
Methodological Instructions
Theme: Sorting methods
Aim: Implementation of sorting algorithms to solve practical tasks
Assessment criteria
Knowledge
· Know how data sorted by insertion sort.
Comprehension
· Understand the mechanism of data moves in insertion sorting
Application
Language objectives
Learners able to …
State what insertion sorting is?
Describe mechanism of data moves in insertion sorting
Vocabulary and terminology specific to the subject:
Insertion sorting, range of data, ordered list, unordered list, entry, iteration
Useful expressions for dialogs and letters:
Well, the range of elements needs an order, ascending or … .
For example, every number has its own … .
Obviously, the sorted data of great convenience for … .
The list can be sorted …. . The element of list compared with … that are in anterior positions. The amount of total steps depends on
Theory
Insertion Sort
Unfortunately bubble sort is a very slow way of sorting data and very rarely used in industry. We'll now look at a much faster algorithm, insertion sort.
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm: a comparison sort in which the sorted array (or list) is built one entry at a time. It is much less efficient on large lists than more advanced algorithms such as quicksort, heapsort, or merge sort and you may cover these at university. However, insertion sort provides several advantages:
· simple implementation
· efficient on small data sets
· uses a fixed amount of memory when running
Insertion sort requires the use of two arrays, one ordered, and one unordered. Each repetition of the algorithm moves an item from the unordered list, into a sorted position in the ordered list, until there are no elements left in the unordered list.
Sorting is typically done in-place without needing extra memory. The resulting array after k iterations has the property where the first k + 1 entries are sorted. In each iteration the first remaining entry of the input is removed, inserted into the result at the correct position, thus extending the result:

becomes
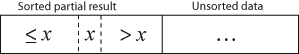
with each element greater than x copied to the right as it is compared against x.
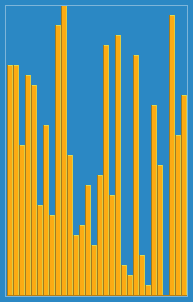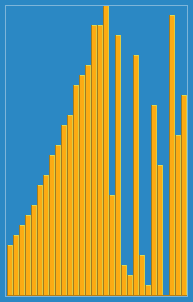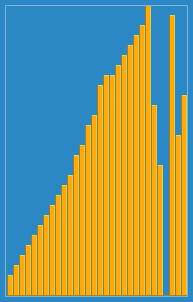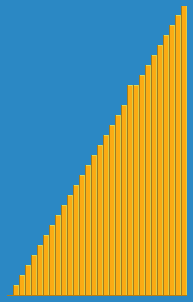
Animation of the insertion sort sorting a 30 element array. Notice how the ordered array (left hand side) slowly consumes the unordered array (right hand side), until the entire data set is ordered
|
Example: Insertion Sort The following table shows the steps for sorting the sequence {5, 7, 0, 3, 4, 2, 6, 1}. For each iteration, the number of positions the inserted element has moved is shown in parentheses. Altogether this amounts to 17 steps. 5 7 0 3 4 2 6 1 (0)
0 5 7 3 4 2 6 1 (2) 0 3 5 7 4 2 6 1 (2) 0 3 4 5 7 2 6 1 (2) 0 2 3 4 5 7 6 1 (4) 0 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 (1) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 (6) for i ← 1 to i ← length(A)-1 {// A[ i ] is added in the sorted sequence A[0, .. i-1] // save A[i] to make a hole at index iHole item ← A[i] iHole ← i// keep moving the hole to next smaller index until A[iHole - 1] is <= item while iHole > 0 and A[iHole - 1] > item {// move hole to next smaller index A[iHole] ← A[iHole - 1] iHole ← iHole - 1 }// put item in the hole A[iHole] ← item } ' a procedure to sort an array of integers |
П. Questions for self-assessment.
What is the insertion sort?
How to go through passages in insertion sort?
Visual Aids and Materials links.
1. Slides
2. https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/A-level_Computing/AQA/Paper_1/Fundamentals_of_algorithms/Sorting_algorithms
Students' Practical Activities:
Students must be able:
· write an algorithm for insertion sort
Скачано с www.znanio.ru
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.