on the bus, over which commands are transmitted. Modern processors from the Intel family are 32-bit.
• The operating voltage of the processor is provided by the motherboard, so different motherboards correspond to different brands of processors. The operating voltage of the processors does not exceed 3 V. The decrease in the operating voltage allows reducing the size of the processors, as well as reducing the heat release in the processor, which allows to increase its performance without the threat of overheating.
Internal multiplication factor clock speed
The internal clock multiplication factor is the coefficient by which the motherboard clock frequency should be multiplied to reach the processor frequency. The processor receives clock signals from the motherboard, which, for purely physical reasons, cannot operate at such high frequencies as the processor. At present, the clock frequency of motherboards is 100-133 MHz. For higher frequencies, internal multiplication by a factor of 4, 4.5, 5 and more occurs in the processor.
Bus
With other devices, and primarily with RAM, the processor is connected by groups of conductors, which are called buses. There are three main tires:
• data bus,
• address bus,
• command bus.
Address Bus. Data transmitted over this bus are treated as addresses of memory cells. It is from this bus that the processor reads the addresses of the commands to be executed, as well as the data with which the commands operate. In modern processors, the address bus is 32-bit, that is, it consists of 32 parallel conductors.
• Data bus. This bus copies data from the RAM to the processor registers and vice versa. The PC is based on Intel Pentium 64-bit data bus. This means that in a single clock cycle, 8 bytes of data arrive immediately.
• Command bus This bus from the RAM receives commands executed by the processor. Commands are in the form of bytes. Simple commands are invested in one byte, but there are also commands for which you need two, three or more bytes. Most modern processors have a 32-bit command bus, although there are 64-bit processors with a command bus.
Bus on the motherboard are used not only to communicate with the processor. All other internal devices of the motherboard, as well as devices that connect to it, interact with each other using tires. From the architecture of these elements depends largely on the performance of the PC as a whole.
П. Tests and Assignments for Self-assessment.
1. Chose 2 CPUs and compare them. Which CPU has better performance, which has lower price. Justify your answer.
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2. Write down at least 2 differences for each Intel and AMD CPUs.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________What does 3MHz mean:
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3. What does a processor clock do:
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4. Name parts of system. Do not worry about the size of this problem; we are going to tackle it bit by bit. the first step is to remember the differences between each of the components:
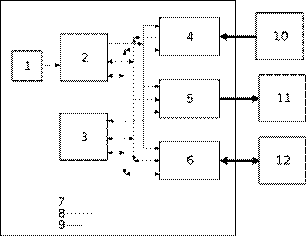
ü Processor - connected to other devices using buses
ü Data bus - bi-directional connection between devices
ü Main memory - internal to the computer and linked through the buses
ü Keyboard - external to the computer, an input device
ü Secondary storage - external device, an input and output device
ü Address bus - uni-directional connection between devices
ü Clock - regulates the processor
ü Monitor - external output device
ü VDU controller - connects system to external monitor
ü Disk controller - connects system to external secondary storage
ü Keyboard controller - connects system to external keyboard device
ü Control Bus - A bi-directional bus used to control signals between the components
5. What does 3MHz mean:
6. Name three ways to increase Processor performance:
7. What draw back might increasing clock speed bring?
8. What is a benefit of increasing word length?
9. How might bus width impact on the speed of a computer?
10. Give two benefits for increasing the word size of a processor?
Visual Aids and Materials.
1. Slides
2. http://userwords.ru/tehnicheskie-harakteristiki-protsesso/
3. processors rating, defining clock speed and bit by processor name: http://www.notebookcheck-ru.com/Vsjo-o-mobilnykh-processorakh-Opisanie-i-bystrodeistvie.14099.0.html
4. Choosing processor by its specs: http://compsovet.com/stati/kompjuternaja-tehnika/processor/76-kak-vybrat-processor-i-chto-jeto-takoe.html
5. http://www.kakprosto.ru/kak-878020-po-kakim-harakteristikam-vybirat-processor
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.