
Methodological Instructions
Theme: User defined procedures and functions 1 lesson 2 variant
Objective: 10.4.1.1 write a code in the programming language using functions and procedures
Assessment criteria
· Students understand and distinguish the definitions of functions and procedures in programming.
· Students can solve problems using functions and procedures
· Knows and can determine the clock speed
Basic Level:
From a grade 7–9 course, students have knowledge and programming skills.
Key words and phrases:
Subprogram, function, procedure, formal and actual parameters, global and local variables
Function - part of the program that has ...
Method is a function that is ...
Function is used for…
Procedure is used for...
I. Theory
Computer programs can consist of thousands of lines of code, just like a textbook can have thousands of words.
In the same way that a textbook is divided into chapters, a program is divided into related functionality using modules.
In a textbook, specific concepts are covered on a section-by-section or paragraph-by-paragraph basis. Similarly, in a computer program, specific functionality is divided up into named functions and procedures.
Programs usually integrate blocks of code and modules that have already been created in other projects.
The algorithms a program uses are implemented as the functions and procedures in these modules.
Functions differ from procedures in that functions return values, unlike procedures which do not. However, parameters can be passed to both procedures and functions.
In a program for drawing shapes, the program could ask the user what shape to draw. The instructions for drawing a square could be captured in a procedure. The algorithm for this action could be a set of tasks, such as these:
Repeat the next two steps four times: Draw a line of length n. Turn right by 90 degrees.
If this were a computer program, this set of instructions could be given the name 'square' and this sequence would be executed by running (calling) that procedure.
Functions and procedures are very similar - in fact, in some programming languages there are only functions, and procedures are seen as a special case of a function, just as a square is a special type of rectangle. Generally speaking, functions return a value, whereas procedures don't (so a procedure is just a function that doesn't return a value). To confuse matters, though, there are certain subroutines, such as msgbox() in VisualBASIC that appear to be both/either (if you specify only the message, msgbox() behaves as a procedure, but if you use the extra options, such as message type, then msgbox() returns a value).
By returns a value, we mean that the function creates some sort of results, which is passed back to the calling function. A subroutine called squared(), for example, that calculates the square of a number, would be a function, because the result of the calculation would need to be passed back.
Variables declared within functions or procedures are said to be local - that is, they can only be used within that function, or other functions called by that function. This is called the scope of the variable (see the variables page).
Local variables are destroyed when the function or procedure finishes executing, and their values are lost. Next time you call the function/procedure, the variable is recreated and reset (usually to zero). If you want your local variables to retain their values when the function or procedure is not being executed, you need to declare it to be static.
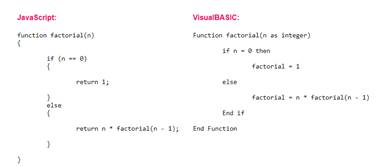
Some functions will require arguments - values upon which the operation performed by the function will be based. If you are using a typed language, then you will need to give the argument a type in your function/procedure declaration. Here are sample function declarations in JavaScript and VisualBASIC:
П. Tests and Assignments for Self-assessment.
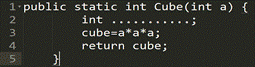
Picture 1
● max
● min
● cube
● square
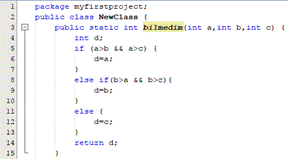
Picture 2
● the greatest common divisor of three numbers
● maximum of three numbers
● a minimum of three numbers
● arithmetic mean of three numbers
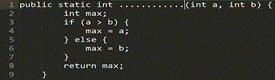
Picture 3
● maxOfFourNumbers
● maxOfThreeNumbers
● maxOfOneNumbers
● maxOfTwoNumbers
4. Specify the result of the program
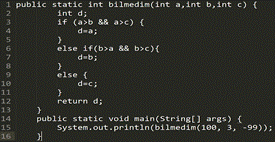
Picture 4
● -99
● the correct answer is missing
● 3
● 100
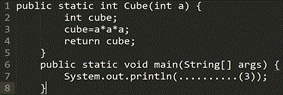
Picture 5
● Cube
● max
● cube
● Max
Answer
1. cube
2. maximum of three numbers
3. maxOfTwoNumbers
4. 100
5. Cube
Visual Aids and Materials.
1. Slides
2. http://physics.herzen.spb.ru/library/03/01/pp/TPHelp/subroutines.htm
3. https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/A-level_Computing/AQA/Paper_1/Fundamentals_of_programming/Subroutines_(functions_and_procedures)
4. Procedures and functions of working with strings: http://pas1.ru/stringfunction
5. http://purecodecpp.com/archives/920
6. https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/guides/z9hykqt/revision/1
7. https://www.advanced-ict.info/programming/functions.html
8. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T3pP5jMV69M
9. Скачано с www.znanio.ru
Материалы на данной страницы взяты из открытых источников либо размещены пользователем в соответствии с договором-офертой сайта. Вы можете сообщить о нарушении.