
Methodological Instructions
Theme: Von Neumann Architecture
Aim: Describe the features of a control unit (CU), arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and a memory register as separate parts of the processor
Assessment criteria
● Know the features a Control unit and ALU of the CPU
● Know the main components of the CPU
● Know the purpose of registers
Basic Level:
Know types of memory main memory and secondary memory (7-9 grades)
Key words and phrases:
The types of operating systems are divided into ____
CU, ALU, Registers, main memory
Main components of the CPU___________
Purpose a main memory is ___________
I. Theory
John von Neumann first published Von Neumann architecture in 1945.
His computer architecture design consists of a Control Unit, Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU), Memory Unit, Registers and Inputs/Outputs.
Von Neumann architecture is based on the stored-program computer concept, where instruction data and program data are stored in the same memory. This design is still used in most computers produced today.
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the electronic circuit responsible for executing the instructions of a computer program.
It is sometimes referred to as the microprocessor or processor.
The CPU contains the ALU, CU and a variety of registers.
Registers are high speed storage areas in the CPU. All data must be stored in a register before it can be processed.
|
MAR |
Memory Address Register |
Holds the memory location of data that needs to be accessed |
|
MDR |
Memory Data Register |
Holds data that is being transferred to or from memory |
|
AC |
Accumulator |
Where intermediate arithmetic and logic results are stored |
|
PC |
Program Counter |
Contains the address of the next instruction to be executed |
|
CIR |
Current Instruction Register |
Contains the current instruction during processing |
The ALU allows arithmetic (add, subtract etc) and logic (AND, OR, NOT etc) operations to be carried out.
The control unit controls the operation of the computer’s ALU, memory and input/output devices, telling them how to respond to the program instructions it has just read and interpreted from the memory unit. The control unit also provides the timing and control signals required by other computer components.
Buses are the means by which data is transmitted from one part of a computer to another, connecting all major internal components to the CPU and memory.
A standard CPU system bus is comprised of a control bus, data bus and address bus.
|
Address Bus |
Carries the addresses of data (but not the data) between the processor and memory |
|
Data Bus |
Carries data between the processor, the memory unit and the input/output devices |
|
Control Bus |
Carries control signals/commands from the CPU (and status signals from other devices) in order to control and coordinate all the activities within the computer |
The memory unit consists of RAM, sometimes referred to as primary or main memory. Unlike a hard drive (secondary memory), this memory is fast and also directly accessible by the CPU.
RAM is split into partitions. Each partition consists of an address and its contents (both in binary form).
The address will uniquely identify every location in the memory.
Loading data from permanent memory (hard drive), into the faster and directly accessible temporary memory (RAM), allows the CPU to operate much quicker.
П. Tests and Assignments for Self-assessment.
1. Fill the missing blocks in the CPU
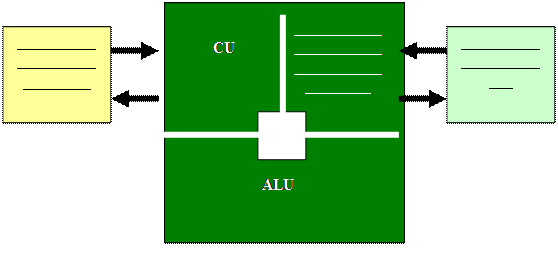
2. Describe the process of working on staged CPUs with Input / Output devices and RAM:
1.____________________________________________________________________________
2.____________________________________________________________________________
3.____________________________________________________________________________
4.____________________________________________________________________________
5.____________________________________________________________________________
Visual Aids and Materials.
1. Slides
2. Von Neumann Architecture http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5BpgAHBZgec
3. Von Neumann Architecture https://www.computerscience.gcse.guru/theory/von-neumann-architecture
4. What’s the difference between Von-Neumann and Harvard architectures? https://www.microcontrollertips.com/whats-the-difference-between-von-neumann-and-harvard-architectures/
5. Features of a Von Neumann architecture http://www.teach-ict.com/as_as_computing/ocr/H447/F453/3_3_3/vonn_neuman/miniweb/pg3.htm
Students' Practical Activities:
Students must know:
● Know the features a Control unit and ALU of the CPU
● Know the main components of the CPU
● Know the purpose of registers
● Скачано с www.znanio.ru
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.